Overview
3D artist jobs encompass a variety of roles focused on creating detailed three-dimensional models and visualizations for industries such as architecture, gaming, and film, where they play a crucial role in transforming concepts into compelling visuals. The article emphasizes that the demand for these professionals is rising due to technological advancements and the need for high-quality visual content, while also addressing challenges such as job security and burnout, highlighting the importance of continuous skill development and adaptability in this competitive field.
Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of 3D artistry, professionals navigate a complex interplay of creativity and technology, shaping the visual narratives that define industries from architecture to entertainment. As the demand for skilled 3D artists surges, driven by advancements in virtual reality and real-time rendering, understanding the multifaceted roles within this field becomes imperative.
This article delves into the diverse specializations of 3D artists, essential skills required for success, and the current job market trends, while also addressing the challenges and opportunities that come with the territory. By exploring the influence of technology and the pathways for career advancement, it sheds light on how artists can thrive in an increasingly competitive environment, ensuring their contributions resonate with stakeholders and elevate the standards of visual storytelling.
Defining 3D Artist Roles: An Overview
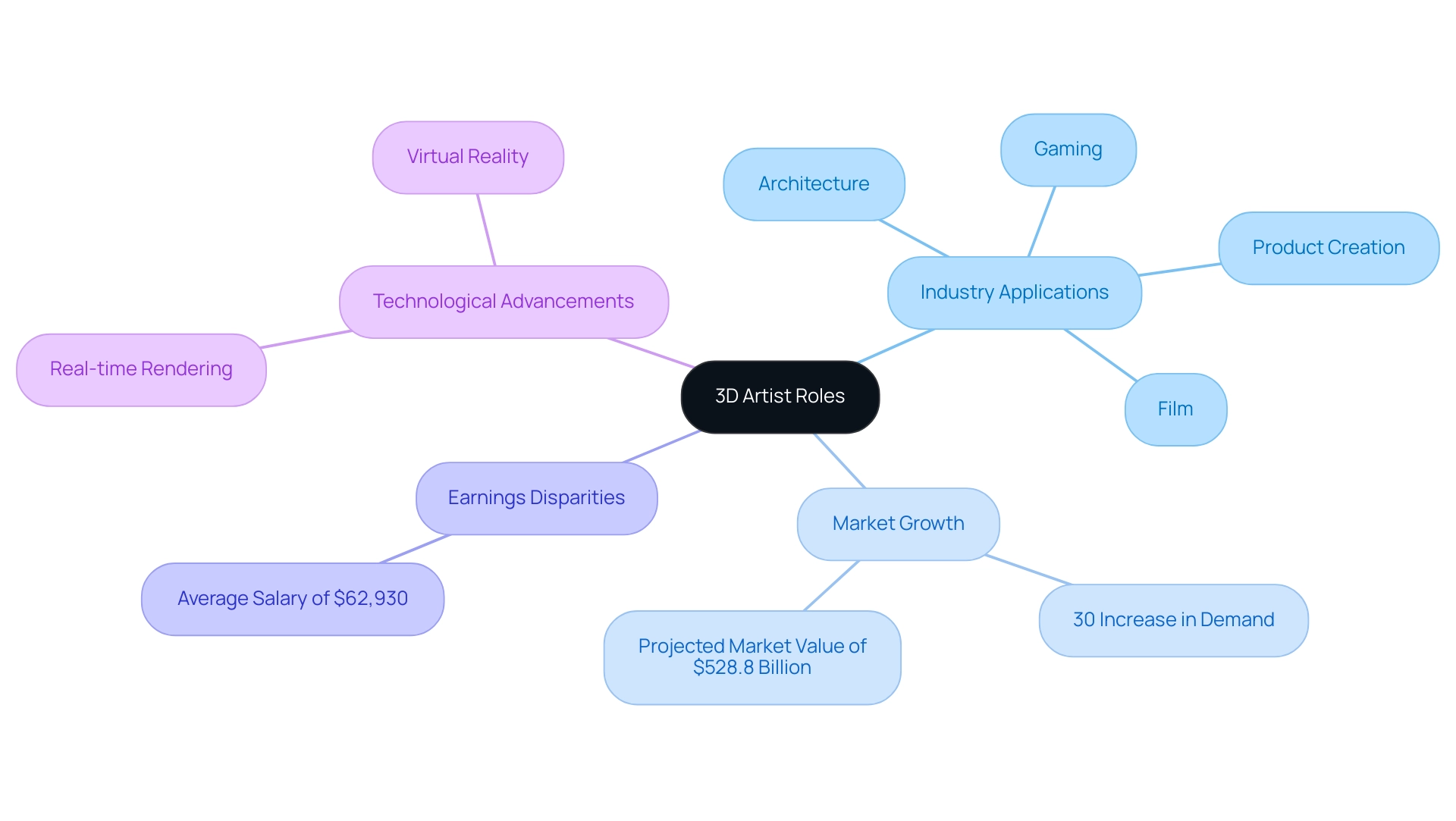
A 3D artist is a specialized professional adept in creating intricate three-dimensional models and visualizations using advanced software tools. Their expertise is crucial in sectors such as architecture, gaming, film, and product creation, where they transform abstract concepts into tangible visual representations. This capability not only enables effective communication of design intent but also plays a significant role in pre-sales visualization, enhancing confidence and generating investment through compelling visuals.
