Overview:
The article addresses the top challenges faced in AI-driven 3D architectural rendering, which include issues related to reflections and lighting accuracy, perspective maintenance, material representation, and the heavy computational load required for high-quality visualizations. These challenges are significant as they can lead to unrealistic outputs and inefficiencies, emphasizing the need for robust data and a careful balance between AI automation and designer control to enhance the overall rendering process.
Introduction
The integration of artificial intelligence into architectural rendering is reshaping the landscape of design, presenting a myriad of technical challenges and transformative opportunities. Architects are now tasked with navigating the complexities of AI-driven 3D rendering, where achieving authenticity in reflections and lighting, maintaining perspective accuracy, and ensuring material representation are paramount. As AI tools enhance workflow efficiency and enable real-time rendering, they also raise critical ethical considerations, including data privacy and the authenticity of generated images.
The balancing act between leveraging AI’s capabilities and preserving the unique human touch in design is more crucial than ever. This article delves into the multifaceted impact of AI on architectural visualization, exploring the challenges, advancements, and future trends that will define the profession in the coming years.
Key Technical Challenges in AI-Driven 3D Rendering
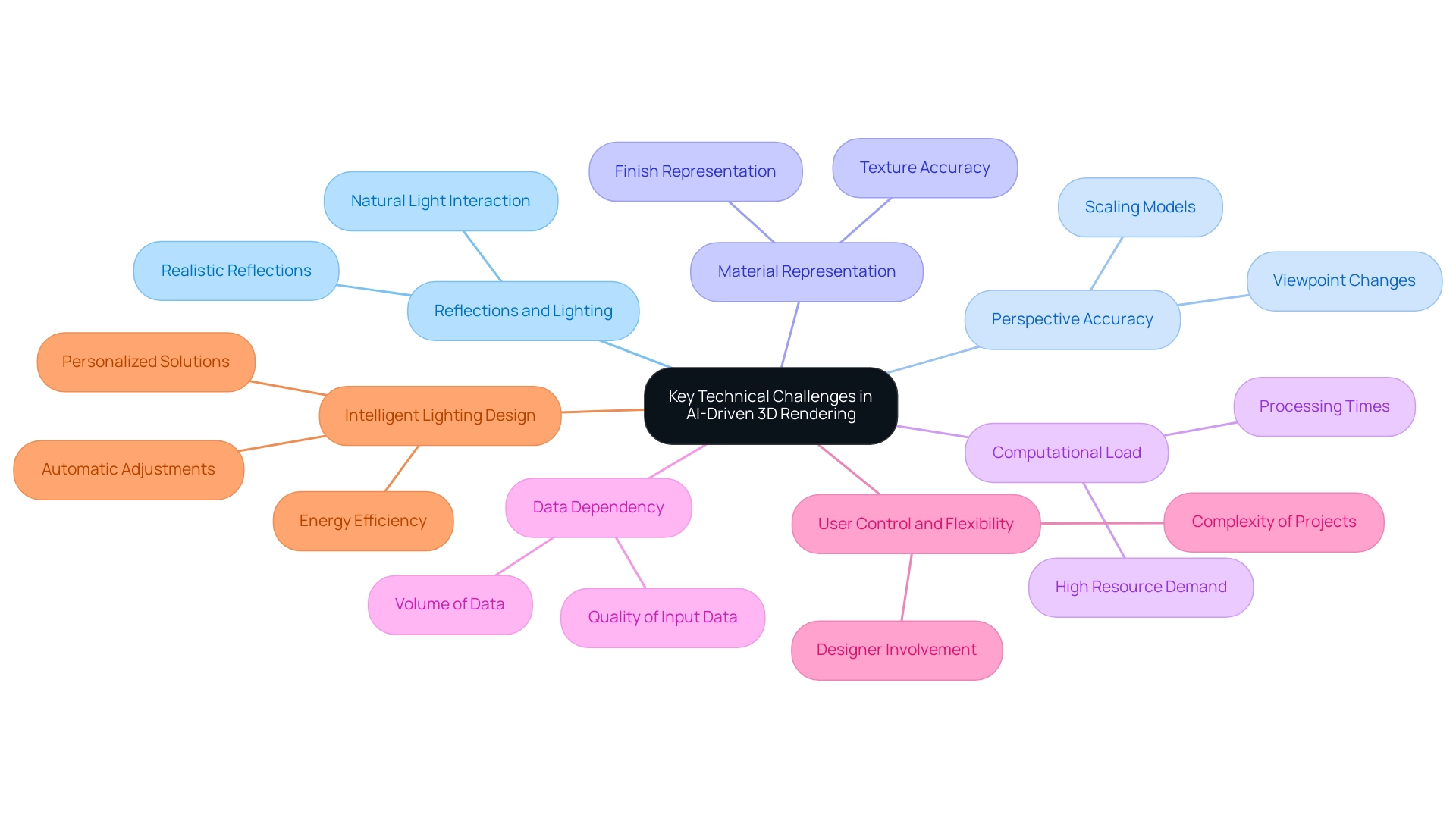
AI-driven 3D visualization presents several substantial technical challenges in AI in 3D architectural rendering that architects must navigate, particularly influenced by the complexity and scale of endeavors.
