Introduction
Architectural rendering stands as a cornerstone of modern design communication, transforming abstract concepts into tangible visual experiences. This multifaceted discipline not only facilitates the visualization of architectural projects but also enhances stakeholder engagement through lifelike representations. With the integration of advanced technologies, including artificial intelligence, the capacity for creating hyper-realistic images has reached unprecedented levels, enabling architects to evoke emotional connections with potential clients.
As the architectural landscape evolves, understanding the nuances of rendering—from the intricacies of software tools to the structured workflows essential for project success—becomes imperative for professionals aiming to excel in this dynamic field. This article delves into the essential aspects of architectural rendering, offering insights into its techniques, tools, and methodologies that are shaping the future of architectural visualization.
Understanding Architectural Rendering: A Beginner’s Overview
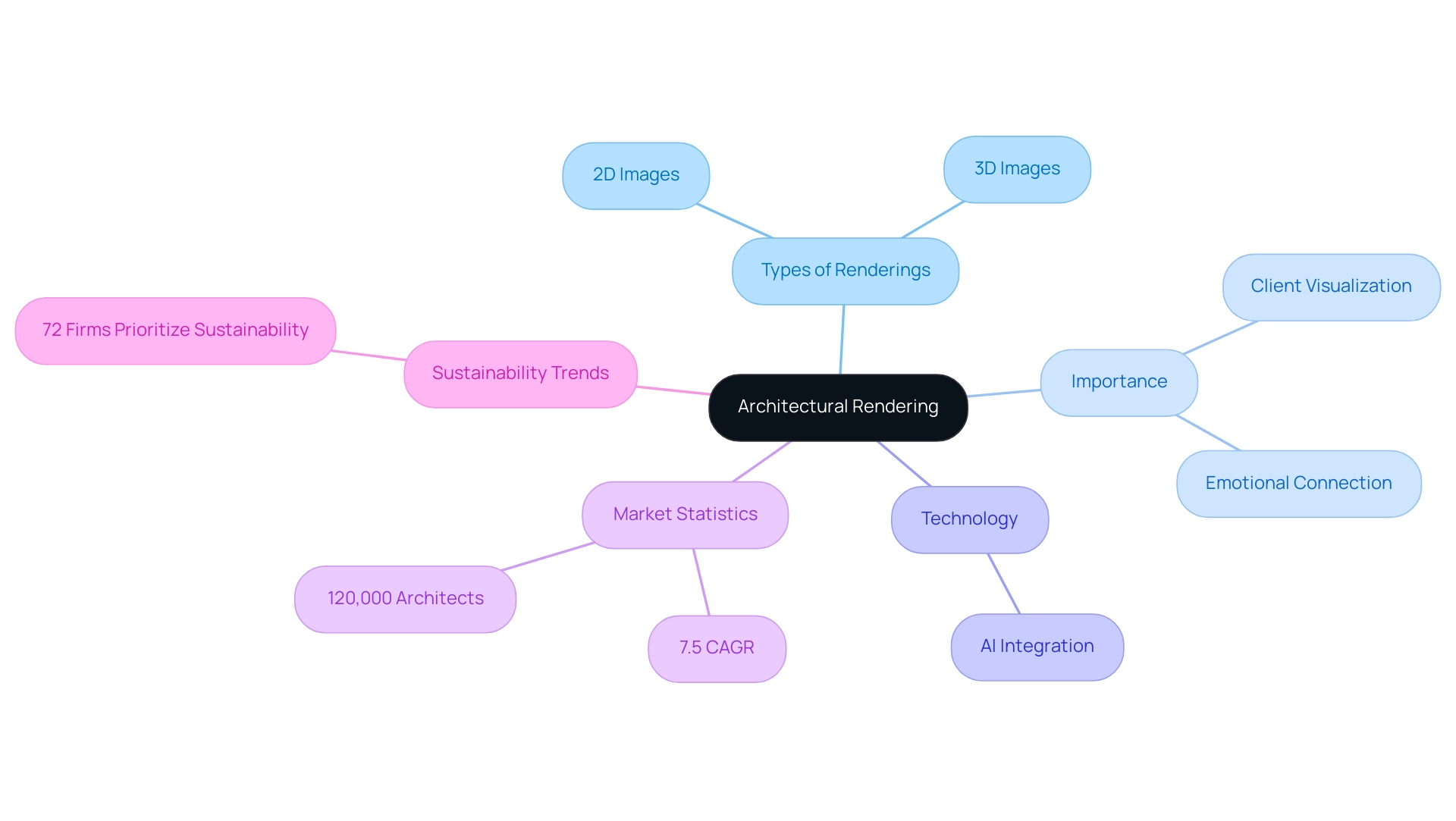
Architectural visualization encompasses the creation of two-dimensional and three-dimensional images that effectively communicate the design of buildings and spaces. This vital technique is integral to the architecture industry, enabling clients and stakeholders to visualize the final product prior to construction. Notably, advancements in AI are revolutionizing the field by enabling the creation of lifelike CG humans in architectural visualizations, bridging the gap between realism and the uncanny valley.
