Introduction
In the realm of architectural innovation, futuristic skyscrapers stand as towering symbols of progress, pushing the boundaries of design and engineering. These structures are not merely about reaching new heights; they embody a profound shift towards sustainability, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. As urban populations swell and the demand for vertical living solutions intensifies, architects are increasingly harnessing cutting-edge technologies and materials to create iconic edifices that redefine city skylines.
From dynamic facades that respond to environmental changes to integrated green spaces that enrich urban ecosystems, the design of these skyscrapers reflects a commitment to both form and function. As the architectural community embraces these advancements, the exploration of futuristic skyscrapers reveals a landscape ripe with opportunity, where innovation meets the pressing needs of modern urban life.
Defining Futuristic Skyscrapers: Innovation in Architecture
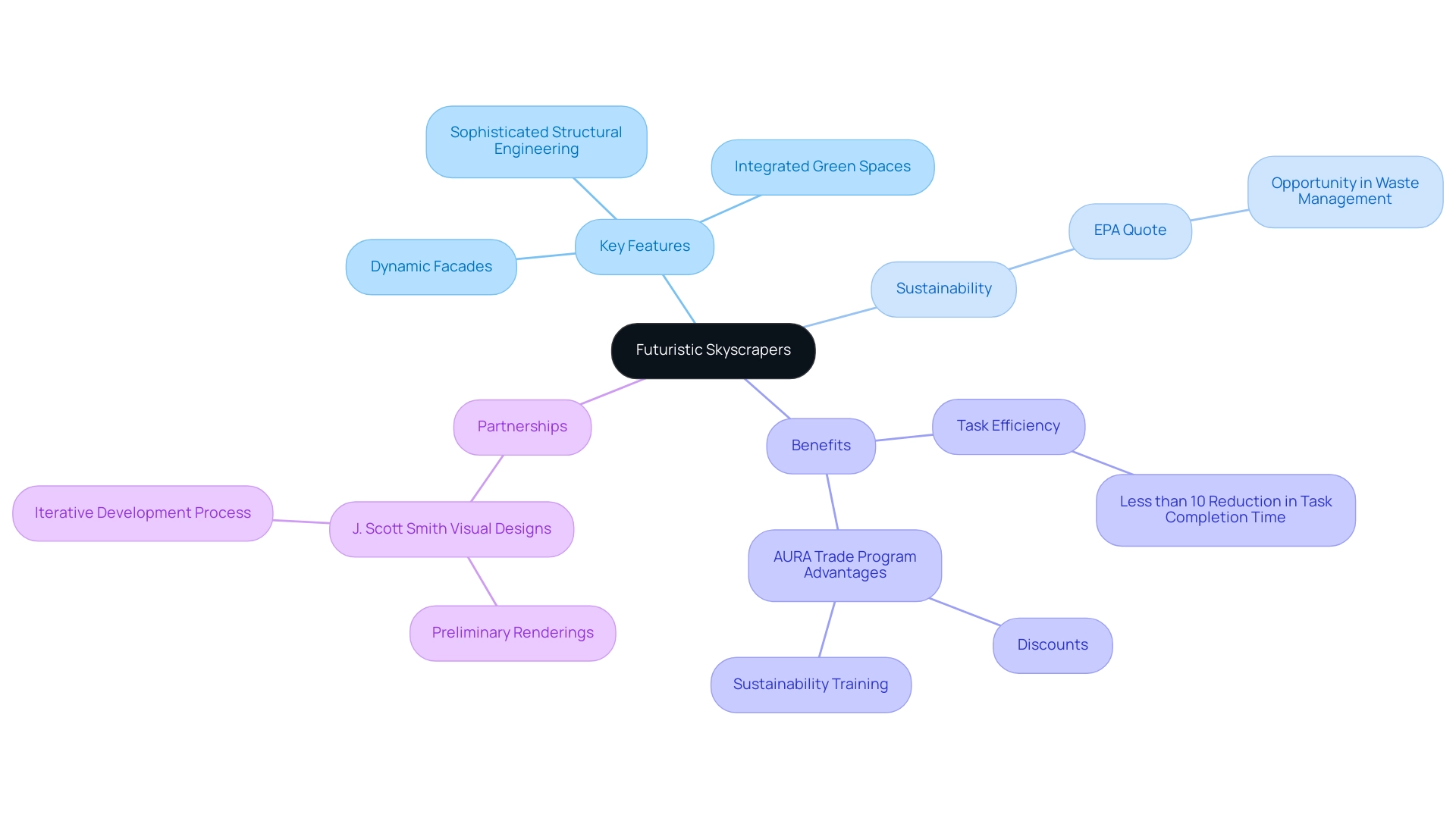
The futuristic skyscraper signifies a transformative evolution in architectural style, distinguished by its avant-garde forms, cutting-edge materials, and groundbreaking technologies. These futuristic skyscrapers challenge conventional norms, highlighting sustainability, functionality, and visual impact alongside their impressive heights. A recent statistic highlights that the use of generative AI can lead to a less than 10% reduction in task completion time for high-complexity tasks, showcasing the efficiency benefits that innovative architectural structures can offer to architects.
