Introduction
The integration of augmented reality (AR) into architectural rendering is revolutionizing the way architects visualize and present their designs. By merging digital elements with physical environments, AR transforms traditional methodologies, allowing for a more immersive and interactive experience for clients. This technology not only enhances the visualization process but also fosters deeper engagement, enabling clients to experience designs in situ before construction begins.
As the architectural landscape evolves, the capabilities of AR are being harnessed to:
- Streamline workflows
- Improve communication
- Facilitate informed decision-making
With significant advancements on the horizon, understanding the implications of AR in architectural practices is essential for professionals seeking to leverage this innovative tool to enhance project outcomes and client satisfaction.
Understanding Augmented Reality in Architectural Rendering
Architectural rendering augmented reality signifies a groundbreaking shift in how designers interact with their physical environments. By integrating digital information with real-world settings, architectural rendering augmented reality allows architects to superimpose 3D models seamlessly into their surroundings. This innovative technology not only enhances visualization but also enriches the client experience through architectural rendering augmented reality and interactive engagement.
Clients can explore designs in context through architectural rendering augmented reality, gaining a clearer understanding of the final product prior to construction. Essential components of AR include mobile applications and AR glasses, which provide immersive experiences that exceed the capabilities of conventional display methods. Moreover, the benefits of preliminary conceptual renderings, such as quick visualization, cost-effectiveness, and informed decision-making, complement the AR experience by facilitating early-stage exploration and enhancing communication among stakeholders.
The iterative design process is also supported by architectural rendering augmented reality, which allows for adjustments based on client feedback, thus improving design outcomes. As the consumer AR advertising market is set to reach $5.2 billion by 2024, the implications for architectural rendering augmented reality are profound, marking a pivotal moment for architects to leverage augmented reality for improved project presentation. Additionally, Threekit’s AR technology has been shown to help retailers increase conversions by up to 40%, indicating a significant return on investment that architects can also anticipate in their projects.
Case studies demonstrate the power of pre-sales visualization, showcasing how images can ignite interest and secure investment long before construction begins. With 73,313 architecture firms currently operating in the U.S. and a growth rate of 1.6% CAGR from 2019 to 2024, the importance of incorporating architectural rendering augmented reality in design practices is increasingly critical. As Jane Smith, CFO, stated, ‘We expect significant growth next quarter,’ highlighting the anticipated advancements in the industry that AR can facilitate.
Current Trends in Architectural Rendering: The Role of AR and VR
The architectural rendering augmented reality landscape is witnessing a significant transformation, driven by the increasing integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies. These innovations are reshaping customer interactions and enhancing visualization capabilities. Recent data indicates that 64% of consumers harbor high expectations for virtual reality’s potential, a sentiment echoed across various sectors, including architecture.
Furthermore, with the architecture industry experiencing a growth rate of 1.6% CAGR from 2019 to 2024, the adoption of architectural rendering augmented reality technologies is becoming increasingly relevant. Utilizing VR headsets, architects can create immersive environments that enable customers to ‘walk through’ their concepts, offering a level of engagement previously unattainable. Concurrently, AR applications facilitate on-site visualizations that overlay digital designs onto real-world contexts, allowing for immediate feedback and adjustments.
This shift towards interactive experiences not only enhances customer satisfaction—evidenced by growing positive responses to AR and VR applications in building projects—but also streamlines the revision process through real-time input. Furthermore, the function of AI in producing lifelike CG humans is becoming essential in closing the uncanny valley, greatly influencing visual presentations by adding a layer of realism that captivates individuals emotionally. As highlighted by a case study on investment growth in AR, businesses globally are seeking competitive advantages as consumers demand richer engagement in shopping experiences, with the United States leading in revenue generation within the AR market.
Mobile Marketer emphasizes this trend, stating that ‘AR is easier than ever to implement, with the widespread use of WebAR in mobile phones.’ As we approach 2024, the ongoing expansion of architectural rendering augmented reality, along with AR, VR, and AI in architectural visualization, is set to transform how architects convey their ideas, nurture stronger relationships with patrons, and enhance project success. This transformation highlights the essential role of high-quality visual representations in project development and decision-making, with intricate details enhancing realism and emotional impact.
Our joint visualization process starts with initial communication to comprehend user goals, followed by detailed modeling and iterative feedback, ensuring that each project not only meets but surpasses expectations. Testimonials from pleased customers affirm the effectiveness of our approach, illustrating how our renderings have played a pivotal role in successfully conveying architectural visions.
Practical Applications of Augmented Reality in Architecture
The practical uses of architectural rendering augmented reality (AR) in architecture are transforming traditional methodologies, significantly enhancing the user experience. Notable uses include:
- Virtual tours
- Interactive models
- On-site visualizations
For instance, during presentations, architects can utilize architectural rendering augmented reality to project photorealistic 3D models into existing physical spaces, allowing users to vividly visualize how a new building will integrate with its surroundings.
