Introduction
In the realm of architectural design, the ability to visualize concepts through 3D rendering has become an indispensable tool for professionals seeking to convey their vision with precision and clarity. This intricate process transforms two-dimensional models into immersive three-dimensional images, enabling architects to explore spatial relationships, material interactions, and the nuanced effects of lighting.
As the demand for high-quality visualizations continues to surge across various industries, understanding the fundamental principles, advanced techniques, and cutting-edge tools of 3D rendering is crucial for architects aiming to stay competitive. From the initial conceptualization to the final delivery, mastering each phase of this sophisticated workflow not only enhances client engagement but also elevates the overall design narrative, making it essential for architects to refine their skills in this dynamic field.
With the global 3D rendering market poised for significant growth, the implications of these advancements stretch far beyond architecture, influencing product design, medical imaging, and even entertainment.
Understanding 3D Rendering: The Basics
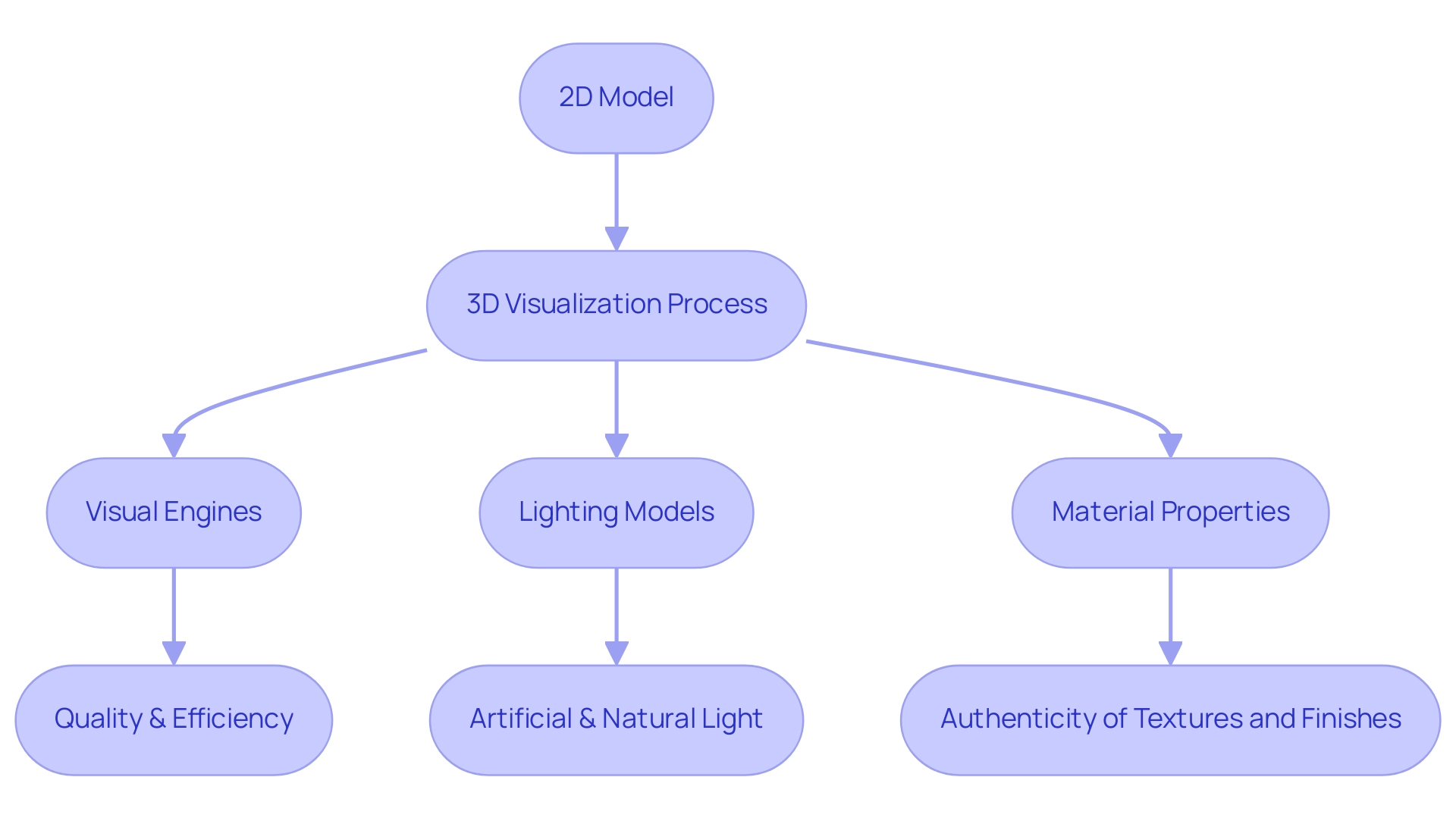
3D visualization denotes the sophisticated process of generating a three-dimensional image from a two-dimensional model utilizing specialized software. This advanced technique acts as a guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life, empowering architects to visualize ideas within a realistic context and facilitating a comprehensive understanding of spatial relationships, material choices, and the intricate effects of lighting. In interior visualizations, the precise portrayal of artificial lighting—such as overhead lights and lamps—is crucial, while exterior visuals depend heavily on natural sunlight to enhance the realism of architectural features.
