Overview:
Virtual reality (VR) enhances architectural presentations by increasing client engagement, improving feedback, and providing a competitive advantage through immersive experiences. The article outlines how VR allows for real-time interaction and visualization of designs, fostering better understanding and collaboration, which ultimately leads to more effective project approvals and investment.
Introduction
The integration of virtual reality (VR) into architectural presentations marks a pivotal evolution in the way architects communicate their visions to clients. By immersing clients in a lifelike virtual environment, architects can enhance engagement, facilitate real-time modifications, and foster a collaborative design process that transcends traditional methods.
This article explores the myriad advantages of VR, including:
- Improved design communication
- Enhanced emotional connection
- Establishing a competitive edge in an increasingly saturated market
Furthermore, it outlines practical steps for successful implementation, addresses common challenges faced during integration, and highlights future trends that promise to reshape architectural visualization. As the industry embraces this transformative technology, understanding its potential becomes essential for architects aiming to elevate their practice and meet the demands of a dynamic landscape.
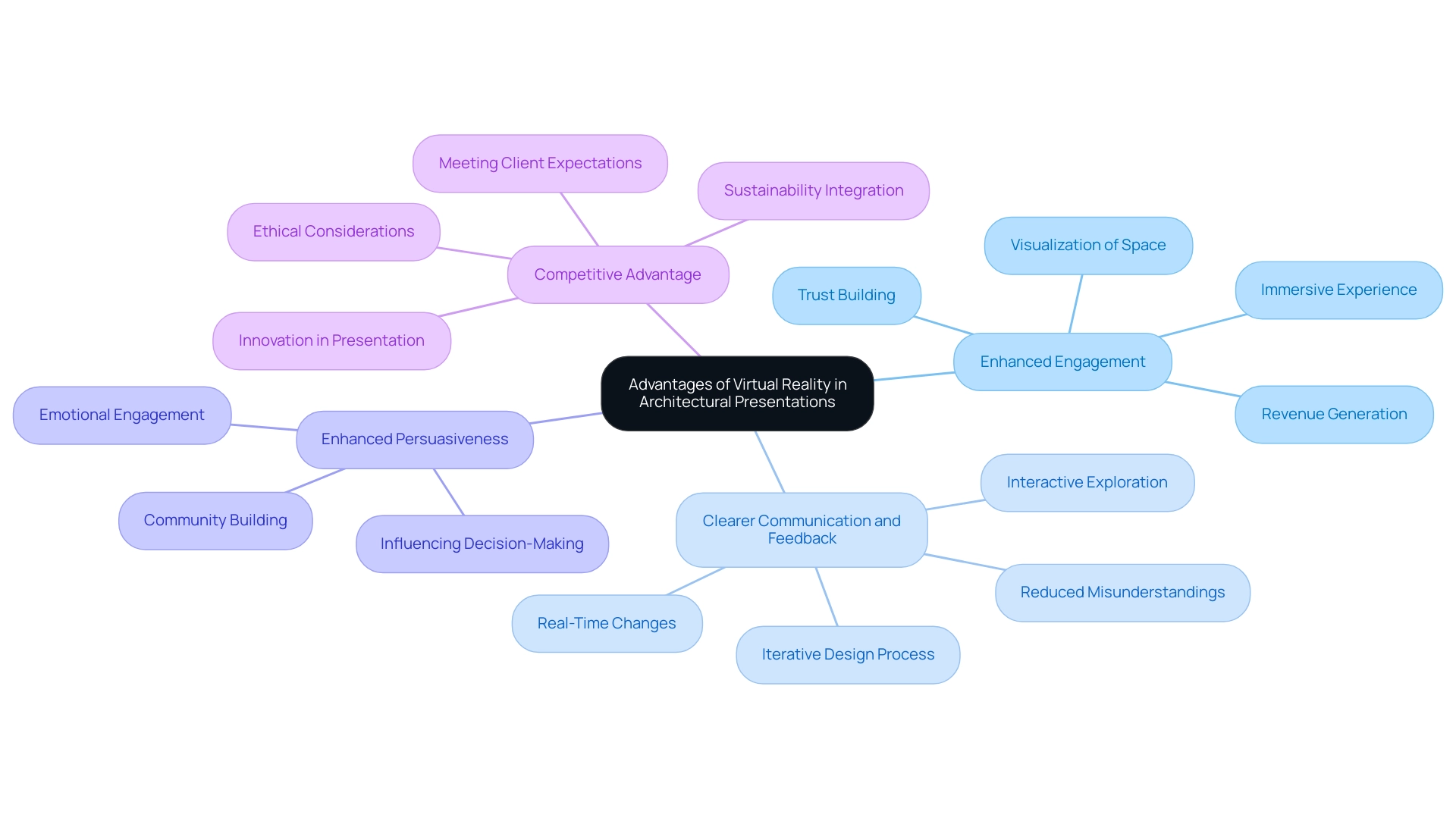
The Advantages of Virtual Reality in Architectural Presentations
Virtual reality (VR) presents a multitude of advantages in architectural presentations, significantly transforming how architects interact with customers:
Enhanced Engagement: This demonstrates how to understand the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations by immersing users within a virtual environment, offering a level of engagement that surpasses traditional 2D presentations. This immersive quality enables clients to better visualize the space, demonstrating how to understand the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations and fostering a deeper understanding of the design. By employing pre-sales visualization methods, designers can deliver renderings that connect the concept with reality, fostering trust in the initiative and attracting interest and funding well before construction starts. This early engagement can also lead to crucial revenue generation for construction projects, as prospective buyers are more likely to commit when they can visualize their future homes.