- Reflections and Lighting: Achieving realistic reflections and precise lighting remains a complex task. AI often struggles to accurately replicate the nuances of natural light and its interactions with various materials, leading to outputs that may lack authenticity.
This challenge is compounded by an unrealistic emphasis on specific features in the visualization process, which highlights the challenges in AI in 3D architectural rendering and can result in 3D models that appear less balanced and authentic.
Perspective Accuracy: Maintaining perspective accuracy in rendered images presents complications, especially when scaling models or changing viewpoints. These adjustments may lead to distorted representations, undermining the integrity of the design.
Material Representation: The depiction of materials by AI algorithms can fall short, particularly regarding textures and finishes. This inconsistency can lead to outputs that do not accurately represent the intended design, compromising the overall aesthetic of the undertaking.
Computational Load: High-fidelity visualization necessitates substantial computational resources, a demand that AI processes can intensify.
This increased load may lead to extended processing times and workflow bottlenecks, adversely affecting project timelines and cost estimations.
- Data Dependency: The efficacy of AI in producing results is heavily influenced by the quality and volume of input data. Insufficient or flawed data can lead to suboptimal results, underscoring the necessity for robust datasets when training AI models.
Determining the appropriate level of detail is crucial for both homeowners and businesses, enhancing client engagement and understanding.
The integration of AI-driven processes with conventional visualization tools presents significant challenges in AI in 3D architectural rendering. Achieving a seamless balance between innovative AI solutions and established practices is essential for effective implementation.
- User Control and Flexibility: While AI facilitates automation, it can inadvertently restrict the designer’s control over the rendering process. This limitation may lead to dissatisfaction with the final output if designers are not adequately involved in the decision-making process. The complexity and scale of projects can exacerbate this issue, as larger and more intricate structures often require more nuanced control to achieve the desired level of detail and accuracy.
A pertinent case study is titled Intelligent Lighting Concept, where AI and 3D technologies are transforming lighting planning by providing personalized and energy-efficient solutions. AI algorithms examine 3D models to enhance lighting arrangements for aesthetics and energy usage. For new office complexes, AI can create lighting systems that adjust automatically based on natural light availability, improving energy efficiency and worker comfort.
As Karin Örarbäck notes, AI algorithms can analyze 3D models of spaces and propose lighting solutions that optimize for both aesthetics and energy consumption. This illustrates the potential of AI in addressing challenges in AI in 3D architectural rendering while highlighting the importance of understanding and tackling these issues to leverage AI’s capabilities effectively in architectural visualization. Moreover, embracing these challenges can lead to significant cost savings in project design development through early issue resolution and client adjustments via 3D visualization.