A significant challenge architects face is balancing these two types of lighting to create a cohesive visual narrative, ensuring that artificial light complements natural light without overpowering it. Mastery of these lighting considerations is imperative for architects, as it enables them to articulate their concepts effectively and make wise choices in their work. Essential components of this process include:
– Visual engines, which dictate the quality and efficiency of the output
– Lighting models that simulate realistic illumination
– Material properties that enhance the authenticity of textures and finishes
Moreover, the degree of detail in architectural visuals acts as a guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life, playing a vital role in interaction with customers and stakeholders by enabling a more precise depiction of the conceptual intention and promoting discussions about particular components. Notably, large enterprises held a significant share of the global 3D visualization market in 2023, leveraging advanced solutions for complex projects. With the market expected to demonstrate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.08% from 2024 to 2033, the guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life highlights the increasing importance of 3D visualization in architectural practice, influencing planning methodologies and improving client interaction.
This technology finds diverse applications across architecture, medical imaging, training simulations, product prototyping, and graphic design, underscoring its vital role in modern design. Furthermore, the automotive segment is predicted to grow at a significant rate during the forecast period, reflecting the broader applications of 3D rendering technology. As noted by Meta Platforms, Inc., ‘A new AI tool from Meta can create or retexture 3D objects in less than a minute,’ highlighting the rapid advancements in this field.
Step-by-Step Process of Creating 3D Renderings
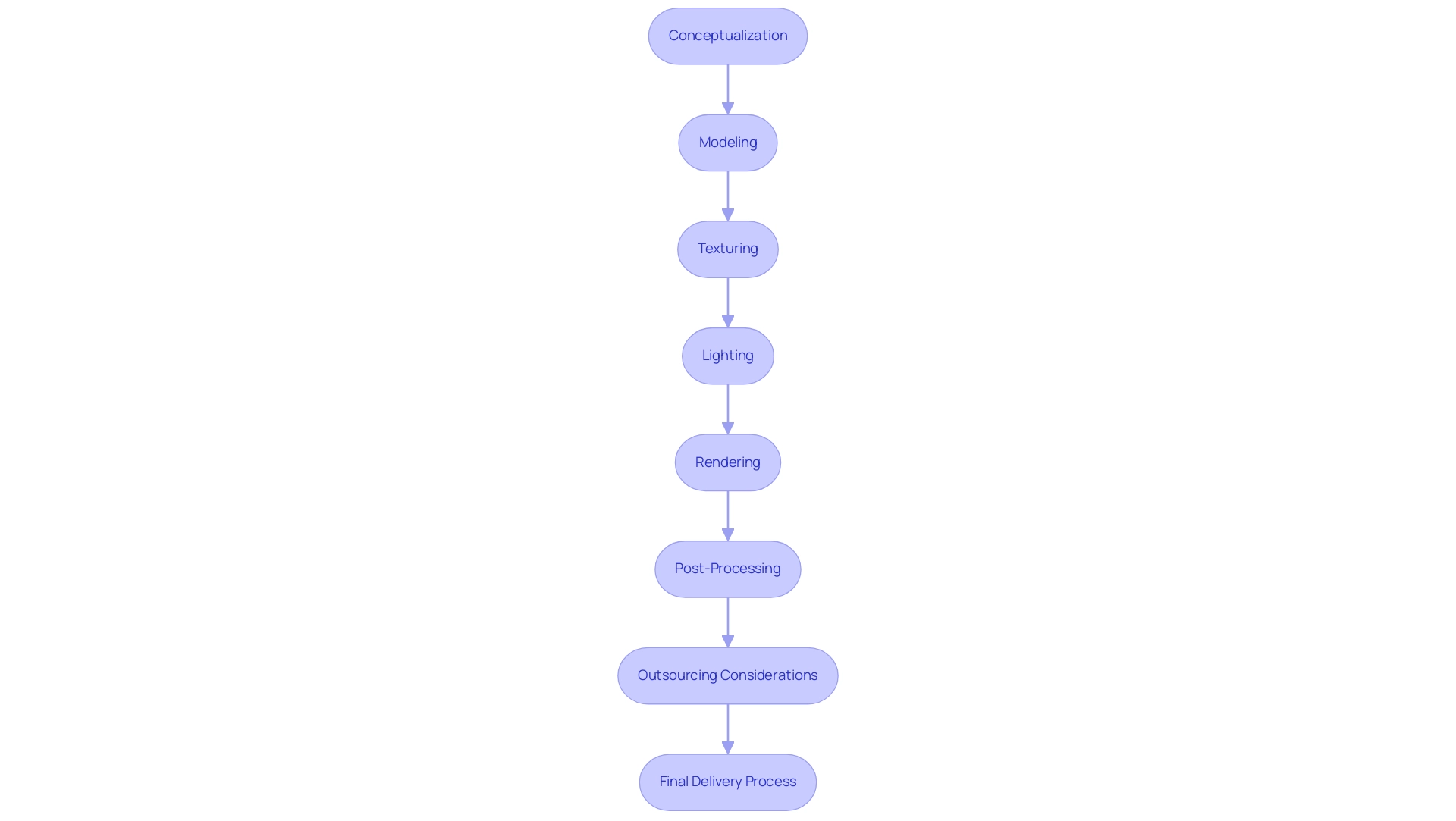
Conceptualization: The initial phase involves clearly defining the project’s objectives and compiling a comprehensive set of reference materials. This foundational step is crucial for accurately visualizing the design intent, as outlined in the guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life, and ensuring alignment with client expectations.
Modeling: Utilize advanced 3D modeling software, such as SketchUp or Revit, to construct the architectural model. Attention to detail is paramount; precise dimensions and material specifications directly influence the model’s integrity and realism. Notably, a ship model can require between 30 to 32 hours to complete, with the low-poly stage taking approximately 12 hours, the high-poly stage around 8 hours, and texturing demanding another 12 hours.
Texturing: In this phase, apply textures and materials meticulously to the model. Utilize high-resolution images to achieve realistic finishes that enhance the visual appeal of the depiction.
Lighting: Setting up the lighting is a critical aspect of producing, as it should replicate natural light conditions as closely as possible. Experiment with various light sources and configurations to create the desired ambiance and depth in the scene. Notably, lighting and reflections can typically take just a day or two, depending on the required level of detail.
