Overview
The benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals include enhanced engagement, improved communication, and increased investment interest, which collectively foster a more effective and inclusive design process. The article supports this by illustrating how 3D visuals provide tangible representations that facilitate understanding, promote active participation, and can lead to significant reductions in construction errors, ultimately transforming stakeholder interactions and project outcomes.
Introduction
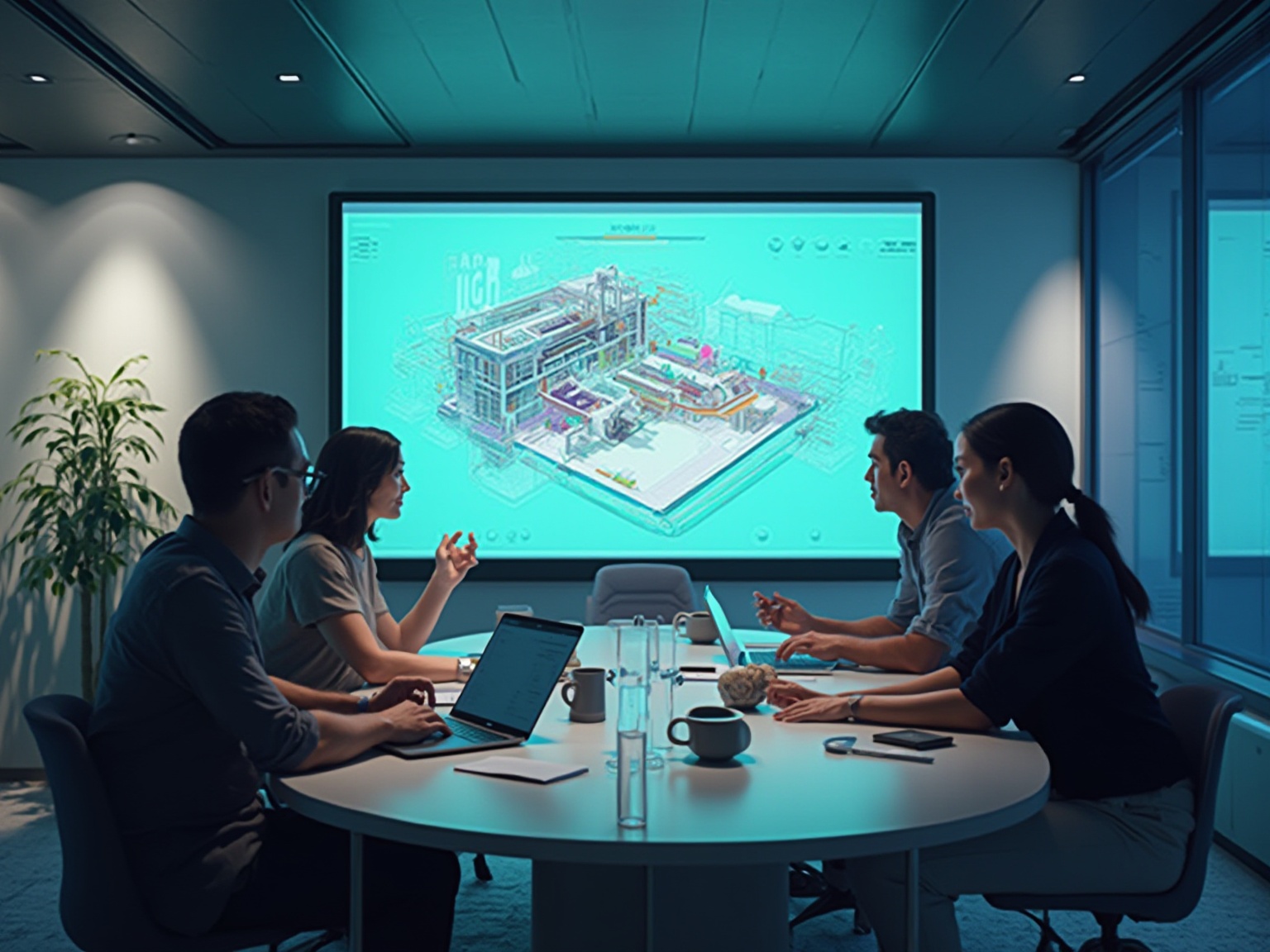
In the evolving landscape of architectural design, the integration of 3D visualization technologies is revolutionizing stakeholder engagement and collaboration. By transcending the limitations of traditional 2D representations, 3D visuals provide an immersive experience that facilitates a deeper understanding of complex concepts. This article delves into the multifaceted role of 3D modeling, exploring its impact on project planning, execution, and communication among stakeholders.
From enhancing clarity and precision to fostering emotional connections with prospective residents, the advantages of advanced visualization techniques are becoming increasingly indispensable. Furthermore, as emerging trends such as artificial intelligence and augmented reality reshape the future of architectural visualization, understanding these developments is crucial for architects aiming to optimize collaboration and drive project success.
