Overview
Exploring augmented reality (AR) in architectural projects enhances design visualization by allowing architects to superimpose 3D models onto real-world environments, facilitating better communication and decision-making among stakeholders. The article supports this by detailing how AR tools improve client satisfaction, streamline workflows, and promote sustainable practices, indicating a significant shift towards innovative design methodologies in the architecture industry.
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of architecture, augmented reality (AR) emerges as a transformative force, reshaping how design concepts are visualized and communicated. By seamlessly blending digital information with physical environments, AR empowers architects to present intricate 3D models in real-time, fostering a more immersive experience for clients and stakeholders alike. This innovative technology not only enhances the clarity of architectural proposals but also streamlines workflows, allowing for more efficient collaboration and informed decision-making throughout the design process.
As the industry increasingly prioritizes sustainability and technological integration, the role of AR becomes even more critical, driving significant advancements in both project outcomes and client satisfaction. The following exploration delves into the multifaceted applications of AR in architectural design, highlighting its benefits, successful implementations, and the promising future that lies ahead for this groundbreaking technology.
Understanding Augmented Reality in Architecture
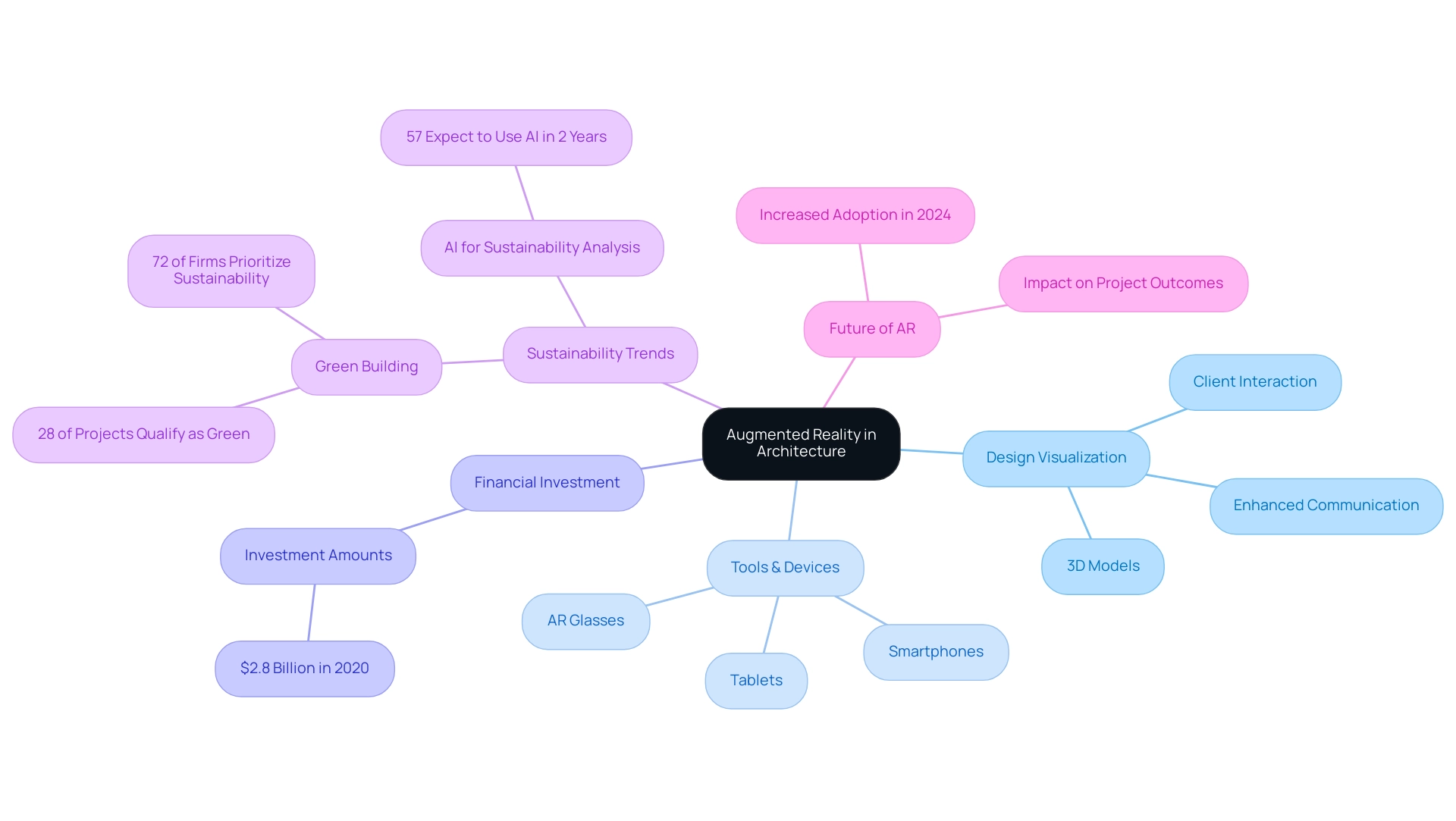
Augmented Reality (AR) in architecture represents a pivotal evolution in design visualization, acting as a guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects by merging digital information with real-world environments. This innovative method allows architects to superimpose 3D models directly onto physical environments, enabling both professionals and stakeholders to interact with projects in a deeply immersive way. By facilitating a tangible connection between conceptualization and reality, AR serves as a critical tool that enhances traditional architectural methodologies, addressing the appropriate level of detail required by homeowners and businesses.
