Introduction
Architects today are navigating an increasingly complex landscape where the demand for high-quality visualizations is paramount. Blender, a powerful open-source software, is emerging as a formidable player in architectural rendering, offering a suite of features that cater to the nuanced needs of design professionals. From its advanced rendering engines capable of producing photorealistic imagery to its extensive community support that fuels continuous learning and innovation, Blender provides architects with the tools necessary to elevate their projects.
As the architectural industry evolves, understanding the effectiveness and versatility of Blender becomes essential for professionals aiming to enhance client engagement and streamline their design processes. This article delves into the key aspects of Blender’s capabilities, comparing its advantages against traditional rendering software, and offering practical tips for achieving stunning visual outcomes.
Evaluating Blender’s Effectiveness for Architectural Rendering
This application stands out as a robust open-source software solution designed for architectural visualization, leading to the inquiry of whether Blender is good for architectural rendering, as it features an array of capabilities that warrant thorough evaluation in the context of project visualization and client engagement. Key factors to consider include:
Rendering Engine: Blender’s Cycles and Eevee engines are pivotal to its rendering prowess. While Cycles is famous for providing photorealistic outputs and Eevee excels in real-time image generation, many users wonder if Blender is good for architectural rendering. Recent updates in version 3.6.2 have further refined these engines, enhancing their performance and usability, leading to the consideration of whether Blender is good for architectural rendering, which is critical for generating high-quality pre-sales renderings that boost project confidence and attract investment. As Dr. Rob Lang notes,
Same on Blender 3.6.2, emphasizing the continuity of powerful features across versions.Versatility: The software’s compatibility with various file formats raises the question of whether Blender is good for architectural rendering, ensuring seamless integration with a range of creation tools. This flexibility is crucial for architects who frequently collaborate across various platforms and is Blender good for architectural rendering, allowing for effective communication with stakeholders and enhancing the overall development process.
Community Support: With over 219,250 openly accessible benchmarks contributed by the community, users benefit from an extensive repository of resources, tutorials, and plugins. This vibrant ecosystem significantly improves the software’s relevance for construction projects, fostering a collaborative atmosphere that promotes creative experimentation. Additionally, users have inquired about accessing scene statistics via Python scripting, which could be a valuable feature for architects looking to analyze specific scene data and improve decision-making.
Customization: A common question is whether Blender is good for architectural rendering, and the answer is yes, as it allows for deep customization of shaders and materials, enabling architects to create highly detailed and specific representations of their designs. This level of detail is essential for precise visualizations that showcase functionality and aesthetics, ultimately enhancing client satisfaction, which raises the question of whether Blender is good for architectural rendering. It is crucial to determine the appropriate level of detail to ensure that the visuals meet the expectations of clients and stakeholders, leading to effective visualization and communication, especially when considering if Blender is good for architectural rendering.
Practical Application: The effectiveness of this software in architectural rendering is further illustrated by the case study titled “Scene Statistics in Version 3.x,” confirming the availability of scene statistics in versions like 3.2.0 and 3.6.2. Users can right-click the bottom bar in the software to add scene statistics, ensuring they have access to relevant data about their models, which aids in early identification of design issues and iterative design support. Furthermore, effective pre-sales visualization through software can significantly contribute to generating revenue for construction projects, as it helps attract potential investors and clients by providing a clear and compelling vision of the final outcome.
Assessing these factors concerning particular project requirements is essential to deciding if this software is the best option for your design visualization needs, particularly if Blender is good for architectural rendering. The effectiveness of the software in design visualization is further demonstrated by various real-world projects that utilize its features for impressive outcomes, emphasizing the significance of 3D visualizations in improving client comprehension and fostering community connections.
Key Features of Blender for Architectural Visualization
Blender presents a suite of essential features that significantly enhance architectural visualization, particularly in the realm of 3D townhome rendering:
- Modifiers: Leveraging modifiers such as Boolean and Array enables architects to efficiently generate complex geometries, streamlining the design process and enhancing clarity in architectural expressions.
- Material and Texture Management: The advanced shader nodes facilitate detailed material setups, which are crucial for achieving photorealistic effects in renders, ensuring the essence is accurately captured.
- Lighting Options: A robust array of lighting tools, including HDRI support, provides architects with the ability to create accurate and dynamic lighting scenarios, crucial for realistic presentations that resonate with clients and stakeholders.
- Camera Settings: The customizable camera settings of the software permit precise control over field of view and depth of field, enhancing the overall visual impact of designs and aiding in effective client evaluation.
