Introduction
Architectural rendering stands at the forefront of modern visualization techniques, bridging the gap between abstract design concepts and tangible realities. As architects and stakeholders increasingly rely on high-quality visualizations to communicate ideas and align expectations, the significance of this discipline cannot be overstated. From the intricate details captured in 3D models to the immersive experiences offered by virtual reality, rendering serves as a critical tool in the architectural process.
With the market projected to expand significantly in the coming years, understanding the nuances of architectural rendering—including essential skills, various types, and the software that drives innovation—becomes imperative for professionals aiming to thrive in this dynamic field.
As the demand for skilled rendering artists grows, so too does the opportunity for those equipped to navigate the complexities of architectural visualization, ultimately shaping the future of design and construction.
Defining Architectural Rendering: The Foundation of Visualization
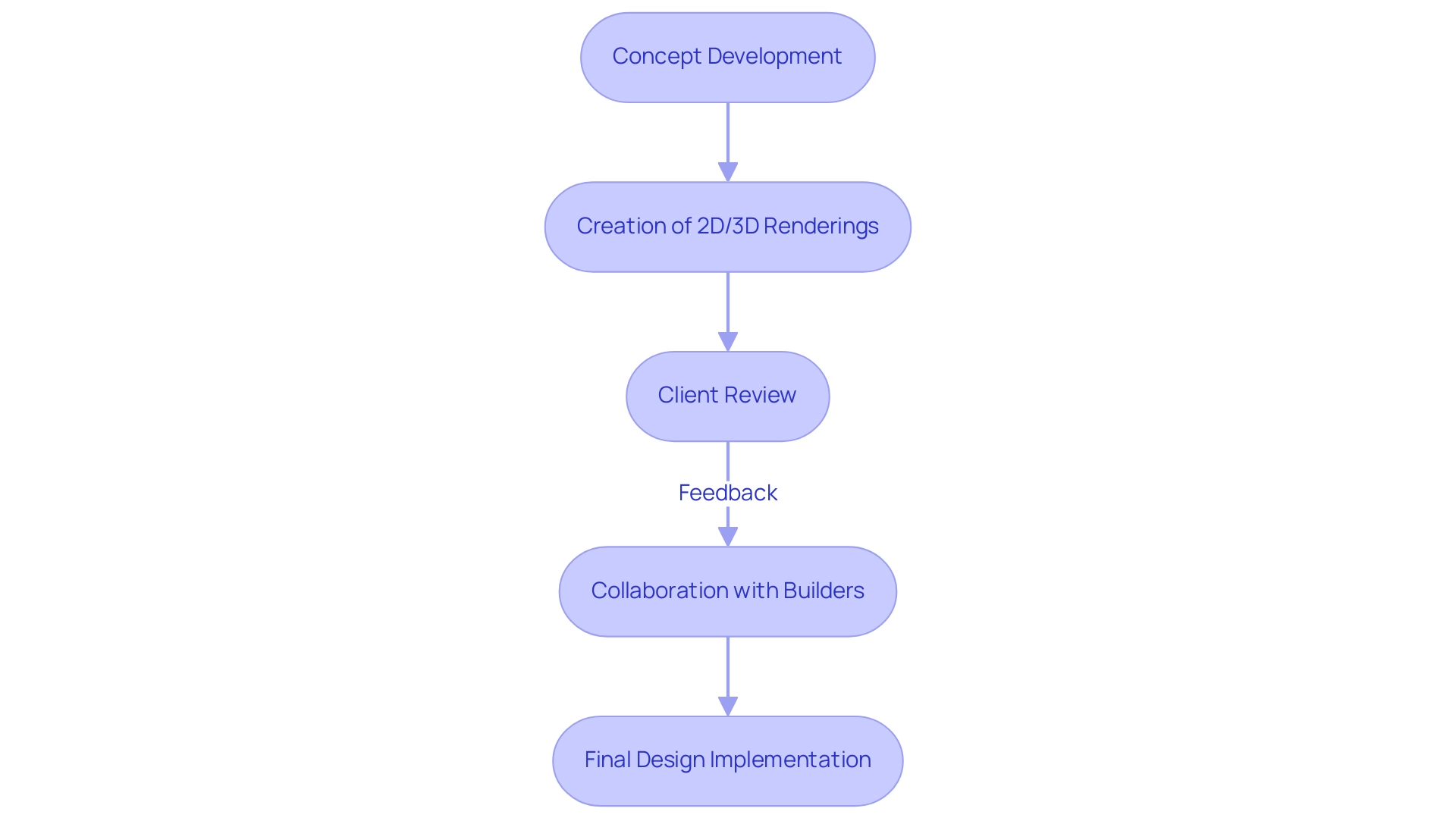
Rendering in architecture includes the creation of both two-dimensional and three-dimensional images that accurately depict the characteristics of proposed designs. This illustrative method acts as a crucial intermediary between abstract concepts and concrete representations, enabling architects, clients, and stakeholders to envision anticipated outcomes prior to the initiation of construction. The role of AI in creating lifelike CG humans is especially transformative, effectively bridging the uncanny valley and enhancing realism in architectural representations.