For instance, a recent initiative in urban development utilized 3D renderings to secure funding by visually demonstrating its potential impact and aesthetic appeal to stakeholders. The scope of a 3D creator’s responsibilities varies considerably depending on industry requirements, project specifics, and individual skill sets. The global demand for skilled animation professionals has surged by 30% since 2018, reflecting a significant increase in opportunities for 3D creators.
With the animation market projected to grow from USD 394.6 billion in 2022 to USD 528.8 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 5.2%, the demand for skilled 3D creators is on the rise. However, it is important to address the disparity in earnings, as Black or African American 3D creators earn an average salary of $62,930, highlighting the need for greater equity in the industry. Technological advancements, such as real-time rendering and virtual reality, are fueling robust growth in the animation sector, creating new avenues for 3D artists to thrive.
This trend underscores the pivotal role these professionals play in delivering high-quality visual content that resonates with audiences and stakeholders alike, while also celebrating creativity and preserving architectural legacy.
Exploring Different Types of 3D Artists
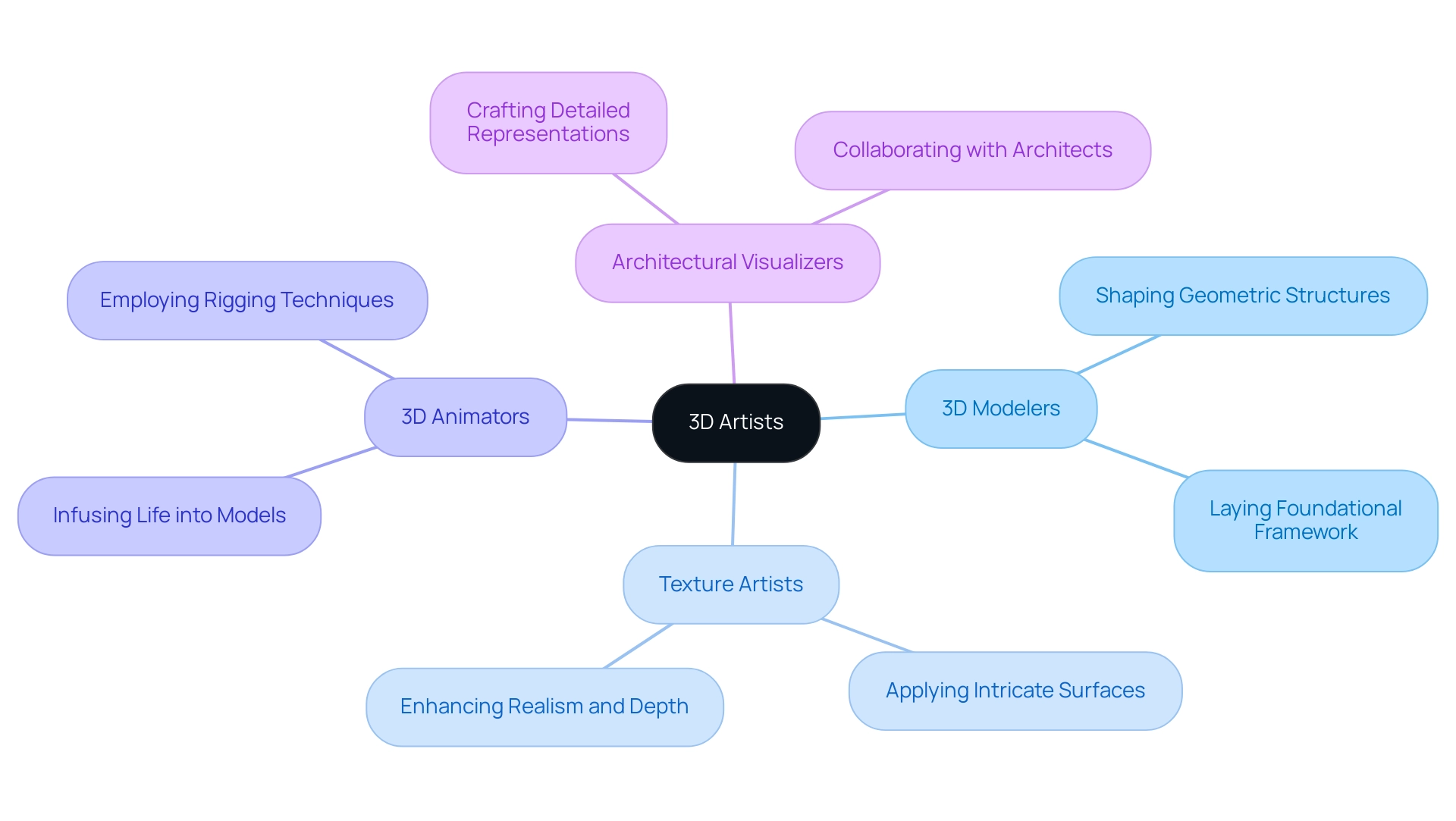
The realm of 3D artistry encompasses a diverse array of specializations, each contributing uniquely to the overall design process. 3D modelers are pivotal in shaping the geometric structures of objects, laying the foundational framework for visual endeavors. Complementing their work, texture artists enhance these models by applying intricate surfaces and colors, which significantly heightens the realism and depth of the visual output.
3D animators then take on the crucial role of infusing life into static models, employing rigging techniques to achieve fluid and lifelike motion. Within the architectural sphere, architectural visualizers play an essential role, crafting detailed and precise representations of buildings and spaces. Their close partnership with architects guarantees that creative intentions are faithfully expressed in visual formats, fostering a deeper connection between endeavors and potential residents.
