Introduction
In the realm of architectural visualization, photorealistic rendering stands as a pinnacle of artistic and technical achievement, enabling architects to transform abstract concepts into vivid representations that resonate with clients and stakeholders alike. This intricate process hinges on a profound understanding of key principles such as:
- Ray tracing
- Global illumination
- Advanced material properties
All of which contribute to the creation of lifelike images. As technology evolves, the integration of high-performance rendering engines and sophisticated lighting techniques has become essential for overcoming challenges such as:
- Render times
- Material accuracy
This article delves into the foundational concepts, essential tools, and innovative practices that define photorealistic rendering, illuminating its vital role in enhancing communication, trust, and decision-making within the architectural design process.
Understanding Photorealistic Rendering: Key Concepts and Definitions
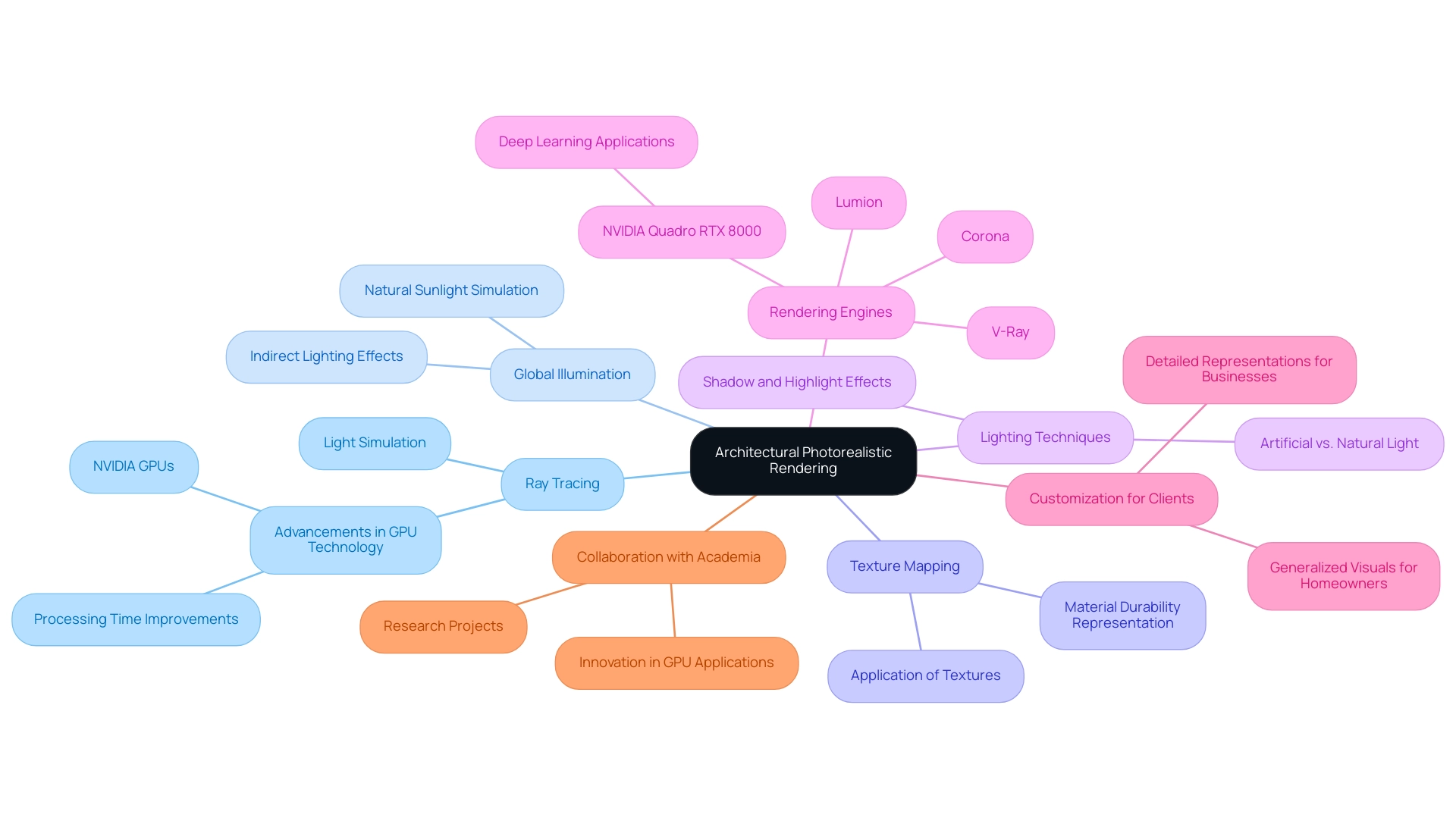
The process of architectural photorealistic rendering is a sophisticated method aimed at producing images that are virtually indistinguishable from actual photographs. Mastering this technique involves understanding several key concepts:
Ray Tracing: This advanced technique accurately simulates the behavior of light as it interacts with various surfaces, resulting in exceptionally realistic imagery. Its recent advancements have significantly improved processing times and quality, particularly with the latest NVIDIA GPUs, which enhance performance through scalable software design. The global GPU market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 21% from 2023 to 2028, underscoring the relevance of advancements in GPU technology to architectural photorealistic rendering.