Enhancing Stakeholder Engagement Through 3D Visuals
3D visuals are crucial in enhancing participant engagement by offering a tangible representation of architectural concepts that transcends traditional 2D drawings. This innovative method showcases the benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals, enabling them to assess the project from multiple viewpoints and perspectives, fostering an immersive experience that promotes active involvement and constructive feedback—elements essential in the collaborative development process. Effective data visualization should be simple, accurate, and tailored to the target audience, reinforcing the argument for 3D visuals.
As highlighted by the statistic that 50% of the brain’s tissue is directly or indirectly related to vision, the clarity and accessibility of complex designs presented in 3D effectively bridge communication gaps. In the pre-sales phase, architectural renderings serve not only as a visual tool but also as tangible assets that instill confidence in a project and help generate interest and investment long before physical construction begins, thus contributing to revenue generation. This is especially clear in the instance of the Adaptive Urban Transformation initiative, where various display technologies have been integrated, combining traditional and digital media for optimal participant engagement.
Moreover, Tomkins and Lange highlight that ‘Unity offers complete access to the rendering engine, enabling custom material shaders,’ which is crucial for tackling creative challenges. The case study on the assessment of AR hardware for stakeholder events demonstrates that while AR representations can improve traditional media, effective communication strategies may need a combination of both hand-held and headset AR until hardware limitations are resolved. By promoting a more inclusive environment, architects can ensure that all voices are heard, ultimately enhancing the overall creation process and illustrating the benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals to build strong community connections from the outset.
Additionally, the architectural visualization townhomes advantage enhances the connection between prospective residents and their future homes, fostering a sense of belonging and community from the very beginning.
The Role of 3D Modeling in Streamlining Project Planning and Execution
The adoption of 3D modeling stands as a transformative force in the realm of planning and execution, enabling architects to produce detailed and precise representations of their designs. This heightened level of accuracy is crucial, significantly diminishing the likelihood of construction errors by allowing stakeholders to detect potential issues early in the process. Notably, 3D modeling technologies provide advantages such as precise component extraction and enhanced safety, essential for effective management.
Furthermore, detailed renderings enhance client collaboration and illustrate the benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals, showcasing both functionality and aesthetics, which elevates client satisfaction and marketing effectiveness. Importantly, these renderings resonate emotionally with clients, reflecting their lifestyles and preferences, which is vital in residential architecture. A notable example can be observed in the Utah Department of Transportation Highway Project, which utilized small Suas for monitoring construction progress alongside GNSS rovers for real-time verification.
This integration not only improved productivity for construction inspectors but also bolstered confidence in cost estimations, illustrating the role of pre-sales visualization in generating investment through compelling renderings. Statistics indicate that the benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals in the pre-sales phase can lead to a significant increase in client engagement and investment interest, further underscoring their importance. Consequently, the strategic use of 3D modeling fosters optimal material utilization and waste reduction, leading to substantial cost savings and improved efficiency.
As Johnny K. W. Wong states, ‘The study enhances the comprehension of the degree to which BIM can be utilized to decrease the number of errors in planning and assist in improving performance.’ However, it is important to acknowledge that 3D modeling also has limitations, such as reliance on accurate data and potential interoperability issues between different software platforms. Additionally, statistics indicate that the implementation of 3D modeling can lead to a reduction in construction errors by up to 30%, underscoring its critical role in enhancing construction accuracy and efficacy in 2024 and beyond.
Facilitating Clear Communication Among Stakeholders with 3D Visualization
The use of 3D visualization emerges as an indispensable asset in showcasing the benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals to foster effective communication among participants in architectural projects. By offering a visual reference, architects facilitate a shared understanding of design concepts, which is crucial when navigating modifications or addressing concerns. A notable study by ScienceDirect indicates that participants who engaged with spatial environments through virtual reality demonstrated a 10% improvement in spatial comprehension compared to those relying solely on 2D floor plans.
This enhanced spatial awareness highlights the benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals in interactions. Additionally, the incorporation of these visuals during meetings highlights the benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals, allowing for real-time adjustments and immediate feedback that significantly accelerates the decision-making process. As a result, initiatives are more likely to adhere to timelines and budget constraints, minimizing the risk of misunderstandings.
To find quality 3D architectural rendering services, consider the following tips:
– Evaluate portfolios to assess the quality of past work.
– Check client reviews to gauge satisfaction.
– Assess communication skills to ensure a collaborative partnership.
These testimonials reflect a company’s reliability and ability to meet expectations. At J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, client feedback emphasizes our dedication to personalized service and innovative problem-solving, further enhancing the visual appeal and market differentiation of properties.
The latest advancements in 3D imaging tools support this approach, as research highlights the varying suitability of different methods for distinct project phases. For example, the case study titled ‘The Future of 3D Visualization’ discusses emerging trends such as AI-generated design options and digital twins, emphasizing the need for strategic information sharing tailored to the needs of involved parties. Additionally, the effectiveness of visualization models can be evaluated using a five-point Likert scale, providing a structured approach to measure their impact on communication and decision-making.
