Overview
The future of architectural visualization technology is shaped by transformative advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and cloud computing, which enhance design efficiency and client engagement. The article illustrates this by highlighting how these technologies facilitate real-time collaboration, automate design processes, and create immersive experiences, ultimately leading to improved project outcomes and client satisfaction in the architectural field.
Introduction
The architectural visualization sector is experiencing a seismic shift, driven by the rapid integration of transformative technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR). These advancements are not merely supplementary; they are fundamentally altering the methodologies architects and designers utilize to conceptualize and communicate their visions.
With substantial investments—over $2.8 billion in software and technology by U.S. architecture firms in 2020—there is a clear commitment to adopting these tools. AI’s ability to generate hyper-realistic representations and automate design processes is enhancing client engagement and streamlining workflows, while VR and AR provide immersive experiences that empower stakeholders to visualize projects before they materialize.
As the industry embraces these innovations, a new paradigm of collaboration and efficiency emerges, setting the stage for a more dynamic architectural practice that not only meets contemporary demands but also anticipates future trends.
Transformative Technologies Shaping Architectural Visualization
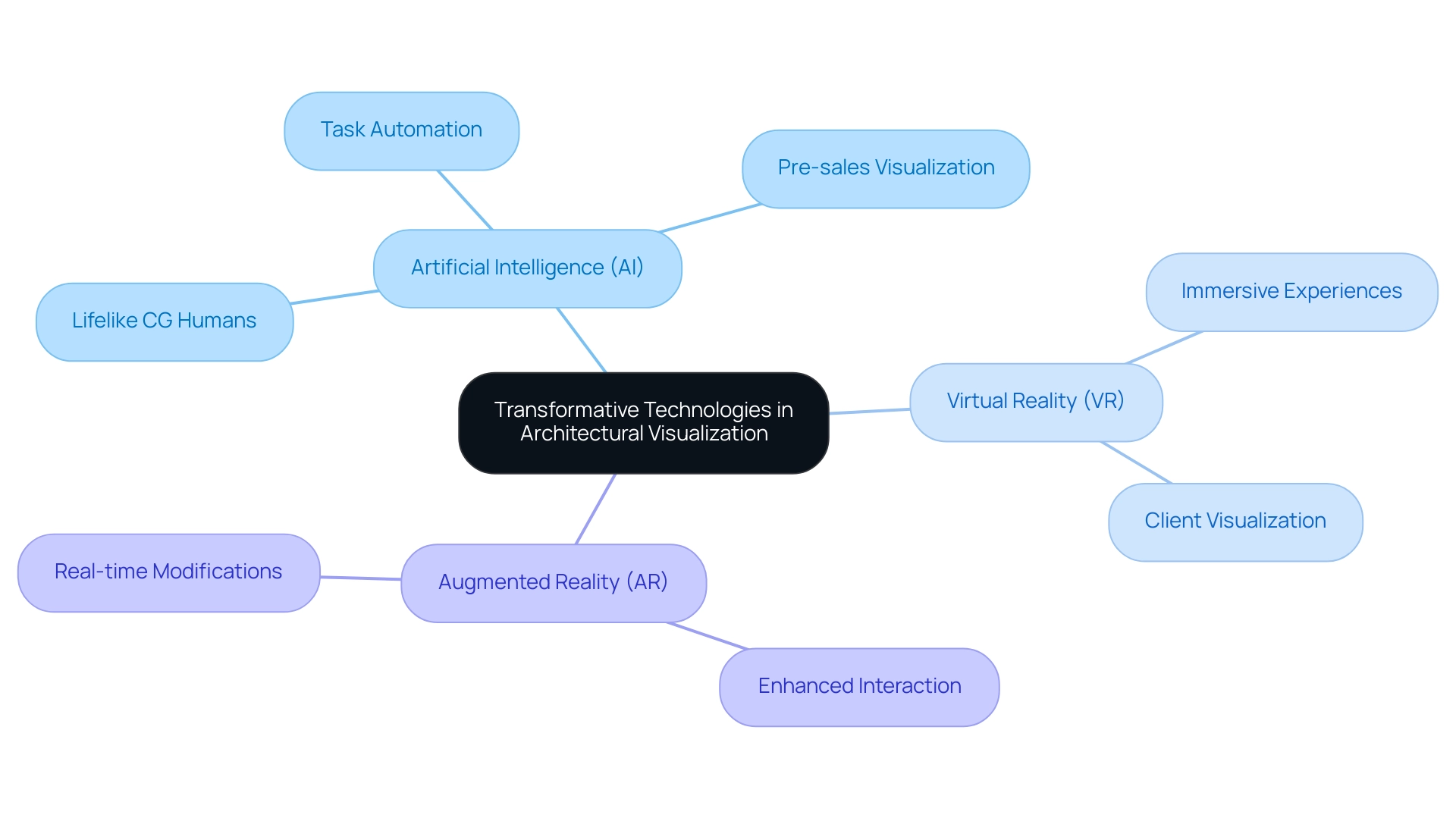
The landscape of architectural visualization is undergoing a profound transformation driven by emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR), which are crucial steps to the future of architectural visualization technology. These innovations represent essential steps to the future of architectural visualization technology, redefining how architects and designers conceptualize and showcase their work. Notably, architecture firms in the U.S. invested over $2.8 billion in software and technology in 2020, highlighting the industry’s commitment to integrating advanced tools into their workflows.