The Transformative Role of AI in Architectural Visualization
AI is set to revolutionize architectural visualization through several key advancements:
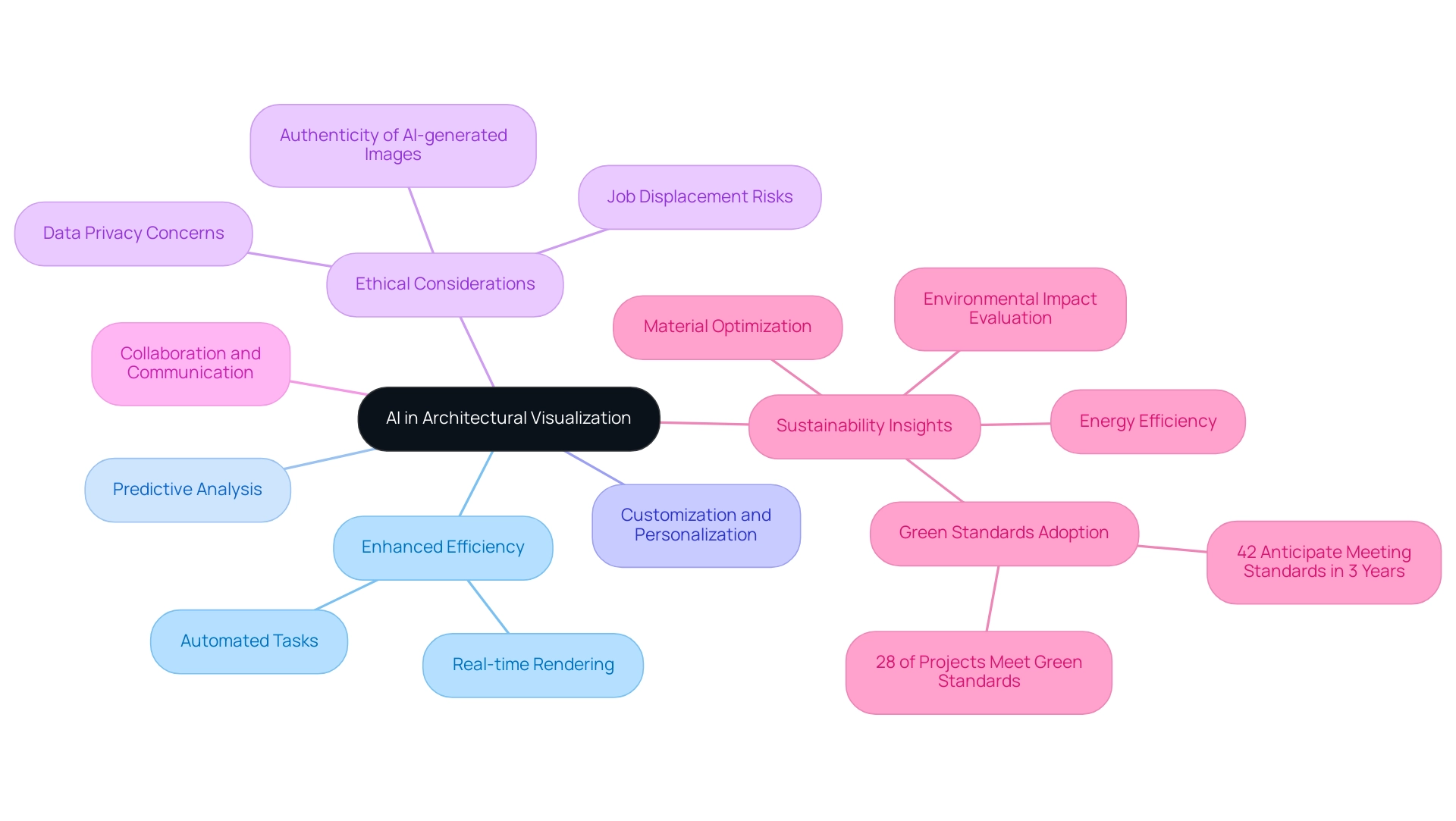
Enhanced Efficiency: By automating repetitive tasks in the visualization process, AI algorithms significantly enhance workflow productivity, allowing designers to focus on the more creative aspects of design.
Real-time Rendering: AI integration enables real-time rendering capabilities, allowing designers to visualize modifications instantly.
This immediacy empowers informed decision-making throughout the development process, aligning with the latest trends in architectural visualization for 2024.Predictive Analysis: Through the examination of previous projects and their results, AI offers predictive insights that aid designers in assessing the potential success of various design choices, thereby enhancing overall project outcomes.
Customization and Personalization: AI’s ability to generate highly customized visualizations tailored to specific client preferences elevates the client experience and satisfaction, catering to the unique demands of each project.
Ethical Considerations: The increasing integration of AI in architectural practices brings forth challenges in AI in 3D architectural rendering, including data privacy concerns, the authenticity of AI-generated images, and the potential displacement of traditional rendering roles.
