Overview
3D artists are skilled professionals who create three-dimensional models and visualizations across various industries, including architecture, gaming, and film, utilizing advanced software and innovative techniques. The article highlights their crucial role in transforming abstract concepts into tangible visual experiences, enhancing client understanding and decision-making, while also addressing the evolving technologies and ethical considerations that shape the future of their craft.
Introduction
In the vibrant and rapidly evolving world of contemporary art, 3D artists stand at the forefront, wielding advanced technology to transform imagination into reality. Their expertise spans various industries—from architecture and gaming to film and product design—creating compelling visual narratives that captivate audiences and drive innovation.
As they navigate the intricate balance between artistic expression and technical proficiency, these artists harness cutting-edge tools and techniques, including AI-driven technologies, to produce hyper-realistic renderings that enhance understanding and engagement.
With the growing integration of digital platforms and the increasing demand for immersive experiences, the role of 3D artists is more critical than ever, prompting a deeper exploration of their skills, specializations, and the challenges they face in this dynamic landscape.
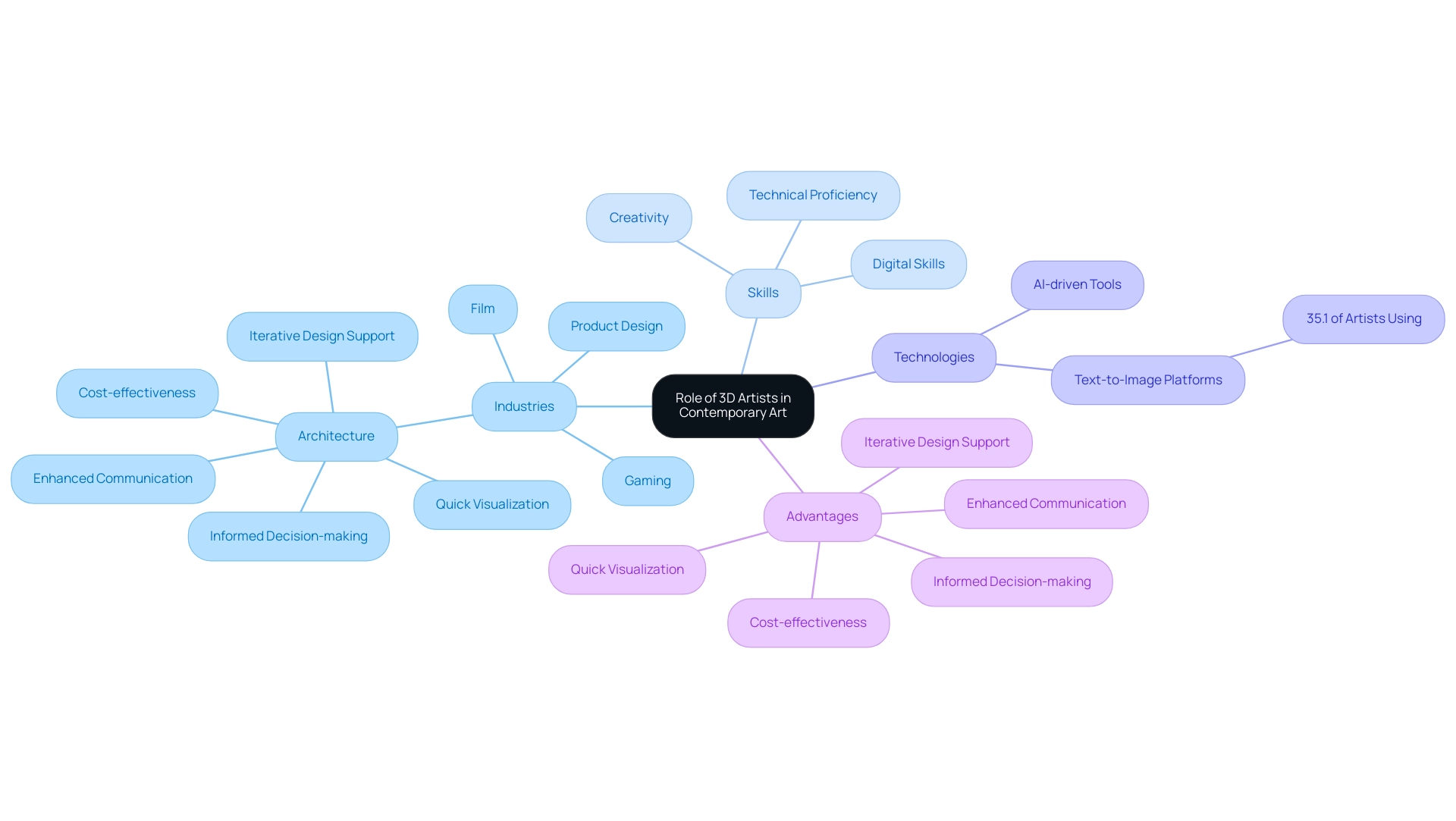
Defining the Role of 3D Artists in Contemporary Art
3D creators are skilled professionals dedicated to the development of three-dimensional models and visualizations utilizing advanced computer software. Their influence spans a diverse array of industries, including architecture, gaming, film, and product design. By harnessing innovative techniques and cutting-edge tools, such as AI-driven technology for lifelike CG humans, artists in 3D transform abstract concepts into tangible visual experiences.