This immersive experience, enhanced by architectural rendering augmented reality, promotes greater customer engagement—statistics indicate that 70% of users report heightened satisfaction with AR-enhanced presentations—by facilitating emotional connections to the visuals. As customers observe their future homes materialize in real time, their feedback becomes essential to the design process, ensuring alignment with their vision. In fact, one customer expressed, ‘Seeing my future home in AR made me feel a deep connection to the space, and it truly influenced my decision to move forward with the project.’
This collaborative method not only enhances satisfaction but also demonstrates the dedication to excellence at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, where testimonials emphasize the worth of personalized service and innovative problem-solving. Emerging trends in architectural rendering augmented reality, including hybrid localization techniques and intuitive gesture controls, as discussed in the case study ‘Future Trends of Augmented Reality in AEC/FM,’ are anticipated to further streamline workflows and enhance collaboration between architects and clients. These innovations represent a change towards a more interactive and responsive development process, with architectural rendering augmented reality becoming an essential tool in the building sector.
The Future of Architectural Rendering: Innovations in Augmented Reality
The architectural rendering augmented reality landscape is on the brink of a significant transformation, primarily driven by advancements in augmented reality (AR). As development progresses, the creation of detailed 3D visualizations becomes essential for customer evaluation, allowing for experimentation with modifications and material selection. This phase of development allows architects to explore various options and make informed decisions that align with client preferences.
Recent advancements in AR technology, including improved tracking and display capabilities, pave the way for architectural rendering augmented reality that enables increasingly realistic and interactive visualizations. These high-quality renderings act as an essential resource, offering stakeholders clarity and comprehension of the vision behind the blueprints, which is crucial for making informed choices and recognizing issues early. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with architectural rendering augmented reality offers opportunities for automated design adjustments tailored to client preferences and site-specific conditions.
As highlighted by industry specialists, architectural rendering augmented reality is simpler than ever to adopt, with the extensive use of Web in mobile devices aiding its effective incorporation into design workflows. However, architects must navigate the challenges of adopting AR technology, as evidenced by the slow uptake in retail sectors where only 1% utilized AR or VR in their customer experience as of 2020. This emphasizes the importance of balancing the opportunities and limitations of architectural rendering augmented reality as emerging technologies.
Current trends indicate that 62% of architecture firms are utilizing cloud-based collaboration tools, reflecting a robust move towards advanced technology for project coordination. Furthermore, the launch of gadgets such as the Apple Vision Pro, costing USD 3,499, highlights the expanding market for AR technology and its effects on design visualization. As these innovations continue to evolve, architects will be empowered to create concepts that are not only visually striking but also highly functional and tailored to meet client expectations, revolutionizing the landscape of construction.
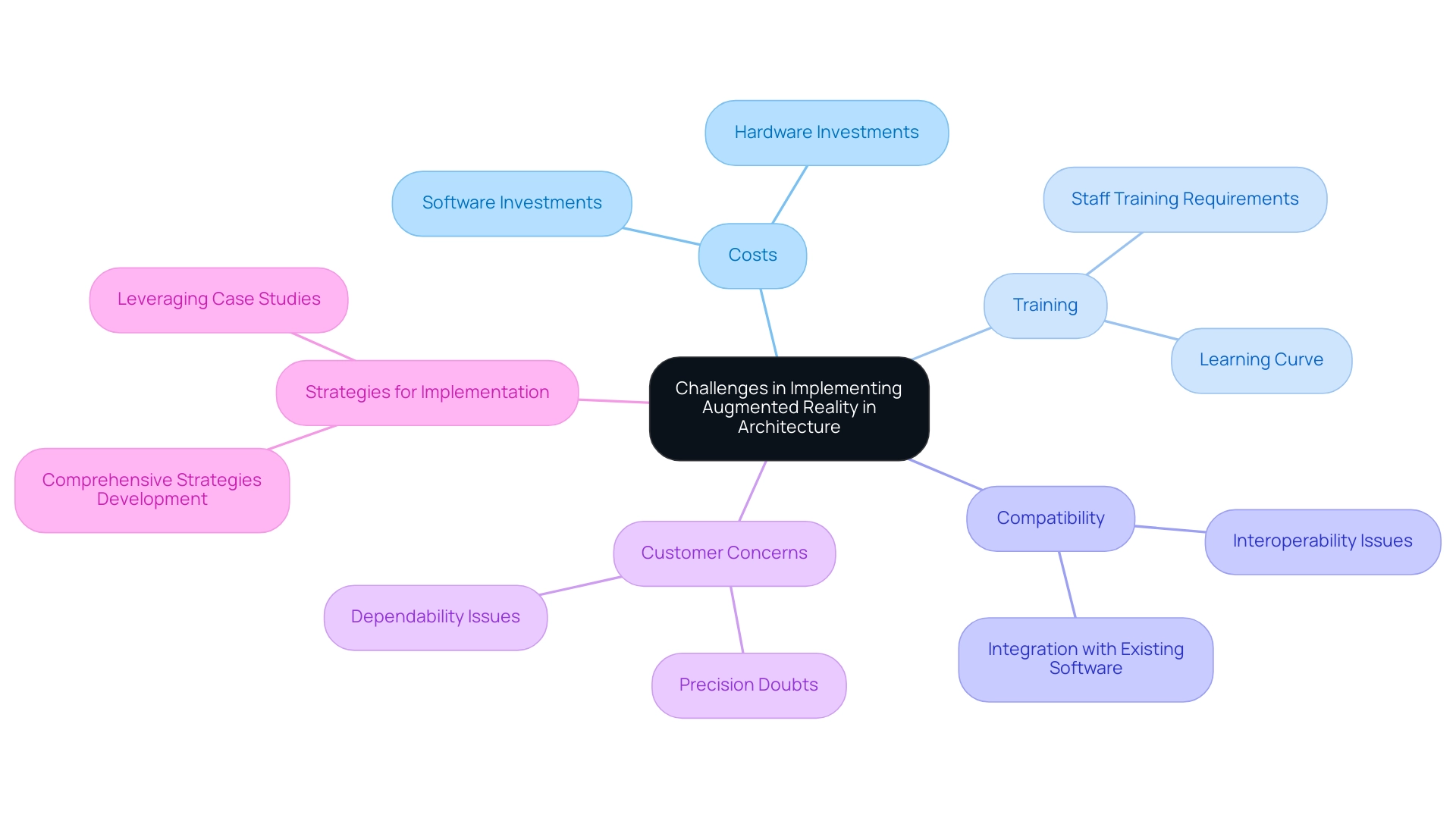
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Augmented Reality