These lifelike representations enhance the emotional connection in presentations, making visuals more relatable and impactful. For example, a recent initiative demonstrated how integrating realistic CG humans in a housing development visualization significantly heightened potential buyers’ emotional involvement, resulting in a 30% rise in pre-sales interest. In North America, which leads the global 3D visualization market, the importance of pre-sales visualization is clear as it fosters project confidence and draws investment long before construction starts.
Renderings vary significantly, ranging from basic sketches to highly detailed photorealistic images, serving distinct functions such as marketing, design validation, and client presentations. Mastering how to learn architectural rendering is essential for professionals entering this field, as it intricately combines artistic expression with technological precision, facilitating the realization of design concepts. Furthermore, understanding how to learn architectural rendering includes recognizing the role of lighting—contrasting artificial lighting in interiors with natural sunlight in exteriors—which plays a crucial part in creating compelling visual narratives.
In 2022, almost 120,000 licensed architects across 55 U.S. jurisdictions showcased the extensive market for design visualization services. As the design industry pivots towards sustainability, with a projected growth rate of 7.5% CAGR from 2021 to 2028, and 72% of firms prioritizing sustainable practices, the demand for advanced visualization techniques continues to evolve, making it imperative for architects to stay at the forefront of these developments.
Essential Software for Architectural Rendering: Tools of the Trade
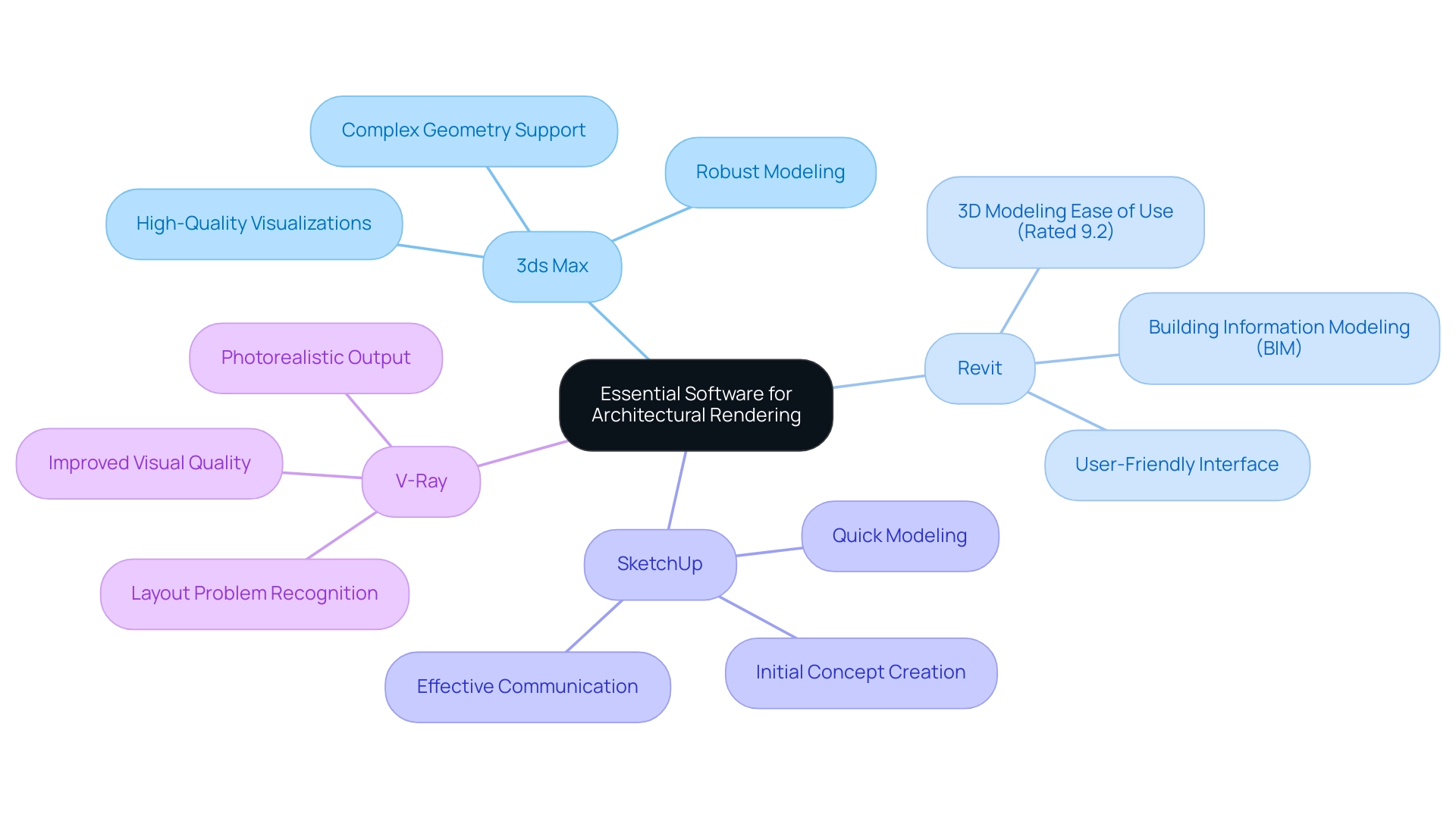
To excel in design visualization, novices must understand how to learn architectural rendering and gain proficiency in several key software tools essential to the industry. Notable options include:
3ds Max: Renowned for its robust modeling and rendering capabilities, 3ds Max stands out as a standard in the industry for producing high-quality visualizations. Its extensive feature set supports complex geometry and advanced visualization techniques, ensuring precision that captures the essence of architectural creations, making it invaluable for professional visualizers.
Revit: As a cornerstone of Building Information Modeling (BIM), Revit is essential for architects, seamlessly integrating planning and rendering processes. With a user-friendly interface and powerful 3D modeling capabilities rated at 9.2 for ease of use, it enables architects to create detailed and accurate representations of their concepts. This accuracy is crucial in visualizing and enhancing residential architecture, thereby substantiating its reputation as a go-to tool in the industry.
SketchUp: Particularly favored by novices due to its user-friendly layout, SketchUp permits quick modeling and is often utilized for initial concept creations. Its user-friendly nature supports quick visualization, facilitating early-stage decision-making and effective communication among stakeholders, which are vital for eliminating misunderstandings in planning.
V-Ray: Functioning as a visualization engine compatible with multiple modeling applications, V-Ray is celebrated for its photorealistic output. It improves the visual quality of architectural illustrations, aiding in better stakeholder communication and assisting in recognizing layout problems early. This is a preferred choice among professionals aiming for a high standard of realism in their work.
Mastering these tools equips beginners with the necessary skills on how to learn architectural rendering and elevate their rendering capabilities. As Abdullah Al Baki, a thought leader in the field, emphasizes, “The right software tools are essential for creating impactful visual narratives in architecture.” Furthermore, the practical application of these tools is exemplified by the increasing use of luxury home virtual tours in real estate marketing, highlighting their relevance in current industry practices.