This capability allows clients and audiences to perceive designs prior to their physical manifestation, which is especially crucial in architecture. Hyper-realistic visualizations not only enhance client understanding but also improve stakeholder communication and help identify design issues early on. In architectural visualizations, the appropriate level of detail is essential, as it can significantly impact how potential homeowners and stakeholders perceive the project.
Detailed renderings can provide a clearer picture of the final outcome, facilitating informed decision-making. In the gaming industry, 3D artists breathe life into animated characters, showcasing their adaptability and creative prowess in the contemporary art landscape. Notably, over a third (35.1%) of creators have adopted text-to-image platforms to explore and develop new ideas, showcasing a growing integration of digital technologies.
As the role of creators evolves, so too does the expectation for them to manage these digital tools, emphasizing the importance of digital skills in their workflows. Furthermore, with seven out of ten (70%) US adults believing that creators should be compensated when generative AI utilizes their work, the ethical considerations surrounding the integration of AI in creative processes are paramount. This evolving landscape positions artists as vanguards of new technologies, exploring the creative potential of AI and its implications for the future of art.
However, the criticism of AI-generated art, which argues that it lacks the emotion, originality, and intent found in human-created art, underscores the ongoing debate about the value and authenticity of both AI-generated and traditional artistic expressions. Through architectural visualization, the immersive effect promotes community connections for prospective homeowners, emphasizing the varied uses and significance of 3D imagery in improving understanding and decision-making.
The advantages of initial conceptual models in architecture include:
- Quick visualization
- Cost-effectiveness
- Informed decision-making
- Enhanced communication
- Iterative design support
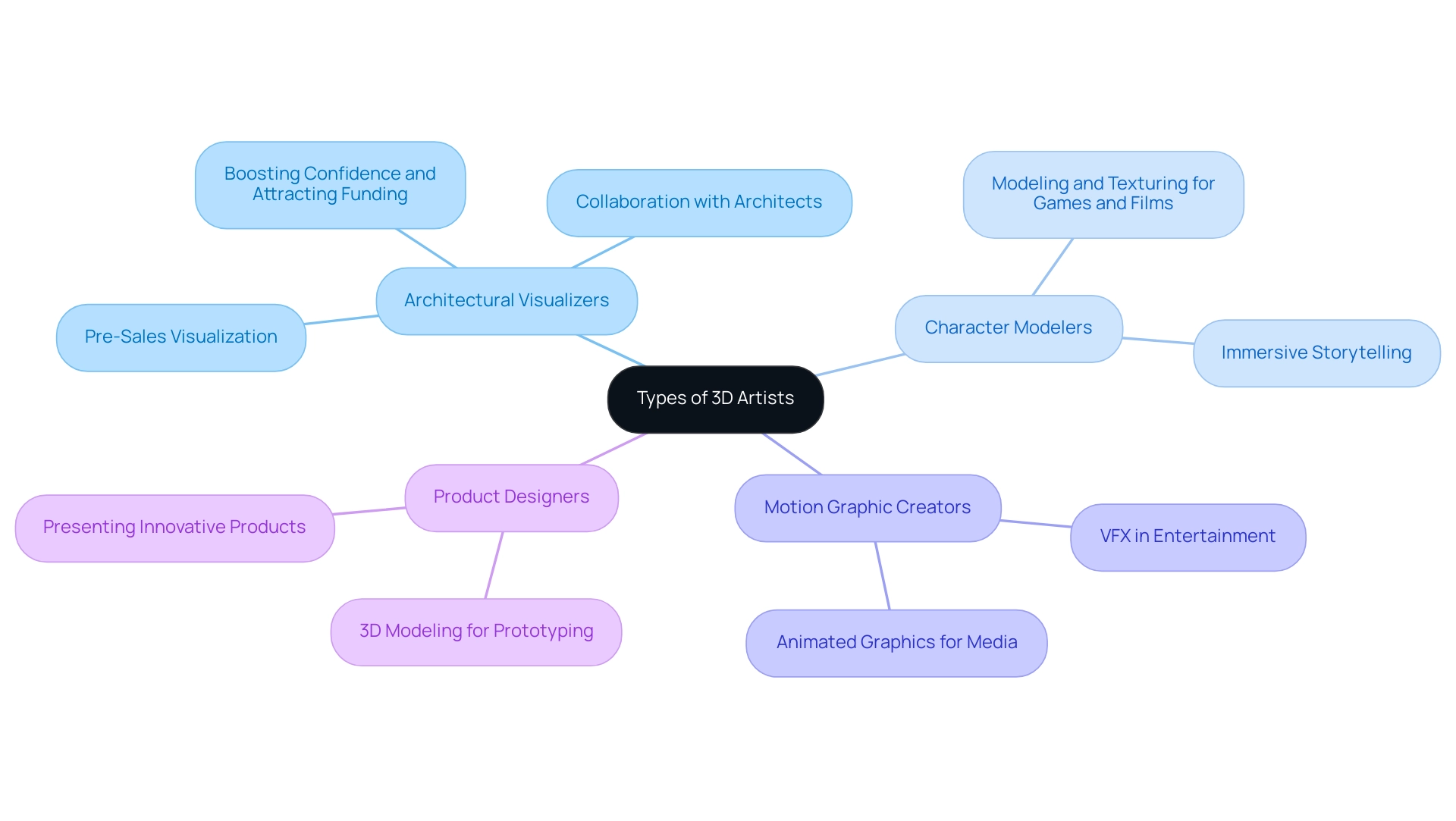
Exploring Different Types of 3D Artists and Their Specializations
The realm of 3D artists encompasses a diverse range of specializations, each requiring a tailored skill set and toolkit. Architectural visualizers are essential in producing detailed representations of structures and interiors, serving not only to illustrate concepts but also to boost confidence in the undertaking and attract funding through persuasive pre-sales visuals. These visualizations act as a bridge between concept and reality, empowering developers with a tangible asset that can ignite interest long before physical construction begins.