This immersive method not only enhances client understanding but also improves stakeholder communication and identifies project issues early in the process. For instance, a recent project demonstrated how detailed exterior illustrations allowed clients to visualize community spaces, leading to valuable feedback that shaped the final designs. As the demand for these specialized skills grows—particularly with a projected increase in employment within many business occupations from 2023 to 2033—understanding the nuances of 3D artist jobs is imperative for navigating the evolving landscape of 3D artistry.
Notably, 65% of creators have utilized text-to-image technology, illustrating how technological advancements are influencing creativity and workflow in 3D artistry. Furthermore, innovations in 3D modeling software and real-time rendering technologies are reshaping the Creator Economy in 3D, lowering barriers for new creators, as evidenced by recent case studies on these advancements.
Essential Skills and Qualifications for 3D Artists
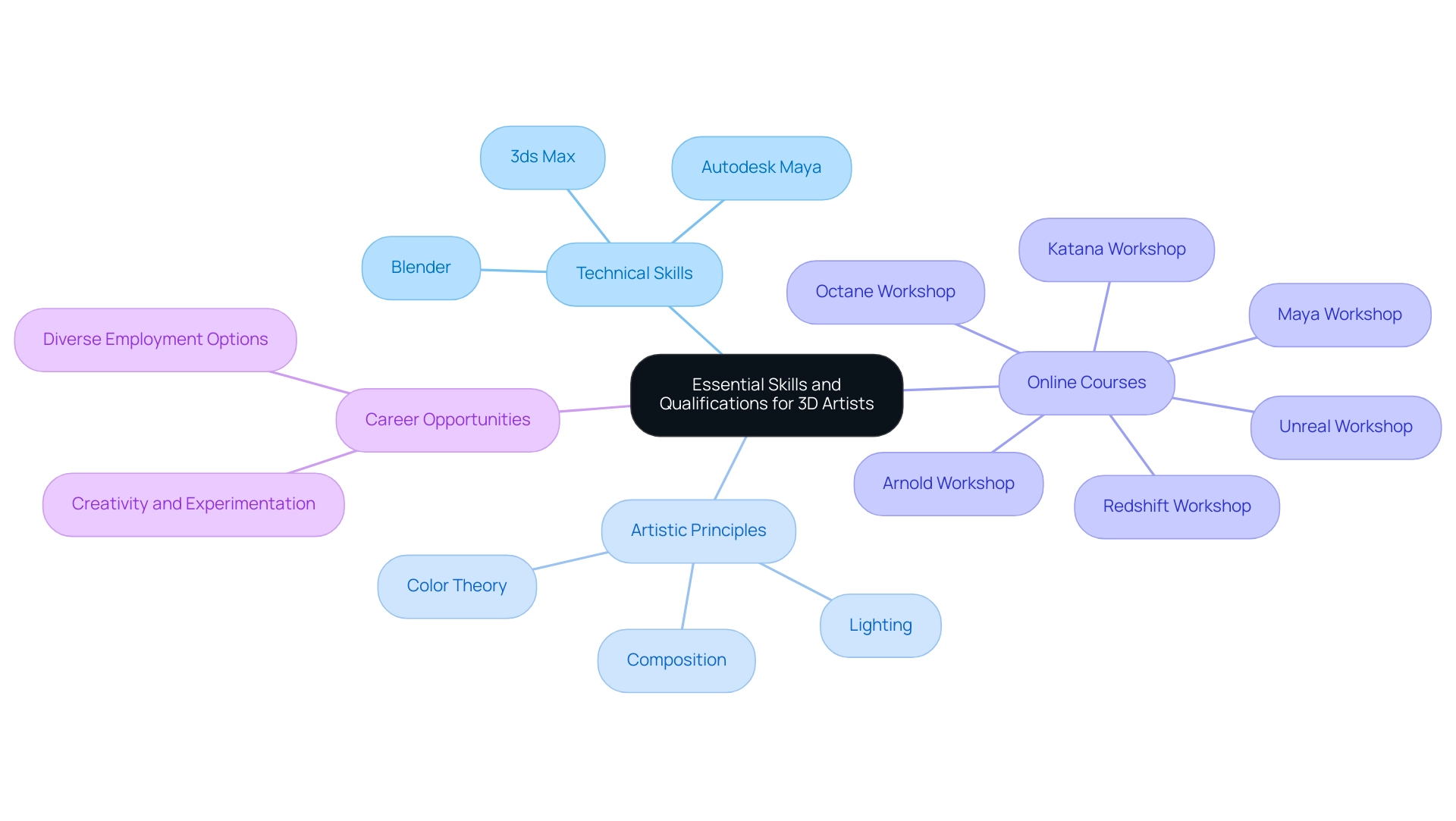
Success in securing 3D artist jobs hinges on a well-rounded skill set that merges technical expertise with artistic insight, particularly in the realm of architectural visualization. Mastery of industry-standard software such as Autodesk Maya, Blender, and 3ds Max is vital for creating intricate models and animations that meet professional standards. Furthermore, a solid grounding in traditional art principles—including color theory, composition, and lighting—serves as the backbone for crafting visually compelling work that captures the subtle details, from the way sunlight dances off surfaces to the texture of materials, adding depth and realism to creations.
