Introduction
The evolution of architectural visualization is marked by a profound integration of advanced technologies, notably artificial intelligence (AI) and virtual reality (VR), which are reshaping how architects communicate their visions. Architectural rendering, encompassing both 2D and 3D representations, serves as a vital tool for stakeholders, enabling them to visualize projects before they materialize. The advent of AI technology enhances this process, facilitating the creation of hyper-realistic visualizations that bridge the gap between imagination and reality.
As architects increasingly leverage VR to immerse clients in interactive environments, the potential for enriched engagement and collaboration expands significantly. This article delves into the multifaceted benefits of incorporating VR into architectural rendering, offering step-by-step techniques for effective integration, while also addressing the challenges and future trends that define this dynamic field.
Through a comprehensive exploration, it becomes evident that the strategic application of these technologies not only enhances project presentations but also fosters deeper client relationships and informed decision-making.
Understanding Architectural Rendering and Virtual Reality
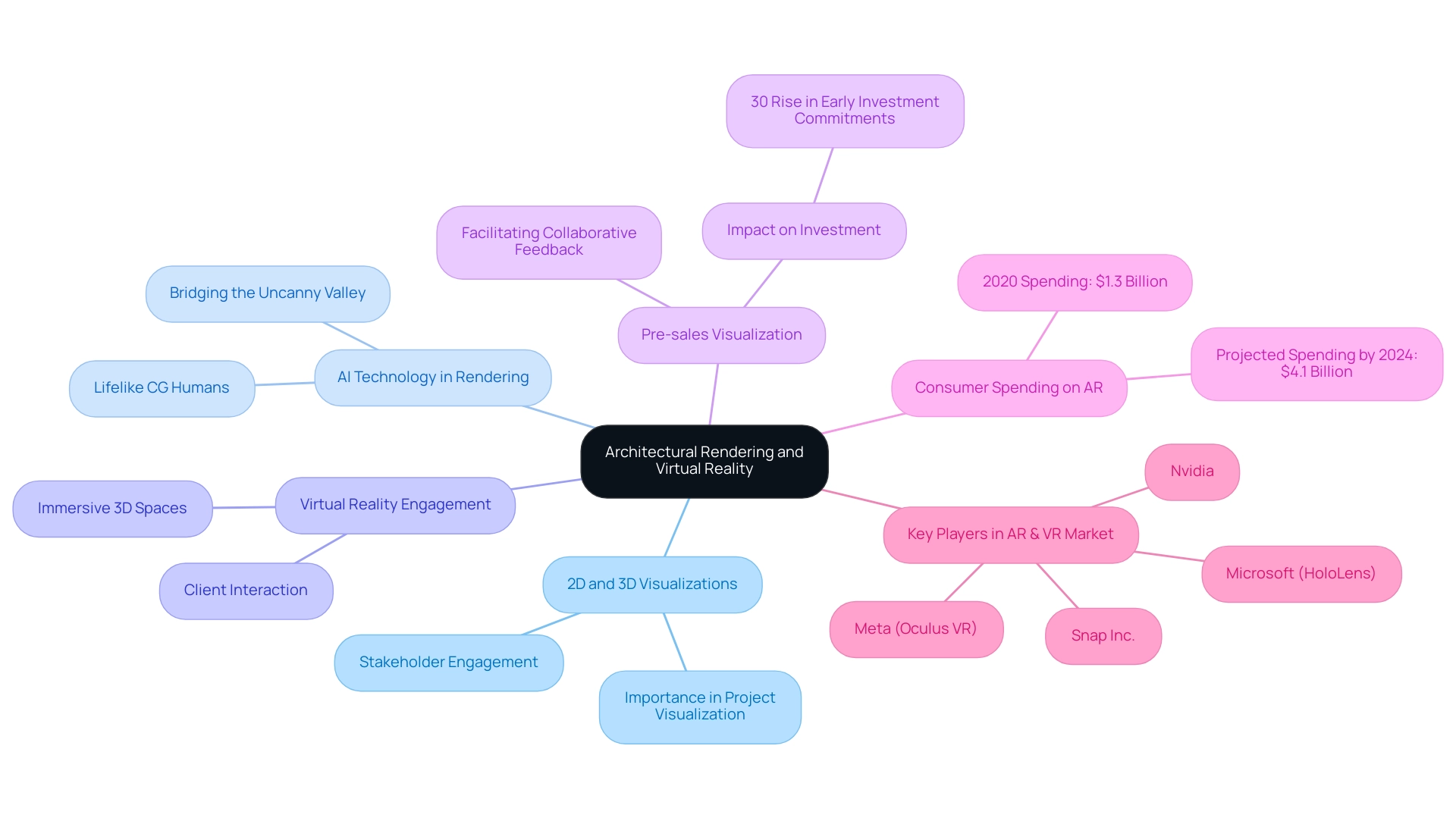
Architectural rendering involves the creation of both 2D and 3D visual representations of concepts, serving as a crucial tool for stakeholders to visualize projects prior to construction. The integration of AI technology is particularly transformative, allowing for the creation of lifelike CG humans that bridge the uncanny valley, enhancing the realism of visualizations in architecture. For instance, recent projects have showcased how AI-generated humans can interact seamlessly within rendered environments, making presentations more relatable and engaging.