Key features include:
- Dynamic facades that adapt to environmental conditions
- Integrated green spaces that enhance city ecosystems
- Sophisticated structural engineering that facilitates unprecedented verticality and complexity
As cities keep growing and urban populations rise, the need for creative vertical living solutions increases, encouraging architects to explore new territories of futuristic skyscraper concepts. The Environmental Protection Agency notes, ‘While the waste totals are daunting, they present an opportunity,’ emphasizing the potential for sustainability in tall building architecture.
Furthermore, the AURA Trade Program offers exclusive advantages, including:
- Discounts
- Sustainability training for designers and commercial partners
These can enhance the attractiveness of embracing sustainable practices in skyscraper construction. To further refine these visionary concepts, partnering with J. Scott Smith Visual Designs for preliminary renderings can provide quick visualizations, support informed decision-making, and facilitate communication among stakeholders. The iterative development process allows for multiple revisions and refinements based on feedback, ensuring that the final outcome aligns with the client’s vision and project goals.
These structures, such as the futuristic skyscraper, go beyond mere functionality; they represent a commitment to progress and innovation in the built environment, setting a new standard for the future of urban living. Ready to explore the potential of your architectural ideas? Reach out to us today to arrange a consultation and discover how we can help realize your concepts.
Iconic Examples of Futuristic Skyscrapers: A Global Perspective
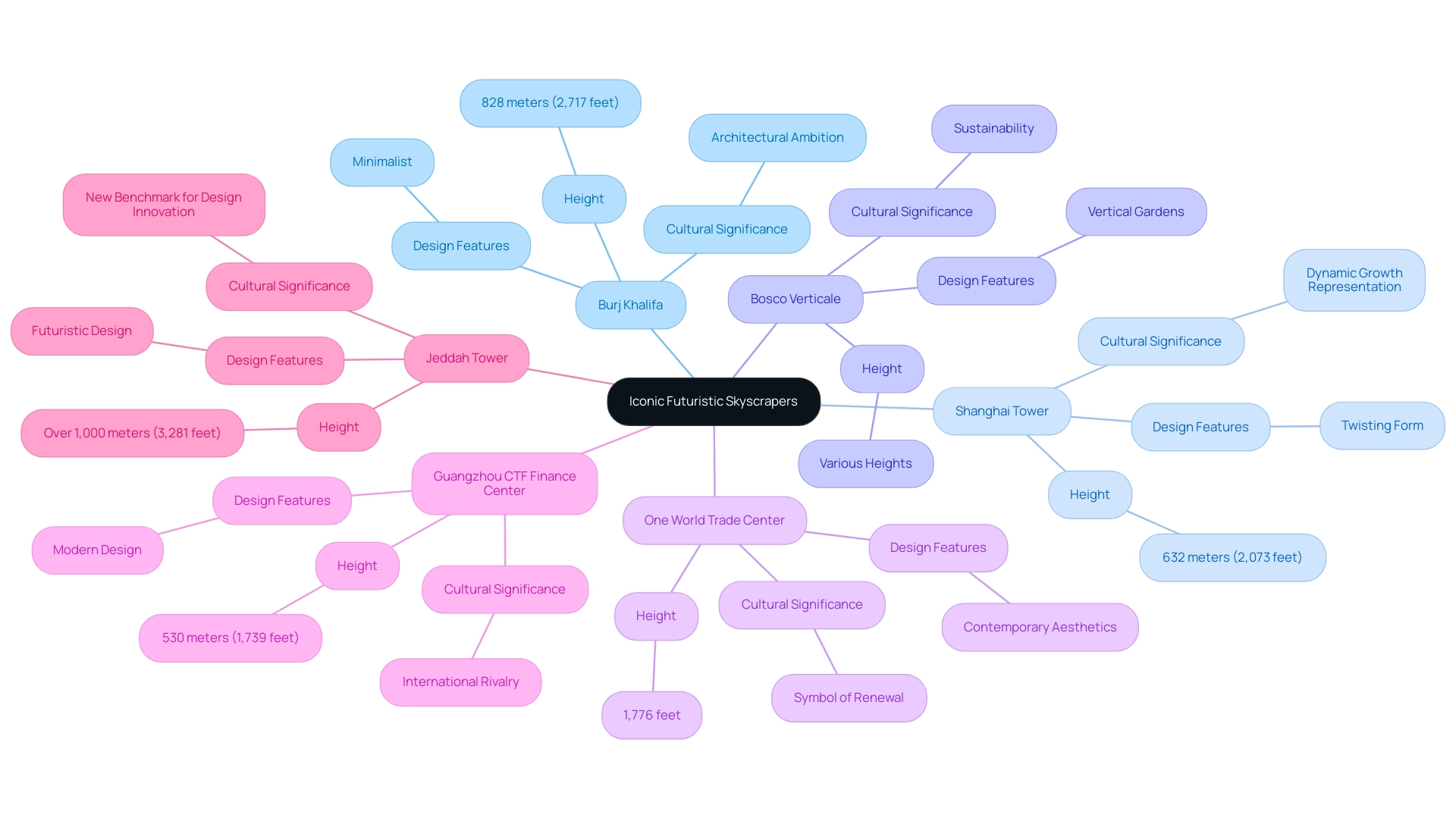