Rendering: Select an appropriate rendering engine such as V-Ray or Lumion. Adjust the settings to balance quality and speed, taking into consideration the deadlines. For instance, in scenarios with strict deadlines, it may be necessary to reduce render quality to meet time constraints; the 3D render calculator can help determine the maximum allowable render time per frame, ensuring efficiency. An example: for 50 frames rendered on two machines needing completion within 8 hours, the calculator suggests a maximum render time of 19.2 minutes per frame. Effectively managing timelines is crucial, as outlined in the guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life.
Post-Processing: Finally, utilize post-processing software like Photoshop to refine the rendered image. This stage includes adjusting colors, enhancing contrast, and adding effects to elevate the final presentation. As Shishir Dwivedi suggests, allow for an additional buffer in timelines to accommodate potential delays, emphasizing the value of monitoring team progress daily to set realistic deadlines. This method not only assists in post-processing but also serves as a guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life, ensuring that the whole visual creation process stays on course while emphasizing the significance of collaboration with stakeholders and quality assurance throughout the project.
Outsourcing Considerations: When contemplating outsourcing 3D architectural visualization, businesses should evaluate which tasks are most time-consuming and how outsourcing can enhance efficiency. Effective outsourcing can lead to improved quality and faster turnaround times, allowing in-house teams to focus on core activities.
Final Delivery Process: The final delivery stage is critical in ensuring customer satisfaction. Once the images meet expectations, we refine the visuals, enhancing their quality and detail to ensure a polished, professional look. Collaborating closely with stakeholders during this stage guarantees that the final visuals perfectly capture the essence of architectural designs, thus reinforcing quality assurance.
Exploring Techniques and Tools for Effective 3D Rendering
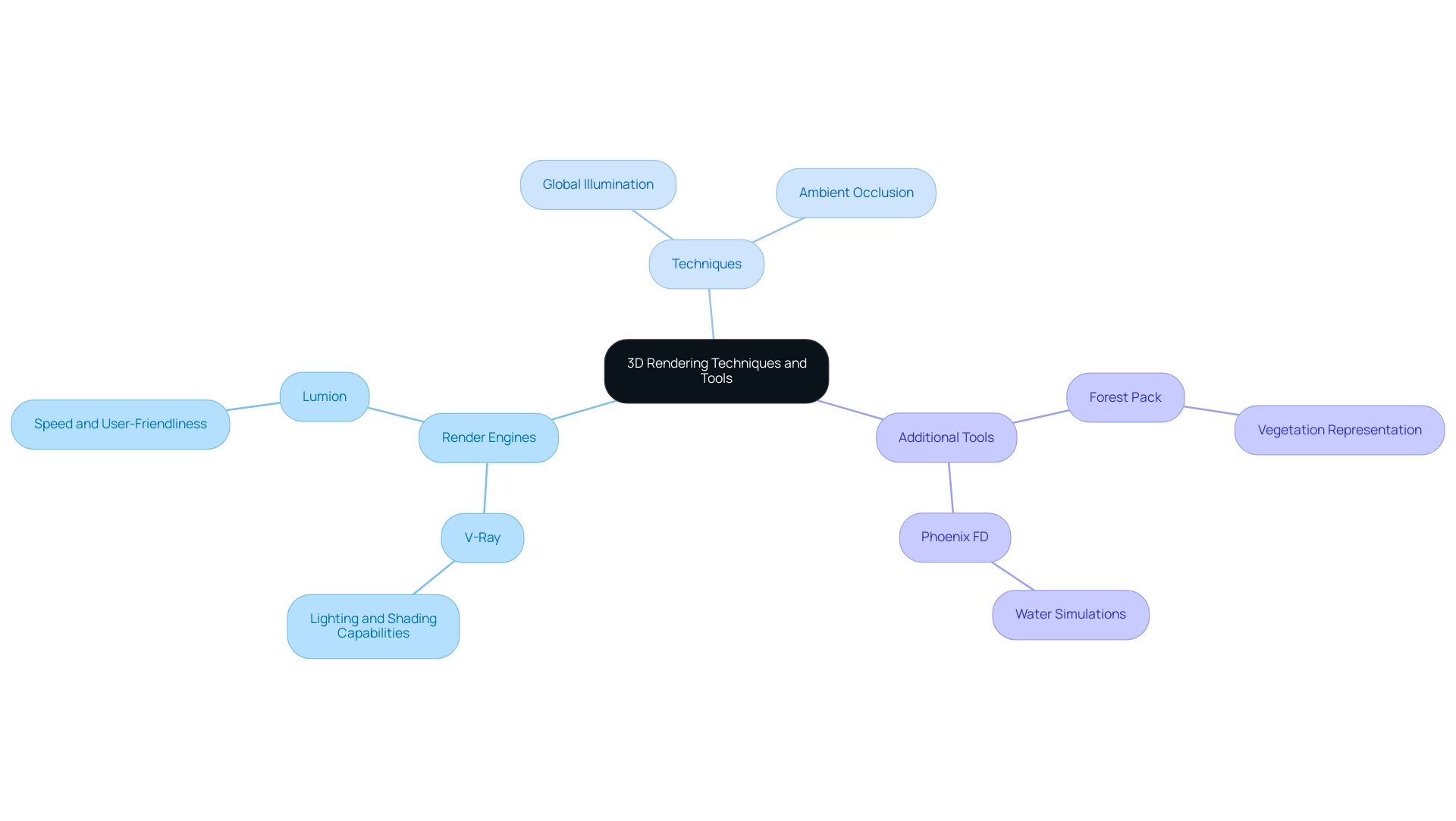