In contrast, virtual reality (VR) immerses users within a fully interactive 3D space, allowing them to engage with designs as if they were physically navigating the environment. The integration of architectural rendering virtual reality with architectural depiction significantly elevates the visualization process, enabling architects to present their concepts in an engaging format that enhances communication with clients and stakeholders. Furthermore, the role of pre-sales visualization becomes evident as illustrations empower developers by providing tangible assets that ignite interest and investment long before the project’s physical manifestation.
Significantly, a case study concerning a high-rise residential project illustrated how effective pre-sales visuals resulted in a 30% rise in early investment commitments. This integration not only facilitates a deeper understanding of spatial relationships but also fosters collaborative feedback, ultimately leading to more refined design outcomes. Moreover, progress in lighting methods, such as the application of physically based techniques (PBR), enables more precise simulations of natural sunlight and artificial illumination, further improving the quality of building visualizations.
Consumer spending on mobile AR amounted to $1.3 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $4.1 billion by 2024, underscoring the growing relevance of VR technologies in various sectors, including architecture. As advancements in VR technology continue to emerge, the architectural industry is poised to leverage architectural rendering virtual reality to further enhance project presentations and client relations.
Step-by-Step Techniques for Integrating VR into Architectural Rendering
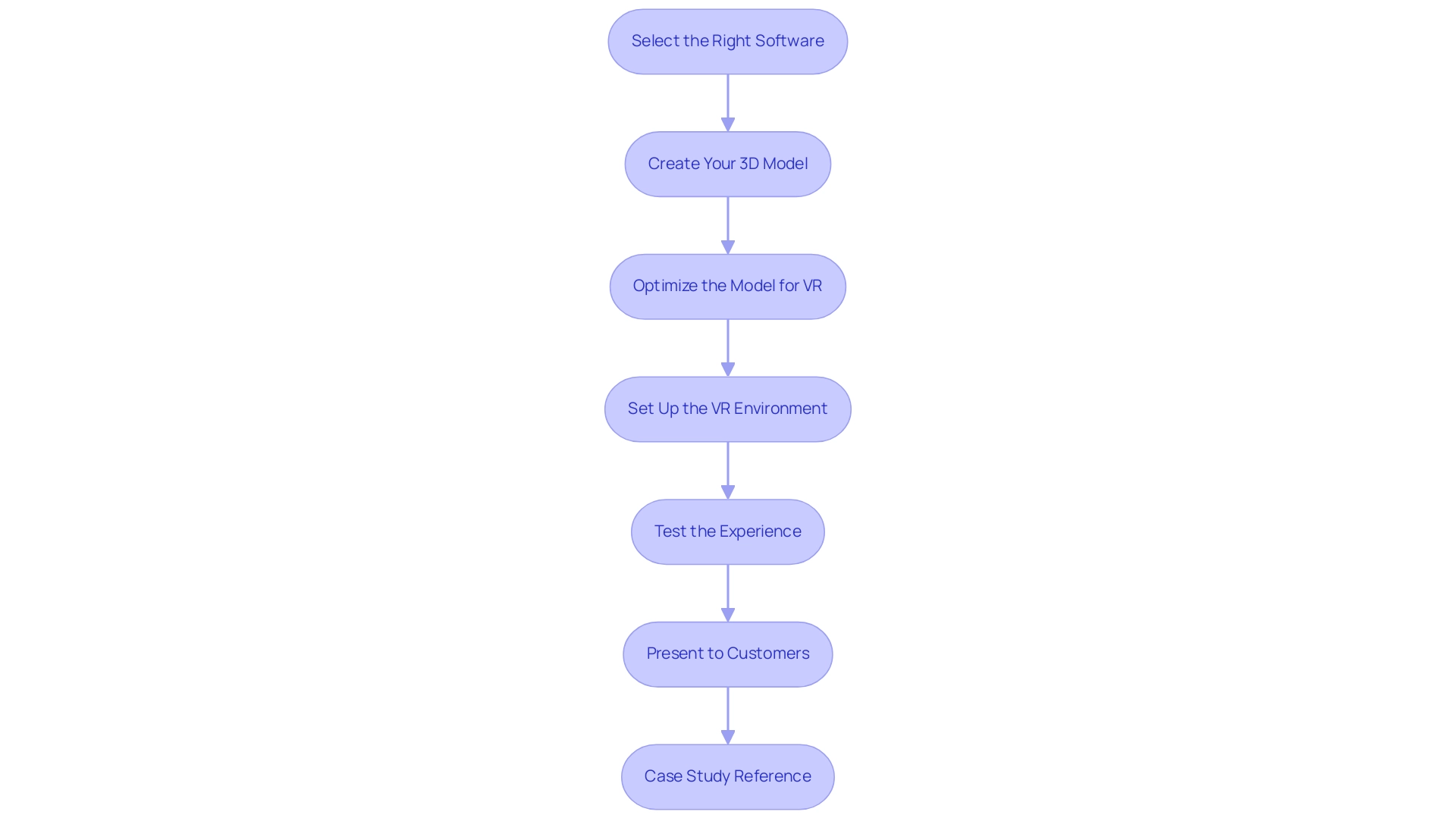