It is imperative for architects to navigate these complexities with prudence and consideration.Collaboration and Communication: AI tools improve teamwork among stakeholders by generating clear visualizations that close communication gaps, ensuring alignment on intent.
This capability is essential for efficient project management and stakeholder involvement, especially during the collaborative creation phase that benefits from iterative renderings based on client feedback.Sustainability Insights: AI’s analytical capabilities extend to evaluating the environmental impacts of decision-making.
By optimizing material usage and energy efficiency, AI assists designers in creating more sustainable buildings, aligning with the growing trend towards green architecture.
According to OpenAsset, 28% of global designers, engineers, and contractors indicate that the majority of their construction endeavors meet green standards, with 42% anticipating to achieve this status within the next three years, highlighting the growing significance of sustainability in building practices.
Additionally, the average income for male professionals in the field stands at $85,968, while female professionals earn $79,033, highlighting the economic implications of adopting AI technologies in the sector.
Furthermore, AI simplifies the process of accessing building codes by allowing architects to input project details into a chatbot that highlights zoning restrictions and requirements, saving hours of research and reducing the risk of costly legal complications during the planning phase.
To fully explore the potential of these AI advancements in architectural creation, consider how AI can facilitate experimentation with alterations and material selection, allowing for rapid adjustments based on client feedback.
Collaborating with J. Scott Smith Visual Designs can improve this process, as our expertise in producing detailed 3D visualizations permits effective experimentation and guarantees client satisfaction.
Reach out to us today to arrange a consultation and discover how we can help bring your architectural ideas to life.
Impact of AI on Design Creativity
AI significantly influences design creativity, presenting both opportunities and challenges:
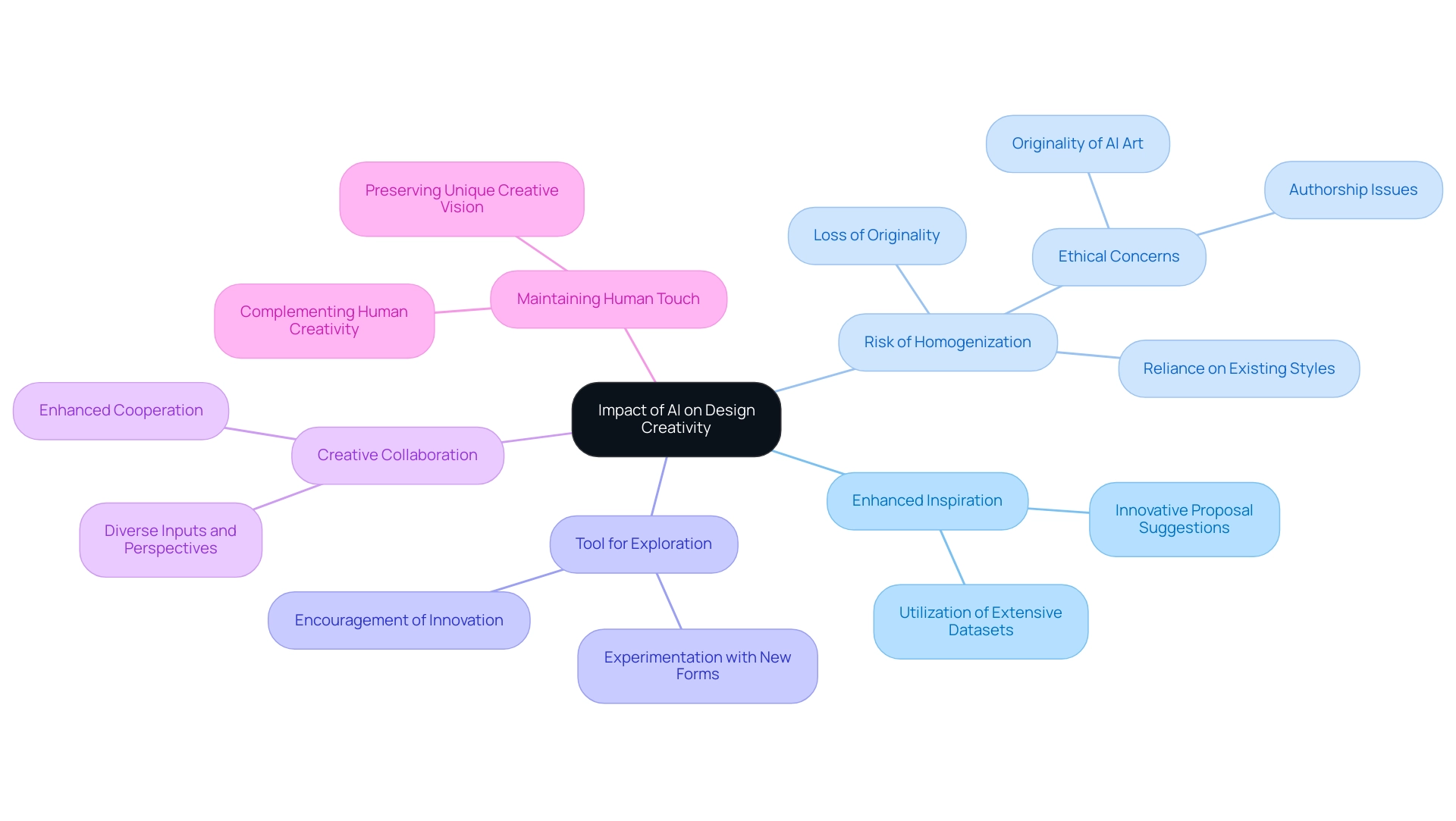
Enhanced Inspiration: Utilizing AI tools enables architects to examine extensive datasets, producing innovative proposal suggestions that may not be readily apparent. This capability can inspire fresh architectural concepts that push traditional boundaries.