Among the most significant advancements in modern architecture are iconic futuristic skyscrapers that transform city skylines. The Burj Khalifa in Dubai stands as a testament to architectural ambition, reaching a staggering height of 828 meters (2,717 feet) and showcasing a sleek, minimalist design that has set new standards for height and aesthetics. Similarly, the Shanghai Tower, with its distinctive twisting form, not only enhances its aerodynamic performance but also represents the dynamic growth of city environments.
Other remarkable examples include:
- The Bosco Verticale in Milan, which innovatively integrates vertical gardens into its facade, promoting sustainability within dense urban settings.
- The One World Trade Center in New York, which combines contemporary aesthetics with profound symbolic significance, serving as a resilient emblem of renewal. Its height of 1,776 feet is a deliberate reference to the year the U.S. became independent, emphasizing the building’s connection to national identity.
- The Guangzhou CTF Finance Center, reaching 530 meters (1,739 feet), ranks eighth among the tallest structures in the world, demonstrating the international rivalry in tall building architecture.
Each of these futuristic skyscrapers exemplifies a commitment to pushing design boundaries, incorporating advanced engineering techniques and innovative thought processes that continue to influence global skyscraper design. As we approach 2024, the design community eagerly anticipates the completion of new projects, including the Jeddah Tower in Saudi Arabia.
This ambitious futuristic skyscraper, designed to exceed 1,000 meters (3,281 feet) in height, is anticipated to not only redefine the skyline but also establish new benchmarks for design innovation and sustainability.