Additionally, these software tools support an iterative creation process, enabling architects to make multiple revisions based on client feedback and evolving ideas. This iterative method not only improves the layout but also encourages collaboration among stakeholders. Furthermore, initial visualizations are economical, enabling architects to investigate different creative possibilities without substantial financial investment, ultimately resulting in more informed choices.
Ultimately, these skills lead to the creation of stunning visual representations of design concepts, enhancing client understanding and fostering collaborative design processes.
Navigating the Workflow of Architectural Rendering Projects
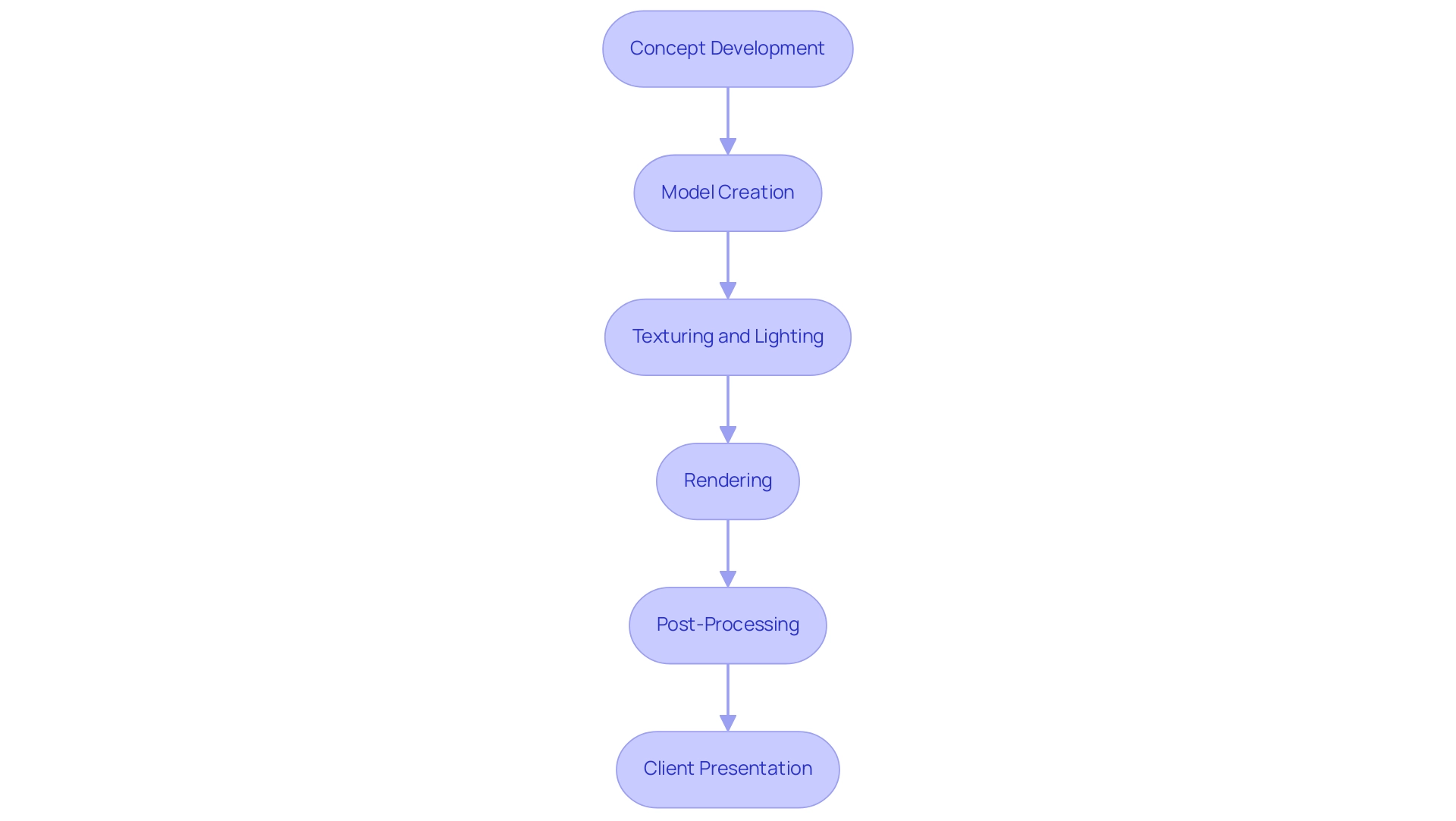
The architectural rendering workflow is a structured process that involves several key steps essential for producing high-quality visualizations:
Concept Development: This initial stage focuses on gathering project requirements and fully understanding the client’s vision. Engaging in sketches and discussions is crucial to clarify design intent and ensure alignment with client expectations. Clear communication during this phase is vital, as the purpose of visual representation is to facilitate effective dialogue between architects and clients. Considering outsourcing at this stage can lead to enhanced efficiency, particularly when tasks overwhelm internal resources. Outsourcing can offer access to specialized skills and technologies that may not be available internally, thus enhancing the quality and speed of the processing task.