Moreover, 3D exterior visuals have emerged as essential tools for facilitating clear communication between homeowners and builders. By offering comprehensive illustrations of natural lighting, landscaping, and construction materials, these images assist in aligning expectations and promoting teamwork throughout the planning process. The importance of building visualization in the design process cannot be overstated; it enhances communication, fosters collaboration, and aids in informed decision-making by delivering a realistic depiction of how a space will look and operate.
As the market develops, with forecasts suggesting strong growth into 2024, the design illustration sector is anticipated to grow considerably, mirroring the rising need for high-quality graphics. In 2023, North America represented 34% of the 3D imaging market share, backed by strong technological infrastructure and high adoption rates of advanced imaging technologies across sectors. This highlights the increasing dependence on creating to aid successful building design projects.
Furthermore, client testimonials play a vital role at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, highlighting our commitment to excellence and the quality of our service. These feedbacks not only demonstrate our reliability but also shape our continuous growth as we strive to exceed client expectations. As Edwyne Fernandes notes, ‘Trained in modern data collection techniques and backed by years of collective experience, our analysts utilize superior research methods to deliver precise, insightful, and actionable market intelligence.’
This demonstrates the essential function of design visualization in modern building practices.
Key Skills and Specializations of Architectural Rendering Artists
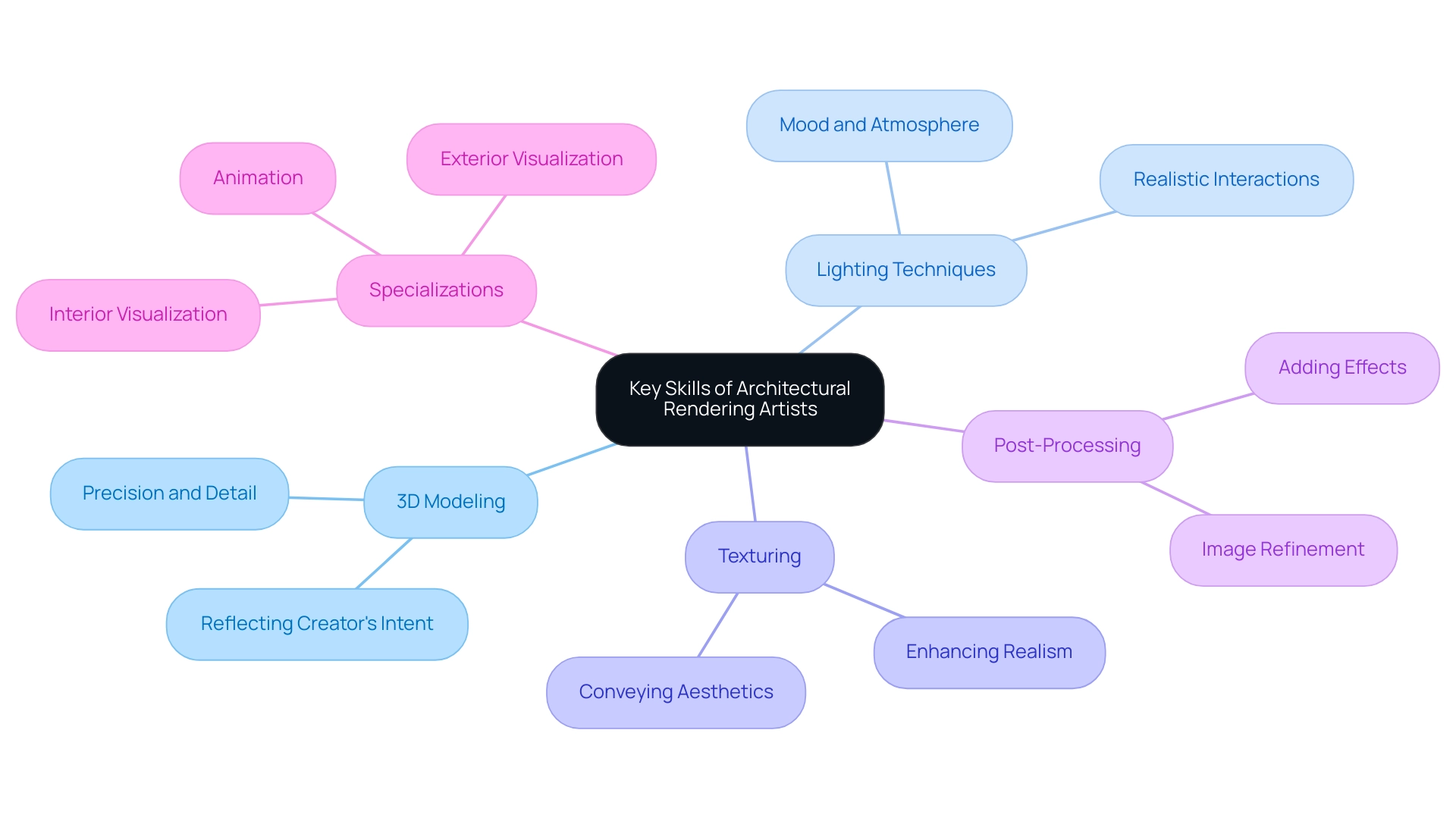
Architectural rendering artists must cultivate a multifaceted skill set encompassing a range of technical proficiencies essential for producing high-quality visualizations. The following skills are considered essential in this evolving field:
- 3D Modeling: Mastery in creating precise and intricate models of architectural concepts is fundamental. This skill ensures that representations accurately reflect the creator’s intent and specifications, capturing the essence of the creation through meticulous detail that tells a compelling story.
- Lighting Techniques: A comprehensive understanding of how light interacts with different surfaces is vital for creating realistic renderings. Proficient use of lighting can dramatically influence the mood and atmosphere of the visualization, enhancing the overall narrative and contributing to the storytelling aspect of the design.
- Texturing: The application of materials and finishes to surfaces not only enhances realism but also provides essential context for the viewer. This skill is crucial in conveying the intended aesthetics of a project, particularly in residential architecture designs where detail is paramount and plays a key role in the narrative.
- Post-Processing: Utilizing advanced software for image refinement and effect addition is key to achieving a polished final product. Post-processing can elevate a depiction from a mere representation to an evocative visual narrative, thereby ensuring accuracy and enhancing client satisfaction.