This collaboration with architects and designers ensures precision and creativity in their visualizations, ultimately showcasing functionality and aesthetics that enhance client satisfaction and marketing effectiveness. A notable example of this is illustrated in the case study ‘The Power of Pre-Sales Visualization,’ which demonstrates how effective renderings can significantly impact project success. On the other hand, 3D artists focus on the modeling and texturing of characters for video games and films, a specialization that has seen significant growth due to the increased demand for immersive storytelling in the entertainment sector.
Motion graphic creators contribute animated graphics for various media, while product designers leverage 3D modeling to prototype and present innovative products. Jasmine Katatikarn aptly remarks,
The industry-wide application of visual effects across several sectors, particularly in the gaming and entertainment industries, has contributed significantly to the 3D animation market’s remarkable growth.
This underscores the evolving landscape of 3D artists, particularly as streaming services such as Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ continue to elevate the demand for high-quality VFX content.
According to recent statistics, the median annual wage for all workers was $48,060, reflecting the financial prospects within the industry. Moreover, the trend of moviemakers incorporating more VFX-based shots and animations in movies and TV series is driving market growth. The case study named ‘Impact of Streaming Services on VFX’ demonstrates how platforms such as Netflix and Disney+ are significant trends affecting this market, resulting in a rise in opportunities for specialized 3D artists, particularly architectural visualizers, whose abilities are increasingly in demand across various endeavors.
For lead architects seeking quality 3D architectural rendering services, it is essential to consider factors such as the provider’s portfolio, client reviews, and the ability to meet specific project needs, as highlighted in the FAQs on hiring rendering services.
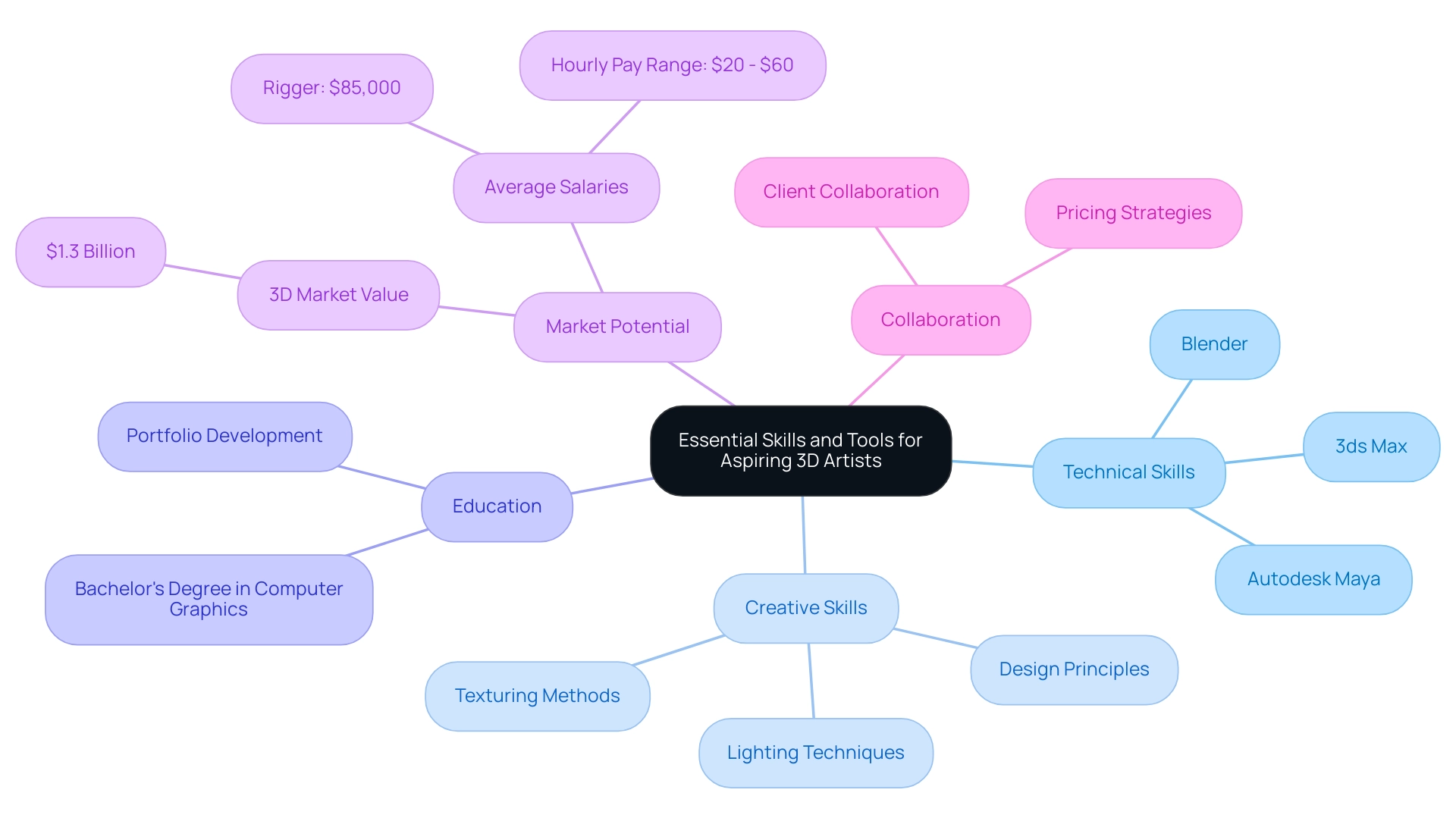
Essential Skills and Tools for Aspiring 3D Artists
For aspiring 3D artists, cultivating a robust blend of technical prowess and creative insight is essential. For 3D artists, mastery of industry-standard software such as Blender, Autodesk Maya, and 3ds Max is vital for crafting high-quality 3D models and animations. Furthermore, a solid grasp of design principles, lighting techniques, and texturing methods is fundamental in producing visually striking work that resonates with architectural vision.