Select the Right Software: Begin by choosing architectural rendering virtual reality software that facilitates VR integration. Leading options include Autodesk Revit, SketchUp enhanced with VR plugins, and Enscape, each known for their robust capabilities. Notably, Unreal Engine, which is free and boasts a rating of 4.7 on Applet and 4.8 on Capterra and GetApp, is an excellent choice for high-quality visuals. Ensure that the software is fully compatible with the VR headsets you intend to use, as this compatibility is crucial for a seamless user experience and accurate architectural rendering virtual reality of your design.
Create Your 3D Model: Develop a meticulously detailed 3D model of your architectural design within your selected software. Focus on the realistic depiction of materials, lighting, and textures, as these elements are vital in enhancing the overall realism of the rendered environment, capturing the essence of your design.
Optimize the Model for VR: To ensure smooth performance in VR, it is essential to optimize your model. This includes reducing polygon counts and optimizing texture sizes without compromising visual quality. Accurate scaling is also critical, allowing users to experience the space as they would in reality, thus ensuring an immersive property exploration.
Set Up the VR Environment: Connect your VR headset to the visualization software and configure the VR environment. This setup may require calibrating the headset and fine-tuning settings for architectural rendering virtual reality to achieve optimal performance, thereby enhancing the overall user experience.
Test the Experience: Prior to presentations, rigorously test the VR experience yourself. Navigate through the virtual space, identifying any potential issues related to navigation or visual fidelity. Make necessary adjustments to rectify these issues, ensuring an immersive and engaging experience for users, which builds confidence in your design vision.