Technological Innovations Shaping the Future of Skyscrapers
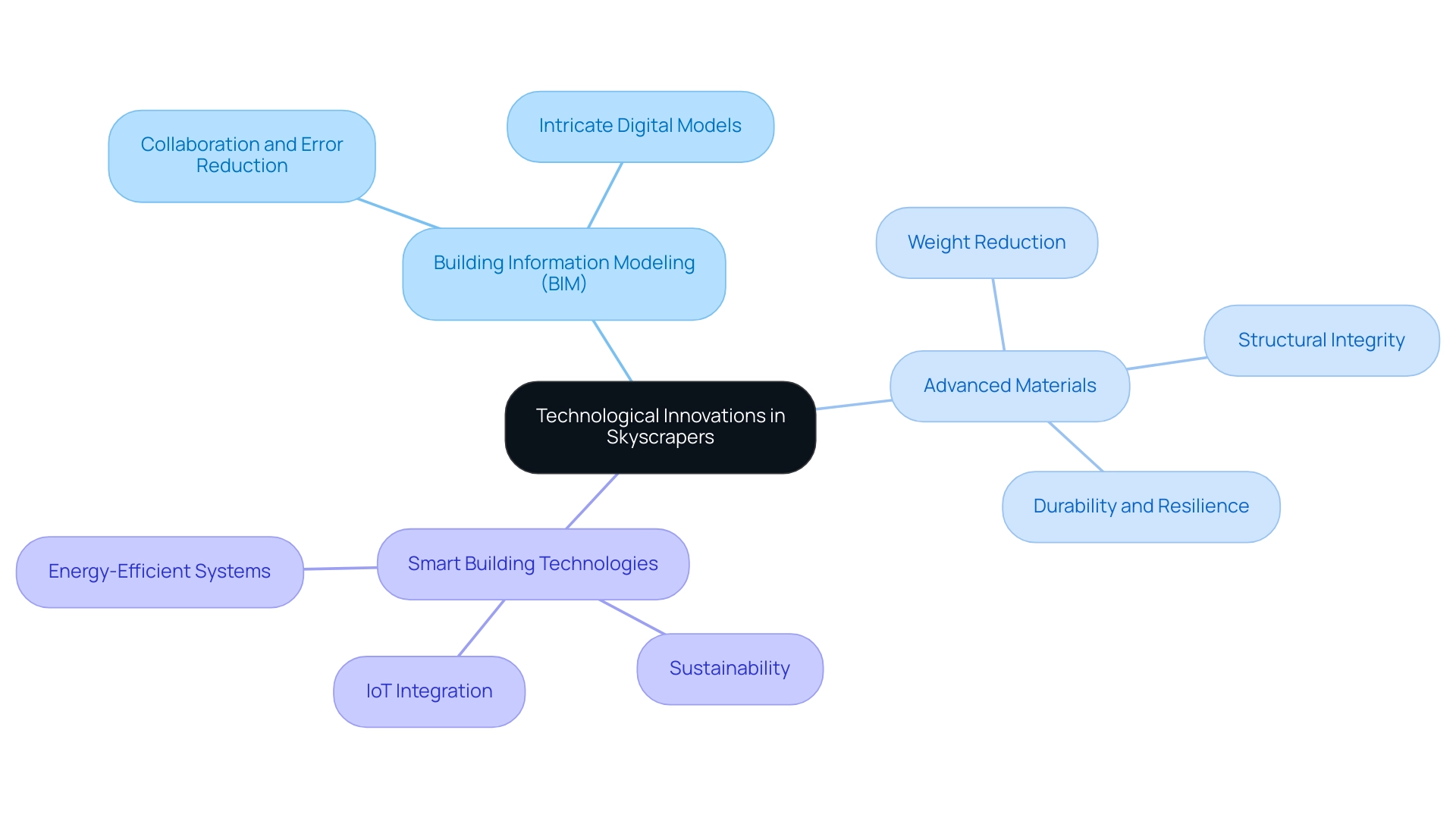
The landscape of futuristic skyscraper construction is being dramatically reshaped by technological innovations such as:
- Building Information Modeling (BIM)
- Advanced materials like carbon fiber and self-healing concrete
- The integration of smart building technologies
BIM facilitates the creation of intricate digital models, fostering improved collaboration among architects and engineers and significantly reducing construction errors. This is critical in an environment where the future of space technologies adoption is projected at 15%, underscoring the urgency for the architectural field to embrace these advanced methodologies.
Furthermore, advanced materials not only bolster structural integrity but also reduce weight, paving the way for taller and more complex designs. Innovations like carbon fiber and self-healing concrete represent a leap forward in construction techniques, enhancing durability and resilience. Additionally, the incorporation of smart technologies in a futuristic skyscraper—ranging from energy-efficient systems to IoT integration—enables tall buildings to function sustainably, dynamically adapting to environmental conditions and user demands.
As Rahul Bodiga aptly states, “Cover image by: Rahul Bodiga,” highlighting the significance of visual representation in showcasing these innovations. These advancements not only elevate the performance standards of futuristic skyscrapers but also enhance their aesthetic appeal, aligning with the global need for investment in futuristic skyscraper infrastructure, which must reach $94 trillion by 2040 to address the burgeoning demands of a growing population. The challenges faced by urban centers, as discussed in the case study ‘The Planet of Cities,’ emphasize the importance of integrating technological advancements to meet these evolving needs.
