Introduction
The intricate world of architectural rendering serves as a vital conduit between abstract design concepts and tangible visualizations, shaping the future of architectural projects. As architects navigate the complexities of transforming ideas into photorealistic representations, a comprehensive understanding of rendering techniques becomes indispensable.
This article delves into the multifaceted process of architectural rendering, from its foundational principles to advanced post-production methodologies. By exploring the nuances of various rendering types, the significance of cutting-edge software, and the challenges faced during post-production, it aims to equip seasoned architects with the knowledge necessary to elevate their visual communication skills.
As the demand for high-quality renderings continues to surge, mastering these techniques not only enhances project outcomes but also reinforces the architect’s role in fostering client engagement and satisfaction.
Understanding Architectural Rendering: A Foundation for Post-Production
Architectural visualization is a critical process that involves the creation of two-dimensional images or animations to visualize proposed architectural designs. This technique is essential for conveying concepts effectively, enabling architects and clients alike to anticipate the final appearance of a project prior to construction. A nuanced understanding of various visualization types—such as photorealistic, conceptual, and technical—is crucial, as each serves distinct purposes throughout the design process.
For instance, photorealistic depiction is increasingly favored for its ability to capture intricate details and realistic lighting, effectively communicating design intent and enhancing client satisfaction. Interior and exterior architectural illustrations exemplify this, showcasing key differences in the treatment of materials, lighting, and design approaches. For example, while artificial lighting plays a critical role in creating inviting interior spaces, natural sunlight is a fundamental aspect in outdoor visuals, influencing the perception of durability and texture.
Additionally, preliminary conceptual designs offer significant advantages, including quick visualization of ideas, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced communication among stakeholders. As noted by the Architect’s Newspaper, there were 35,621 candidates actively pursuing licensure, highlighting a robust interest in mastering these essential skills. Moreover, with 70% of design firms intending to invest more in technology over the coming year, it is evident that progress in visualization methods will play a crucial role in influencing the future of building representation.
The market for digital asset management is projected to reach $16.18 billion by 2032, underscoring the importance of these advancements in the industry. Comprehending the appropriate level of detail in architectural visuals is also essential for homeowners and businesses, facilitating clearer communication and minimizing misunderstandings. The use of sophisticated 3D modeling applications, like SketchUp, enables designers to customize concept visuals according to particular requirements.
A solid grasp of these concepts not only empowers architects to craft more compelling presentations but also enhances their capability to manipulate and refine renders during post-production, ultimately influencing the decision-making process and project outcomes. Incorporating precedence statistics pertinent to the 3D visualization sector further highlights the importance of construction visualization in the current market landscape.
Essential Post-Production Techniques in Architectural Rendering
In architectural rendering post production, software such as Adobe Photoshop is predominantly used, remaining an industry standard. A critical aspect of this process is color correction, playing a vital role in achieving visually impactful images that resonate emotionally with clients. Begin by adjusting brightness and contrast to enhance the vibrancy of your images, as this can significantly influence client connection and satisfaction.
Utilizing layers is essential for isolating specific adjustments, granting you finer control over the final appearance. Incorporating overlays—such as figures, vegetation, or furniture—adds context and scale, making the visuals more relatable and enhancing the overall design essence. Furthermore, the application of filters can help unify the image’s aesthetic, ensuring it aligns with the project’s vision.
The precision and detail in exterior visuals are crucial as they tell a compelling story about the future of a building or home, capturing its essence and inviting emotional engagement from clients. Recent updates in rendering software, particularly with the latest version of 3Ds Max (2024), have introduced advanced functionalities that streamline these processes, making them more intuitive and precise. For instance, tools that allow for real-time adjustments can significantly enhance the accuracy of the details showcased.
As industry expert Sevinch Sadeghie notes, ‘OctaneRender is regarded as the most powerful engine for 3D design,’ emphasizing its effectiveness in architectural rendering post production techniques. Additionally, case studies, such as ‘Health Related Landscape Architecture Ideas,’ illustrate how lifelike visuals significantly enhance buy-in and funding, showcasing the power of pre-sales visualization in generating investment and reinforcing the importance of mastering architectural rendering post production techniques to elevate the quality of your final output and instill confidence in prospective investors.