Every element in our renderings is a brushstroke in a larger picture, making the project feel real and lived-in. While many 3D creators possess degrees in disciplines such as fine arts, graphic design, or architecture, an impressive portfolio demonstrating their capabilities can often compensate for formal education. Aspiring 3D creators can enhance their skills through recommended online courses such as:
- Arnold Workshop
- Katana Workshop
- Redshift Workshop
- Maya Workshop
- Unreal Workshop
- Octane Workshop
These courses provide flexible and cost-effective alternatives for learning at their own pace.
The case study titled ‘Working as a 3D Professional’ illustrates the diverse employment options and responsibilities of 3D creators, highlighting how 3D artist jobs allow for creativity and experimentation. As Nishant Verma, VP of 3D creation at Ikarus 3D, asserts,
As a 3D creator, it’s your chance to seize the opportunity and get equipped with the first mover’s advantage in this field.
This highlights not only the significance of skill development but also the crucial role of high-quality visual representations in development and decision-making, as well as the importance of intricate details in enhancing the emotional effect of architectural designs.
Current Job Market Trends for 3D Artists
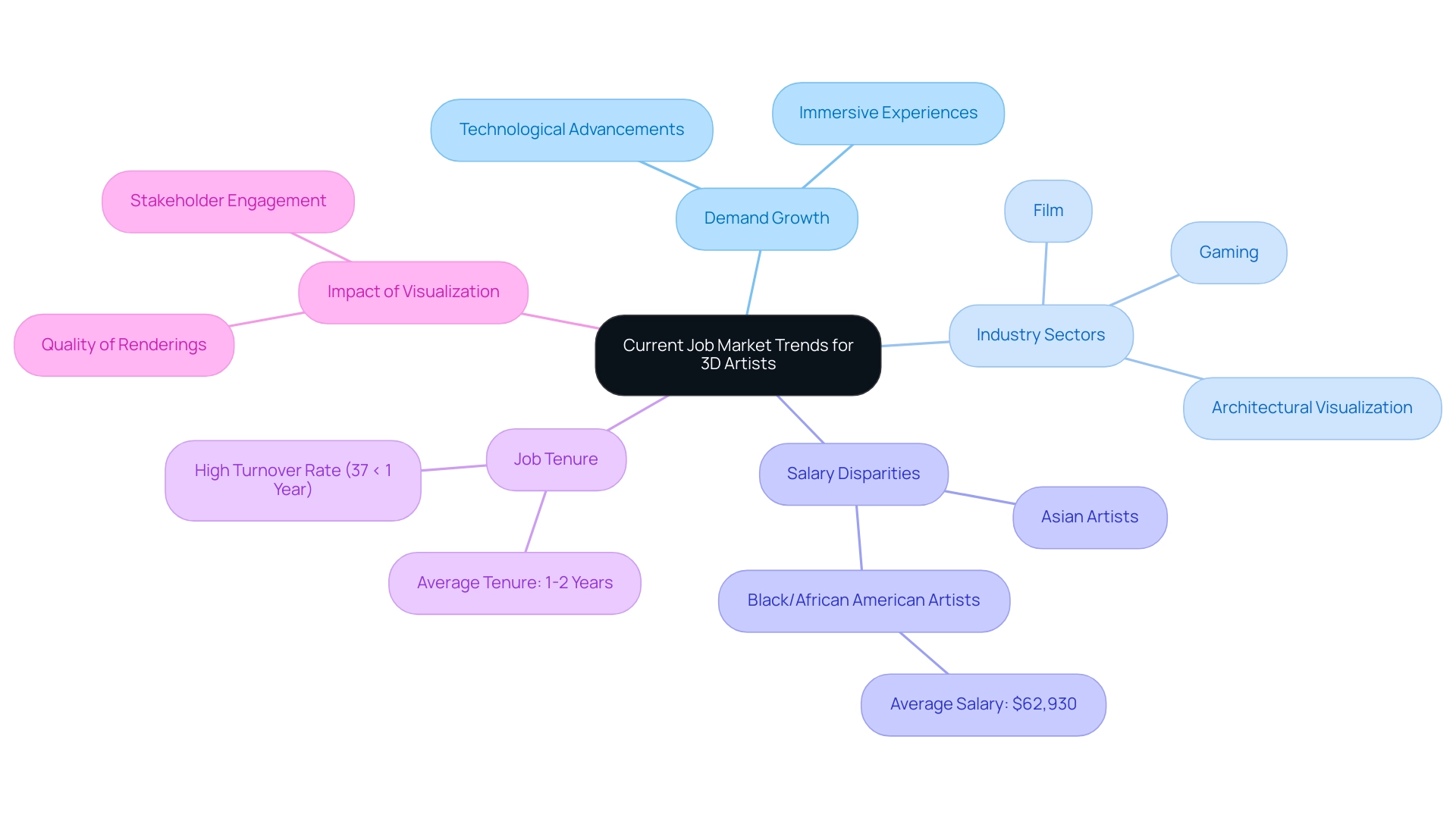
The demand for 3D artist jobs is experiencing robust growth across various industries, notably within gaming, film, and architectural visualization sectors. Experts in these areas are assigned the responsibility of developing intricate graphic 3D models of buildings and structures, where high-quality renderings act as an essential glimpse into the future of the endeavor. These visualizations allow stakeholders to grasp the project’s potential and the vision behind the designs, making informed decisions and generating excitement about what’s to come.