As such, the role of BIM and other technological innovations is crucial in addressing these challenges while influencing the future of building creation.
Aesthetics and Functionality: The Design Philosophy of Futuristic Skyscrapers
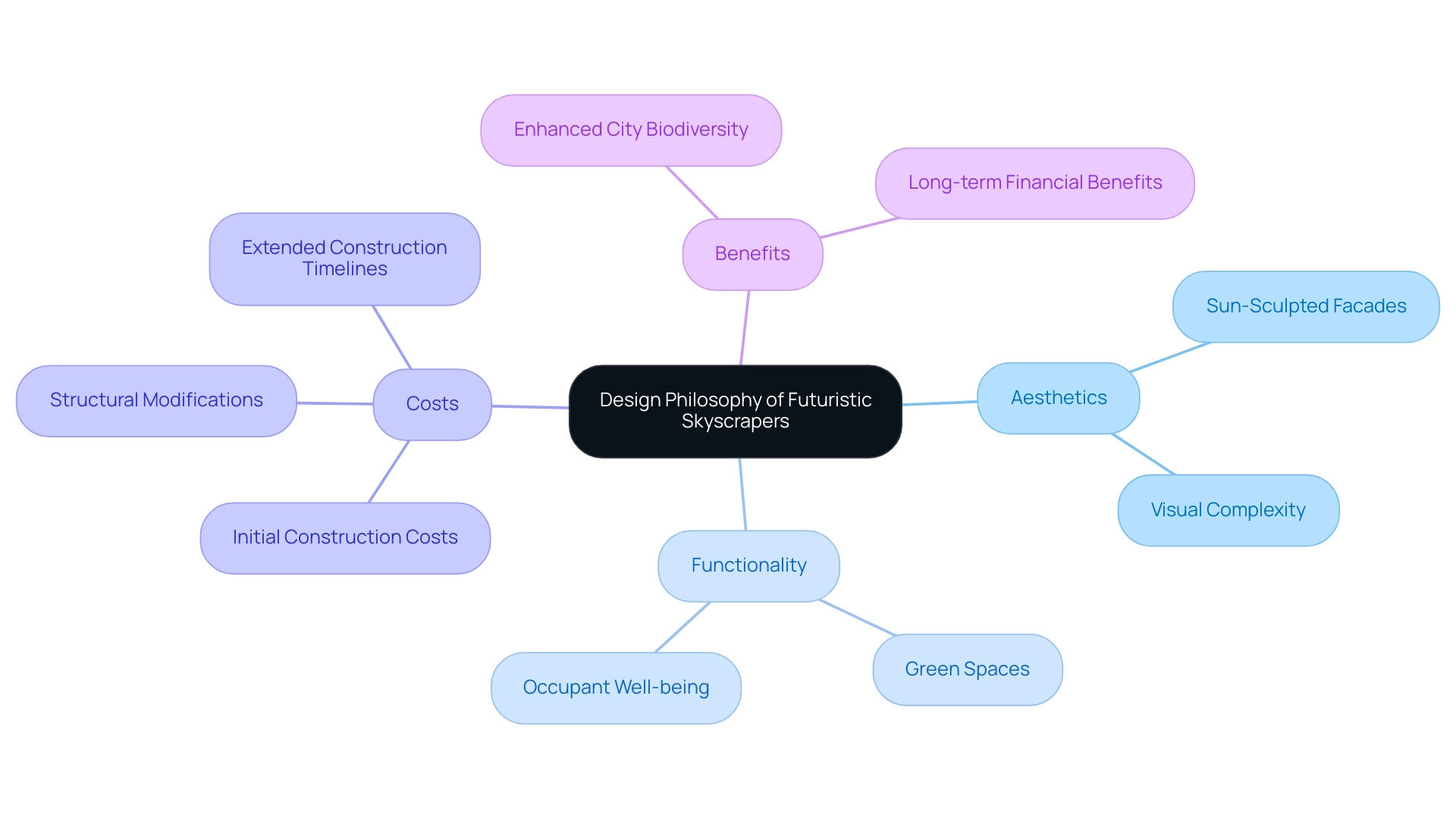
A creative philosophy that intricately intertwines aesthetics and functionality is exemplified by futuristic skyscrapers, reflecting the contemporary architectural ethos. Architects are increasingly committed to creating structures that not only captivate with their visual appeal but also fulfill the practical demands of occupants and the broader environment. This commitment manifests in the thoughtful integration of green spaces, which serve as essential components of building structure.