In addition to these foundational skills, specialization in areas such as interior visualization, exterior visualization, and animation allows artists to address specific project requirements more effectively. The function of detailed illustrations extends beyond mere visualization; it enhances project confidence and generates investment, especially during pre-sales phases. As the design visualization market continues its upward trajectory—projected to be worth $4.59 billion in 2024 and reach $16.18 billion by 2032, exhibiting a CAGR of 17.0%—the demand for skilled professionals who can navigate these complexities will only grow.
Moreover, with a considerable share of worldwide designers, engineers, contractors, owners, and investors concentrating on sustainability, the importance of accurate visualization in maintaining design heritage and honoring creativity becomes progressively essential. Furthermore, off-site construction techniques are said to generate 30% less emissions than conventional on-site construction, demonstrating the environmental effect of contemporary architectural practices and the essential role of visualization in this context.
Exploring Different Types of Architectural Renderings
Architectural renderings can be classified into several types, each serving essential roles in the creation and presentation process:
- Conceptual Renderings: Utilized primarily in the initial phases of a project, these renderings provide a broad overview, allowing stakeholders to grasp the fundamental vision without delving into intricate details. They aid in rapid representation of ideas, enabling informed decision-making before committing significant resources. Moreover, they support an iterative design process, allowing for multiple revisions based on feedback, which is crucial for refining the project vision.
- Presentation Renderings: These high-quality images are meticulously crafted for client presentations, emphasizing the aesthetic elements of the design. They serve to captivate potential clients and stakeholders, effectively communicating the project’s visual appeal and enhancing client understanding.
- Technical Renderings: Focused on construction specifics, these detailed images highlight materials, dimensions, and structural components. They are crucial for conveying essential information to contractors and engineers, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of the project’s technical requirements and improving stakeholder communication.
- Virtual Reality Renderings: This cutting-edge approach offers immersive experiences, enabling clients to explore spaces interactively. With advancements in technology, such visualizations are becoming increasingly popular, allowing for real-time modifications and improved client engagement.