Global Illumination: This method calculates how light reflects off surfaces, simulating indirect lighting effects that contribute to the overall realism of a scene. It is crucial in achieving lifelike representations, particularly in understanding how natural sunlight affects exterior visuals, showcasing the building’s facade at various times of the day.
Texture Mapping: This technique involves applying images (textures) to 3D models, enriching their surfaces and adding intricate details that elevate realism. The meticulous application of textures, particularly in showcasing durability and texture of materials, is essential in creating visually compelling models that resonate with clients.
Lighting Techniques: Contrasting the nuances of artificial lighting in interior spaces with the dynamics of natural light in outdoor visuals is crucial. Designers must accurately depict various light sources, ensuring a true sense of how spaces will feel in real life. This understanding enhances contractor communication and eliminates misunderstandings, as stakeholders can effectively visualize the interplay of light and material through architectural photorealistic rendering. Furthermore, capturing the challenges of natural light in outdoor visuals, such as how it casts shadows and highlights architectural features throughout the day, is essential for achieving realism in architectural photorealistic rendering.
Rendering Engines: Software such as V-Ray, Corona, and Lumion are integral to achieving architectural photorealistic rendering. These engines employ advanced algorithms for light and material simulation, allowing architects to create stunning architectural photorealistic renderings that effectively convey their intent. Notably, crafted by PNY, the NVIDIA Quadro RTX 8000 is recognized as the world’s most potent graphics card, meticulously designed for deep learning matrix multiplications, highlighting the significance of high-performance graphics cards in visual processes.
Furthermore, it is crucial to consider the level of detail in architectural photorealistic rendering for effective architectural visualizations. Homeowners may require more generalized visuals to understand the overall design, while businesses may benefit from detailed representations that highlight specific features and materials. This customized method enhances client understanding and improves stakeholder communication.
Leading GPU manufacturers are collaborating with academic institutions on research projects, driving innovation by exploring new applications and enhancing existing technologies in display. Understanding these essential concepts is vital for mastering the advanced techniques that will further improve your capabilities.