- Add-ons: The use of specialized extensions, such as Archimesh and ArchiCAD, broadens the modeling capabilities of the software, catering specifically to the needs of professionals in the field and enhancing collaborative development.
These features collectively empower users to optimize their workflows and evaluate if Blender is good for architectural rendering, allowing them to produce outstanding architectural visualizations. As highlighted by architect Samuel Woodward, the software’s extensibility through add-ons also shouldn’t be understated, further emphasizing the platform’s adaptability and relevance in contemporary design practices. Importantly, 3D townhome visualization serves as a powerful narrative tool for developers, and this raises the question of whether Blender is good for architectural rendering, allowing them to not only present homes but also sell futures, thereby enhancing communication with builders, lenders, and municipalities.
With the recent launch of version 4.0 on November 14, 2023, which features significant updates like improved Geometry nodes and advanced Principled BSDF shader functionalities, professionals are equipped with the latest tools to elevate their architectural projects. Furthermore, the community-driven development of the software is demonstrated in the case study titled ‘Community and Expandability of Blender,’ which highlights how collaborative efforts enhance workflows and improve visual output, making it a valuable addition to any studio’s toolkit. Moreover, with a current promotion providing 33% off all 3D visualization at the render farm, architects have a practical motivation to consider this software for their projects.
The historic dates of Maio 2023, Janeiro 2020, Dezembro 2018, Fevereiro 2018, Janeiro 2018, and Dezembro 2017 emphasize the continuous development of the software, reinforcing its position as a cost-effective solution and a crucial resource in any design studio’s toolkit. The significance of accuracy and detail in external presentations cannot be emphasized enough, as these components are vital in capturing the essence of concepts and ensuring effective expression of creative visions.
Advantages of Using Blender Compared to Other Rendering Software
This software provides various benefits that establish it as a formidable rival to conventional visualization programs in design:
- Cost-Effective: Being an open-source platform, this tool is entirely free to utilize. This accessibility not only benefits small firms but also empowers freelancers to produce high-quality work without significant software investments.
- Frequent Updates: This software is known for its commitment to innovation, with regular updates that introduce new features and enhancements. This consistent flow of enhancements guarantees that users can access the most recent tools to remain competitive in the constantly changing design landscape.
- Integrated Workflow: One of the software’s standout features is its ability to combine modeling, visual output, and animation within a single platform. Employing both Eevee for real-time visualization and Cycles for photorealistic outcomes, this integration minimizes the necessity for various software solutions, optimizing the workflow and improving efficiency throughout the design process.
- Extensive Community Resources: The strong community surrounding this software is a valuable asset, offering a wealth of tutorials, forums, and plugins. This support network promotes ongoing learning and allows users to tackle challenges efficiently, nurturing a cooperative atmosphere.
- Flexibility and Customization: The software’s extensive customization options enable users to adjust it to meet specific project needs, which is essential for addressing the unique aspects of each design project. This adaptability boosts productivity and enables a more tailored workflow, addressing the varied requirements of design projects.
Furthermore, high-quality visual renderings generated by the software serve as an essential resource in project development, allowing designers to communicate their vision effectively and make informed choices. A case study highlights that while the software can produce animations, it is better suited for asset creation, with Maya excelling in complex animations. This distinction demonstrates the software’s strengths in creating high-quality assets for building projects.
Furthermore, as noted by industry expert Alan, ‘Blender’s flexibility and cost-effectiveness make it an invaluable tool for architects looking to innovate without breaking the bank.’ It is essential to provide estimates for unique projects, as customization and specific requests can significantly influence the overall investment in execution. These benefits reinforce the software’s status as an appealing option for visualizing architecture, especially for individuals looking for a flexible and economical solution in their design projects, while also prompting the discussion on whether Blender is good for architectural rendering, considering the influence of project intricacy and personalization on visualization results.
For instance, in a recent project, the customization of lighting and texture settings led to a 30% reduction in processing time, showcasing how tailored adjustments can enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
Tips and Techniques for High-Quality Architectural Renders in Blender
Obtaining top-notch design visuals in the software demands careful focus on various essential components of the process. A project commissioned by Ton Roosendaal, chairman of the Blender Foundation, raises the question of whether Blender is good for architectural rendering, exemplifying the software’s capabilities in design visualization. Our company specializes in creating high-quality renderings for both interior and exterior design projects across a wide range of sectors.