Present to Customers: Utilize your VR setup during meetings to provide an immersive design experience. Motivate users to engage with the model, allowing them to investigate different facets of the layout in real-time. This interactive method not only boosts client involvement but also promotes a deeper comprehension of the design vision through architectural rendering virtual reality, emphasizing the significance of collaboration and detailed visualizations.
Case Study Reference: Consider using techniques like Premise Rendering, which allows users to upload real photos of a specific location where a building will be constructed and visualize the plan in context. This approach guarantees that building concepts integrate smoothly into their intended settings, offering a practical use of your VR visualization process and highlighting the high-quality structural representations that can be accomplished. Furthermore, when selecting 3D visualization services, seek providers who showcase a robust portfolio of intricate visuals and comprehend the significance of narrative in design. Request examples of how they integrate feedback from customers into their work, ensuring that the final product aligns with the intended vision.
The Benefits of Virtual Reality in Architectural Design
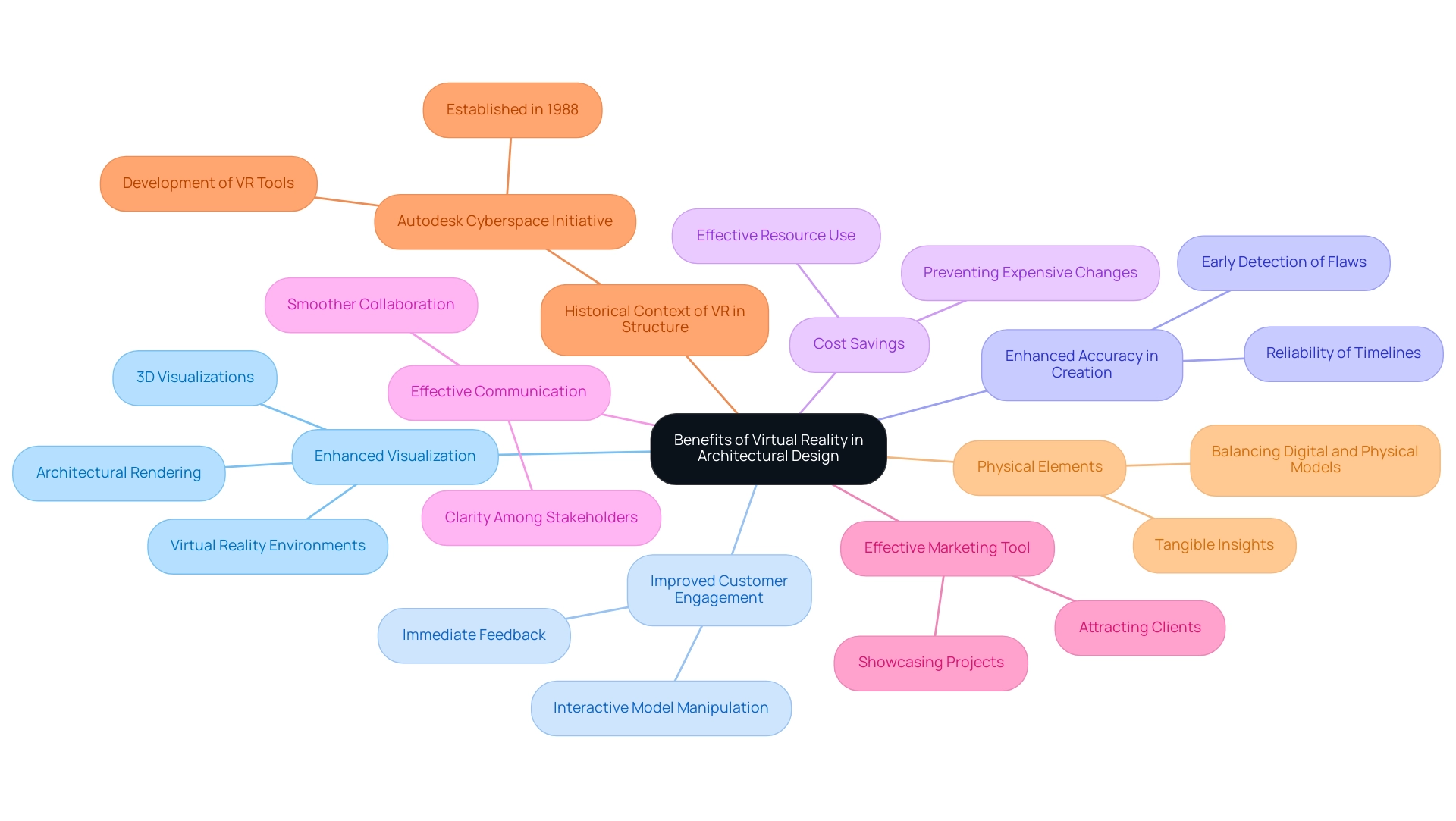
Enhanced Visualization
The procedure of building visualization is significantly enriched through collaborative techniques employed at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs. Our 3D visualizations provide customers with a clear and lifelike perspective of their projects, aiding in a comprehensive grasp of creative details and spatial connections. By employing advanced visualization techniques, such as architectural rendering virtual reality, customers can immerse themselves in fully developed environments, enhancing their appreciation of architectural concepts and leading to more informed decision-making.