AI, in particular, is pivotal in generating lifelike CG humans that bridge the uncanny valley in architectural visualizations, enhancing realism and client engagement. The uncanny valley concept refers to the discomfort experienced when CG humans appear almost, but not quite, lifelike. This capability not only showcases the potential of projects but also plays a crucial role in pre-sales visualization, enabling developers to provide tangible assets that can ignite interest and investment long before construction begins.
Furthermore, AI automates labor-intensive tasks, including the creation of options and the optimization of layouts based on user inputs and environmental considerations. This efficiency allows architects to concentrate on creativity and innovation. Meanwhile, VR and AR provide immersive experiences that enable clients to visualize spaces before construction, fostering more informed choices.
Beyond architectural visualization, 3D imaging has various applications in areas such as medical imaging, training simulations, product prototyping, and graphic creation, all of which benefit from the advancements in AI technology. As public sentiment towards AI improves across various demographics, the integration of these technologies is becoming more widely accepted. Insights from recent studies reveal that younger generations tend to be more optimistic about AI’s potential benefits compared to older demographics, indicating a shift in perception that could significantly influence architectural practices.
As these technologies continue to advance, they represent important steps to the future of architectural visualization technology, improving collaboration and communication among stakeholders and ultimately resulting in a more unified development process. Additionally, the demand for sustainable architecture is projected to increase by 16.4% annually through 2027, highlighting the steps to the future of architectural visualization technology in shaping the relevance of these technologies in architectural practice.