The integration of architectural rendering augmented reality (AR) in architectural visualization presents a range of challenges that architects must navigate. Chief among these are the initial costs associated with AR technology, which encompass both software and hardware investments. Moreover, there is an inherent learning curve as staff must be trained to utilize new tools effectively.
This training requirement is underscored by the significant confidence in future AR/VR technologies, evidenced by a p-value of 0.001, indicating robust support for their adoption in architecture. Compatibility issues between AR applications and existing design software can further complicate the integration process, as architects often rely on specific software that may not seamlessly interface with new AR tools. Furthermore, customer concerns about the precision of augmented reality visuals compared to conventional techniques can present substantial challenges; customers may be doubtful about the dependability of AR results, worrying about inconsistencies in representation.
Addressing these factors is crucial; architects can develop comprehensive strategies that not only enhance the adoption of architectural rendering augmented reality but also maximize its potential benefits. High-quality visual renderings, particularly those rich in intricate details, are essential in project development and decision-making, providing a realistic and emotionally engaging view of the project. The use of 3D visualizations supports quicker buy-in from clients and enables early identification of issues, ultimately streamlining project workflows.
For instance, studies exploring the economic viability of integrating virtual reality into educational contexts reveal that such technologies can enhance educational outcomes while providing substantial cost savings in training and development. As Jonghoon Kim notes in his study, ‘Exploring the Economic Viability of Virtual Reality in Architectural, Engineering, and Construction Education,’ leveraging existing cost taxonomies from Information Systems literature can further inform the analysis of AR implementation costs. By proactively identifying these challenges and leveraging successful case studies, architects can pave the way for effective implementation of architectural rendering augmented reality within their practices, ultimately enhancing communication and resolving design issues early.
Conclusion
The integration of augmented reality (AR) in architectural rendering is fundamentally transforming the industry by enhancing visualization and client engagement. By superimposing digital elements onto physical environments, AR allows architects to create immersive presentations that streamline workflows and facilitate informed decision-making. Clients can experience their future spaces in real time, leading to improved communication and satisfaction.
AR’s practical applications, such as virtual tours and interactive models, foster emotional connections between clients and designs, increasing overall satisfaction. As AR technology advances, along with artificial intelligence, architects can anticipate even greater realism and interactivity in their visualizations, enabling them to deliver tailored designs that align with client expectations.
Despite these advantages, challenges such as initial costs, training needs, and compatibility with existing software must be addressed to maximize AR’s potential. Overcoming these hurdles is essential for architects to enhance project presentations and drive client satisfaction.
In conclusion, the adoption of augmented reality in architectural rendering presents a significant opportunity for architects to redefine their practices and improve project outcomes. By effectively leveraging AR, architects can create designs that are not only visually striking but also resonate deeply with clients, paving the way for a more engaging and successful architectural experience.

0 Comments