Here are key strategies to elevate your visualizations:
Utilize Realistic Textures: Employ high-resolution textures and precise UV mapping techniques to enhance the realism of materials. As noted by industry expert Samuel Woodward, the significance of realistic textures in building visualization cannot be understated. Realistic textures serve as the foundation for compelling visuals, capturing the essence of your design.
Optimize Lighting: Experiment with diverse lighting configurations, incorporating soft shadows and ambient occlusion to add depth and dimension to your scenes. Effective lighting techniques are paramount in showcasing design details, significantly impacting the overall render quality. For instance, using add-ons like Grasswald can introduce realistic foliage, further enhancing lighting effects and ensuring accuracy in your visualizations.
Camera Composition: Apply established principles of composition, such as the rule of thirds, to create visually engaging scenes. Considerate camera angles and framing can significantly affect the viewer’s perception and involvement with the layout, emphasizing the significance of accuracy in building renderings.
Post-Processing: Utilize Blender’s compositor to implement post-processing effects like glare, bloom, and color correction. These enhancements refine the final output, ensuring that the rendered images meet the highest aesthetic standards while conveying your creative intent effectively.
Practice and Experiment: Regularly engage in practice and experimentation with various techniques. Investigating various techniques not only enhances visualization abilities but also nurtures creativity, allowing builders to find innovative solutions to planning challenges. Integrating these approaches, along with the flexibility offered by add-ons such as GIS and Archimesh, will greatly improve the quality of visual representations created in the program, demonstrating that Blender is good for architectural rendering. Furthermore, we employ cutting-edge technology to record current environments, facilitating better expression of creative intent and highlighting the complete capabilities of the software in visual presentation, ensuring that every detail adds to the overall story of your project.
The Future of Architectural Rendering with Blender
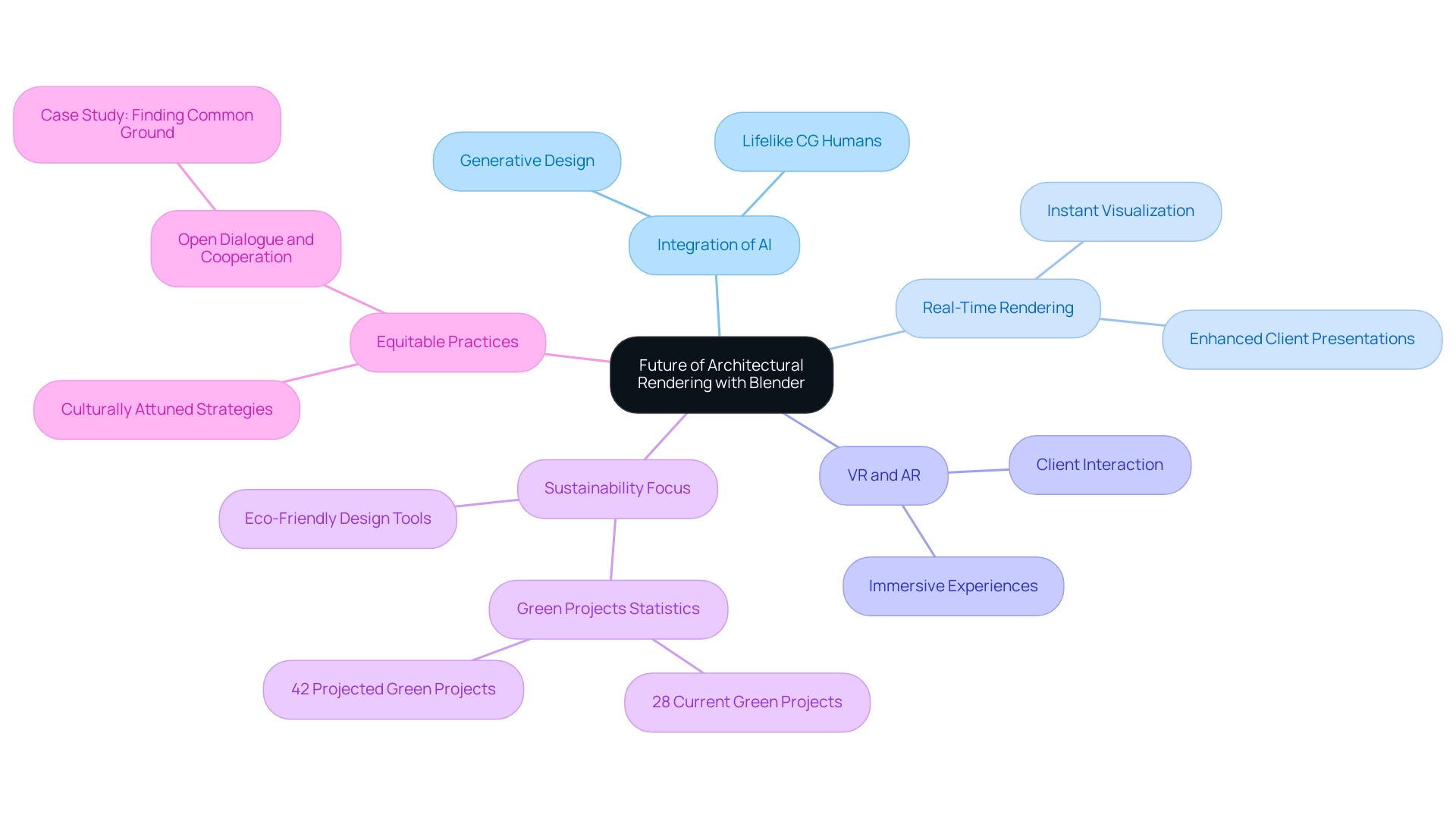
The future of architectural rendering with Blender is marked by several transformative trends that architects should closely monitor:
Integration of AI: The adoption of AI-driven generative design and rendering tools is expected to revolutionize the rendering process. These innovations will enable architects to create lifelike CG humans and multiple iterations based on specified parameters, enhancing both efficiency and creative output while overcoming the uncanny valley in architectural visualizations. This capability will play a crucial role in pre-sales visualization, allowing developers to present projects in a more compelling manner, thereby attracting investment.
Real-Time Rendering: Advances in real-time rendering technology will empower architects to visualize projects instantaneously. This capability will significantly enhance client presentations and streamline iterations, allowing for more dynamic interactions and quicker decision-making.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): The evolution of VR and AR technologies will expand Blender’s functionalities to include immersive visualization experiences. This shift will enable architects to showcase their creations in a more engaging manner, facilitating better client understanding and interaction.