Architects can demonstrate how to understand the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations by enabling clients to explore and interact with concepts in a simulated context, allowing for clearer expression of intent. This not only reduces misunderstandings but also promotes constructive feedback, enhancing the collaborative creation process. The iterative nature of 3D visualizations further supports this by identifying issues early and facilitating informed decision-making. One of the hallmark features of VR is how to understand the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations by enabling real-time changes during presentations. Architects can promptly showcase how changes influence the overall endeavor, promoting a dynamic conversation focused on enhancements. This flexibility is essential during renovation tasks, where customer feedback can enhance interior renderings effectively.
Enhanced Persuasiveness: The immersive quality of VR illustrates how to understand the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, cultivating deeper emotional ties to the concept and making it a potent instrument for convincing clients and obtaining approvals. This emotional engagement can significantly influence decision-making processes and contribute to the formation of a strong community from the outset of a project. By instilling confidence in the concept, planners can enhance the likelihood of investment during the pre-sales phase.
Competitive Advantage: In a market saturated with traditional presentation methods, understanding how to assess the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations distinguishes designers as innovators. By adopting advanced technology, professionals not only improve their creative processes but also showcase a dedication to fulfilling changing client expectations. Significantly, 42% of architects expect that their building projects will meet green standards within the next three years, and VR can play a crucial role in supporting sustainable practices. Furthermore, integrating ethical considerations and human-centric principles ensures that VR-enhanced creations prioritize user well-being, solidifying its importance in modern architecture.