By using devices like smartphones, tablets, and specialized AR glasses, architects can produce dynamic visualizations that not only enhance communication with customers but also simplify the creation process, thus removing misunderstandings frequently encountered in contractor interactions. The integration of detailed interior renderings showcases both functionality and aesthetics, significantly enhancing client satisfaction and marketing effectiveness. Moreover, the role of pre-sales visualization becomes evident, as these renderings instill confidence in potential investors and stakeholders, generating crucial revenue long before construction begins.
As the architecture industry invests heavily in technology—spending over $2.8 billion on software and tools in 2020—it’s clear that the guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects signifies not just a trend but a fundamental shift towards more innovative and sustainable design practices. With 28% of architects, engineers, contractors, owners, and investors reporting that most of their building endeavors qualify as green, and 42% anticipating reaching that level within the next three years, the focus on sustainability is becoming more pronounced. Furthermore, the anticipated increase in AR adoption within the field in 2024 highlights the potential for these advancements to enhance project outcomes and client satisfaction.
This aligns with the ongoing demand for sustainable design, as highlighted by a case study showing that 72% of design firms prioritize sustainability, with 57% expecting to utilize AI for environmental sustainability analysis in the next two years. Thus, the architecture industry is undergoing significant changes, propelled by technological innovations and a focus on sustainability efforts, emphasizing the need for a guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects to shape the future of creation.