Risk of Homogenization: A critical concern surrounding AI-generated creations is the potential for homogenization. Algorithms often rely on existing styles and trends, which can lead to a lack of originality in outputs. This risk necessitates a mindful approach to ensure that unique creative elements are not lost in the pursuit of efficiency. Ethical concerns regarding authorship and originality of AI-generated art further complicate this issue, highlighting the need for careful consideration in the creation process.
Tool for Exploration: AI serves as a robust platform for exploring unconventional design solutions. By enabling designers to experiment with new forms and materials, AI fosters a creative environment that encourages innovation beyond conventional limits.
Creative Collaboration: The integration of AI can enhance cooperation among designers and stakeholders, streamlining brainstorming sessions and idea generation. This synergy enriches the creative process, allowing for a more diverse range of inputs and perspectives.
Maintaining Human Touch: Despite the advancements AI offers, architects must remain vigilant in preserving their unique creative vision. The key lies in ensuring that AI complements human creativity rather than overshadowing it, allowing architectural professionals to maintain their distinct perspectives in the design landscape.
Incorporating a thorough collaborative creation process, as exemplified by J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, ensures that every endeavor is tailored to meet client needs and specifications. The process includes initial communication and FAQs, detail modeling, and material and lighting selection, which are crucial for achieving client satisfaction. Investing in quality and detailed 3D images not only enhances realism but also leaves a lasting emotional impact.
Customization and revisions are vital in determining the overall investment in unique projects, reinforcing the importance of a tailored approach in achieving client satisfaction. The balance between embracing AI’s capabilities and safeguarding originality is crucial in navigating the evolving architectural landscape, where 62% of industry leaders recognize the transformative potential of AI in content creation and design. A recent case study titled “A Risk of AI In Design: Will AI Replace Our Jobs?” emphasizes that while AI can enhance efficiency, it cannot replace the attention to detail and direction provided by human designers. Ultimately, it is the skilled designers who effectively utilize AI that will excel in the industry.