As emphasized in the artistic journey of exterior 3D visualization, every detail—from the way sunlight dances off surfaces to the texture of materials—plays a crucial role in enhancing realism and emotional impact. A bachelor’s degree in computer graphics, animation, fine arts, or a related field typically equips students to become 3D artists with the necessary skills and portfolio development crucial for employment in the field. Creativity, coupled with a meticulous eye for detail, empowers artists to conceptualize and realize their artistic visions effectively.
As the market for 3D drops expands, valued at $1.3 billion, the economic potential in this field is significant. Moreover, experienced professionals can earn competitive salaries, with roles such as Riggers averaging around $85,000 annually, according to Indeed. As the field continues to evolve, embracing continuous learning and adapting to emerging tools and technologies is imperative for maintaining relevance and competitiveness in this dynamic landscape.
Furthermore, participating in client collaboration during the creation process ensures that the artistic vision aligns with client expectations, ultimately enhancing the quality and satisfaction of the final product. Understanding the pricing strategies associated with high-quality renderings is also essential, as it reflects the value of the detailed work and the investment in creating impactful architectural visuals.
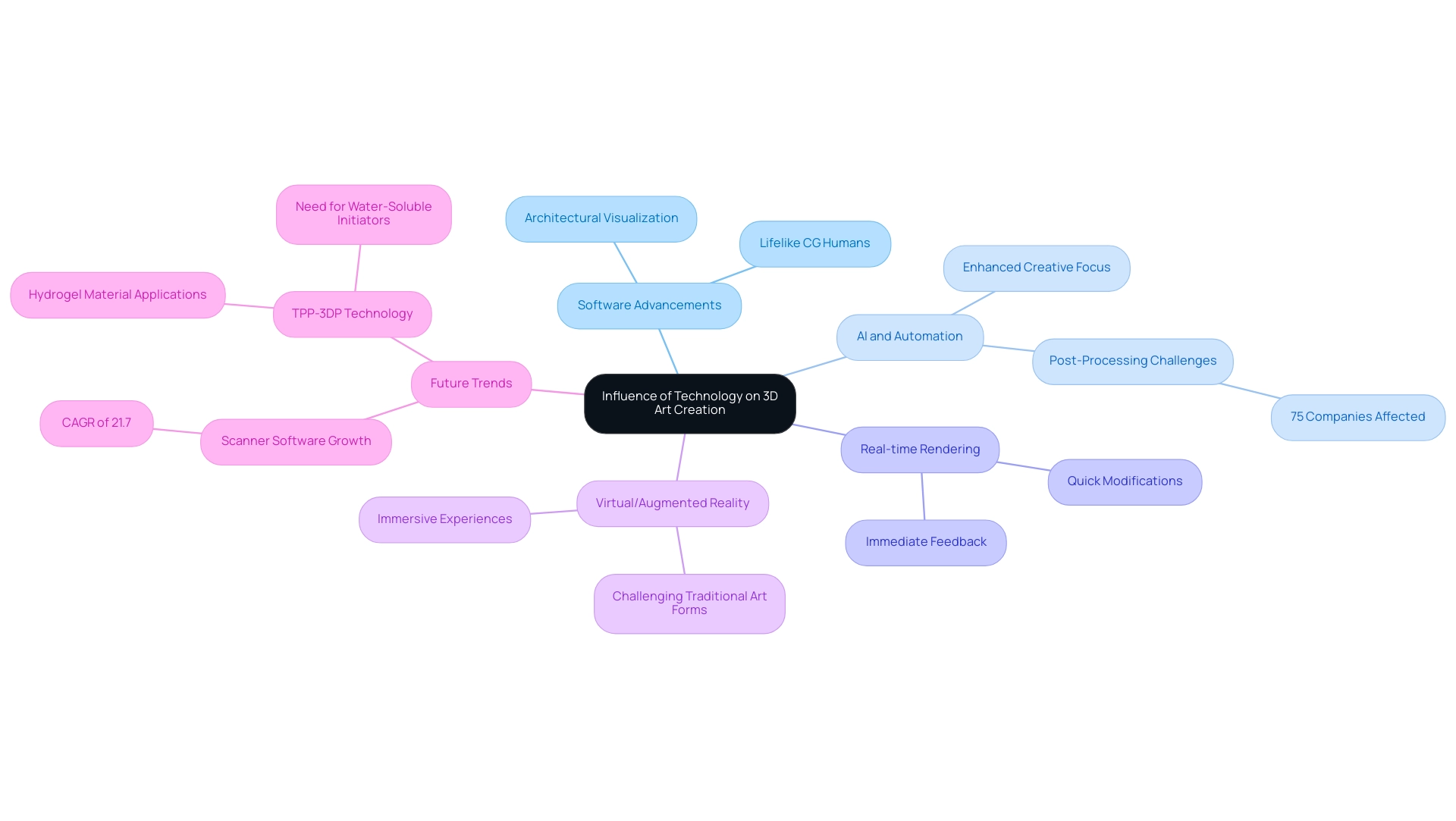
The Influence of Technology on 3D Art Creation
The influence of technology on 3D art creation is nothing less than revolutionary, with advancements in software enabling creators to attain higher levels of sophistication and realism in their visuals. Architectural visualization, in particular, offers an immersive experience that not only transforms prospects into active participants in envisioning their future spaces but also fosters community connections among future homeowners. This immersive approach is essential for building a strong sense of community from the outset.