Each type of visualization created by architectural rendering artists plays a distinct role in the design process, significantly enhancing communication and visualization. The significance of investing in high-quality visualizations produced by architectural rendering artists cannot be overstated; they serve as a window into the future of projects, helping to build excitement and clarity among all involved. This investment is crucial for making informed decisions and ensuring that every detail aligns with the overall vision.
As the market for these visualization types evolves, leading players in the 3D architectural sector, such as 3DTRIXS and Autodesk, are driving innovation through strategic investments in advanced technologies, underscoring the critical role of these services in today’s competitive landscape.
Essential Tools and Software for Architectural Rendering
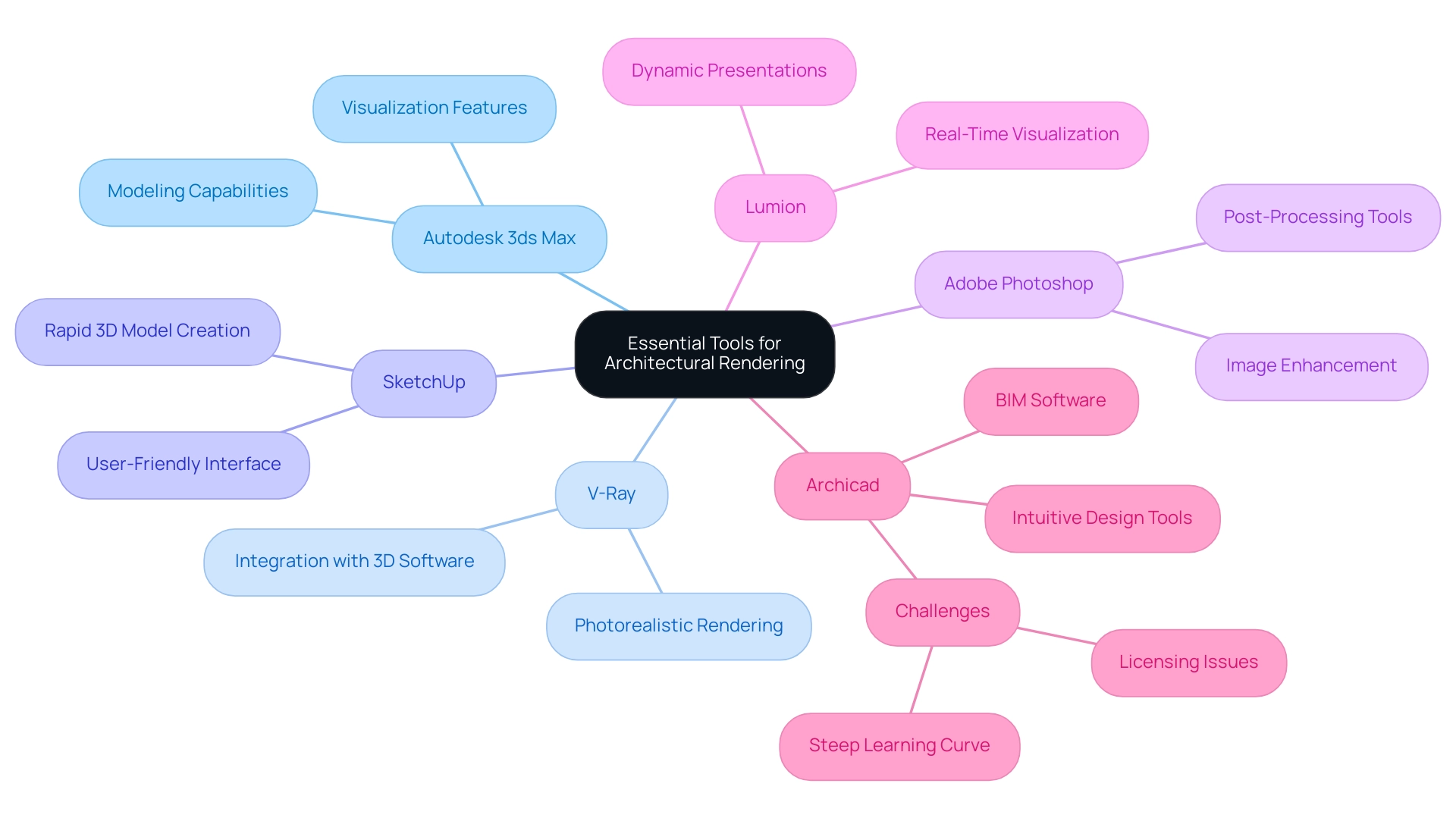
Architectural visualization artists leverage a diverse array of tools and software to produce compelling visualizations that meet client expectations and project demands. Among the most prominent software applications is Autodesk 3ds Max, celebrated for its strong modeling and visualization capabilities, allowing architects to create intricate structures with precision. Complementing this is V-Ray, a powerful visualization engine that integrates seamlessly with various 3D modeling software to generate photorealistic images that capture the essence of architectural intent, thereby enhancing the emotional impact and realism of projects.
Another essential tool is SketchUp, celebrated for its user-friendly interface that facilitates the rapid creation of 3D models, making it particularly valuable during the preliminary design phases and allowing for quick revisions that are crucial for client satisfaction. For post-processing and refinement of images, Adobe Photoshop remains indispensable, providing architects with the necessary tools to enhance visual presentations effectively, ensuring that all intricate details are captured.
Moreover, Lumion offers a unique advantage as a real-time visualization software, enabling quick visualizations and animations that are critical for dynamic presentations. Notably, Archicad is used by 86% of small businesses and 10% of mid-market companies, reflecting its relevance in the industry. However, a case study highlights that while Archicad is acknowledged for its intuitive creation tools and visualization capabilities, users have reported challenges with licensing and a steep learning curve, thus underscoring the importance of selecting the right software based on project needs.
When searching for quality 3D design services, consider aspects such as the provider’s portfolio, client testimonials, and responsiveness to feedback. A clear understanding of your project requirements and effective communication with the service provider can significantly enhance the outcome.