Enhancing Design Efficiency with Real-Time Rendering and AI
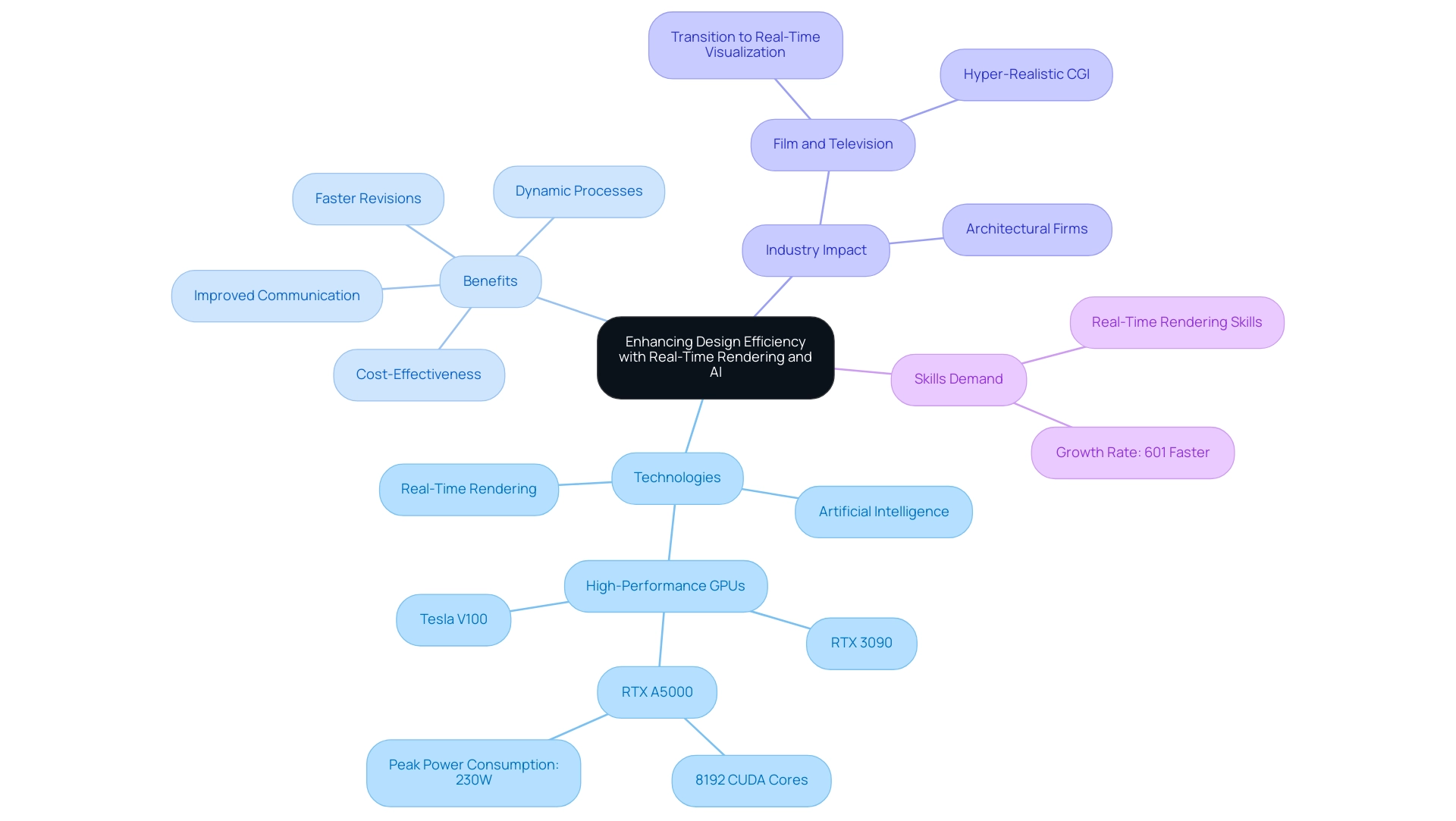
Real-time rendering technology and artificial intelligence are revolutionizing efficiency within architectural visualization, significantly enhancing contractor communication and eliminating misunderstandings. High-performance GPUs, such as the RTX A5000 with its 8192 CUDA cores and peak power consumption of 230W, alongside versatile options like the RTX 3090 and Tesla V100, empower architects to achieve instantaneous updates to their plans. This immediacy fosters a more dynamic and iterative creation process, allowing for quick visualizations that facilitate informed decision-making while significantly accelerating revisions and reducing overall project timelines.
The cost-effectiveness of initial conceptual visuals is clear since they are less expensive to create than detailed images, making them perfect for early-stage exploration. The demand for real-time visualization skills is expanding at an astonishing rate—601% faster than the overall job market—as firms strive to harness these advancements.
AI further amplifies this efficiency by deploying predictive analytics and design recommendations based on historical data and user preferences. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze past assignments to suggest optimal materials and layouts, effectively minimizing errors and the need for rework. Tajammul Pangarkar, CMO at Prudour Pvt Ltd, emphasizes the importance of these technologies in modern architecture, asserting that they are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in the industry.