Model Creation: Using advanced software such as Revit or SketchUp, create a detailed 3D model that accurately represents all architectural elements. Accuracy in this phase is crucial for the integrity of the final outputs, especially when following project complexity and quality standards.
Texturing and Lighting: In this step, apply realistic materials and textures to the model while strategically setting up lighting to enhance the visual appeal. Achieving photorealistic results relies heavily on the effectiveness of this phase, which can often be optimized through collaboration with specialized visualization companies.
Rendering: Using software such as V-Ray to produce high-quality images of the model. Experimenting with various settings can help refine the output and meet the desired aesthetic while ensuring a quick turnaround based on the project’s intricacy.
Post-Processing: After producing, utilize image editing software to fine-tune the final output, making adjustments to colors, contrast, and other visual elements to enhance overall presentation quality. This step is crucial for delivering polished visuals that resonate with clients.
Client Presentation: Finally, present the finished visuals to the client, emphasizing key design features while being prepared to address any feedback for necessary revisions. As Jason, a co-owner of a successful architectural firm, states, ‘Efficient workflows are essential for managing tasks effectively, especially when navigating client expectations while on the go.’
Comprehending that an interior depiction from a site photo for a residential house usually requires around nine days with five views highlights the significance of efficient management throughout this workflow. By following these steps and reflecting on the insights from client testimonials, architects can not only simplify their visualization tasks but also enhance the collaboration process with clients, which can help them understand how to learn architectural rendering and ultimately achieve more successful outcomes.
For instance, one of our clients noted, “Working with Render3DQuick significantly reduced our turnaround times and improved our overall client satisfaction.” The collaboration between Render3DQuick and architects exemplifies this, as their partnerships have led to more efficient workflows and profitable results. By adopting organized procedures, Render3DQuick has assisted architects in decreasing turnaround times and enhancing client satisfaction, reinforcing the importance of structured visualization methods in design practice.