As artificial intelligence (AI) continues to incorporate into development processes, it enables remarkable automation and efficiency, allowing creators to redirect their focus toward creative expression rather than repetitive tasks. This includes the creation of lifelike CG humans, which bridge the gap between realism and the uncanny valley, enhancing client understanding and stakeholder communication. A pertinent example of this is the ongoing challenge of post-processing in 3D printing; 75% of companies identify the time it takes to finish parts as a major issue.
Addressing these challenges is essential for improving the efficiency of 3D printing operations. The introduction of real-time rendering engines has significantly transformed how 3D artists visualize their projects, offering immediate feedback and enabling quick modifications to their concepts. Furthermore, the rise of virtual and augmented reality is opening up new dimensions for 3D artists, encouraging them to create immersive experiences that challenge traditional art forms.
As the scanner software segment is projected to experience a robust growth rate of 21.7% from 2022 to 2030, it underscores the continued evolution and relevance of technology in shaping the future of 3D artists. According to Amy J.C. Trappey, ‘The findings of this review confirm the TPP-based 3D printing (TPP-3DP) technology has broad application prospects, of which the hydrogel material applied in tissue engineering and drug delivery is the future trend.’ This technological momentum indicates that progress in AI will further improve the abilities of creators, making 2024 a crucial year for innovation in 3D creation.
Additionally, there is a growing need for highly-initiated water-soluble initiators to enhance resolution in TPP-3DP technology, further highlighting the technological demands in 3D art creation.
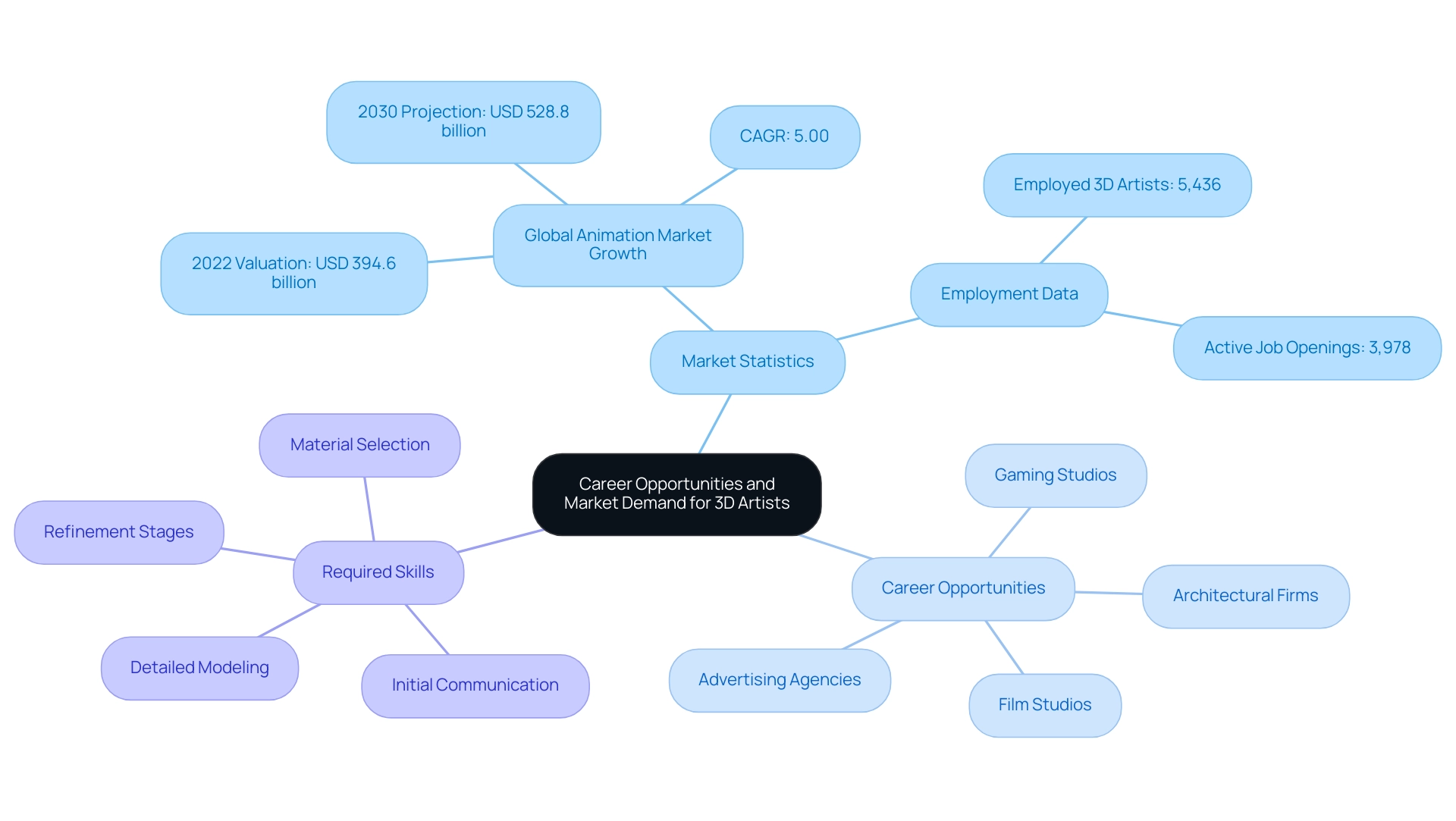
Career Opportunities and Market Demand for 3D Artists
The demand for 3D creators is on a remarkable upward trajectory, fueled by the escalating need for visual content across marketing, entertainment, and design sectors. In 2022, the global animation market was valued at USD 394.6 billion and is projected to grow to USD 528.8 billion by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.00%. This growth, emphasized in the case study titled ‘Future Growth,’ results in various career opportunities for 3D artists, which include roles in:
- Gaming studios
- Film studios
- Architectural firms
- Advertising agencies
At companies such as J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, 3D artists play an essential role in the collaborative visualization process, which includes:
- Initial communication
- Detailed modeling
- Material selection
- Refinement stages
These steps are essential for producing high-quality visual renderings that enhance architectural vision and ensure client satisfaction. Currently, there are over 5,436 3D artists employed in the United States, alongside 3,978 active job openings, clearly indicating a strong job market for aspiring 3D artists.