Essential Techniques and Tools for Achieving Photorealistic Results
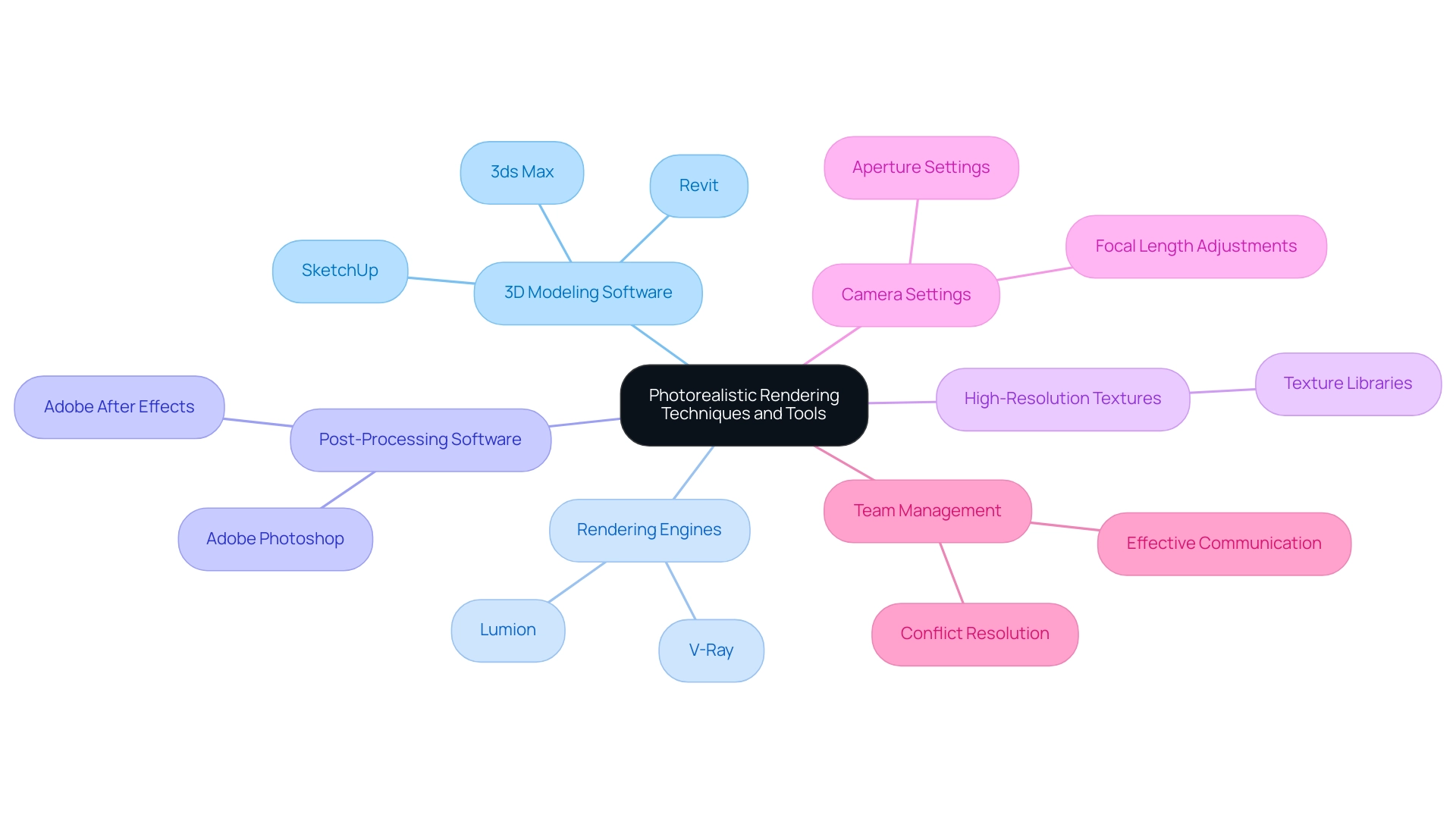
Achieving architectural photorealistic rendering in architectural visuals demands a meticulous approach that prioritizes precision and detail, incorporating advanced techniques and tools. Here are the essential components:
3D Modeling Software: Leading software such as SketchUp, Revit, and 3ds Max are indispensable for crafting intricate and detailed models. These robust tools enable architects to create precise representations of their designs, laying a solid foundation for high-quality visuals that capture the essence of architectural vision.
Rendering Engines: Selecting the appropriate rendering engine is crucial for achieving realistic outcomes. V-Ray stands out for its exceptional capabilities in simulating realistic lighting and materials, while Lumion excels in providing rapid visualizations without compromising quality. As of 2024, V-Ray continues to be a leading option, with a substantial portion of architects noting its efficiency in improving their visual presentations, thus fostering trust in prospective customers and stakeholders.
Post-Processing Software: To elevate your renders, employ software like Adobe Photoshop or After Effects for post-processing. These tools allow for detailed color correction and the application of visual effects that can dramatically enhance the final output, further enriching the storytelling aspect of the design.
High-Resolution Textures: Investing in high-quality texture libraries is essential for ensuring that models feature realistic surfaces. The quality of textures can significantly affect the perception of realism in a visual representation, serving as a crucial element in customer engagement and satisfaction.