Crafting Effective Briefs for Architectural Rendering
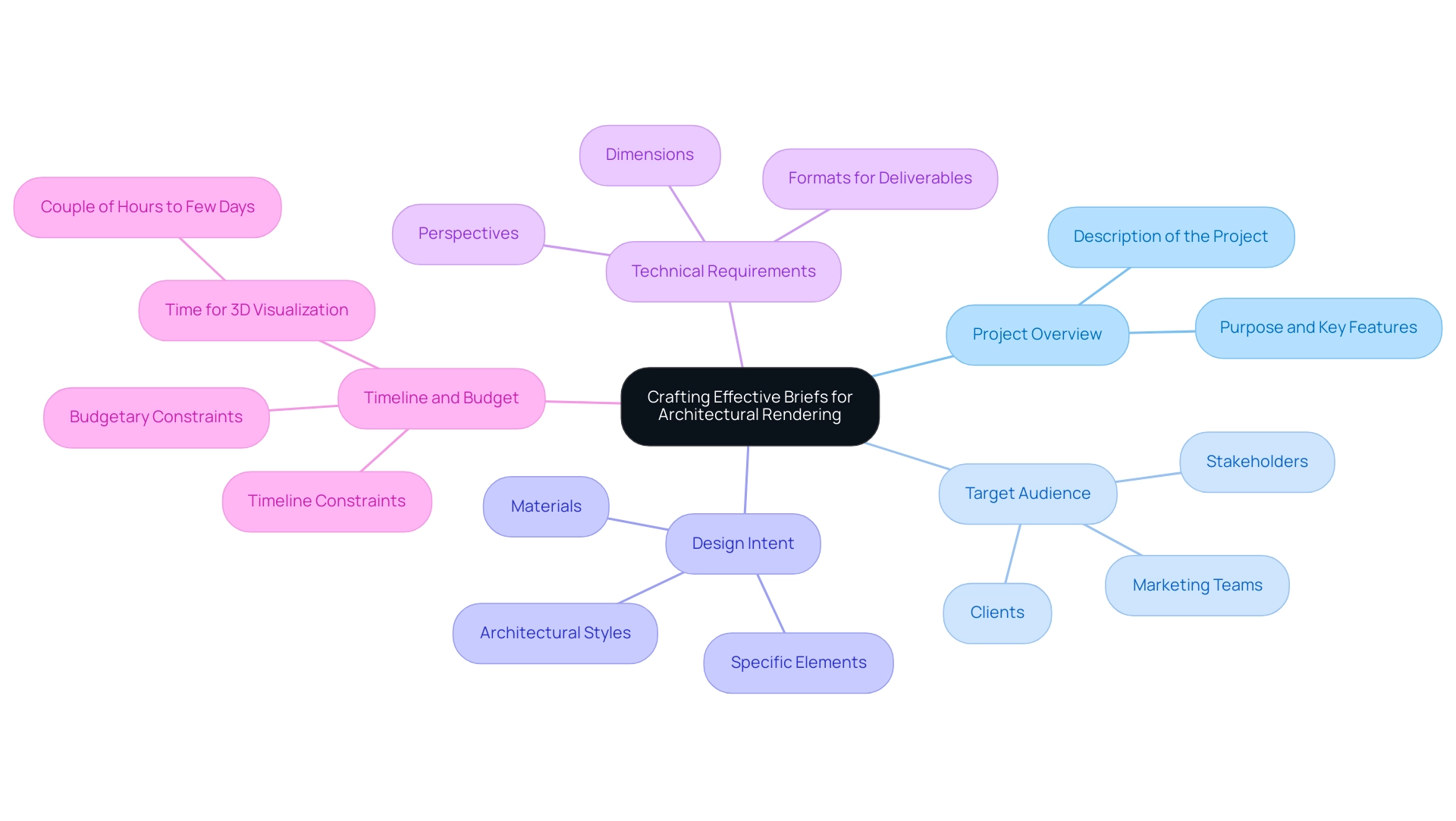
To develop an effective project brief for architectural rendering, it is essential to incorporate several key elements:
- Project Overview: Start with a succinct description of the project, detailing its purpose and key features. This offers context and prepares the groundwork for the process.
- Target Audience: Clearly identify the intended recipients of the renderings. This could include clients, stakeholders, or marketing teams, each of whom may have different expectations and needs.
- Design Intent: Articulate the design vision with precision, covering architectural styles, materials, and specific elements that should be prominently displayed. This clarity ensures that the visual output aligns with the original intent.
- Technical Requirements: Outline the necessary technical specifications, including dimensions, perspectives, and formats for the final deliverables. These details are crucial for meeting the initiative’s standards and expectations.
- Timeline and Budget: Define the timeline and budgetary constraints, establishing realistic expectations for both the process and outcomes. Note that creating a single 3D visualization can take anywhere between a couple of hours to a few days, depending on complexity.