Practical Applications of Augmented Reality in Architectural Design
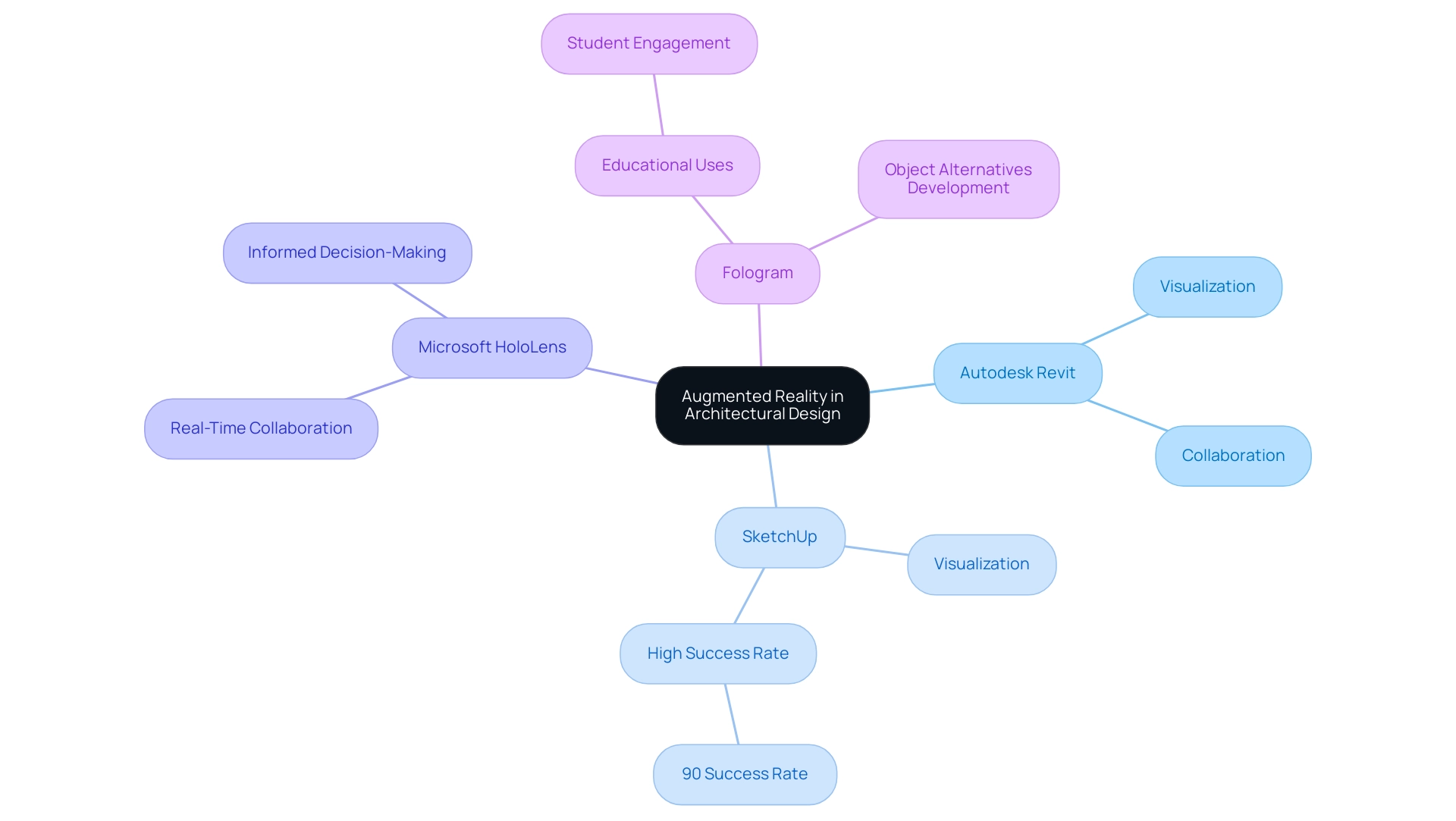
In the field of building creation, the guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects has emerged as a revolutionary technology, enabling architects to utilize various tools and applications efficiently. Software such as Autodesk Revit and SketchUp can be seamlessly integrated with AR capabilities, allowing for the visualization of architectural models within their intended real-world contexts. This integration not only improves the creation process but also highlights the significance of delivering clear and timely information early in the project to optimize timelines and costs, saving both time and money.
Specific information regarding dimensions, materials, and intent should be provided upfront to ensure accuracy in renderings. Additionally, meticulous attention to detail ensures accuracy in renderings, fostering collaboration with stakeholders at every stage to align with their vision. Microsoft HoloLens acts as a guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects by empowering architects to superimpose 3D models onto construction sites, significantly enriching real-time collaboration and informed decision-making.