The Workflow of 3D Architectural Rendering: From Concept to Post-Production
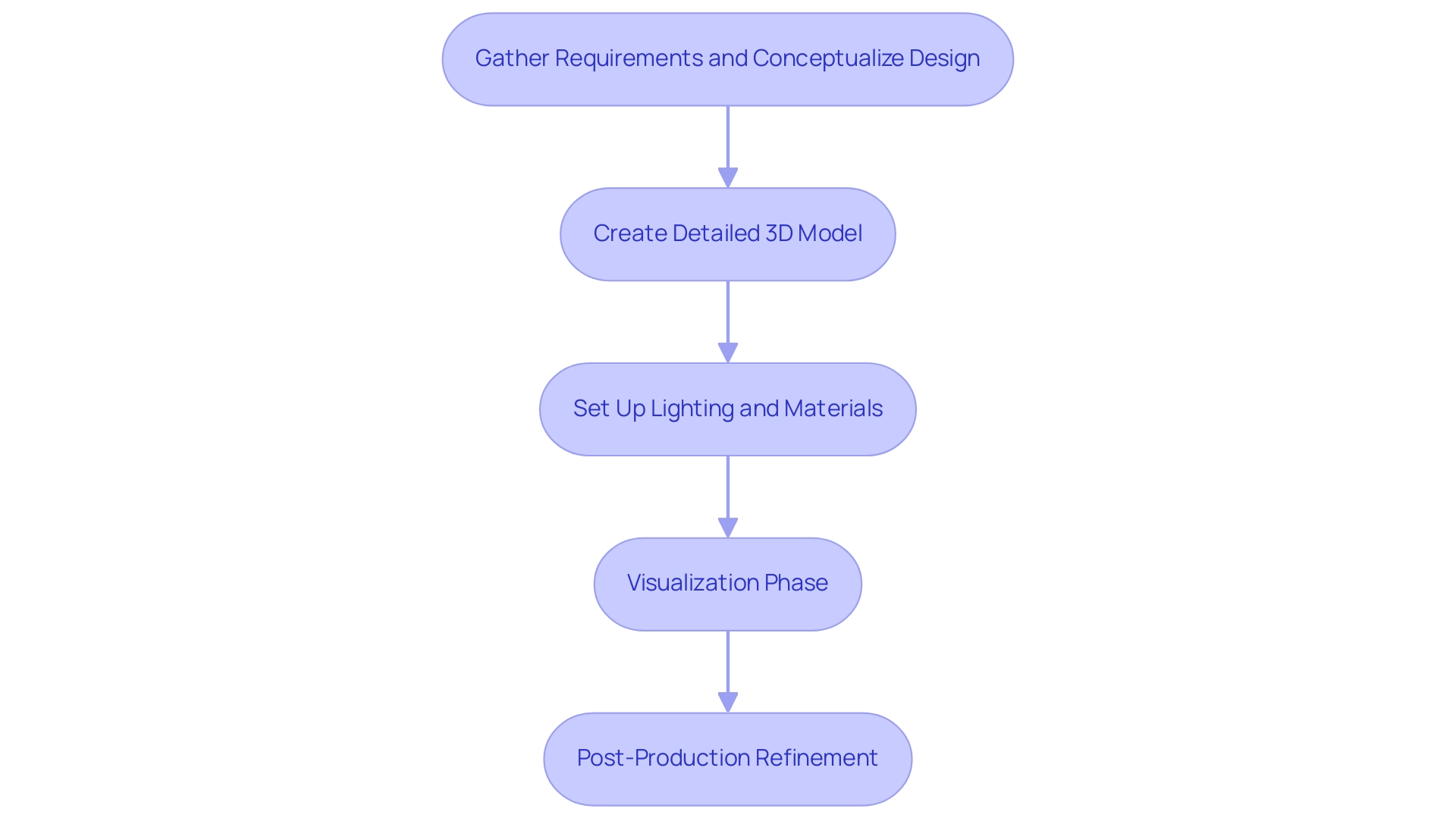
The workflow of 3D architectural rendering is a structured process that encompasses several critical stages, designed to maximize the benefits of photorealistic visualizations. Initially, architects gather comprehensive requirements and conceptualize the design, ensuring all client expectations are met. This early phase is crucial, as it enhances communication and sets the foundation for effective collaboration among stakeholders.
Following this, the creation of a detailed 3D model is undertaken, utilizing industry-standard software such as SketchUp or Revit, which allows for precise modeling customized to specifications. With over 73,313 businesses in architecture in the U.S., the scale of the industry underscores the importance of efficient workflows in maintaining competitiveness. Once the model is complete, attention shifts to setting up lighting and materials, employing advanced techniques to achieve a high degree of realism that resonates with clients and investors alike.
The visualization phase utilizes powerful engines like V-Ray or Lumion, which are essential for producing visually stunning images that enhance property value through visual appeal and market differentiation. Significantly, 28% of worldwide designers, engineers, contractors, owners, and investors state that most of their construction efforts qualify as green, indicating a trend towards sustainability that efficient visualization workflows can support. Furthermore, outsourcing 3D design visualization can greatly affect business efficiency by enabling companies to concentrate on core strengths while utilizing specialized abilities and resources from outside providers.