Entry-level positions provide competitive salaries, while seasoned 3D artists can anticipate considerably greater earnings, with a median pay of $99,060 for special effects creators and animators. Freelancing also offers a profitable pathway, allowing creators to participate in a range of endeavors and develop their brands. As noted by industry expert Steve Hughart II, ‘With AI growing so fast, digital media work will all be AI-generated, so focusing on improving your editing skills and creating with your hands will be where the jobs are.’
This insight underscores the necessity for 3D artists to adapt and enhance their skill sets in order to remain relevant in a rapidly evolving landscape. The investment in top-notch visualizations is essential, as they act as a glimpse into the future of initiatives, enabling stakeholders to envision possible results and make educated choices. Notably, the success of ‘Super Mario Bros.’ as the highest-grossing movie in 2023 further exemplifies the increasing market demand for 3D artists in the entertainment industry.
The intricate details in architectural renderings not only enhance realism but also evoke emotional responses, making them essential in development and decision-making.
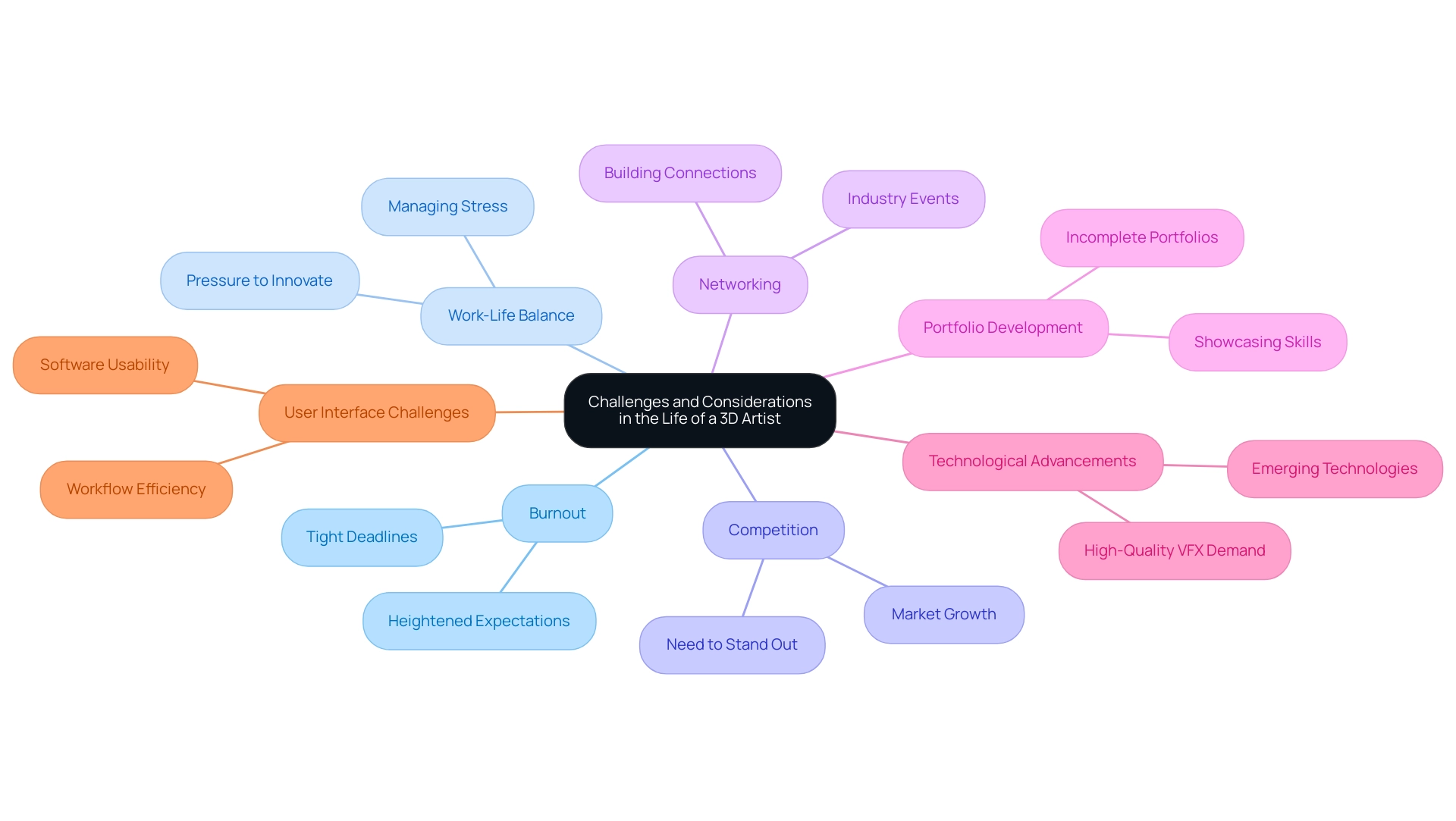
Challenges and Considerations in the Life of a 3D Artist
A career as a 3D artist can be immensely rewarding, yet it is fraught with challenges that require resilience and strategic planning. Many creators face the risk of burnout, largely fueled by tight deadlines and heightened expectations prevalent in the industry. The need for a healthy work-life balance becomes crucial as the pressure to continuously innovate and master new technologies mounts.