For instance, a study found that the SketchAR software can be an effective tool in architectural planning, boasting a success rate of over 90%. Furthermore, Weissenböck noted that students utilized the Fologram application during online lessons to develop object alternatives for their rooms, demonstrating the educational applications of AR technology. By facilitating these interactions, AR acts as a guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects, not only streamlining the workflow but also enhancing client presentations, allowing stakeholders to visualize and engage with concepts as they would appear in their actual environments.
The emotional and practical benefits of high-quality visual renderings are crucial, as they build excitement and clarity for all stakeholders involved. The essential role of high-quality visual renderings in project development is emphasized by the User Experience Questionnaire (UEQ) evaluation of AR systems, which indicated positive evaluations across all categories, particularly in novelty. This heightened level of interaction fosters a deeper understanding of the proposed concepts, ultimately leading to more informed feedback and decisions.
Benefits of Integrating Augmented Reality into Architectural Workflows
The integration of augmented reality (AR) into architectural workflows serves as a guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects, presenting a multitude of advantages that resonate with the evolving demands of the industry. One notable advantage is improved communication; the guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects enables customers to visualize concepts with precision, resulting in more informed feedback and faster decision-making processes. According to recent studies, 56.8% of architects rank client satisfaction as their top priority, and the guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects plays a vital role in achieving this by facilitating clearer understanding and engagement with design concepts.
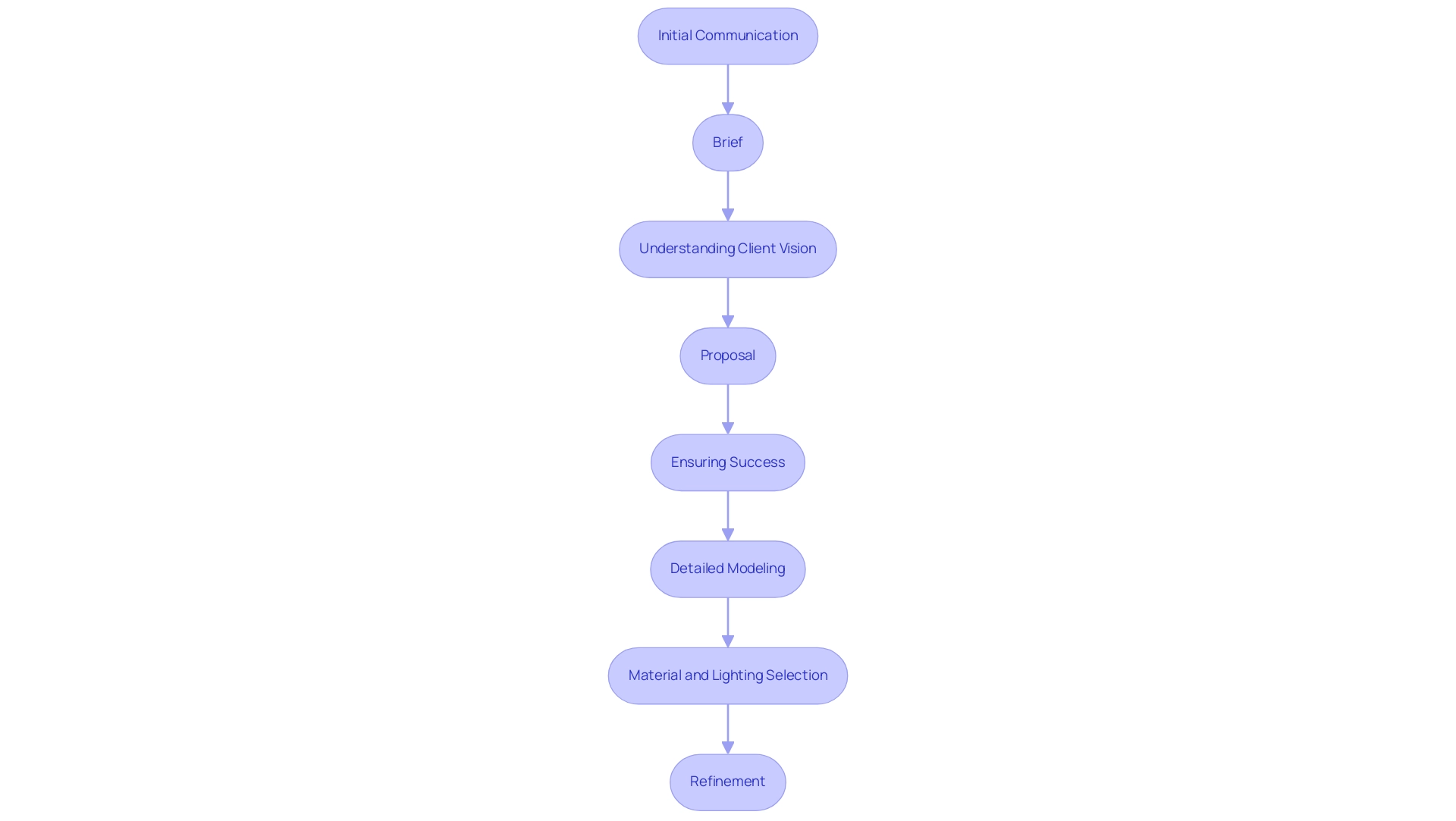
Moreover, as demonstrated in our collaborative rendering process at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, which includes:
- Initial communication
- Brief
- Understanding client vision
- Proposal
- Ensuring success
- Detailed modeling
- Material and lighting selection