Camera Settings: To achieve a true-to-life representation, mimic real-world camera settings such as aperture and focal length within your rendering software. This practice adds depth of field and perspective realism, contributing to a more immersive viewer experience that resonates with clients.
Team Management: Effective management of your creative group is crucial, especially in the face of revisions and tight deadlines. Regular communication and coordination help mitigate conflicts, ensuring that everyone is aligned with project goals. A recent statistic emphasizes that managing conflicts within teams is crucial for sustaining productivity and attaining high-quality outputs.
By incorporating these tools and techniques, alongside strong team management practices, architects can notably improve the quality of their architectural photorealistic rendering. This approach not only enhances communication and engagement with stakeholders throughout the development process but also plays a pivotal role in pre-sales visualization. As one architect noted, “Build trust with stakeholders during a private equity exit by communicating regularly, involving them in decisions, and being transparent about risks.”
This level of detail not only fosters trust but also establishes the architect as a leader in innovative visualization techniques, reinforcing the importance of thorough visuals in conceptualizing and improving residential architecture projects and generating investment confidence.
The Role of Lighting and Materials in Photorealistic Rendering
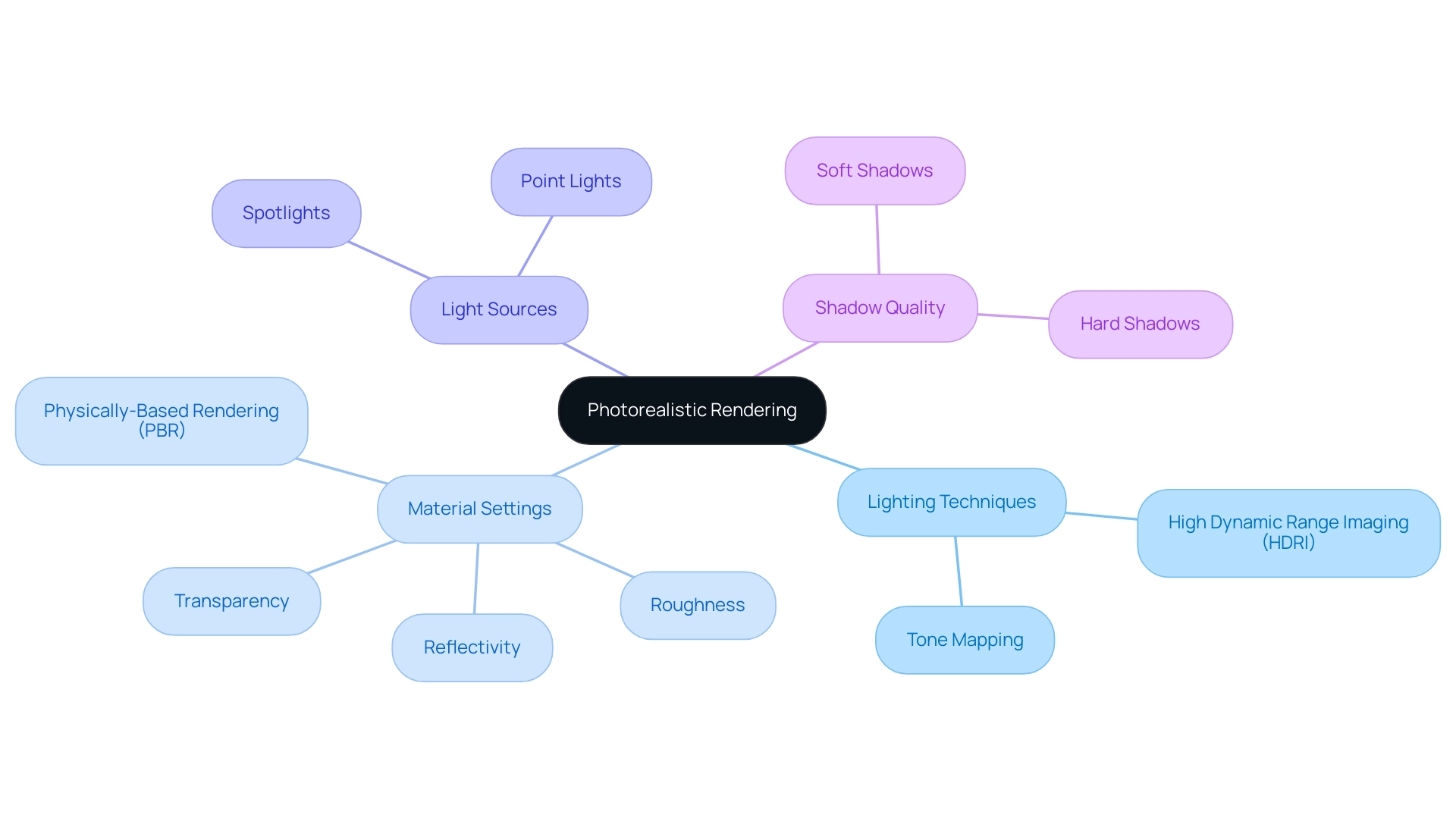
Achieving architectural photorealistic rendering in architectural visualization relies on the meticulous integration of lighting and materials, especially during the design development phase where detailed 3D visualizations are created for client evaluation and design experimentation. Consider the following key aspects:
- Lighting Techniques: A successful depiction employs a blend of natural and artificial lighting. For interior scenes, High Dynamic Range Imaging (HDRI) is essential to replicate realistic sunlight and shadow interplay, providing a dynamic range that enhances visual fidelity. As highlighted by Stokkermans M et al. (2012), the choice of tone mapping operators can significantly influence the perception of lighting under different viewing conditions, making it a critical factor in rendering.