A meticulously crafted brief serves not only as a roadmap for the rendering process but also ensures that all stakeholders are aligned. This alignment is essential in achieving the desired outcomes, as shown by recent case studies like the one titled “Goals and Objectives in Design Briefs,” which illustrate how clearly defined goals and objectives lead to significant enhancements in user experience and success. By leveraging advanced 3D visualizations, creators and developers can communicate their ideas clearly, resolve potential issues early, and streamline workflows, significantly reducing expensive changes later in the process.
The purpose of this project is to showcase [what] for [who] to [achieve a desired outcome], underscoring the importance of clarity in communication from the outset.
Ready to explore the potential of your architectural design concepts? Collaborate with J. Scott Smith Visual Designs to visualize and confirm your concepts with our initial images. Whether you’re seeking to validate the feasibility of a project or enhance your vision, our conceptual visuals offer the clarity you need to proceed confidently. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and see how we can help bring your concepts to life.
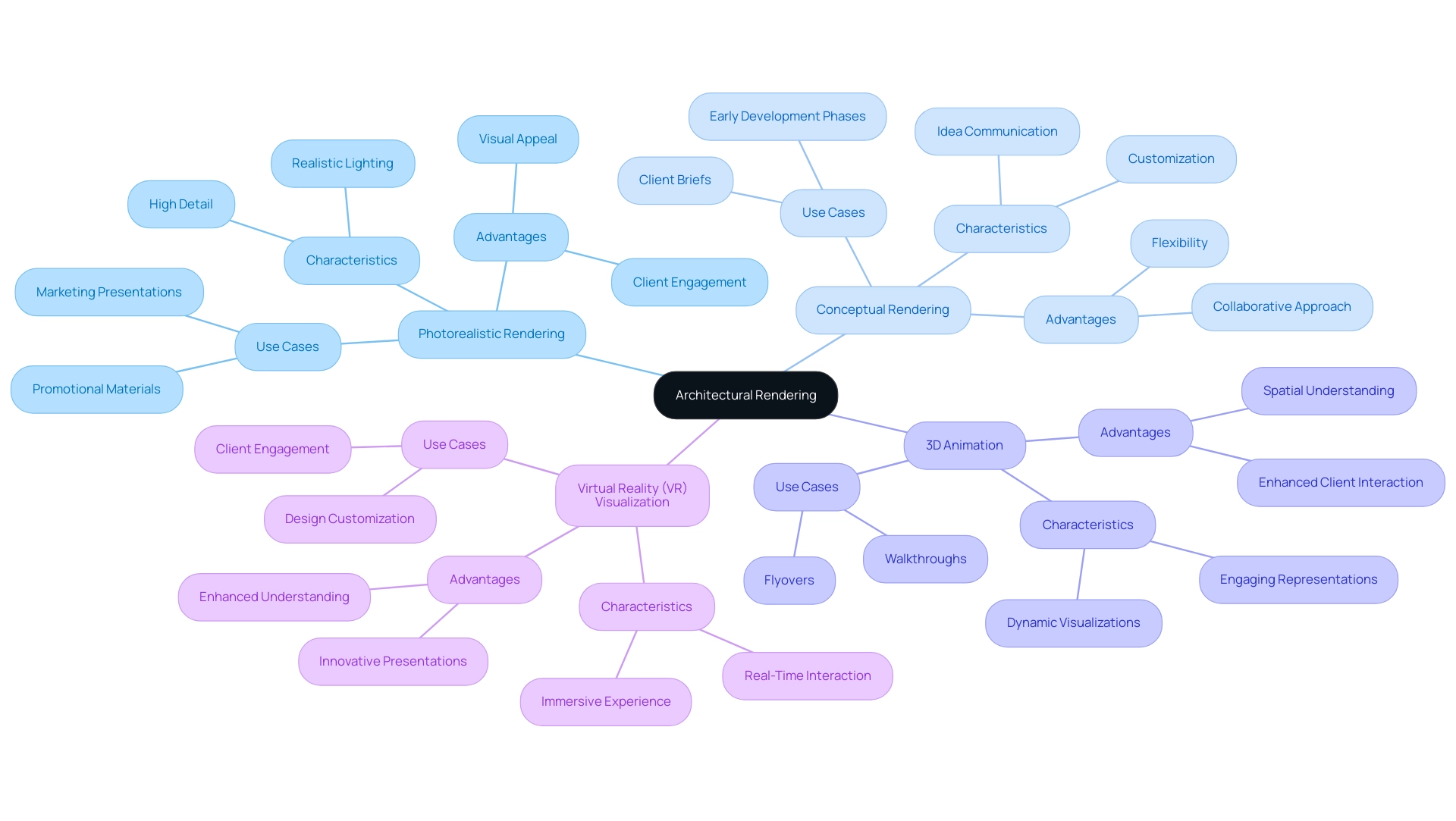
Exploring Different Types of Architectural Rendering
Architectural rendering encompasses a diverse array of styles, each tailored to specific objectives within the design and presentation process:
Photorealistic Rendering: This technique aspires to produce images virtually indistinguishable from high-quality photographs. It is primarily used for marketing and promotional presentations, effectively showcasing the potential of finished endeavors. The meticulous detail involved in this process ensures that every element—from the way sunlight dances off the windows to the subtle texture of the bricks—is captured, making your work feel real and ready to be built.
Conceptual Rendering: Unlike photorealistic rendering, this style emphasizes the communication of ideas rather than realism. It is particularly advantageous during the early development phases, where communicating the vision is paramount. The collaborative approach taken by our team, starting from initial communication and project briefs, allows for customization and revisions, ensuring client satisfaction throughout the process.
3D Animation: This method employs dynamic visualizations, such as walkthroughs and flyovers, to provide an engaging representation of built environments. It enables stakeholders to understand the spatial relationships and flow of a concept more intuitively. As mentioned by clients at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, these animations convert concepts into breathtaking visuals that capture the essence of the project.