The final stage of architectural rendering post production involves refining the output with software like Photoshop, where adjustments and enhancements are made to perfect the visuals. Mastery of this comprehensive workflow not only aids architects in identifying potential areas for improvement but also significantly enhances overall productivity and project outcomes. By enhancing each phase, including factors for outsourcing, companies can more effectively satisfy the rising need for high-quality, lifelike images, as shown by the growing acknowledgment of visual communication’s significance in design.
Tools and Software for Architectural Rendering and Post-Production
In the field of design visualization, several essential software applications are crucial for creating detailed 3D models and attaining outstanding visual accuracy. Prominent among these are:
- Autodesk 3ds Max
- Blender
- Rhino
Each offering unique capabilities that cater to the demands of lead architects. For visualization, V-Ray and Corona Renderer stand out as preferred choices, renowned for their ability to deliver stunningly photorealistic images that meet the high standards of the industry, thus underscoring the importance of impressive 3D visuals in conveying architectural visions.
High-quality visuals act as a ‘window into the future’ of your initiative, enabling all participants to perceive the possibilities and comprehend the vision behind the blueprints. The significance of intricate details—like the way sunlight dances off windows or the texture of bricks—enhances realism and emotional impact, making projects feel real and ready to be built. Post-production, particularly architectural rendering post production, is equally important, with Adobe Photoshop reigning as the industry standard for image enhancement.
Furthermore, tools such as Lumion provide real-time visualization features, greatly simplifying the process and allowing designers to see their creations immediately. A comprehensive understanding of these tools not only sharpens your skills but also enhances your ability to produce high-quality outputs with efficiency. As stated by OpenAsset, a significant 28% of professionals—including architects, engineers, contractors, owners, and investors—indicate that their initiatives are regarded as eco-friendly, emphasizing the increasing importance of sustainable practices in design.
This trend is anticipated to grow, with 42% expecting to attain green status within the next three years. Such advancements in architectural visualization technologies, including the implementation of AI and machine learning, are set to improve performance and automate various aspects of architectural rendering post production, thereby enhancing production efficiency and image quality. This evolution not only expands the limits of creativity in digital media but also mirrors the industry’s adjustment to innovative tools and practices, reinforcing the essential role of high-quality visual representations in project development and decision-making.
Overcoming Challenges in Architectural Rendering Post-Production
The challenges in architectural rendering post production can significantly impact the final output. Common issues include:
- Color mismatches
- Inconsistent lighting
- Inherent software limitations
To ensure precision in representations, meticulous detail is paramount, as it shapes environments that resonate with emotions and lifestyles.
Color calibration tools play a vital role in guaranteeing that monitors accurately display colors, which is crucial for achieving photorealistic results. Effective calibration techniques mitigate detrimental color discrepancies that may occur during the visualization process. Furthermore, inconsistent lighting often stems from misalignment between the lighting setup in the 3D model and the settings in post-production software.
A thorough review of both environments is critical for achieving coherence in lighting, which enhances the overall realism of the render and reflects the nuanced interplay of light and shadow. Working together with clients during this phase is crucial, as comprehensive illustrations enable a mutual vision and permit modifications based on client input. When faced with software limitations that may impede workflow, integrating advanced plugins or supplementary software can provide innovative solutions to bridge these gaps.
Proactively tackling these challenges not only maintains the quality and integrity of visual representations but also enables architects to utilize advancements in architectural rendering post production. Given the design visualization sector is anticipated to expand from $4.59 billion in 2024 to $16.18 billion by 2032, the significance of addressing these challenges becomes even more evident. Moreover, as emphasized in recent industry insights, the transformative roles of real-time visualization and AI are becoming standards, enhancing efficiency and innovation in architectural practices.
This shift underscores the critical need for accurate rendering, especially in the context of sustainable architecture, where 28% of professionals report that most of their projects qualify as green.
Conclusion
The exploration of architectural rendering and its post-production techniques underscores the essential role these processes play in modern architectural practice. Through a detailed examination of rendering types, such as photorealistic and conceptual, the article illustrates how each variant serves distinct purposes, facilitating clearer communication and enhancing client engagement. The significance of utilizing advanced software and tools, including Autodesk 3ds Max and Adobe Photoshop, is emphasized as crucial for achieving high-quality visual outputs that resonate with stakeholders.
Moreover, understanding the comprehensive workflow from concept to post-production is vital for architects seeking to elevate their projects. By mastering each stage, from initial design to the refinement of final renderings, architects can enhance productivity and deliver visually compelling presentations that not only reflect their creative vision but also foster trust and satisfaction among clients.
As the architectural rendering market continues to expand, overcoming challenges such as color mismatches and lighting inconsistencies becomes increasingly important. The integration of real-time rendering and AI technologies further highlights the industry’s shift towards innovation, reinforcing the necessity for architects to stay adept with evolving tools and methodologies. Ultimately, the mastery of architectural rendering and post-production techniques is not merely an enhancement of visual communication; it is a critical investment in the future of architectural design and client relations.

0 Comments