As technological advancements pave the way for new opportunities, companies are increasingly in search of skilled professionals capable of producing immersive experiences and realistic visualizations. Industry analyses indicate that the market for 3D artist jobs is poised for significant expansion, particularly with the rising prominence of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications. Notably, Asian 3D creators earn the highest average salary compared to their peers, while Black or African American 3D creators have the lowest average salary at $62,930.
However, the competitive landscape for 3D artist jobs is underscored by a high turnover rate, with many 3D artists averaging tenures of just 1-2 years; 37% remain in their positions for less than one year. This high turnover may reflect job satisfaction challenges or limited career progression opportunities, emphasizing the importance of effective networking and staying attuned to industry trends for job seekers aiming to thrive in this dynamic field. Moreover, grasping the significance of personalization and adjustments in deciding investments for distinctive design endeavors is crucial for lead architects.
The intricacy and magnitude of undertakings directly influence rendering duration and resource needs, highlighting the importance of investing in quality visual representations to effectively showcase distinctive traits. Poor investment in visualization can lead to misunderstandings about the project’s potential, ultimately diminishing stakeholder excitement and engagement.
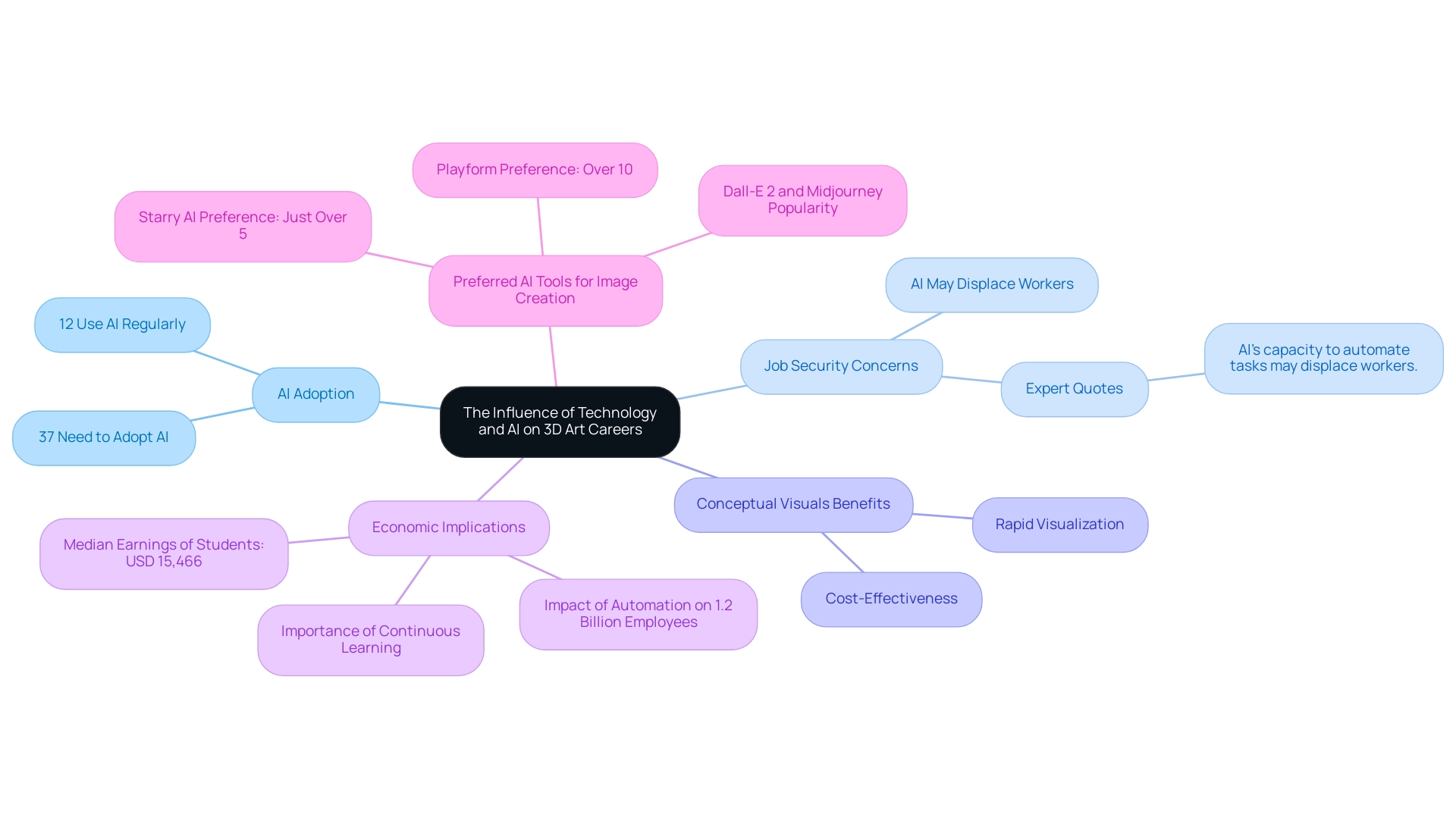
The Influence of Technology and AI on 3D Art Careers
The integration of technology, particularly artificial intelligence (AI), is dramatically reshaping 3D artist jobs. Recent trends indicate that a significant 12% of workers now regularly employ AI technologies, while an additional 37% recognize the necessity to adopt these tools to remain competitive. AI-driven solutions are increasingly capable of automating various aspects of the design process, including texture generation and model optimization for enhanced performance.