- Refinement
The guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects streamlines efficiency by minimizing reliance on physical models and mock-ups. This not only conserves time but also optimizes resource allocation, ensuring that specifications are met with high detail levels. The global digital asset management market is projected to surge from $3.96 billion in 2023 to $16.18 billion by 2032, making the adoption of such technologies increasingly critical for architectural firms aiming to remain competitive.
Notably, 34.9% of surveyed firms express a desire to hire for marketing and business development, highlighting the industry’s focus on growth and client engagement.
Collaboration among teams is further enhanced through real-time interactions with shared visualizations, ensuring all stakeholders are aligned throughout the design process. As emphasized during our initial communication and briefing stages, effective collaboration is fundamental to the success of any initiative. Pierre Proulx, Team Lead at Rossmann Architecture, emphasizes this efficiency, stating, ‘We use the data inside Monograph to make important decisions on how to manage our work and our staff, which is making us more efficient, more profitable and in turn hire more people.’
This viewpoint emphasizes the wider consequences of incorporating AR, serving as a guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects, to enhance not only project results but also company growth. Furthermore, as 66% of architecture firms express a wish to update their financial planning processes, a guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects can greatly enhance both communication with customers and overall project delivery. The case study on client satisfaction as a key performance indicator further illustrates this, as many architects struggle to provide a consistent client experience.
With 65% of architecture students believing that technology will drastically change the field, it is evident that a guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects is crucial for the future of design practice. Furthermore, businesses considering outsourcing 3D architectural rendering should weigh its potential to enhance efficiency and focus on core competencies, addressing common FAQs regarding the benefits and considerations of outsourcing.