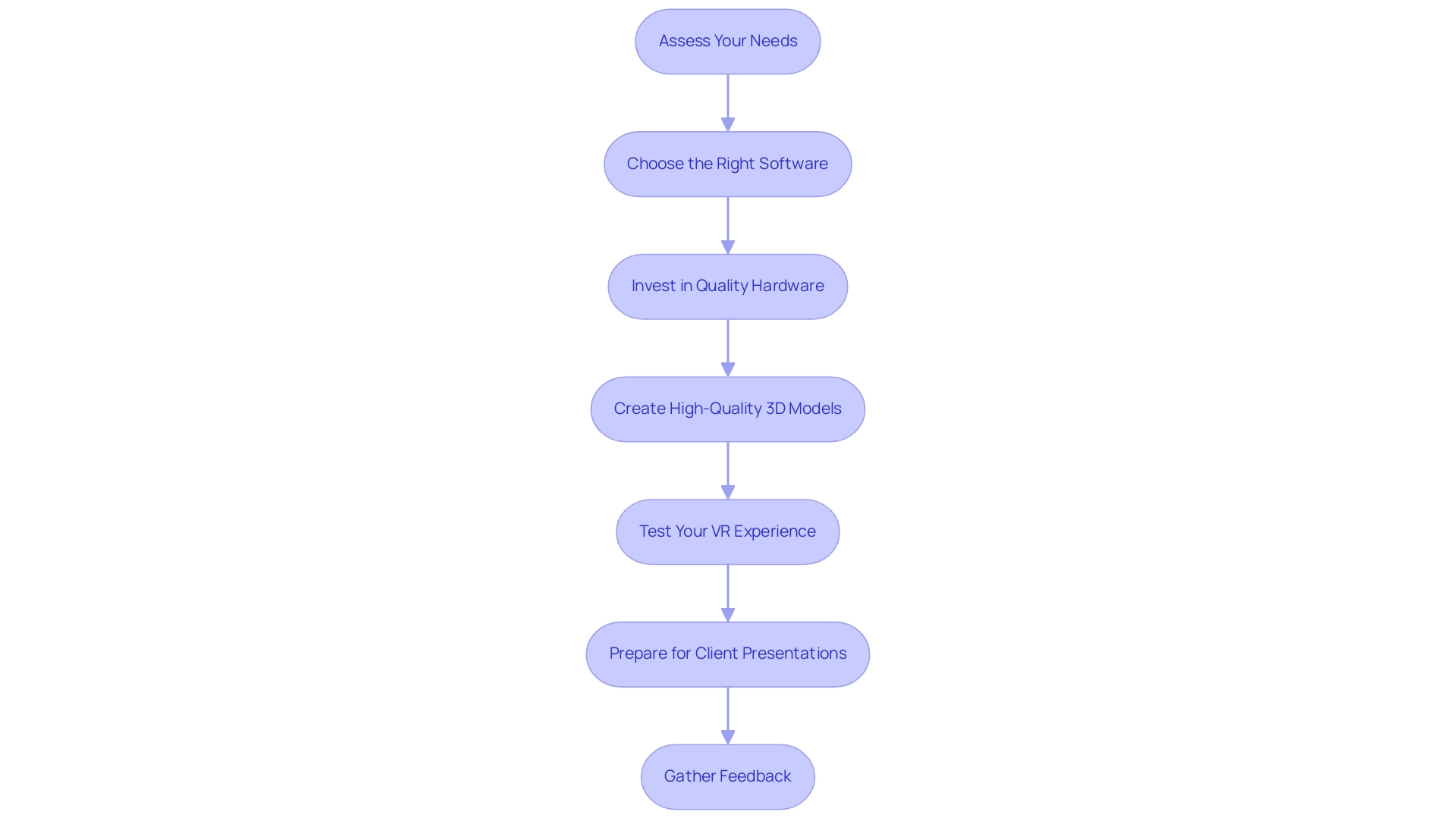
Integrating Virtual Reality: Practical Steps for Architects
Understanding how to The impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations can significantly enhance client engagement and design feedback. With over 900 assignments delivered, our experience underscores the effectiveness of VR in this domain. Providing clear and timely information is crucial to optimizing time and costs in construction endeavors.
To ensure a successful implementation, please provide us with the following information early in the process:
Assess Your Needs: Begin by defining the specific objectives you aim to achieve with VR. Consider whether your focus is on enhancing client engagement, improving feedback on visuals, or facilitating streamlined project approvals.
Choose the Right Software: Select VR software that aligns with your objectives and is compatible with your current creation tools. Options such as Enscape, Twinmotion, and Unreal Engine are popular choices among architects for their robust features in architectural visualization.