A successful approach to 3D visualization acts as a guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life, requiring a strategic combination of advanced methods and state-of-the-art tools, especially when addressing the intricacies and scope of distinct architectural endeavors. Selecting the right render engine is a nuanced process that requires careful consideration of pricing, features, compatibility, and user satisfaction. V-Ray stands out as a leading visualization engine, especially for its sophisticated lighting and shading capabilities, which allow for the creation of highly realistic images that capture the intricate details essential for engaging clients.
As noted by David, ‘One thing to comment on is when Vray 5 came along, people were criticizing Chaos Group for being complacent, but even in this limited test it is clear Vray is the overall best.’ In contrast, Lumion is favored for its speed and user-friendly interface, making it a popular choice for architects who need to produce visualizations quickly without sacrificing quality. Techniques such as global illumination and ambient occlusion are essential for enhancing realism, accurately simulating the behavior of natural light within a scene.
The importance of intricate details—such as the texture of bricks or the interplay of sunlight—cannot be overstated, as they enhance the emotional effect of designs and make creations feel authentic and inhabited. Furthermore, utilizing specialized plugins like Forest Pack can significantly improve vegetation representation, while Phoenix FD excels in delivering lifelike water simulations. Notably, OSPRey demonstrates strong GPU utilization with peaks of 45%, showcasing its performance capabilities among visualization engines.
By mastering these tools and techniques, architects can use a guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life, tailoring their visualization strategies to meet the unique demands of each project, resulting in visually compelling and effective architectural representations. Comprehending the implications of engine performance, as discussed in the case study ‘Warm-starting Render Engine Implementations,’ is crucial for making informed decisions about engine selection. As the industry evolves, staying informed about the latest tools and techniques is imperative for maintaining a competitive edge in architectural visualization.
Furthermore, it’s crucial to take into account the particular difficulties linked to complexity; for example, developing an entire community demands considerably more resources and time than a single-car garage. This difference emphasizes the need for architects to adjust their visualization strategies based on the scale and intricacy of the project at hand.