Ethical Implications of AI in Architectural Rendering
As artificial intelligence becomes increasingly integrated into architectural visualization, several ethical implications warrant careful consideration:
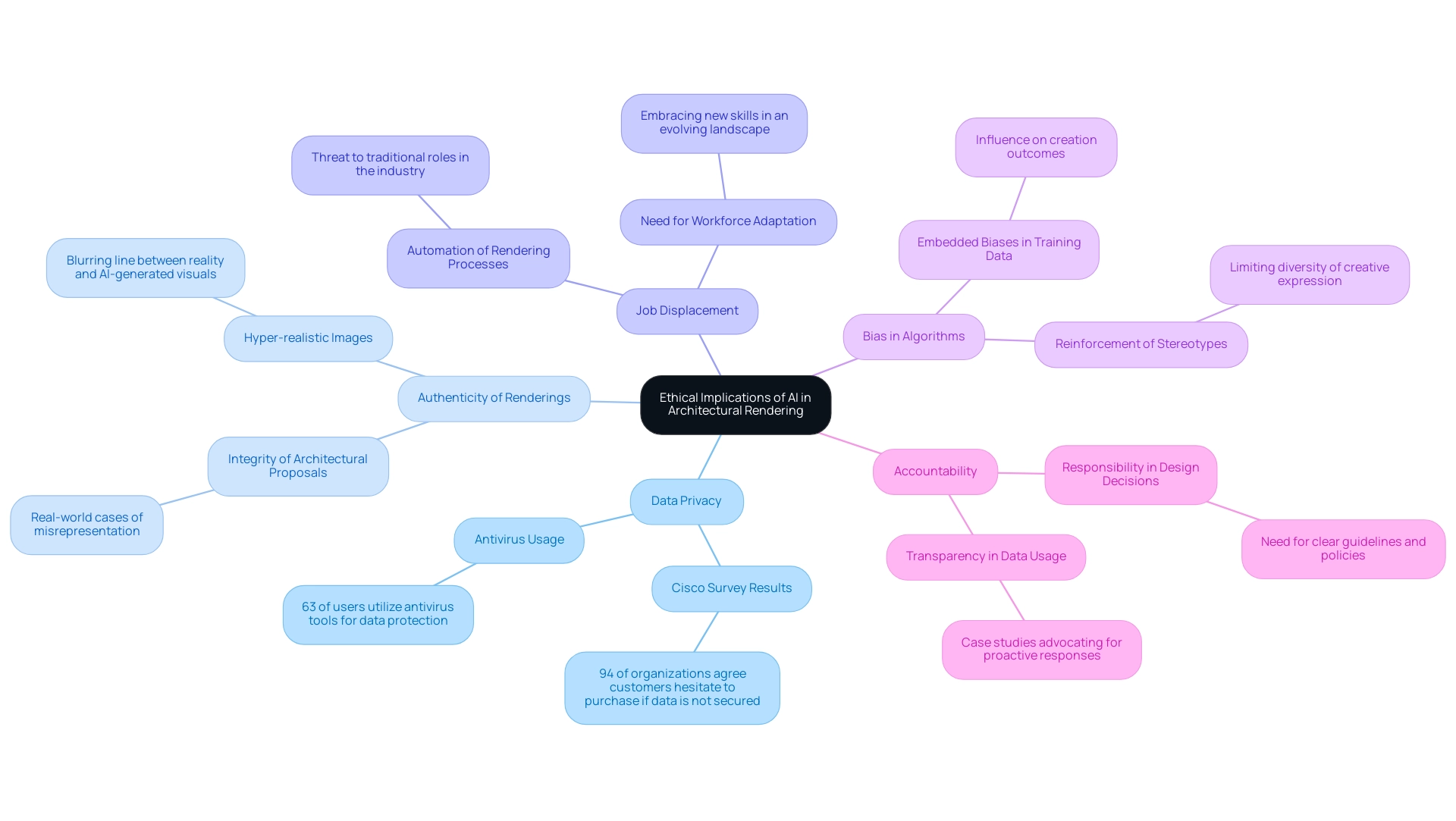
Data Privacy: The deployment of AI technologies necessitates the collection and analysis of substantial amounts of data, raising critical concerns regarding the privacy of clients and users. A recent Cisco survey highlighted that 94% of organizations agree that customers hesitate to purchase their products and services if they don’t think their personal data is adequately secured. Additionally, with antivirus tools being the most prominent in securing data, utilized by 63% of users worldwide, the importance of robust data protection measures cannot be overstated.
Authenticity of Renderings: AI’s capacity to produce hyper-realistic images can obscure the distinction between actual projects and their digital representations. This raises significant concerns about potential misrepresentation, especially due to the challenges in AI in 3D architectural rendering, as the line between reality and AI-generated visuals becomes increasingly blurred. Real-world cases illustrate instances where challenges in AI in 3D architectural rendering have compromised the integrity of architectural proposals.
Job Displacement: The challenges in AI in 3D architectural rendering, particularly the automation of rendering processes, pose a potential threat to traditional roles within the industry, leading to fears of job losses. This situation calls for urgent discussions about workforce adaptation and the necessity for architects to embrace new skills in an evolving landscape.