- Material Settings: The properties of materials—such as reflectivity, roughness, and transparency—are crucial. Implementing Physically-Based Rendering (PBR) materials ensures accurate surface interactions, which are fundamental to achieving a lifelike appearance. Recent statistics indicate that the use of PBR materials has increased significantly, reflecting a growing trend towards realism in architectural photorealistic rendering. Moreover, it is essential to match client-specified materials to improve understanding and satisfaction.
- Light Sources: The choice and configuration of light sources, including point lights and spotlights, are vital for establishing depth and ambiance. Each type of light source offers unique characteristics that can dramatically affect the mood of the scene. Mackenzie Brown, founder and CEO of Cad Crowd, emphasizes that understanding these nuances is essential for architects aiming to create impactful designs.
- Shadow Quality: Fine-tuning shadow settings to produce either soft or hard edges is imperative for realism. This nuanced control over shadows can profoundly impact the overall perception of depth and space in the final image. The analysis of stereoscopic images as a method for daylighting studies, published in ACM Trans. Appl. Percept., illustrates how efficient lighting methods improve the aesthetic charm and authenticity of 3D models.
Mastering these components not only helps in recognizing conceptual problems early but also boosts stakeholder communication, enabling architects to produce architectural photorealistic rendering that closely matches customer expectations. Furthermore, the development phase emphasizes experimentation with modifications, enabling architects to refine their concepts based on client feedback. To begin the visualization process effectively, be prepared to provide architectural blueprints, design preferences, material specifications, and any specific requirements that align with your vision, such as color palettes and texture choices.