As noted by industry experts, ‘AI’s capacity to automate tasks may displace workers, heightening concerns about job security, particularly in creative fields.’ While these advancements offer the potential to significantly boost productivity, they simultaneously raise critical questions regarding the future of 3D artist jobs in a landscape where automation is on the rise.
In parallel, the advantages of initial conceptual visuals in architecture cannot be overlooked. These illustrations offer rapid visualization of concepts, allowing architects and clients to view proposals in three dimensions promptly. This promotes improved communication, ensuring that all stakeholders comprehend the vision and requirements, thus eliminating misunderstandings.
Furthermore, their cost-effectiveness allows for early-stage exploration of basic shapes and massing, supporting informed decision-making without significant resource commitment. For instance, creating a preliminary version can often cost a fraction of a detailed version, enabling more iterations and refinements. The iterative design process facilitated by these renderings encourages multiple revisions based on feedback, allowing for the identification of design issues early on.
Statistical forecasts suggest that the widespread adoption of current automation technologies could impact approximately 1.2 billion employees globally, further intensifying concerns about job security in creative sectors. The recent survey on preferred AI tools for image creation reveals that over 10% of creators favor Platform, while Dall-E 2 and Midjourney remain the most popular choices. This emphasizes how creators are currently leveraging AI technologies to enhance their workflows.
Moreover, the economic implications of AI adoption are underscored by the statistic that students reported the lowest earnings, with a median annual compensation of USD 15,466. Those who proactively embrace these technological advancements and integrate new tools into their workflows will uncover opportunities to refine and elevate their craft. Conversely, those who resist change may find it increasingly challenging to maintain relevance in this fast-evolving environment.
Continuous learning and skill development serve as essential strategies for navigating this transformative terrain, ensuring that individuals pursuing 3D artist jobs remain at the forefront of innovation in design.
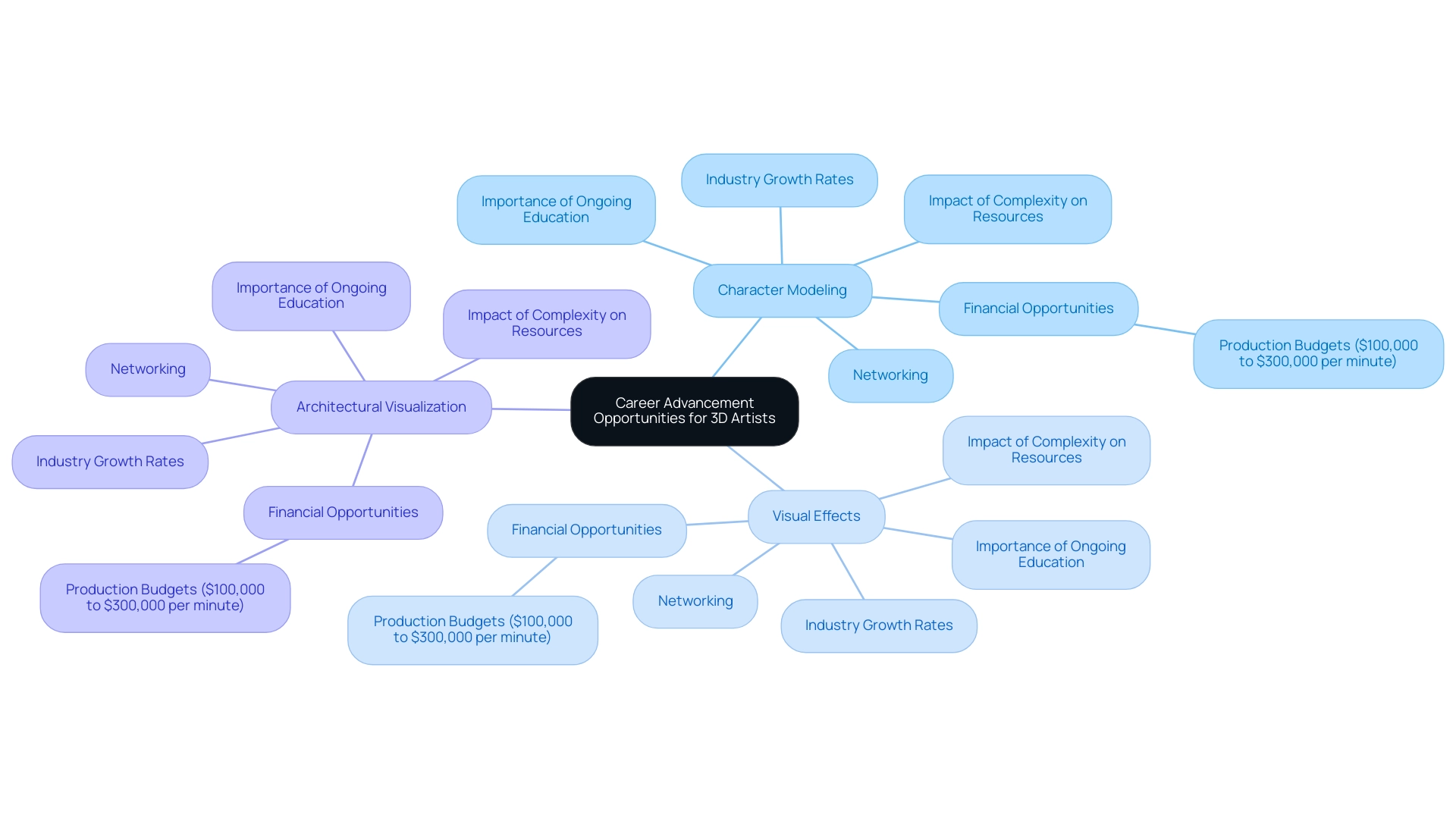
Career Advancement Opportunities for 3D Artists
In 2024, career advancement for 3D artist jobs presents a multitude of pathways, often centered around specialization in distinct areas such as:
- Character modeling
- Visual effects
- Architectural visualization
Comprehending the influence of complexity and scale on processing time and resource needs is essential. For example, the complexity of a pattern can greatly affect the funding required for high-quality exterior 3D visualizations, which are essential in attracting investors and facilitating approvals.