The integration of real-time visualization and AI not only empowers architects to deliver high-quality visualizations more swiftly and accurately but also enhances overall project outcomes.
As evidenced by the film and television industry’s transition towards real-time visualization, which has streamlined post-production and elevated the cinematic experience through hyper-realistic CGI visuals, architectural firms stand to gain significantly from embracing these innovations. This case study demonstrates the practical advantages of embracing real-time visualization technologies, highlighting how they can improve the overall creation process. Ultimately, the collaborative synergy of real-time visuals and AI, along with the cost-effectiveness and iterative support provided by preliminary images, represents important steps to the future of architectural visualization technology, setting a new standard for design efficiency in 2024 and beyond.
The Impact of Cloud Computing on Collaboration
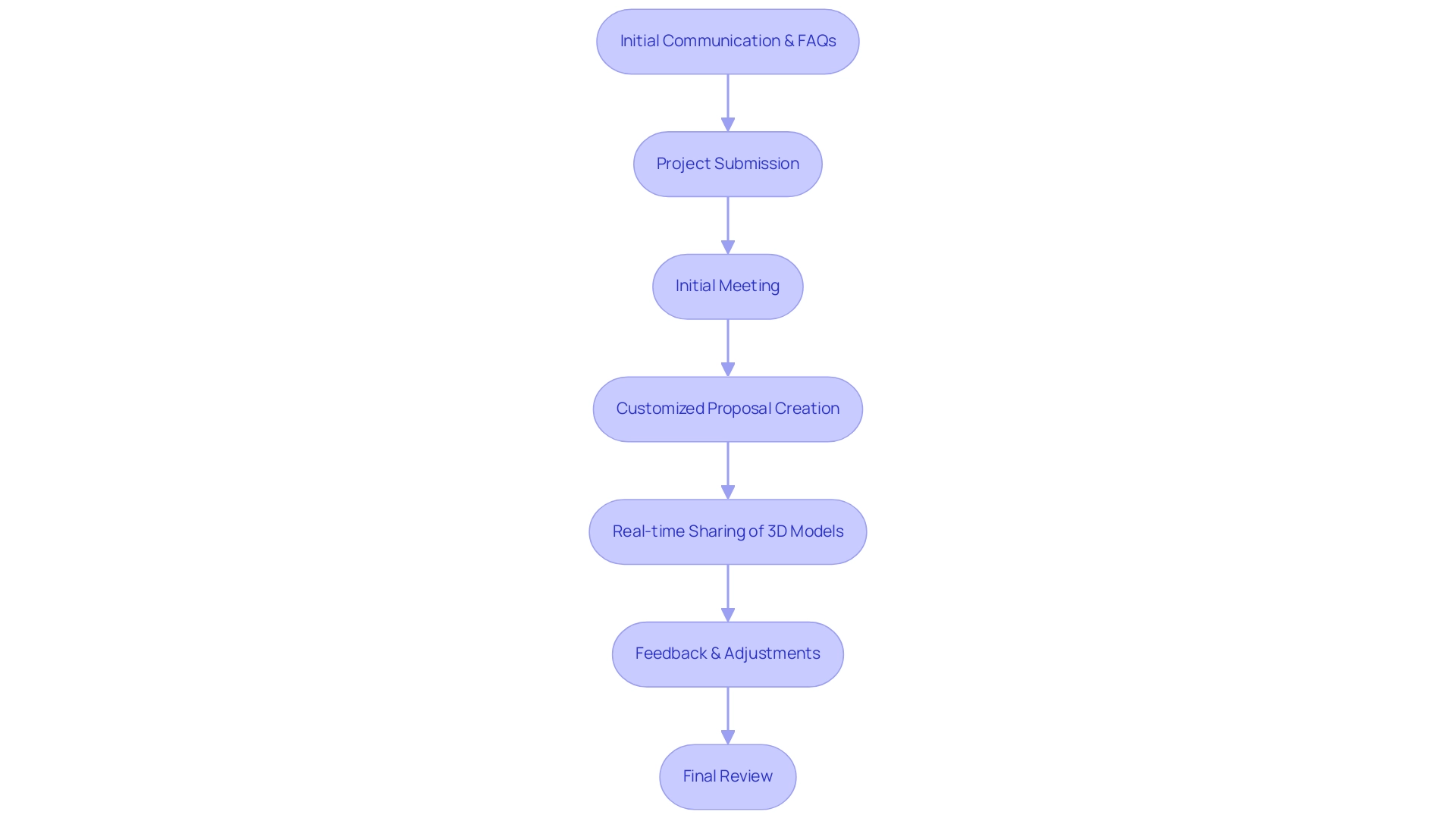
Cloud computing has become an essential technology in architectural visualization, representing crucial steps to the future of architectural visualization technology by facilitating seamless collaboration among architects, customers, and stakeholders, regardless of their geographical locations. At J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, our collaborative design process begins with initial communication and FAQs, where our virtual assistant provides 24/7 support for basic inquiries. This virtual assistant plays an essential role in guiding users through the initial phases of their endeavors, ensuring they have the information they require at their fingertips.