The inclusion of greenery, as emphasized in the case study titled ‘Construction Costs of Greenery-Covered Buildings,’ requires additional materials and specialized techniques, which can increase initial costs. Factors such as structural modifications and extended construction timelines further contribute to these costs. However, the long-term benefits—such as enhanced occupant well-being and city biodiversity—often outweigh these initial costs.
Techniques like sun-sculpted facades not only optimize natural light and energy efficiency but also contribute to the visual complexity of the structure. Furthermore, the average of the digital elevation model in this context was determined to be 108.36, with a standard deviation of 108.98, offering a quantitative foundation for assessing tall building structures. Additionally, the structure of these buildings, particularly the futuristic skyscrapers, is profoundly embedded in their cultural and environmental settings, guaranteeing they surpass simple architectural novelty to become essential components of the cityscape.
As Kheir Al-Kodmany observes in his review, ‘the combination of aesthetics and functionality in tall building construction is crucial for attaining sustainable city environments,’ emphasizing the significance of this integration.
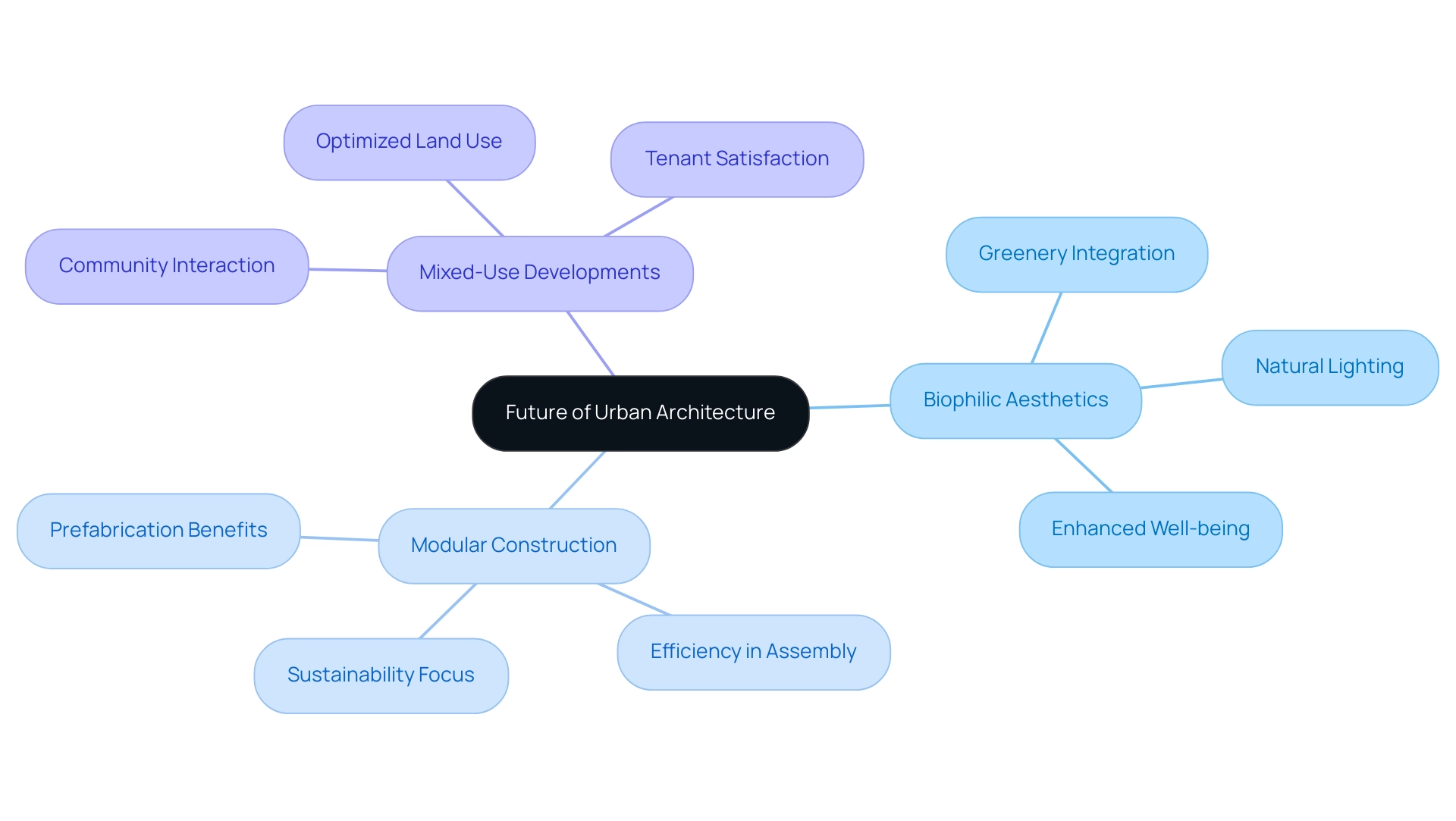
The Future of Urban Architecture: Trends in Skyscraper Design
The future of city architecture is set for a substantial change, with futuristic skyscrapers being shaped by essential principles such as biophilic aesthetics, modular construction, and mixed-use developments. Biophilic architecture promotes a deep bond between nature and city life, leading to skyscrapers that effortlessly incorporate greenery, natural lighting, and organic features. This method not only improves the appearance of city areas but is also backed by studies indicating that settings featuring natural components boost productivity and well-being, thereby harmonizing beauty with practicality.
Historically, the principle of ‘form follows function’ has directed building creation, highlighting that the shape of a structure should mainly depend on its intended use or goal. In 2023, the adoption rate of space technologies reached 15%, reflecting a growing interest in innovative building practices that align with these principles. Technologies such as advanced materials and smart building systems, along with 3D modeling tools and CAD, are transforming practices by enabling more efficient and sustainable construction techniques, which support the integration of biophilic elements into city architecture.