Improved Customer Engagement
The interactive nature of our visualization process transforms customer involvement, encouraging immediate feedback and fostering a collaborative atmosphere. Clients can manipulate the virtual model, which not only strengthens the client-architect relationship but also improves the overall development process. This level of engagement guarantees that customers feel involved in their projects, aligning outcomes closely with their vision.
Enhanced Accuracy in Creation
One of the significant benefits of our immersive visualization techniques is the early detection of potential flaws in the concept. By visualizing projects in a virtual space, architects can scrutinize plans for inconsistencies, significantly reducing the risk of costly changes during construction. This proactive approach enhances the reliability of project timelines and budgets.
Cost Savings
Nearly detection of potential issues through 3D visualization can save money by preventing expensive changes during construction.
Clients can make modifications in the planning stage instead of during or after construction, ensuring that financial resources are used effectively and efficiently.
Effective Communication
3D visuals enhance better communication between architects, clients, and contractors. Everyone involved can see and understand the design, leading to smoother collaboration and project execution. This clarity ensures that all parties are aligned, reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings and enhancing the overall workflow.
Effective Marketing Tool
High-quality 3D renderings serve as compelling marketing instruments that differentiate architects’ offerings in a competitive landscape.
By showcasing projects through immersive visualizations, architects can attract potential clients and investors, securing their confidence and support. According to Chiu-Shui Chan from Iowa State University, this approach to architectural rendering virtual reality provides varied media for experiencing structure interactively, empowering creators to manipulate three-dimensional elements within the VR space.
Historical Context of VR in Structure
The historical evolution of VR in spatial creation highlights its growing relevance. Initiatives like the Autodesk Cyberspace Initiative established in 1988 aimed to integrate VR into creative practices, showcasing ongoing advancements in technology. This context highlights the crucial role that architectural rendering virtual reality plays in modern design practices, enhancing both user engagement and project visualization.
Physical Elements
While digital elements offer flexibility and interactivity, physical models provide tangible insights into scale and materiality. Balancing these approaches enables architects to improve the overall experience and client involvement, ensuring projects are effectively communicated and comprehended.