The intricate details in architectural renderings—such as the way sunlight dances off the windows or the subtle texture of bricks—are not merely embellishments; they are essential for creating realistic, emotionally resonant projects that captivate clients and stakeholders alike. Jasmine Katatikarn notes,
The industry-wide application of visual effects across several sectors, particularly in the gaming and entertainment industries, has contributed significantly to the 3D animation market’s remarkable growth.
This growth, while promising, also intensifies competition and the pressure to stand out.
Aspiring 3D artists must prioritize networking and the development of a compelling portfolio; however, statistics reveal that many 3D Game Design graduates never finish their portfolios, which can severely limit the job prospects for 3D artists. Furthermore, the rise of streaming services has driven the demand for high-quality VFX, adding to the challenges as creators strive to keep up with industry standards. Furthermore, the intricacy and size of projects can greatly influence processing time and resource needs, making it crucial for creators to manage their time efficiently.
Enhancing the user interface and experience of 3D rendering software continues to be a challenge for developers, affecting creators’ workflow and creativity. By acknowledging these challenges and actively pursuing strategies to handle stress and sustain their enthusiasm for creativity, 3D artists can more effectively navigate their careers in this dynamic field.
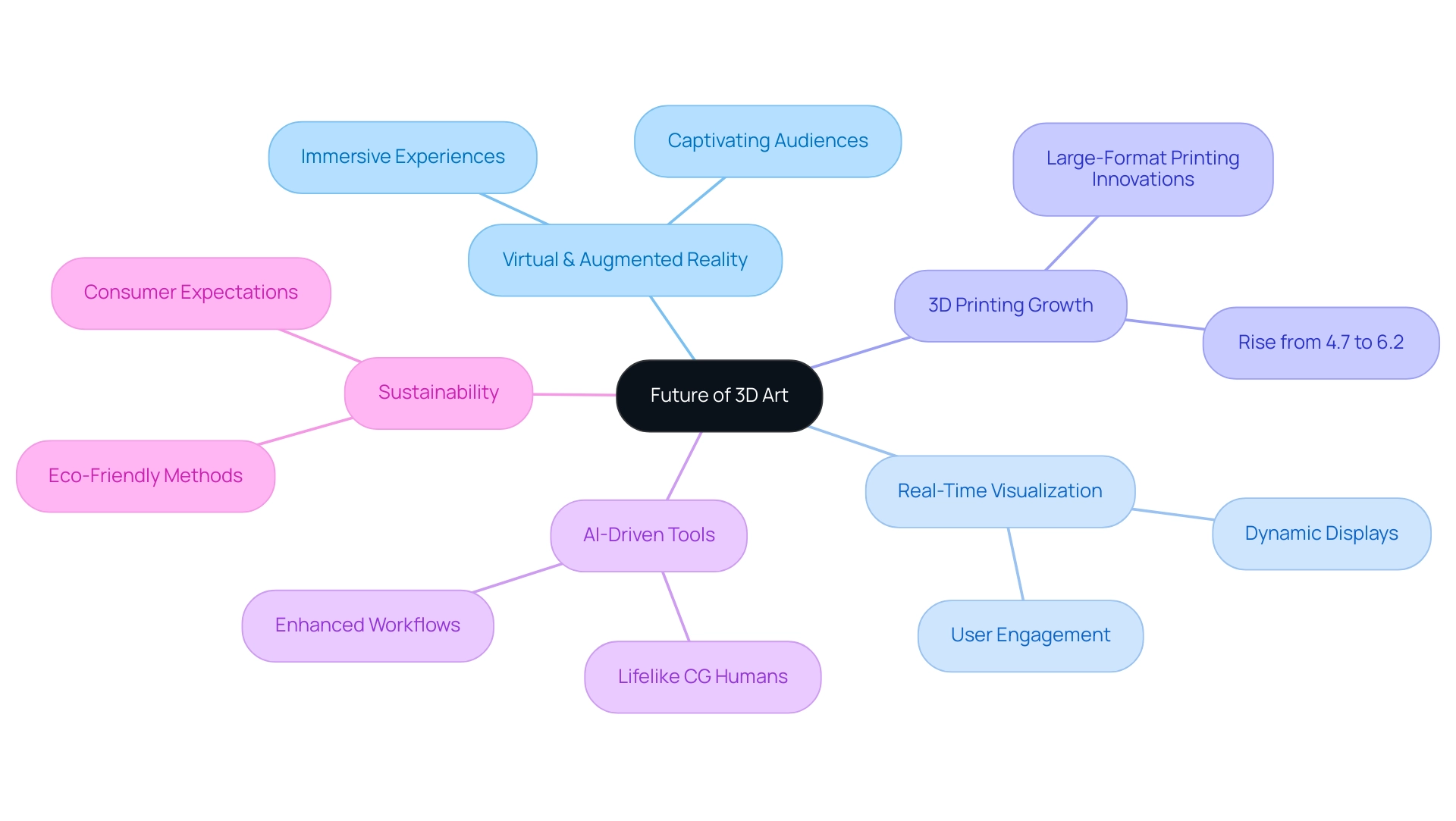
The Future of 3D Art: Trends and Innovations
The future of 3D art is on the brink of transformative advancements. With projections for 2024 indicating a marked shift towards virtual and augmented reality, 3D artists are expected to play a pivotal role in creating immersive experiences that captivate audiences. Top-notch visuals act as a ‘window into the future’ of initiatives, enabling stakeholders to envision possible results and make informed choices.