Modular construction is redefining efficiency in the architectural landscape. By permitting prefabrication in controlled settings, this approach facilitates faster assembly on-site and greatly minimizes material waste—essential in today’s sustainability-oriented ethos. As an engineer from a leading laser manufacturing firm observed, “A challenge has been meeting company objectives regarding how quickly we want to reach the market and the availability of resources such as how much time, money, and personnel we wish to allocate to bring this project to fruition.” This underscores the urgent need for agile construction techniques like modular construction, which can adjust to changing market requirements while improving efficiency.
Additionally, mixed-use developments are gaining popularity, combining residential, commercial, and recreational areas to foster vibrant city environments. These developments not only optimize land use but also enhance community interaction, fostering a sense of place and belonging. For instance, case studies have shown that projects incorporating biophilic principles lead to increased tenant satisfaction and reduced turnover rates, illustrating the tangible benefits of these approaches.
The use of local materials further supports sustainability, reducing transportation emissions and promoting regional economies.
As cities expand and evolve, these architectural trends will not only redefine the skyline but also enhance sustainability, livability, and connectivity within the urban fabric. The convergence of these innovative approaches heralds a new era in futuristic skyscraper design, characterized by resilience and harmony with the natural world.
Conclusion
Futuristic skyscrapers represent a pivotal evolution in urban architecture, where innovation seamlessly merges with sustainability, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. The exploration of these structures reveals a commitment to pushing the boundaries of design through cutting-edge technologies and advanced materials. From the dynamic facades of iconic buildings like the Burj Khalifa and Shanghai Tower to the integration of green spaces that enhance urban ecosystems, the architectural landscape is undergoing a transformative shift.
Technological advancements such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and smart building systems are reshaping construction methodologies, enabling architects to create structures that are not only taller and more complex but also environmentally responsive. The adoption of biophilic design principles and modular construction further emphasizes the importance of harmonizing urban living with nature, fostering environments that promote well-being and sustainability.
As the architectural community continues to embrace these trends, the future of skyscraper design holds immense potential. The commitment to creating resilient, multifunctional spaces that enhance urban connectivity will not only redefine skylines but also contribute to the livability and vibrancy of cities. This approach underscores the vital role architects play in addressing the challenges of modern urbanization, ensuring that the skyscrapers of tomorrow are not just monuments of ambition but integral components of sustainable urban ecosystems.

0 Comments