Complex projects, such as large commercial developments, may require more detailed visualizations and longer production times compared to simpler designs, thereby increasing resource allocation and costs. This strategic focus not only sharpens a creator’s skill set but also aligns with industry demand, which has seen a robust growth rate of 4% year-over-year in TV animation production since 2020, fueled by shifting viewer preferences for dynamic storytelling. The animation industry is experiencing robust global growth, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for animation content.
Additionally, 3D animation production budgets typically range from $100,000 to $300,000 per minute, highlighting the financial opportunities within the industry. Ongoing education plays a crucial role in this landscape; creators often pursue certifications in advanced software and attend workshops to enhance their technical skills, which can also improve their understanding of detail levels in 3D visualization. Research indicates that acquiring relevant certifications can significantly impact salary potential, positioning individuals for higher compensation in a competitive job market.
Moreover, customization and modifications are crucial in assessing the investment for unique design endeavors, as personalized solutions frequently demand extra time and resources. Networking within the industry is equally vital for finding 3D artist jobs, fostering collaborations and freelance opportunities that enrich portfolios and expand professional visibility. As echoed by industry experts, the pursuit of specialization and ongoing skill development is essential for creators aiming to navigate and excel in the evolving 3D art field, where a consistent graphic design approach can lead to a notable 33% increase in brand sales.
This connection emphasizes the significance of specialization in improving career advancement opportunities, especially as creatives recognize the strategic investment of quality renderings in their projects.
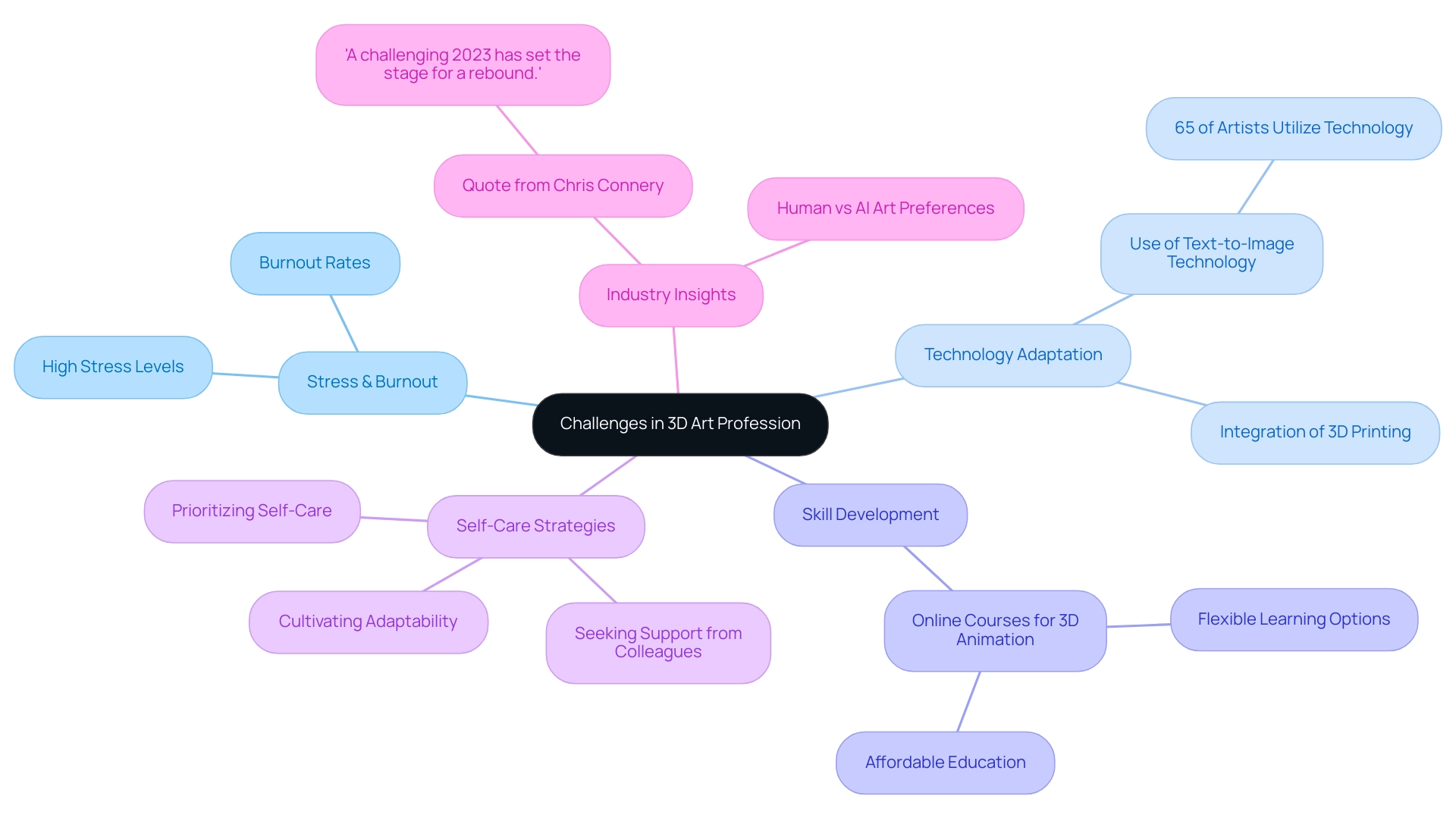
Challenges and Considerations in the 3D Art Profession
The 3D artist jobs profession is fraught with challenges that can significantly impact a creator’s well-being. With tight deadlines and elevated client expectations, many professionals experience heightened stress levels, contributing to burnout rates that are notably concerning in the industry. Studies indicate that a significant percentage of 3D creators report experiencing burnout, underscoring the urgent need for effective stress management strategies.