Proficiency with these tools is essential for architectural rendering artists, as it greatly influences the quality and effectiveness of visual results in communicating concepts and making informed choices. Investing in quality visuals is not just beneficial; it is essential for highlighting distinctive features and enabling cooperation between architects and clients. As Amanda Reid, a designer, mentions, “I’m a designer and employed Applied to create some 3D visuals for my client and was beyond impressed.”
The illustrations were of excellent quality and perfectly conveyed my design. The team was very responsive, professional, and easy to work with. Quick turnaround and fairly priced.
I plan to use them again and would definitely recommend them for all of your 3D needs.” This emphasizes the importance of high-quality visualizations in the design illustration process.
Career Opportunities for Architectural Rendering Artists
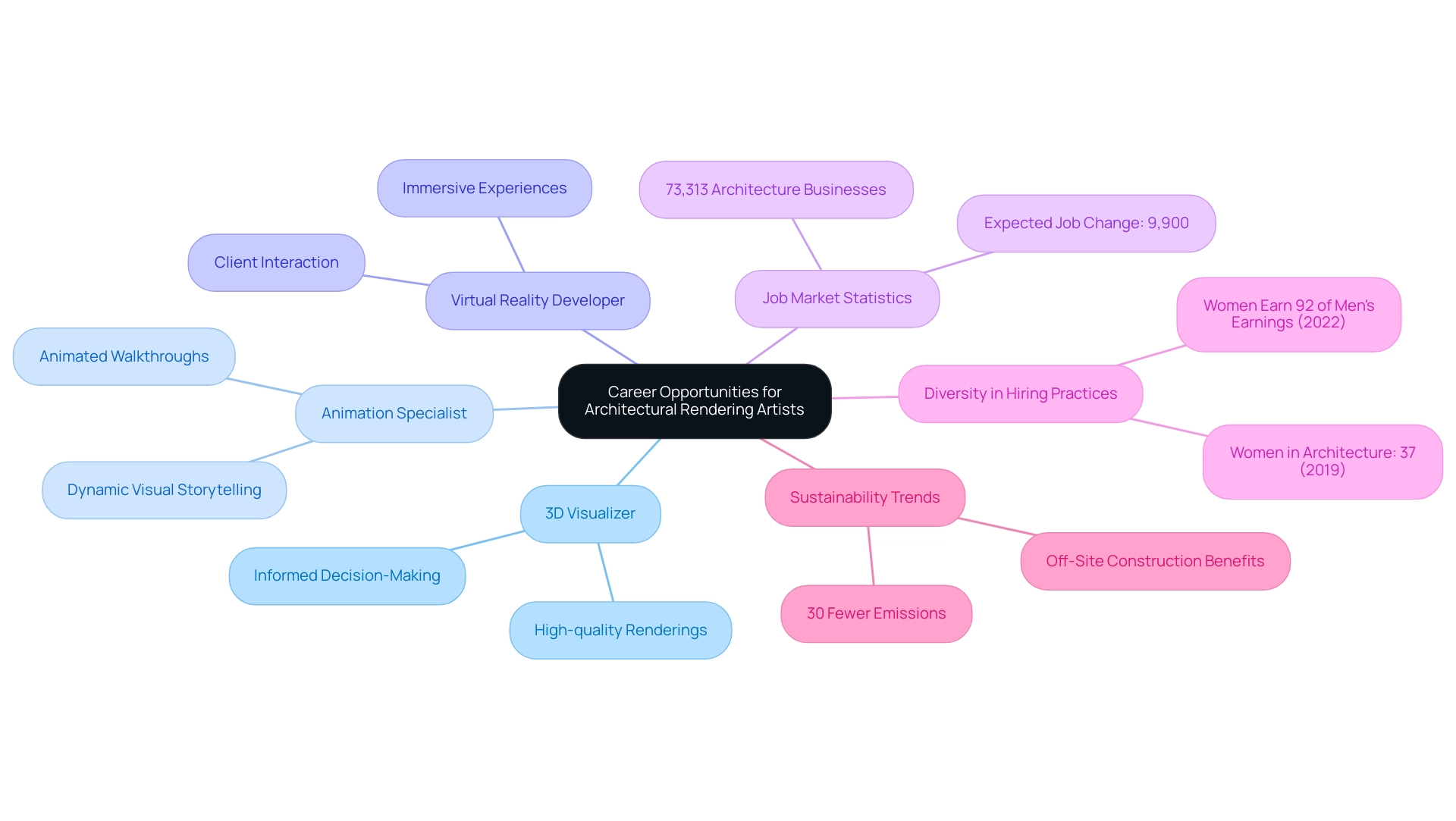
The need for architectural rendering artists is undergoing substantial expansion, driven by technological progress and the rising complexity of construction projects. Top-notch visuals act as a gateway to the future of your project, enabling stakeholders to envision possible results and grasp the concept behind the creations. This surge in demand has opened a variety of career opportunities across different sectors, including architectural firms, creative studios, and freelance environments.