Overcoming Challenges in Photorealistic Rendering
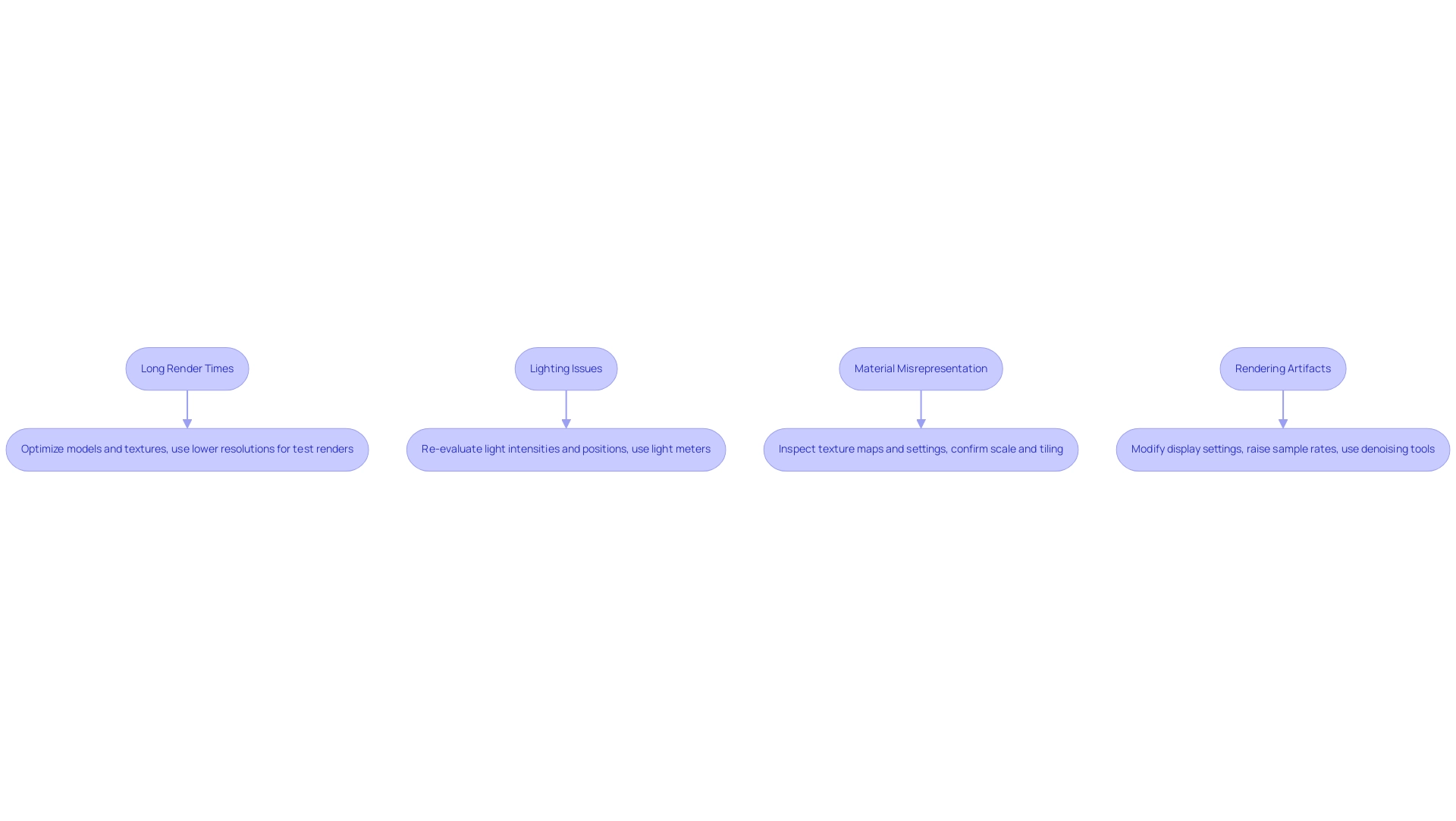
Photorealistic depiction presents several common challenges that can significantly impact workflow efficiency and image quality:
Long Render Times: One predominant issue in architectural visualization is prolonged processing durations. To mitigate this, focus on optimizing your models and textures to reduce complexity. Implementing lower resolutions for test renders can expedite the process, allowing for quicker iterations without compromising final output quality. Utilizing high-quality 3D rendering software is essential, as it supports the creation of high-poly props and assets that improve detail and realism, crucial for pre-sales visualization that boosts project confidence and attracts investment.
Lighting Issues: Achieving the perfect lighting can be complex. If your scene appears overly dark or excessively washed out, re-evaluating your light intensities and positions is critical. Utilizing light meters can facilitate accurate exposure settings, ensuring that the intended ambiance is achieved without sacrificing detail—a vital aspect in showcasing the functionality and aesthetics of creations to improve client satisfaction and marketing effectiveness.
Material Misrepresentation: Realistic materials are essential for achieving photorealism. If your textures do not render as expected, inspect your texture maps and settings rigorously. It is crucial to confirm that the scale and tiling of textures are appropriate for the objects they cover; discrepancies can lead to unrealistic appearances, undermining the design essence captured in detailed exterior renderings.