Case Studies: Successful Implementations of Augmented Reality in Architecture
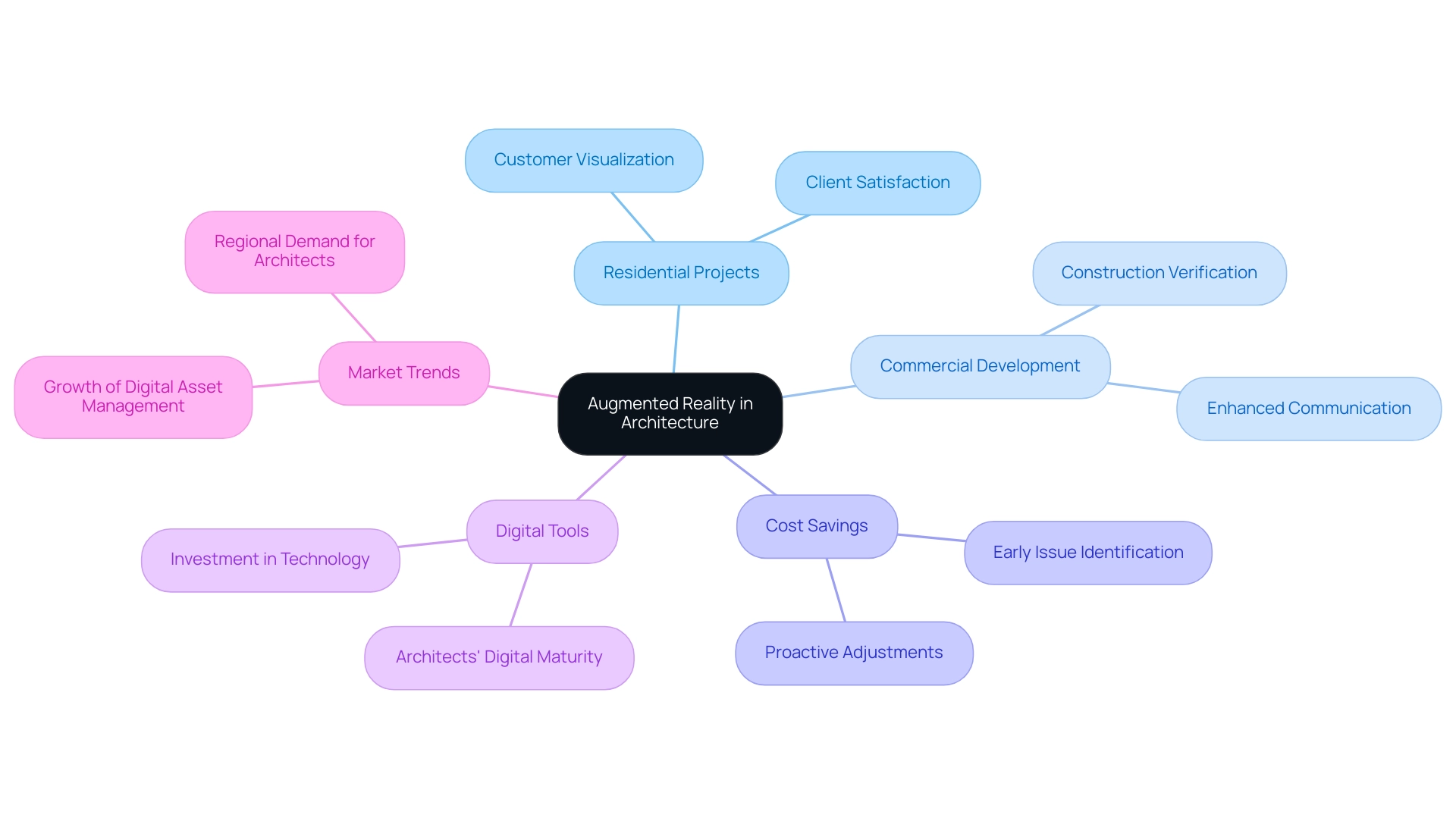
A captivating example of augmented reality (AR) in action can be found in a luxury residential endeavor where AR technology was utilized to showcase various options to the customer. By utilizing AR applications, architects were able to superimpose various layout alternatives directly onto the site, offering the customer a clear visualization of how each option would integrate into the existing environment. This innovative approach not only facilitated a more informed decision-making process but also resulted in heightened client satisfaction and confidence in the initiative.
Moreover, the use of detailed interior renderings significantly enhances functionality and aesthetics, serving as a crucial bridge between concept and reality, and further boosting marketing effectiveness.
In the realm of commercial development, AR was instrumental during the construction phase, enabling architects to verify that the undertaking adhered strictly to specifications. This proactive measure significantly minimized the potential for costly rework and delays, showcasing the practical benefits of AR in enhancing execution and contractor communication. Furthermore, clients have consistently reported substantial cost savings in construction processes by identifying issues early through 3D visualizations and making proactive adjustments while plans are still on screen.