Moreover, 65% of artists have utilized text-to-image technology to expand on their ideas or find new ones, showcasing how artists are adapting to industry pressures and enhancing their creative processes. The intricate details captured in architectural illustrations, from the way sunlight dances off the windows to the texture of bricks, are not just elements of design; they are a testament to our passion for creating spaces that feel real and lived-in. These details play a pivotal role in enhancing realism and emotional impact, influencing the complexity and scale of a project, which directly affects rendering time and resource requirements.
The relentless pace of technological advancement necessitates that creators continually refine their skills to remain competitive. This pressure, coupled with an increasing demand for high-quality visuals, fosters an environment of intense competition among professionals. To effectively navigate these challenges, those in 3D artist jobs are encouraged to prioritize self-care, seek support from colleagues, and cultivate adaptability in response to industry changes.
One alternative approach to skill development and stress management is taking online courses for 3D animation, which allow learners to study at their own pace without quitting their jobs, making it more affordable and flexible for those looking to switch careers or start fresh in 3D animation. As Chris Connery, Global VP of Analysis, noted, ‘A challenging 2023 has set the stage for a rebound, and 3D printer shipments look to accelerate in the years to come,’ highlighting the evolving landscape that artists must be prepared to engage with.
Conclusion
The exploration of 3D artistry reveals a complex and evolving landscape where creativity meets technology, underscoring the critical roles that specialized artists play across various industries. From 3D modelers to architectural visualizers, each specialization contributes uniquely to the design process, enhancing communication and fostering stakeholder engagement through high-quality visualizations. As the demand for skilled 3D artists continues to rise, propelled by advancements in virtual and augmented reality, understanding the nuances of these roles becomes essential for professionals aiming to thrive in this competitive environment.
Moreover, the necessity for a robust skill set—combining technical proficiency with artistic insight—cannot be overstated. Mastery of industry-standard software and a solid foundation in traditional art principles are key to creating compelling visual narratives that resonate with audiences and clients alike. As the job market for 3D artists expands, embracing continuous learning and specialization emerges as a strategic pathway for career advancement, allowing artists to position themselves favorably within this dynamic field.
However, the profession is not without its challenges. High turnover rates and the pressures of tight deadlines can lead to burnout, emphasizing the importance of effective stress management and networking. As technology continues to reshape the industry, particularly with the increasing integration of AI, 3D artists must remain adaptable and proactive, continually refining their skills to maintain relevance. In doing so, they ensure that their contributions not only meet the expectations of an ever-evolving market but also elevate the standards of visual storytelling, ultimately enriching the architectural legacy for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a 3D artist?
A 3D artist is a specialized professional skilled in creating detailed three-dimensional models and visualizations using advanced software tools. They play a crucial role in industries such as architecture, gaming, film, and product creation.
How do 3D artists contribute to various industries?
3D artists transform abstract concepts into visual representations, which aids in effective communication of design intent, enhances pre-sales visualization, and boosts confidence among stakeholders, ultimately generating investment through compelling visuals.
Can you provide an example of how 3D artists have been used in a project?
In a recent urban development initiative, 3D renderings were used to secure funding by visually demonstrating the project’s potential impact and aesthetic appeal to stakeholders.
What is the current demand for 3D artists in the job market?
The global demand for skilled animation professionals has increased by 30% since 2018, and the animation market is projected to grow significantly, indicating rising opportunities for 3D creators.
What are the average earnings for Black or African American 3D creators?
Black or African American 3D creators earn an average salary of $62,930, highlighting a disparity in earnings within the industry.
What factors are driving growth in the 3D artistry sector?
Technological advancements such as real-time rendering and virtual reality are fueling growth in the animation sector, creating new opportunities for 3D artists.
What are the different specializations within 3D artistry?
Specializations include 3D modelers who create geometric structures, texture artists who enhance models with surfaces and colors, 3D animators who add motion to models, and architectural visualizers who produce detailed representations of buildings and spaces.
How do architectural visualizers assist in the design process?
Architectural visualizers work closely with architects to express creative intentions in visual formats, improving client understanding and stakeholder communication while identifying potential project issues early.
What impact does technology have on 3D artistry?
Technological advancements, including text-to-image technology and innovations in 3D modeling software, are reshaping the Creator Economy in 3D, making it easier for new creators to enter the field.
Why is understanding the roles of 3D artists important?
As the demand for specialized skills in 3D artistry grows, understanding the nuances of these roles is essential for navigating the evolving landscape of the industry.

0 Comments