Virtual Reality (VR) Visualization: As an emerging frontier in spatial representation, VR visualization immerses users in a designed environment, enabling them to interact with and explore spaces in real-time. This innovative approach significantly enhances client engagement and understanding of the design. The combination of augmented, artificial, and virtual reality visualization has transformed building presentations, enabling designers and clients to see and tailor components dynamically.
By exploring how to learn architectural rendering through these different visualization styles, experts can maneuver through the intricacies of design representation and choose the most suitable method for their endeavors. The architectural visualization market is projected to grow from $4.59 billion in 2024 to $16.18 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.0%. This trend highlights the critical demand for advanced visualization techniques, emphasizing the essential role of high-quality visual outputs in project development and decision-making.
Furthermore, AI technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing the realism of these renderings, bridging the gap between virtual and real-world experiences, a sentiment echoed in client testimonials highlighting the transformative impact of our services.
Conclusion
Architectural rendering is an indispensable tool in the modern architectural landscape, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of design concepts through vivid visualizations. By harnessing advanced software and technologies, architects can create everything from photorealistic images to engaging 3D animations, each serving distinct purposes within the design process. The integration of lifelike elements, such as CG humans, enhances emotional engagement and has been shown to significantly impact client interest and investment in projects.
A structured workflow is essential for successful architectural rendering, guiding professionals through critical phases from concept development to client presentations. The importance of a well-crafted project brief cannot be overstated, as it lays the groundwork for effective communication and alignment among stakeholders, ultimately leading to improved project outcomes. As the industry increasingly emphasizes sustainability, the demand for proficient rendering techniques continues to grow, reflecting the evolving needs of clients and the market.
The future of architectural rendering is bright, with continuous advancements in technology and an expanding market poised for significant growth. By embracing these developments and mastering the essential tools and methodologies, architects can elevate their practices and deliver exceptional visual narratives that resonate with clients and stakeholders alike. The ability to effectively visualize and communicate design intent not only enhances client satisfaction but also reinforces the architect’s role as a key driver in the successful realization of architectural visions.
0 Comments