Invest in Quality Hardware: Ensure you acquire the necessary VR hardware, including a powerful computer and a VR headset, such as the Oculus Rift or HTC Vive. It is crucial that the hardware can handle high-fidelity renderings without performance issues.
Create High-Quality 3D Models: Develop detailed 3D models of your concepts, optimizing them for VR. Focus on the quality of textures, lighting, and scale to create a truly immersive experience for users. We guarantee that we can produce high-quality architectural renderings for both interior and exterior projects, including thorough site documentation, which are vital for visualizing and improving residential architecture concepts.
Test Your VR Experience: Conduct comprehensive testing of the VR experience before presentations. Verify that navigation is user-friendly and that all interactive elements function as expected.
Prepare for Client Presentations: Familiarize yourself with the VR setup and devise a clear presentation strategy. Plan how to assist users through the VR experience, emphasizing key design features while being prepared to address their feedback in real-time. Encouraging feedback and collaboration at every stage ensures alignment with their vision.
Gather Feedback: After the presentation, actively seek input from customers regarding their VR experience. This feedback is invaluable for refining your approach and enhancing future presentations. The role of 3D renderings in enhancing property value through visual appeal and market differentiation cannot be overstated.
As we navigate the challenges of integrating technology in architecture, it is essential to advocate for responsible usage. As Forough Farhadi states, “Architects must navigate these challenges, fostering ethical AI practices, advocating for responsible usage, and addressing biases to ensure that AI-driven solutions align with societal values and user needs.” Furthermore, imagining a cooperative AI environment where designers, engineers, urban planners, and AI developers collaborate can encourage innovation, specifically in how to understand the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations to tackle intricate challenges in design and urban planning.
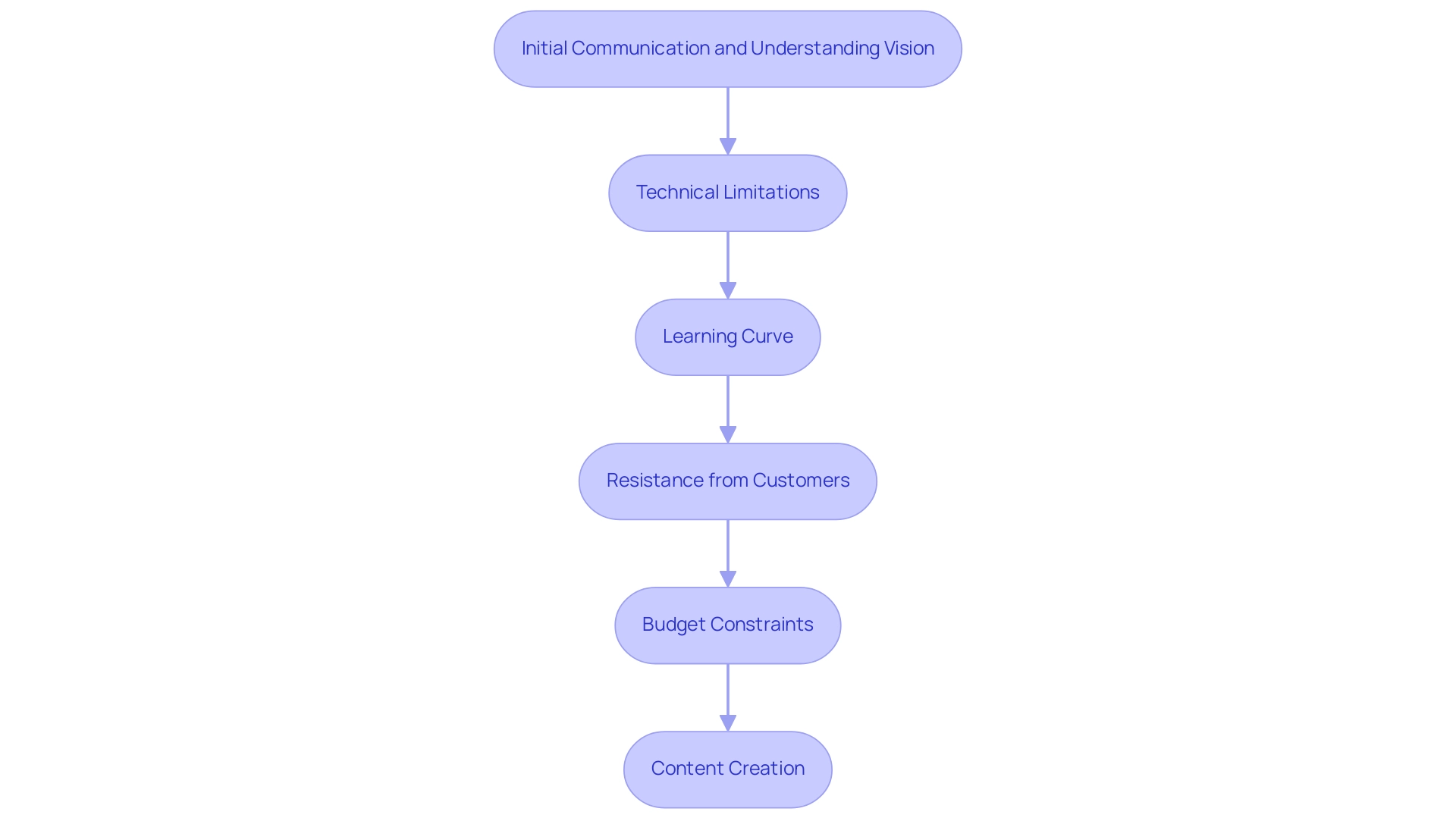
Overcoming Common Challenges in VR Integration
Understanding how to The impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations reveals numerous advantages in integrating this technology into architectural practice, though it is not without its challenges. Key issues include:
Initial Communication and Understanding Vision: Before diving into VR applications, architects must engage in thorough initial communication to understand the vision. This foundational step ensures that the endeavor aligns with client expectations and sets the stage for successful collaboration throughout the rendering process.