Once a project is submitted through our web portal, we hold an initial meeting to comprehend the customer’s vision and specific requirements. Following this, we create a customized proposal that describes the process, ensuring that all client expectations are met. Recent data indicates that 63% of technical and business professionals reported heavy cloud usage in 2022, reflecting a significant shift towards cloud-based solutions.
Notably, 91% of organizations claim that using the cloud makes it easier to fulfill government compliance requirements, underscoring the importance of cloud adoption in architecture for meeting regulatory standards. By utilizing cloud platforms, teams can effectively share large 3D models and visuals in real-time, which are essential steps to the future of architectural visualization technology, allowing instant feedback and iterative adjustments. This dynamic interaction not only enhances communication but also accelerates timelines, representing essential steps to the future of architectural visualization technology, as all participants can access the latest information without the delays characteristic of traditional file-sharing methods.
Our intricate 3D models and superior visual renderings are essential in recognizing design problems early, ultimately optimizing workflows and ensuring customer satisfaction. Furthermore, by showcasing projects in their best light, 3D visualizations help secure quicker buy-in from stakeholders and investors while reducing costly changes later in the process. However, it is important to acknowledge that the steps to the future of architectural visualization technology present challenges, with technical feasibility being a significant barrier for many organizations.
Despite these hurdles, cloud computing provides essential steps to the future of architectural visualization technology by fostering the integration of diverse software tools, ensuring that all team members operate within a unified digital ecosystem. This cohesive environment is crucial in attaining high-quality results, representing important steps to the future of architectural visualization technology and leading to greater satisfaction among customers. Furthermore, as the cloud, virtualization, and serverless computing are projected to generate approximately $2 billion in revenue for African markets by 2024, it is evident that despite being behind other regions, there is immense growth potential for cloud services in architecture.
In light of this, Cody Slingerland aptly notes that 95% of organizations grapple with unexpected outages, highlighting the need for robust cloud infrastructure to mitigate such challenges and maximize the benefits of cloud collaboration.