Future Trends in Architectural Visualization: AI and Real-Time Rendering
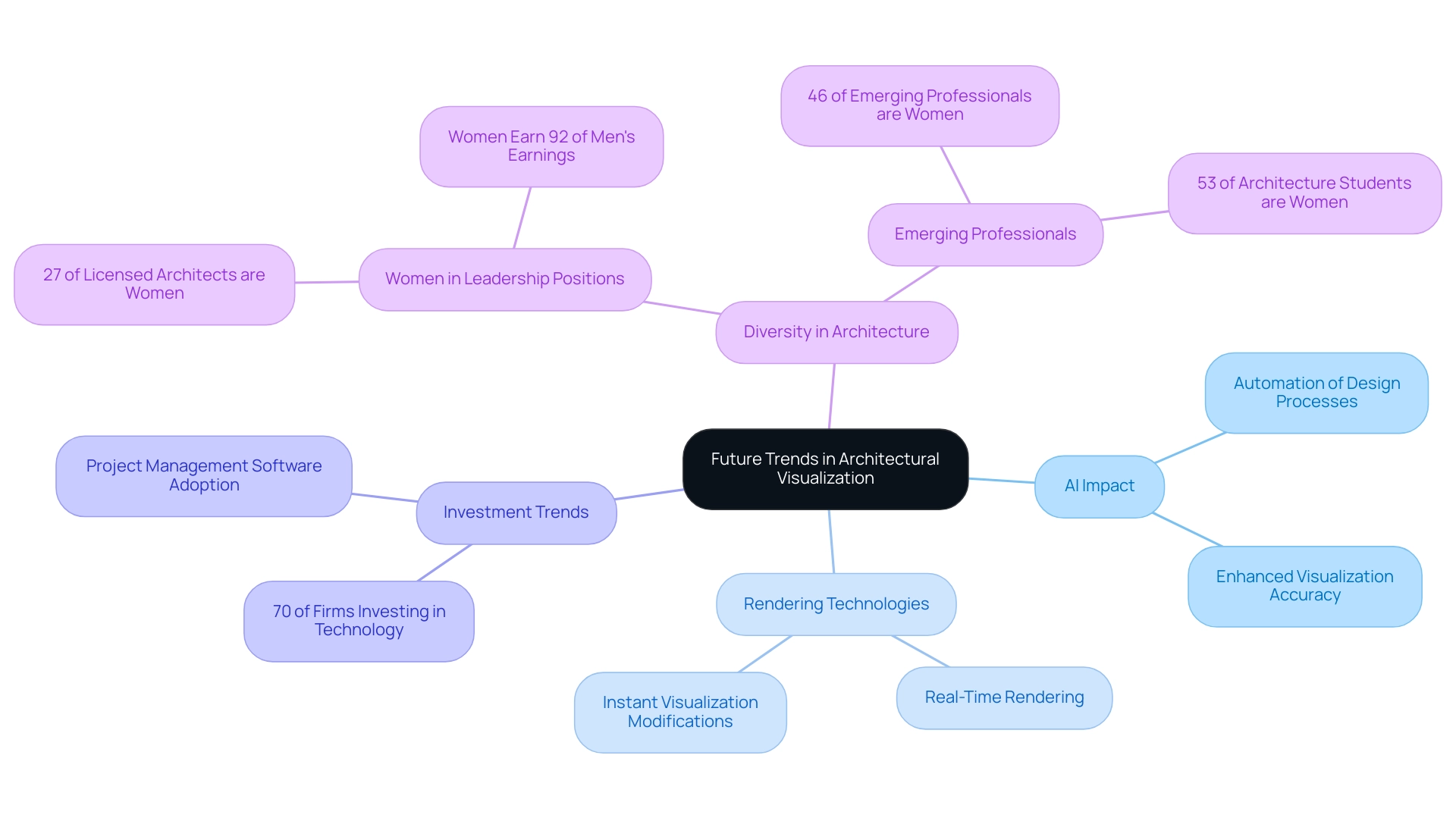
The landscape of architectural rendering virtual reality is undergoing a profound transformation, as artificial intelligence (AI) emerges as a pivotal force in automating design processes and enhancing visualization accuracy. High-quality visualizations serve as a window into the future of projects, allowing stakeholders to see potential and understand the vision behind blueprints. Viewing these external 3D visuals as an investment rather than merely an expense is essential; this clarity is not just a luxury but crucial for informed decision-making and fostering excitement about what’s to come.
One of the most significant advancements is the rise of architectural rendering virtual reality technologies, which allow architects to visualize modifications instantaneously. This capability not only enhances the quality of architectural presentations but also accelerates decision-making and streamlines approval processes. As noted by The Architect’s Newspaper, ‘there were 35,621 candidates actively working on licensure’ in 2022, underscoring the growing demand for innovative visualization methods.