Bias in Algorithms: AI systems are only as good as the data they are trained on, which can often include embedded biases. These biases may influence creation outcomes, inadvertently reinforcing stereotypes in architectural styles and limiting the diversity of creative expression.
Accountability: As AI assumes greater responsibility in the design process, questions surrounding accountability for design decisions arise. It is crucial to set clear guidelines and policies that outline the functions of algorithms and human designers, ensuring a responsible approach to AI in architectural visualization. The necessity for transparency and accountability is underscored by case studies on data collection and storage, which advocate for organizations to respond proactively to inquiries regarding their data usage in AI systems.
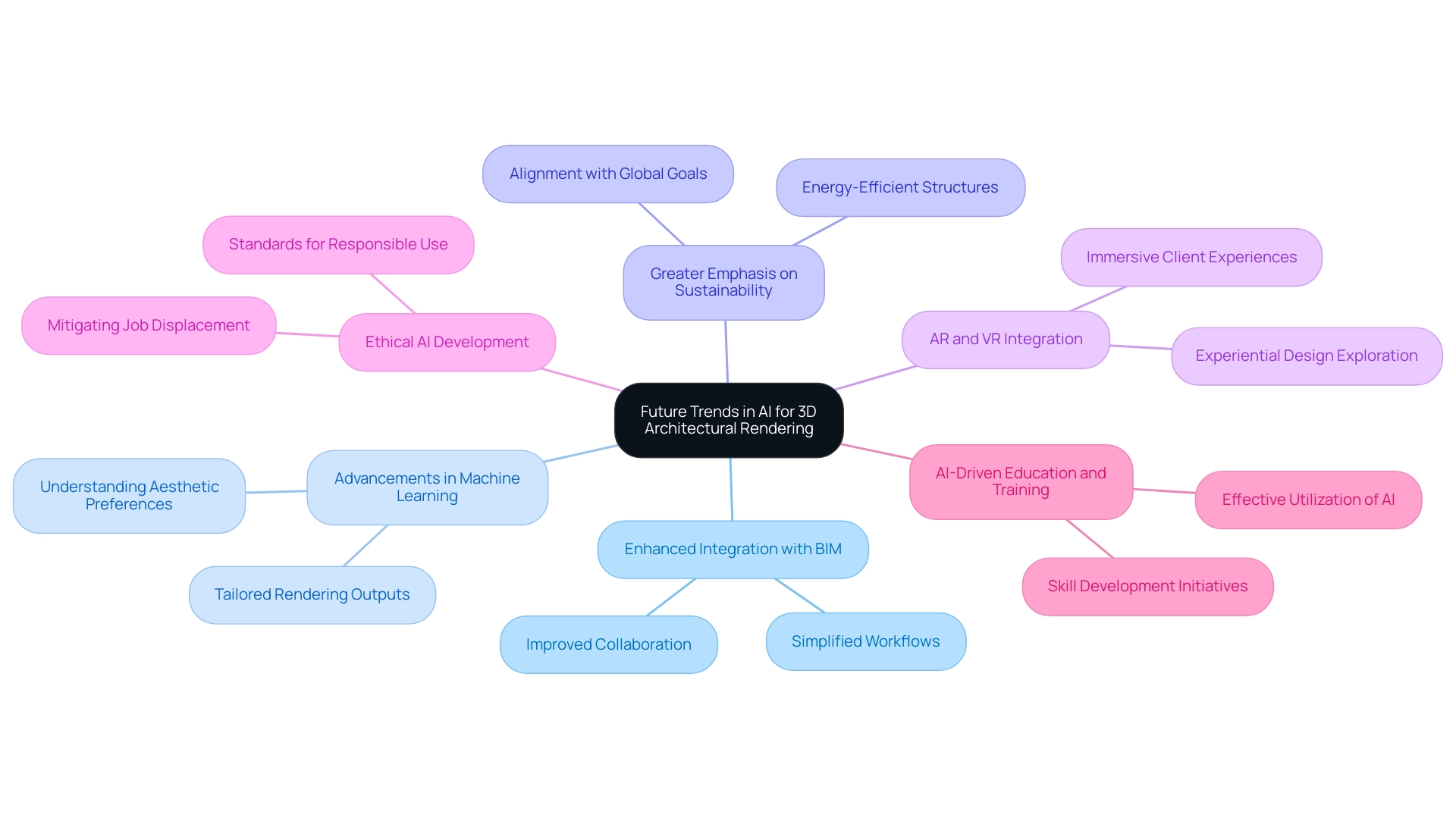
Future Trends in AI for 3D Architectural Rendering
The landscape of 3D architectural rendering is on the verge of significant transformation due to advancements in artificial intelligence, particularly in addressing the challenges in AI in 3D architectural rendering, such as creating lifelike CG humans for architectural visualizations and overcoming the uncanny valley. Several key trends are poised to redefine how architects approach creation:
Enhanced Integration with BIM: The merging of AI with Building Information Modeling (BIM) systems is poised to transform collaboration and simplify workflows throughout the planning and construction phases. This integration will facilitate seamless communication between stakeholders, enhancing overall project efficiency.