Sustainability Focus: With 28% of global architects, engineers, contractors, owners, and investors indicating that most of their projects qualify as green—projected to increase by 42% in the next three years, according to OpenAsset—there is a growing emphasis on sustainability within design. Consequently, Blender is likely to develop tools that prioritize eco-friendly design practices, aligning with industry demands for sustainable solutions.
Equitable Practices: As the design field evolves, there is a critical need for developing concrete strategies to foster a more equitable and culturally attuned practice. This involves navigating differing views and promoting cooperation among stakeholders, as demonstrated by the case study titled “Finding Common Ground on Account Plans,” which highlights the significance of open dialogue and shared objectives in design processes.
By staying informed about these key trends, including the significance of 3D interior design renderings in preserving design legacy and celebrating creativity, architects can effectively determine if Blender is good for architectural rendering to enhance their workflows and adapt to future industry requirements. The integration of lifelike CG humans not only enhances the realism of architectural visualizations but also serves as a powerful tool in pre-sales efforts, bridging the gap between concept and reality.
Conclusion
Blender has established itself as a pivotal tool for architects, offering a comprehensive suite of features that significantly enhance architectural rendering capabilities. Its advanced rendering engines, Cycles and Eevee, enable the production of both photorealistic visuals and real-time renderings, catering to diverse project requirements. The software’s versatility, evidenced by its compatibility with various file formats and extensive community support, facilitates seamless integration into existing workflows, essential for collaborative design processes.
The unique advantages of Blender over traditional rendering software further solidify its position in the architectural domain. Its cost-effectiveness, frequent updates, and extensive customization options empower architects to produce high-quality visualizations without the burden of substantial financial investment. The platform’s integrated workflow simplifies the rendering process, providing a cohesive environment for modeling, rendering, and animation. As highlighted, the ability to leverage realistic textures, optimize lighting, and apply effective composition techniques are critical for achieving stunning results that resonate with clients.
Looking ahead, the future of architectural rendering with Blender appears promising, driven by trends such as AI integration, real-time rendering advancements, and the incorporation of VR and AR technologies. These innovations not only enhance visualization capabilities but also align with the industry’s growing emphasis on sustainability and equitable practices. By adapting to these trends and harnessing Blender’s evolving functionalities, architects can remain competitive and continue to elevate their design processes, ultimately enhancing client engagement and project outcomes.

0 Comments