By closely examining client testimonials, potential clients can gain insights into the experiences of others, guiding them toward making informed choices in their selection process.
Leveraging Advanced 3D Technologies for Improved Collaboration
The incorporation of advanced 3D technologies, especially Building Information Modeling (BIM) and virtual reality (VR), highlights the benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals, significantly transforming collaboration among participants in architectural endeavors. With BIM, teams benefit from real-time updates and seamless data sharing, ensuring all members remain aligned throughout the lifecycle. This collaborative environment is further enhanced by VR, highlighting the benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals, enabling them to navigate and engage with designs before construction commences.
Such functionality not only enhances understanding of the endeavor but also fosters a deeper connection between future homeowners and their prospective communities, allowing them to visualize their contributions to the final product. Specific features of architectural representation, such as interactive 3D walkthroughs and detailed renderings, enhance this connection by allowing potential residents to envision their roles in the community. Recent applications of VR in client presentations have demonstrated the benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals; for instance, one notable initiative reported heightened stakeholder engagement and more productive discussions as a direct result of utilizing VR.
Furthermore, statistics indicate that organizations utilizing advanced 3D technologies have experienced the benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals, resulting in up to a 30% improvement in collaboration effectiveness. As Jennings aptly noted, ‘Organizations will cherry-pick what they like from each and blend it into their own standards,’ emphasizing the adaptive nature of architectural practices in response to these technological advancements. Furthermore, the function of pre-sales representation in boosting confidence has been apparent, as renderings act as a link between concept and reality, sparking interest and investment well before physical construction commences.
For instance, a recent case study demonstrated that projects using pre-sales presentation tools experienced a 25% rise in early-stage investments. However, despite these advancements, a recent case study titled ‘Management Education on AR/VR’ highlights a 7% increase in the limitations of upper management knowledge over the past year, underscoring the ongoing need for education in AR/VR technologies. Overall, the adoption of BIM and VR showcases the benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals, marking a fundamental shift towards more collaborative, informed, and effective architectural development processes.
Future Trends in 3D Visualization and Stakeholder Collaboration
The landscape of architectural representation is rapidly transforming, with emerging trends poised to highlight the benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals in 2024. A crucial aspect of this evolution is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in 3D modeling, which promises to enhance design accuracy and operational efficiency significantly. This technology is essential in creating lifelike CG humans, effectively bridging the uncanny valley in architectural representations, thus elevating the realism and engagement of project presentations.
Notably, the large enterprises segment represented a substantial portion of the 3D rendering market in 2023, underscoring the growing dependence on advanced display tools. In September 2024, CADIZ introduced its latest 3D rendering tool designed for engineers, 3D modelers, and designers, which is aimed at transforming how professionals interact with 3D models and improve their workflow. The case study titled ‘Visualization and Simulation to Show Dominance in Market in 2023’ illustrates how innovations in visualization and simulation are driving market growth.
The adoption of cloud-based platforms is streamlining remote collaboration, enabling professionals from diverse locations to engage seamlessly in the design process. Additionally, as augmented reality (AR) becomes a standard presentation tool, the benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals provide immersive, interactive experiences that significantly enhance understanding and engagement with initiatives. High-quality renderings are not merely a luxury; they are an investment that offers a clear vision of the endeavor’s potential, essential for informed decision-making.
Architects must remain vigilant about these trends to effectively harness the benefits of collaborating with stakeholders through 3D visuals in their future endeavors, as they recognize the essential role of high-quality visual renderings in project development and decision-making. Furthermore, the diverse applications of 3D rendering extend beyond architecture to fields such as medical imaging, training simulations, product prototyping, and graphic design, showcasing its versatility and importance across various sectors.
Conclusion
The integration of 3D visualization technologies into architectural design has proven to be a game changer, enhancing stakeholder engagement, project planning, and communication. By offering immersive and interactive representations, 3D visuals facilitate a deeper understanding of architectural concepts, bridging communication gaps and fostering collaboration among all parties involved. The evidence presented demonstrates that these technologies not only improve clarity and accuracy but also evoke emotional connections, which are critical in residential architecture.
Moreover, the role of 3D modeling in streamlining project execution cannot be understated. Its precision significantly reduces the likelihood of construction errors and enhances client satisfaction by accurately reflecting their preferences. The strategic use of advanced visualization tools allows for optimal material utilization and waste reduction, leading to substantial cost savings and improved efficiency. As demonstrated through various case studies, organizations that leverage these technologies witness marked improvements in collaboration effectiveness and stakeholder engagement, ultimately driving investment and project success.
Looking ahead, the future of architectural visualization is poised for further transformation with the advent of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and augmented reality. These innovations promise to enhance the realism and interactivity of architectural presentations, ensuring that high-quality renderings remain an essential investment for informed decision-making. As architects continue to adapt to these advancements, the importance of 3D visualization in fostering collaboration and driving project outcomes will only become more pronounced, solidifying its place as an indispensable tool in the architectural toolkit.

0 Comments