Rendering Artifacts: Various artifacts such as noise or banding can detract from the overall quality of your render. To tackle these problems, think about modifying your display settings—such as raising sample rates or utilizing denoising tools—to improve image clarity and lessen unwanted visual noise. As noted by industry professional ramon73, using the denoiser in specific configurations can yield faster results, highlighting its practical benefits despite initial setbacks.
By anticipating these challenges and implementing the suggested solutions, you can significantly enhance the efficacy of your workflow. The case study of PIXREADY illustrates this well; the company, founded in 2018, focuses on delivering high-quality architectural photorealistic rendering while ensuring precision in every detail. Their success in architectural photorealistic rendering not only showcases effective strategies that streamline processes but also highlights how detailed images can generate revenue for construction projects by attracting early investment.
This emphasizes the essential function of intricate representations in visualizing and improving residential architecture plans.
Applications of Photorealistic Rendering in Architecture and Beyond
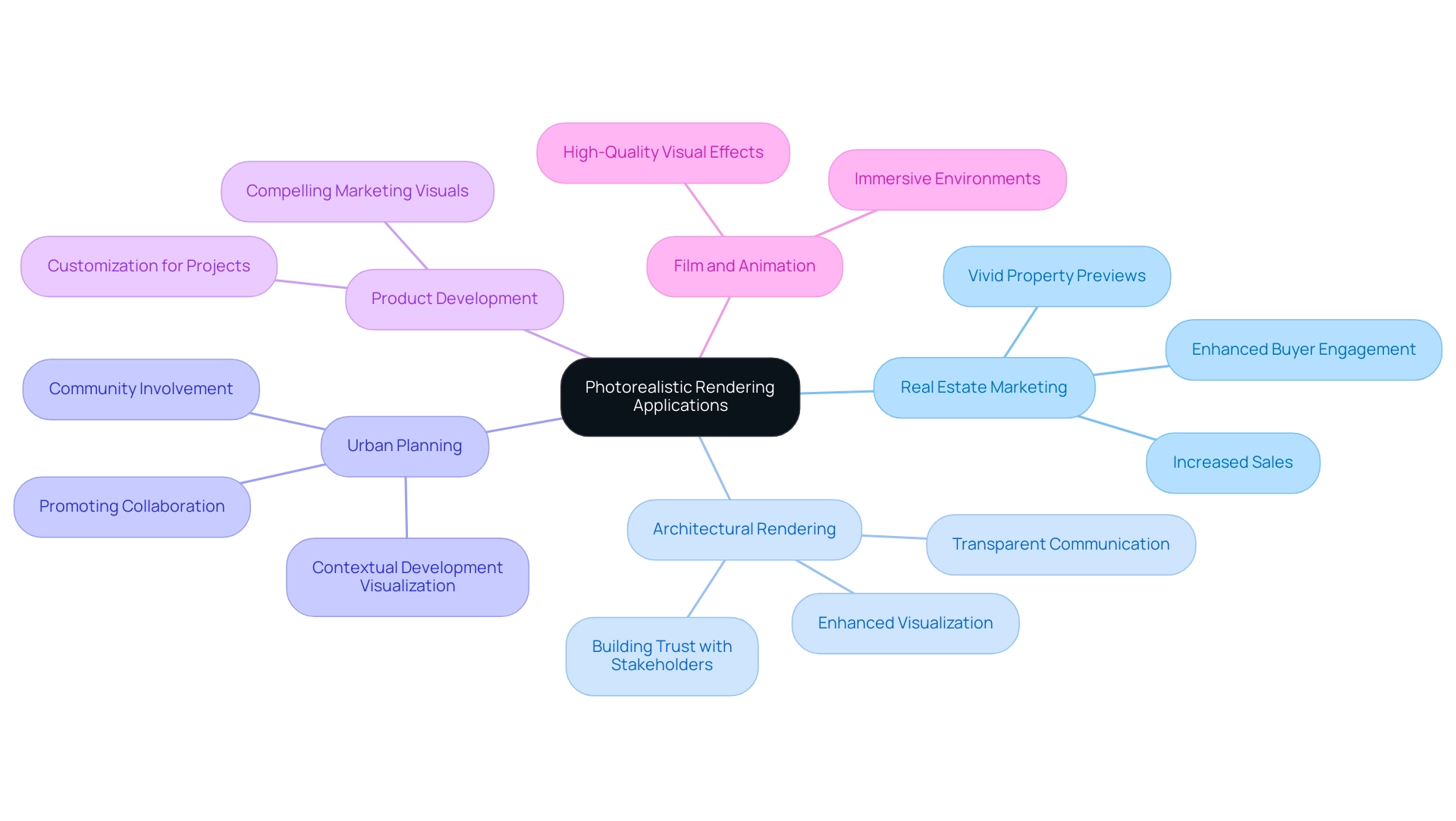
Photorealistic visualization serves a multitude of applications that are critical for architects and designers aiming to enhance their projects and communication strategies:
- Real Estate Marketing: High-quality visualizations play a pivotal role in attracting potential buyers by effectively showcasing properties before they are constructed. The impact of this technique on marketing strategies is profound, as it provides stakeholders with a vivid preview, thereby facilitating informed purchasing decisions. Testimonials from pleased customers emphasize how remarkable visuals have greatly impacted their marketing achievements, frequently leading to faster sales and increased property values.