Moreover, with 70% of architecture firms intending to invest more in technology over the next 12 months, integrating architectural rendering virtual reality, along with project management software and AI tools, is crucial for architects seeking to retain a competitive advantage. The strategic investment in high-quality exterior 3D visuals can attract investors, impress customers, and greatly enhance the approval process. Additionally, while women represent 27% of licensed U.S. architects, they hold only 20% of leadership positions in firms, highlighting ongoing disparities in income and representation within the industry.
By incorporating these advancements into their workflows, architects can meet the evolving expectations of clients and position themselves as leaders in the field.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing VR in Architecture
Technical Limitations: To ensure optimal performance in VR visualization, equipping your firm with hardware that meets specific technical requirements is crucial. High-performance computers and advanced VR headsets are essential to mitigate lag and enhance the overall user experience. Regularly updating these technologies can significantly improve rendering capabilities and facilitate smoother interactions within virtual environments. Additionally, the ‘uniqueness effect’ in virtual reality presents a challenge, as it can affect how users perceive and interact with virtual spaces, necessitating careful consideration in design and implementation.
Learning Curve: Adopting VR technology requires a commitment to training and skill development. Familiarizing your team with the intricacies of VR software is vital. Organizing targeted training sessions or workshops can effectively build proficiency and confidence, enabling your team to leverage VR tools to their fullest potential. A relevant example is the pilot study titled “A Pilot of Student-Guided Virtual Reality Tours,” which demonstrates how VR can enhance students’ BIM skills in a construction management classroom. This investment in human capital not only enhances productivity but also fosters a culture of innovation within your firm.
Cost Considerations: A thorough cost analysis is imperative when integrating VR technology into architectural practices. This includes evaluating expenses related to software licenses, hardware investments, and potential training costs. Developing a comprehensive budget that encompasses these elements will help avoid financial strain and ensure that your firm can sustain VR initiatives over the long term. Given the rapid evolution of this technology, it is advisable to regularly reassess these costs in conjunction with market trends and advancements.
Customer Acceptance: Resistance from customers towards new technologies can pose a significant challenge. It is crucial to inform customers about the numerous advantages that VR provides during the creation process. Providing demonstrations that showcase the immersive capabilities of architectural rendering virtual reality can effectively illustrate its value. According to PwC, half of U.S. consumers find the virtual reality metaverse to be ‘exciting’, indicating a growing acceptance of such technologies. By addressing customer concerns and highlighting VR’s advantages, architects can facilitate smoother transitions towards contemporary design practices. Moreover, the integration of architectural rendering virtual reality alongside 3D visualizations, such as interactive models and customizable design options, not only enhances communication but also helps in resolving design issues early, ultimately streamlining project workflows and fostering stronger client relationships. For instance, a recent project showcased how our 3D visualizations directly contributed to securing a significant investment by providing potential investors with a clear, interactive view of the project, demonstrating the power of pre-sales visualization in enhancing project confidence.
Conclusion
The integration of virtual reality (VR) and artificial intelligence (AI) into architectural rendering represents a significant evolution in how architects visualize and present their designs. By employing advanced technologies, stakeholders are now equipped to experience hyper-realistic environments that enhance understanding and engagement. The adoption of VR not only allows clients to navigate designs in an interactive manner but also fosters collaboration and feedback that refine the overall project outcome.
The article outlined essential techniques for effectively incorporating VR into architectural practices, emphasizing the importance of:
- Selecting appropriate software
- Creating detailed 3D models
- Optimizing these models for virtual environments
Testing the VR experience prior to client presentations ensures a seamless interaction that bolsters client confidence in the architectural vision. Furthermore, the benefits of enhanced visualization, improved client engagement, and increased design accuracy underscore the transformative impact of these technologies on the architectural process.
Looking ahead, the challenges associated with implementing VR, such as technical limitations and client acceptance, can be effectively managed through:
- Strategic planning
- Ongoing training
- Clear communication of the benefits
As the architectural landscape continues to evolve, embracing these cutting-edge tools will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and meeting the growing expectations of clients. The future of architectural visualization lies in the ability to leverage AI and VR not merely as enhancements but as integral components that revolutionize project presentations and client relationships.

0 Comments