The Role of Interactive Presentations in Client Engagement
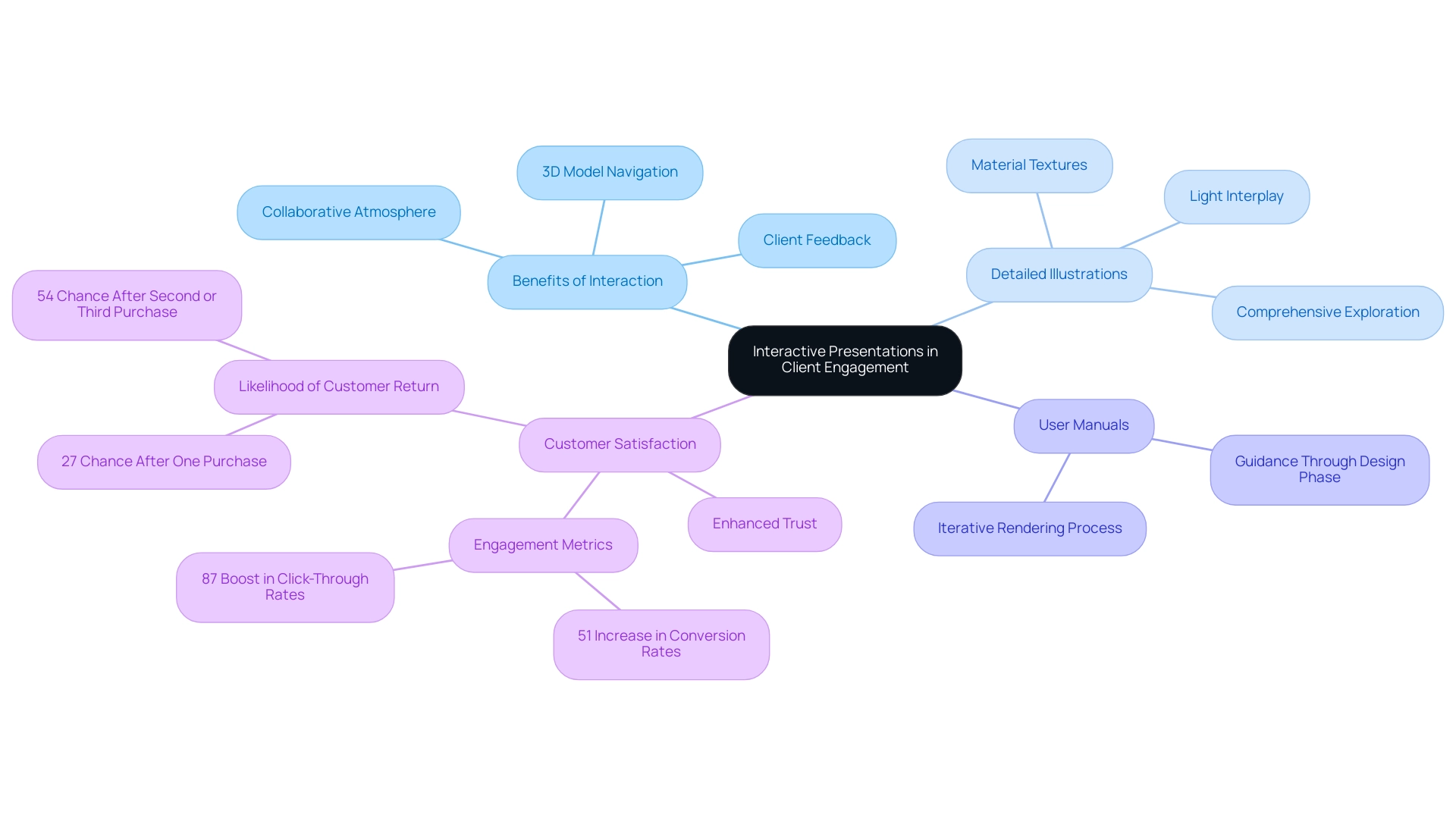
The incorporation of interactive presentations into architectural visualization represents important steps to the future of architectural visualization technology, effectively engaging customers and improving their comprehension of conceptual ideas. By employing advanced tools that enable users to navigate 3D models, manipulate views, and partake in virtual walkthroughs, architects can significantly elevate the experience. This interactivity not only facilitates a clearer visualization of the final product but also encourages clients to actively contribute feedback during the design process, thereby fostering a collaborative atmosphere and a sense of ownership.
Moreover, the role of detailed illustrations in visualizing residential architecture cannot be overstated. These visualizations enable architects to showcase every element of the design—from material textures to light interplay—bringing concepts to life and facilitating comprehensive exploration of ideas. To assist users in utilizing these detailed renderings effectively, user manuals are provided, guiding them through the design phase and the iterative rendering process.
As emphasized by industry specialists, adopting these techniques can result in enhanced customer satisfaction and trust, essential elements in the architectural field. Twilio emphasizes that 44% of brands cite finding a balance between customer experience and security as their top engagement challenge, underscoring the importance of enhancing user interactions while maintaining security. Moreover, recent discoveries suggest that companies focusing on adapting to changing customer expectations, like those employing interactive presentations along with detailed visuals, see significant enhancements in engagement metrics, with Ninetailed by Contentful reporting a 51% rise in conversion rates.