Applications of 3D Rendering in Various Industries
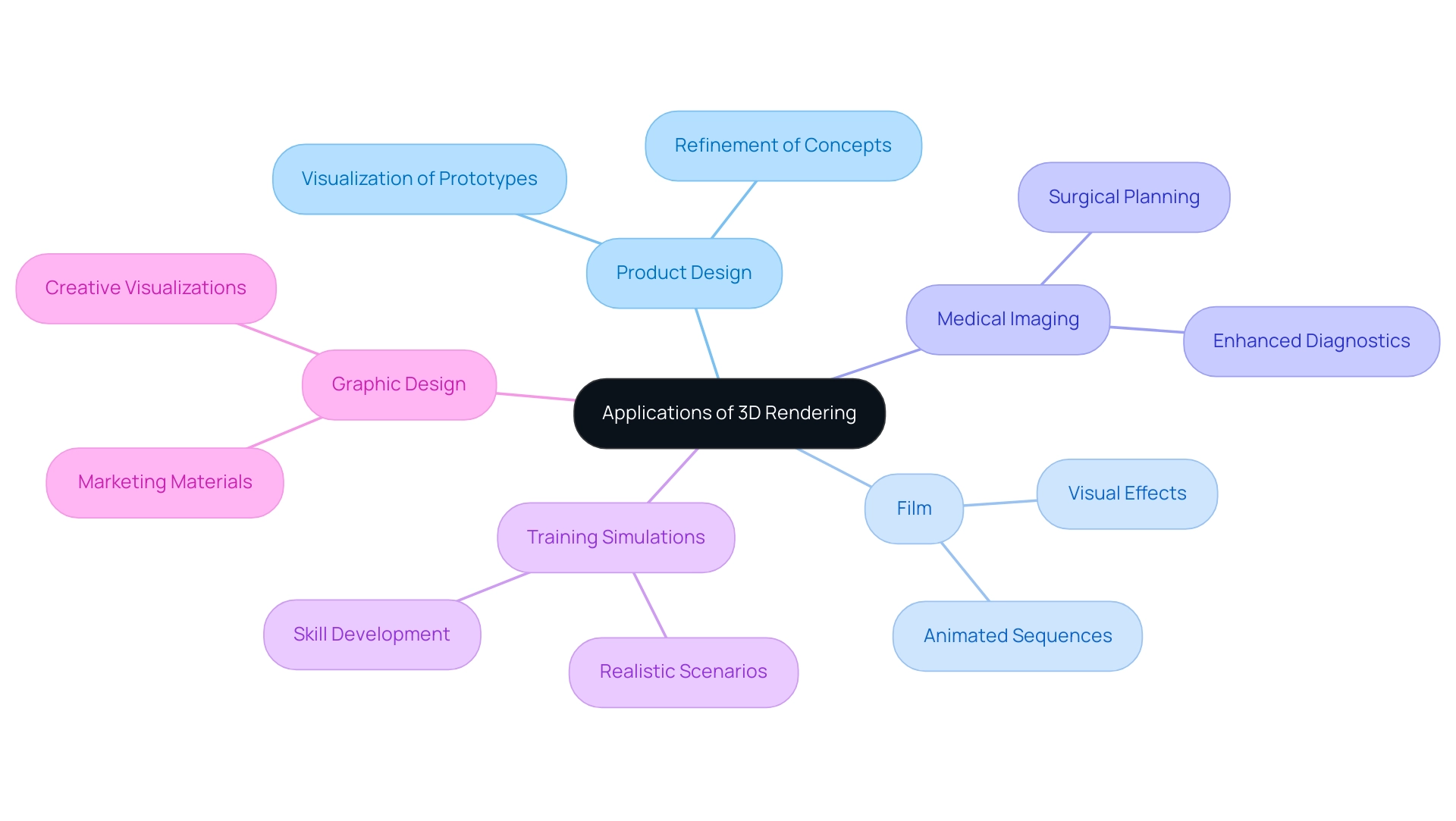
3D rendering transcends the realm of architecture and serves as a guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life in numerous industries, including:
- Product design
- Film
- Medical imaging
- Training simulations
- Graphic design
At J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, we understand that testimonials are not just feedback; they reflect our commitment to excellence and the lasting partnerships we build. You can find genuine reviews from our clients on platforms like Google, Facebook, and Houzz.