Such successful applications of AR in building endeavors act as a guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects, underscoring its transformative potential in both design and construction while highlighting the increasing reliance on digital tools within the industry. Furthermore, renderings play a vital role in generating revenue for construction projects by attracting investment and interest before the physical manifestation of the project. As the global digital asset management market is projected to reach $16.18 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 17.0%, the significance of adopting digital tools like AR becomes even more apparent.
Additionally, with 47% of British architects believing their digital maturity is average, the industry’s willingness to embrace new technologies is evident. This trend is further reflected in the fact that U.S. architecture firms spent over $2.8 billion on software and technology in 2020, reinforcing the significance of integrating AR into design practices.
The Future of Augmented Reality in Architectural Projects
The guide to Exploring augmented reality in architectural projects indicates that the future of augmented reality (AR) in architecture appears exceptionally promising, driven by relentless technological advancements that are set to broaden its applications. A notable trend is the integration of artificial intelligence, which enhances AR experiences by creating lifelike computer-generated (CG) humans that effectively bridge the uncanny valley. This advancement not only enhances visualizations but also enables various applications ranging from medical imaging to product prototyping, demonstrating the significance of 3D rendering across multiple disciplines.
As AR hardware becomes increasingly accessible and affordable, architectural practices are expected to refer to the guide to Exploring augmented reality in architectural projects at an accelerated pace. This shift is further emphasized by the potential for AR to facilitate remote collaboration and virtual walkthroughs, thereby transforming the way architects interact with customers and stakeholders. For instance, Boeing’s MR-based maintenance solutions have demonstrated a 20% decrease in maintenance time and a 15% increase in operational efficiency, showcasing practical benefits in a related field.
Moreover, the collaborative rendering process at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs emphasizes stakeholder engagement, beginning with initial communication and project briefing, followed by detailed modeling and material selection. This meticulous method guarantees that the final product corresponds with customer expectations. While immersive tech offers many benefits, it also raises privacy concerns, especially regarding data collection and user tracking, which architects must consider as they integrate these technologies.
The swift advancement of AR technology serves as a guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects, establishing it as an essential instrument within the construction toolkit and improving both planning processes and client interactions. Furthermore, industry statistics indicate that firms embracing digital maturity through such technologies are better positioned for growth, reflecting the increasing importance of AR and AI in design. As architects look toward the future, the guide to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects, along with AI, will continue to play a crucial role in shaping innovative architectural practices.
Conclusion
The exploration of augmented reality (AR) in architecture reveals its transformative impact on design visualization and client engagement. By merging digital data with physical spaces, AR allows architects to present intricate 3D models in real-time, fostering a deeper understanding of concepts among clients and stakeholders. This technology enhances communication, streamlines workflows, and significantly improves client satisfaction, addressing the industry’s increasing demand for innovative and sustainable design practices.
Successful applications of AR have demonstrated its ability to facilitate early-stage decision-making and minimize costly rework during construction phases. The integration of AR tools into architectural workflows not only optimizes resource allocation but also cultivates collaboration among project teams, ensuring alignment and clarity throughout the design process. As highlighted by various case studies, the use of AR in real-world scenarios has yielded substantial benefits, including enhanced client confidence and substantial cost savings.
Looking ahead, the future of AR in architecture is poised for remarkable growth, driven by technological advancements and the integration of artificial intelligence. As the accessibility of AR hardware increases, architectural firms are expected to adopt these innovations more rapidly, revolutionizing client interactions and project delivery. The ongoing emphasis on sustainability and the desire for digital maturity within the industry further underscore the critical role AR will play in shaping the future of architectural design. Embracing this technology is not just a trend; it is a strategic move toward enhanced efficiency, client satisfaction, and competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving marketplace.

0 Comments