With 73,313 businesses in architecture in the U.S., the job market is robust and diverse. Potential roles within this field include:
- 3D Visualizer: Responsible for producing high-quality renderings that effectively convey intent and aesthetics, serving as a vital tool for informed decision-making.
- Animation Specialist: Tasked with creating animated walkthroughs and presentations, enhancing stakeholder engagement through dynamic visual storytelling.
- Virtual Reality Developer: Focused on crafting immersive experiences that allow clients to interact with designs in a virtual space.
Moreover, the case study on off-site construction methods illustrates how design practices are evolving; these methods contribute to a more environmentally friendly and resource-efficient building industry, resulting in 30% fewer emissions compared to traditional onsite construction. As the design visualization industry evolves, professionals must commit to continuous learning and adapt to emerging technologies, ensuring their skills remain relevant and competitive. With an anticipated employment change of 9,900 jobs for architects from 2023 to 2033, the landscape for architectural rendering artists is poised for expansion, reflecting broader trends within the architectural sector.
Furthermore, high-quality visual renderings—comprised of intricate details, such as the way sunlight dances off windows and the subtle texture of bricks—are essential for showcasing unique design characteristics and enhancing emotional impact. It is also important to note that in 2019, 37% of all architecture staff were women, and women earned 92% of what men earned in 2022, highlighting the need for diversity and equity in hiring practices within the industry.
Conclusion
Architectural rendering plays a pivotal role in the modern architectural landscape, serving as the essential bridge between conceptual design and tangible reality. The exploration of various types of renderings, from conceptual to virtual reality, highlights their unique contributions to the architectural process, enhancing communication and fostering collaboration among stakeholders. As the market for architectural rendering continues to expand, the emphasis on high-quality visualizations has become increasingly evident, reflecting the significant investment required to ensure that designs are accurately represented and effectively communicated.
The skills and specializations required of rendering artists have never been more critical. Mastery in 3D modeling, lighting techniques, texturing, and post-processing is indispensable for producing compelling visual narratives that resonate with clients and stakeholders alike. As the demand for skilled professionals grows, the architectural rendering market is projected to reach remarkable heights, underscoring the importance of continuous learning and adaptation to new technologies in this dynamic field.
Furthermore, the integration of advanced software tools not only enhances the quality of renderings but also streamlines the workflow for architects and designers. As technological advancements reshape the rendering landscape, professionals must remain vigilant in selecting the right tools to meet their project needs. Ultimately, high-quality architectural renderings are not just a luxury; they are a necessity for realizing the future of architectural design, enabling informed decision-making and ensuring that every project aligns with its intended vision. The evolution of this discipline will undoubtedly continue to shape the construction industry, paving the way for innovative, sustainable, and aesthetically compelling built environments.


0 Comments