For instance, in product design, the guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life aids the visualization of prototypes prior to production, enabling designers to refine their concepts effectively. The film industry serves as a guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life, utilizing 3D imagery to create stunning visual effects and intricate animated sequences that enhance storytelling and audience engagement. In the real estate industry, developers use a guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life as a powerful marketing tool, offering prospective buyers engaging and lifelike images of future developments.
This approach acts as a guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life, captivating audiences while also accelerating decision-making processes. As one of our clients stated, ‘The visualization helped us see our project come to life before it was built, which was invaluable.’ Comprehending the applications of 3D visualization is essential for remaining competitive in the market, especially as industries seek a guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life, increasingly depending on top firms like Adobe, Autodesk, and NVIDIA for advanced solutions.
Additionally, the partnership between TechViz and Lenovo ThinkReality showcases how 3D visualization technologies can transform design and engineering by providing AR data representation solutions from CAD files, allowing users to transition seamlessly to 3D AR representations. By exploring these varied applications, architects can use the guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life to harness the potential of 3D visualization, elevate their work, adapt to industry trends, and connect with broader audiences.
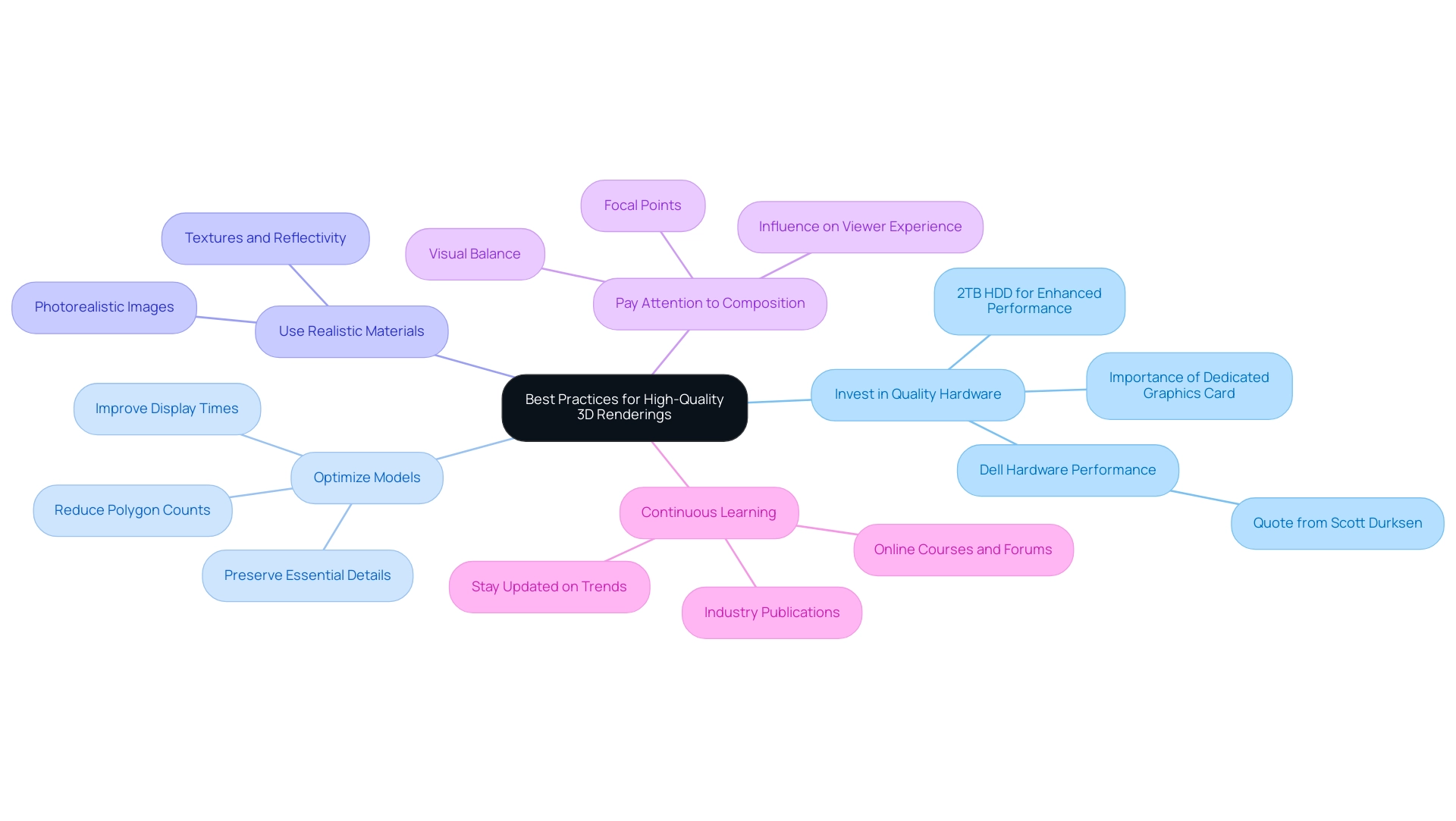
Best Practices for High-Quality 3D Renderings
To achieve high-quality 3D visuals, architects should adhere to the following best practices:
- Invest in Quality Hardware: A robust computer equipped with a dedicated graphics card is essential for efficiently managing complex processing tasks. As Scott Durksen, CSWE, states, “We are confident that Dell hardware will provide the best performance for your team and increase the efficiency of your regular workflows.”
Recent advancements in hardware, such as the option for a 2TB HDD, can significantly enhance performance and storage capacity.
- Optimize Models: Reducing polygon counts while preserving essential details is crucial for ensuring quicker display times.
This optimization not only improves performance but also enhances the overall quality of the final output.
Use Realistic Materials: Choosing materials that accurately represent real-world properties, including textures and reflectivity, plays a vital role in achieving photorealistic images.