- Architectural photorealistic rendering: This method is essential for showcasing plans to customers, enabling them to clearly envision the end result. By bridging the gap between concept and reality, architects can foster trust and confidence in their designs, which aligns with the importance of building trust with stakeholders through transparent communication. The joint creation procedure, as highlighted in customer feedback, guarantees that expectations are met and frequently surpassed, reinforcing dedication to quality. Personalized solutions designed for particular customer needs further strengthen this trust, showcasing a profound comprehension of distinct project requirements.
- Urban Planning: Architectural photorealistic rendering plays a crucial role in depicting developments within current surroundings, which is vital for community involvement and planning processes. It allows stakeholders to see potential changes and developments in context, promoting transparency and collaboration. This corresponds with the input from clients who have encountered improved community support through clear visual displays.
- Product Development: Beyond architecture, architectural photorealistic rendering is widely employed in product development, creating compelling visuals that improve marketing and presentations. This application emphasizes the versatility of photorealistic visualization across various industries and the need for customization based on specific project requirements.
- Film and Animation: Within the entertainment sector, architectural photorealistic rendering is essential for crafting immersive environments and delivering high-quality visual effects. This application showcases the artistic potential of visual representation in creating engaging narratives.
In the context of managing a creative team amidst design revisions and tight deadlines, architects can leverage architectural photorealistic rendering to not only enhance their creative output but also improve their communication and marketing strategies. The inclusion of customer testimonials into the development process allows teams to navigate challenges effectively, ensuring that the final product aligns with customer expectations. Furthermore, investing in quality rendering services often results in a measurable return on investment, such as increased client satisfaction and project success rates.
Understanding these diverse applications empowers architects and designers to align with current trends and stakeholder expectations, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes.
Conclusion
The exploration of photorealistic rendering reveals its profound impact on architectural visualization, underscoring the necessity of mastering key principles such as:
- Ray tracing
- Global illumination
- Advanced material properties
These foundational concepts not only enhance the quality of visual representations but also facilitate clearer communication between architects and clients, fostering trust and informed decision-making.
The integration of sophisticated tools and techniques, including high-performance rendering engines and precise lighting strategies, is essential for overcoming common challenges in the rendering process. By focusing on detail and accuracy, architects can elevate their renderings, ensuring that they resonate with stakeholders and effectively convey design intent. The role of lighting and material settings further emphasizes the importance of realism, as they significantly influence the perception of a space.
Moreover, the diverse applications of photorealistic rendering extend beyond architecture, impacting fields such as:
- Real estate marketing
- Urban planning
- Product design
This versatility highlights the relevance of photorealistic techniques in contemporary design practices, reinforcing their role in enhancing project visibility and stakeholder engagement.
In summary, the mastery of photorealistic rendering is not merely an artistic endeavor but a strategic advantage that empowers architects to communicate their visions more effectively. As technology continues to evolve, embracing these advanced rendering practices will be vital for maintaining a competitive edge in the architectural landscape.

0 Comments