This trend highlights the necessity for architects to take steps to the future of architectural visualization technology by adopting a comprehensive 3D development process that not only improves communication but also aligns with the latest market demands, ensuring a more effective and engaging interaction with customers. Moreover, the probability of customer return is greatly enhanced through organized engagement strategies, emphasizing the significance of cultivating a cooperative environment through both interactive presentations and detailed renderings, while also actively involving participants in the iterative development phase.
Future Trends in Architectural Visualization Technology
The scenery of architectural visualization is on the brink of change, with various emerging technologies driving steps to the future of architectural visualization technology, promising to redefine creation methods and customer interaction. A notable trend is the increasing adoption of machine learning algorithms, which enhance efficiency and accuracy by analyzing data from past projects. This capability allows architects to optimize their designs in real-time, responding to client needs with unprecedented precision.
At J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, our collaborative design process begins with initial communication facilitated by our virtual assistant, who addresses basic inquiries 24/7. Upon submission through our web portal, we conduct a brief to understand your vision, target audience, and specific rendering needs. This attention to detail—from initial communication to the crafting of intricate 3D models—plays a crucial role in achieving customer satisfaction.
Every element, from the way sunlight dances off the windows to the subtle texture of the bricks, is meticulously rendered to create a space that feels real and lived-in. The importance of feedback loops and refinement throughout the process ensures that we align closely with your expectations. The advent of immersive technologies, particularly mixed reality (MR), represents important steps to the future of architectural visualization technology by revolutionizing how architects present their visions.
By seamlessly merging digital and physical environments, MR facilitates more interactive and engaging experiences for clients, fostering deeper connections with the design process. As sustainability continues to gain traction—projected to grow by 16.4% annually through 2027—architects are taking steps to the future of architectural visualization technology in order to assess and enhance energy efficiency in their projects. According to a market analysis conducted in 2013, the worldwide APM software market share provides a context for the technological advancements shaping the industry.
Additionally, experts emphasize that ‘the integration of technology is not just a trend, but a necessity for architects to thrive in a competitive environment.’ Staying abreast of these technological advancements is essential for architects as they take the steps to the future of architectural visualization technology, allowing them to capitalize on new opportunities and remain competitive in an industry marked by rapid innovation and a strong emphasis on sustainable practices. Furthermore, leveraging social media strategies for direct engagement can enhance how architects present and promote their visualization efforts, similar to successful case studies in direct sales.
Conclusion
The architectural visualization landscape is undergoing a remarkable evolution, primarily driven by the integration of transformative technologies such as artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and augmented reality. These advancements are not only enhancing the realism of visualizations but also revolutionizing workflows, enabling architects to engage clients with unprecedented clarity and immediacy. The substantial investment in technology by architecture firms underscores a collective commitment to harnessing these tools, paving the way for a more efficient and collaborative approach to design.
As real-time rendering and AI continue to reshape design efficiency, architects are increasingly able to produce high-quality visualizations at a faster pace, minimizing errors and facilitating informed decision-making. Cloud computing further enhances collaboration, allowing stakeholders to access and modify designs in real-time, thereby streamlining communication and project timelines. The shift towards interactive presentations has also proven essential in elevating client engagement, fostering a participatory atmosphere that encourages feedback and collaboration throughout the design process.
Looking ahead, the continued evolution of architectural visualization technologies, including machine learning and mixed reality, promises to further refine design accuracy and client interaction. As sustainability emerges as a critical focus, these technologies will play a vital role in optimizing energy efficiency and meeting contemporary demands. The integration of advanced tools is not merely a trend; it is an essential component of future architectural practice, ensuring that firms remain competitive and responsive to the ever-changing landscape of the industry. Embracing these innovations will ultimately lead to a more dynamic, collaborative, and sustainable architectural environment.

0 Comments