Innovations in real-time visualization are gaining traction, allowing for dynamic and interactive displays that enhance user engagement. As Eric Utley from Protolabs notes, There's geometries and quantities that only 3D printing can do at that scale, emphasizing the unique capabilities that modern 3D technology offers. This ability is especially essential for intricate undertakings where the scale—such as an entire community compared to a single-car garage—and creative details—like whether to display a clock on the wall or its internal gears—require high-quality visuals to effectively visualize potential outcomes.
Recent statistics reveal that the percentage of respondents printing more than 1,000 parts has risen from 4.7% in 2022 to 6.2% in 2023, highlighting significant growth in the 3D printing sector. Furthermore, advancements in large-format 3D printing, supported by new robotic systems, illustrate how the industry is evolving to meet complex demands. Grasping the anatomy of a 3D building rendering is crucial for lead architects, as it guides the development process and improves outcomes through detailed visualizations that enable informed decision-making.
The incorporation of AI-driven creation tools is anticipated to enhance workflows and broaden creative opportunities for creators, especially in producing lifelike CG humans that bridge the uncanny valley in architectural visualizations. Sustainability is also emerging as a critical driver in 3D design practices, with creators increasingly adopting eco-friendly methods and materials in their projects. This shift not only addresses environmental concerns but also aligns with consumer expectations for responsible artistry.
As the industry evolves, those 3D artists who embrace these trends will be well-positioned to lead the charge in innovation and creativity, setting new benchmarks for excellence in their field.
Conclusion
The role of 3D artists in contemporary art is increasingly vital, as they harness advanced technologies to create immersive experiences across various industries. From architectural visualizations that enhance stakeholder understanding to character animations that bring stories to life, these artists shape the way audiences interact with visual narratives. The integration of AI and real-time rendering tools is revolutionizing their creative processes, allowing for greater efficiency and realism in their work.
As the demand for skilled 3D artists continues to rise, so does the need for specialized training and a strong portfolio. Navigating the challenges of tight deadlines and evolving technologies is essential for success in this competitive field. The future of 3D artistry promises exciting advancements, particularly with the growing emphasis on virtual and augmented reality, which will further expand the creative possibilities for artists.
Embracing sustainability and ethical practices will also play a crucial role in shaping the future of 3D art. As artists adapt to these trends, they will not only enhance their own careers but also contribute to a more responsible and innovative artistic landscape. Ultimately, the fusion of technology and artistry will continue to redefine the boundaries of creativity, inviting audiences to engage with art in unprecedented ways.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do 3D creators do?
3D creators develop three-dimensional models and visualizations using advanced computer software, impacting various industries such as architecture, gaming, film, and product design.
How do 3D visualizations benefit architecture?
3D visualizations allow clients to perceive designs before physical construction, enhancing understanding, improving stakeholder communication, and helping to identify design issues early on. Detailed renderings facilitate informed decision-making.
What role do 3D artists play in the gaming industry?
In the gaming industry, 3D artists create animated characters, showcasing their adaptability and creativity to enhance immersive storytelling.
What percentage of creators use text-to-image platforms?
Over a third (35.1%) of creators have adopted text-to-image platforms to explore and develop new ideas.
What are the ethical considerations regarding AI in creative processes?
With 70% of US adults believing creators should be compensated when generative AI utilizes their work, ethical considerations surrounding the integration of AI in creative processes are significant and evolving.
What are the advantages of initial conceptual models in architecture?
The advantages include quick visualization, cost-effectiveness, informed decision-making, enhanced communication, and iterative design support.
What specializations exist within the realm of 3D artists?
Specializations include architectural visualizers, 3D modelers for video games and films, motion graphic creators, and product designers.
How has the demand for 3D artists changed with the rise of streaming services?
The demand for high-quality visual effects (VFX) content has increased due to streaming services like Netflix and Disney+, contributing to market growth and creating more opportunities for specialized 3D artists.
What should lead architects consider when hiring 3D architectural rendering services?
Lead architects should consider the provider’s portfolio, client reviews, and the ability to meet specific project needs.

0 Comments