Pay Attention to Composition: Considerate arrangement of visuals, with an emphasis on focal points and visual balance, can significantly influence the viewer’s experience and comprehension of the layout.
Continuous Learning: Staying abreast of the latest trends and techniques in 3D rendering through online courses, forums, and industry publications is essential for maintaining a competitive edge in this rapidly evolving field.
By applying these best practices, architects can create compelling visualizations that act as a guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life, while also enhancing their marketing strategies and online visibility. Furthermore, utilizing 3D visualizations will facilitate clearer communication with clients and investors, reduce costly changes, resolve design issues early, and streamline workflows, ultimately leading to more informed decision-making and heightened excitement about the potential.
High-quality renderings act as a guide to how 3D renderings bring concepts to life, serving as a ‘window into the future’ of your project and allowing everyone involved to visualize the potential and understand the vision behind the blueprints.
Conclusion
The exploration of 3D rendering in architecture reveals its pivotal role in transforming concepts into compelling visual narratives. By mastering the foundational processes—from conceptualization and modeling to lighting and post-processing—architects can effectively communicate their design intentions, thereby enhancing client engagement and satisfaction. The integration of advanced techniques and tools, such as V-Ray and Lumion, further underscores the importance of selecting the right rendering engine to achieve high-quality outputs that resonate with various stakeholders.
Moreover, the applications of 3D rendering extend beyond architecture into diverse fields, including:
- Product design
- Medical imaging
- Entertainment
This versatility highlights the growing demand for skilled professionals who can leverage rendering technology to meet industry needs. As the market for 3D rendering continues to expand, architects are encouraged to adopt best practices, invest in quality hardware, and stay informed about emerging trends to maintain a competitive edge.
In conclusion, the mastery of 3D rendering is not merely a technical skill but a vital component of modern architectural practice. As the industry evolves, embracing this sophisticated tool will not only enhance the design narrative but also shape the future of architectural visualization, ensuring that architects can effectively convey their visions in an increasingly dynamic and competitive landscape.

0 Comments