Advancements in Machine Learning: As machine learning algorithms continue to evolve, AI will gain the capacity to better comprehend and anticipate aesthetic preferences. This ability will enable designers to produce more tailored rendering outputs that resonate with client expectations and aesthetic desires, particularly in creating detailed and realistic visualizations.
Greater Emphasis on Sustainability: A critical trend will be the focus on sustainability metrics within AI tools. These advancements will empower builders to create energy-efficient structures that significantly reduce environmental impact, aligning practices with global sustainability goals.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) Integration: AI will enhance AR and VR technologies, enabling immersive client experiences by overlaying BIM models on real-world sites. This capability allows for experiential exploration of designs prior to construction, fostering better client engagement and more informed decision-making.
Ethical AI Development: The architectural profession is increasingly recognizing the importance of ethical AI development. As the field evolves, establishing standards and practices for the responsible use of AI technologies will be paramount to mitigate potential job displacement and ensure equitable access to innovative tools. To protect the workforce and promote fair use of technology, we must address the challenges in AI in 3D architectural rendering.
AI-Driven Education and Training: AI-powered BIM is essential in educating designers, engineers, and construction professionals. By incorporating AI into training initiatives, the industry can boost skill development and guarantee that professionals are prepared to utilize these advancements effectively.
As Prex Poojara observes, > With the shift towards AI, utilizing AI to enhance collaboration, data management, and parametric modeling is not a concept of the future; the future is now! The architectural community stands at a critical juncture, where embracing these trends will not only improve visualization capabilities but also redefine the role of architects in the design process. The intricate details incorporated into architectural renderings will further enhance realism and emotional impact, ensuring client satisfaction and engagement throughout the lifecycle.
At J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, our collaborative rendering process begins with initial communication and understanding your vision. We customize our proposals based on your objectives and maintain smooth communication throughout the process. Our clients have praised our work, with one stating, ‘Scott’s attention to detail made our project shine!’
These testimonials reflect our commitment to delivering high-quality renderings that accurately represent your design intent and exceed expectations.
Conclusion
The integration of artificial intelligence into architectural rendering presents a transformative opportunity for the profession, albeit accompanied by significant challenges. As outlined, architects must navigate the complexities of:
- Achieving realistic reflections
- Maintaining perspective accuracy
- Ensuring accurate material representation
The computational demands and reliance on quality data further complicate the rendering process, necessitating a careful balance between innovation and traditional practices.
Advancements in AI are reshaping architectural visualization through:
- Enhanced efficiency
- Real-time rendering
- Predictive analysis
These advancements enable architects to focus on creativity while improving client engagement. However, the ethical implications—ranging from data privacy concerns to the authenticity of AI-generated images—demand a thoughtful approach to ensure responsible implementation. The potential for job displacement and algorithmic bias underscores the need for architects to adapt and embrace new skills in this evolving landscape.
Looking ahead, the trends in AI-driven rendering, including:
- Increased integration with BIM
- A focus on sustainability
- The incorporation of AR and VR
will redefine the architectural process. As the profession stands at this critical juncture, the successful application of AI technologies hinges on maintaining the unique human touch in design while leveraging AI’s capabilities to enhance creativity and efficiency. Ultimately, the future of architectural rendering will be shaped by a commitment to ethical practices and a dedication to preserving the artistry that defines the profession.

0 Comments