Technical Limitations: Architects must ensure that both hardware and software are sufficiently advanced to support VR applications. Regular updates to drivers and software are essential to prevent compatibility issues that could impede development. For instance, VR was instrumental in the upkeep of the Sydney Opera House, predicting repairs and maintenance accurately, which avoided unnecessary part replacements.
Learning Curve: Gaining mastery over VR tools and techniques can be daunting. However, engaging with online tutorials or specialized workshops can significantly enhance one’s proficiency in learning how to The impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, ultimately leading to a more effective use of VR in projects.
Resistance from customers is a common hurdle when introducing new technologies. It is crucial to educate customers on how to understand the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, using demonstrations to showcase its capabilities and alleviating any apprehensions they may have. As noted by Kamran Arabi, ‘VR is revolutionizing the construction industry, promoting efficient resource utilization and substantially reducing waste,’ which illustrates how to understand the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations to convince customers about its value.
Budget Constraints: Assessing the return on investment is vital when implementing VR solutions. Beginning with pilot initiatives enables companies to assess effectiveness without dedicating significant resources to broad VR integration right away. Discussing budget considerations openly with stakeholders can help manage expectations and align project goals.
Content Creation: The process of developing detailed 3D models can be labor-intensive. To mitigate this, architects should leverage existing models whenever feasible and consider collaborating with visualization specialists to expedite the content creation process. This collaborative method corresponds with the rendering process at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, where meticulous detail modeling and material selection result in high-quality outputs that surpass expectations. Understanding how to assess the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations is crucial for selecting materials and lighting to create realistic visuals, enhancing client engagement and satisfaction. Additionally, the Cube case study highlights the innovative use of VR in architectural education, demonstrating how a VR environment can facilitate interaction with building materials, a crucial skill for designers.
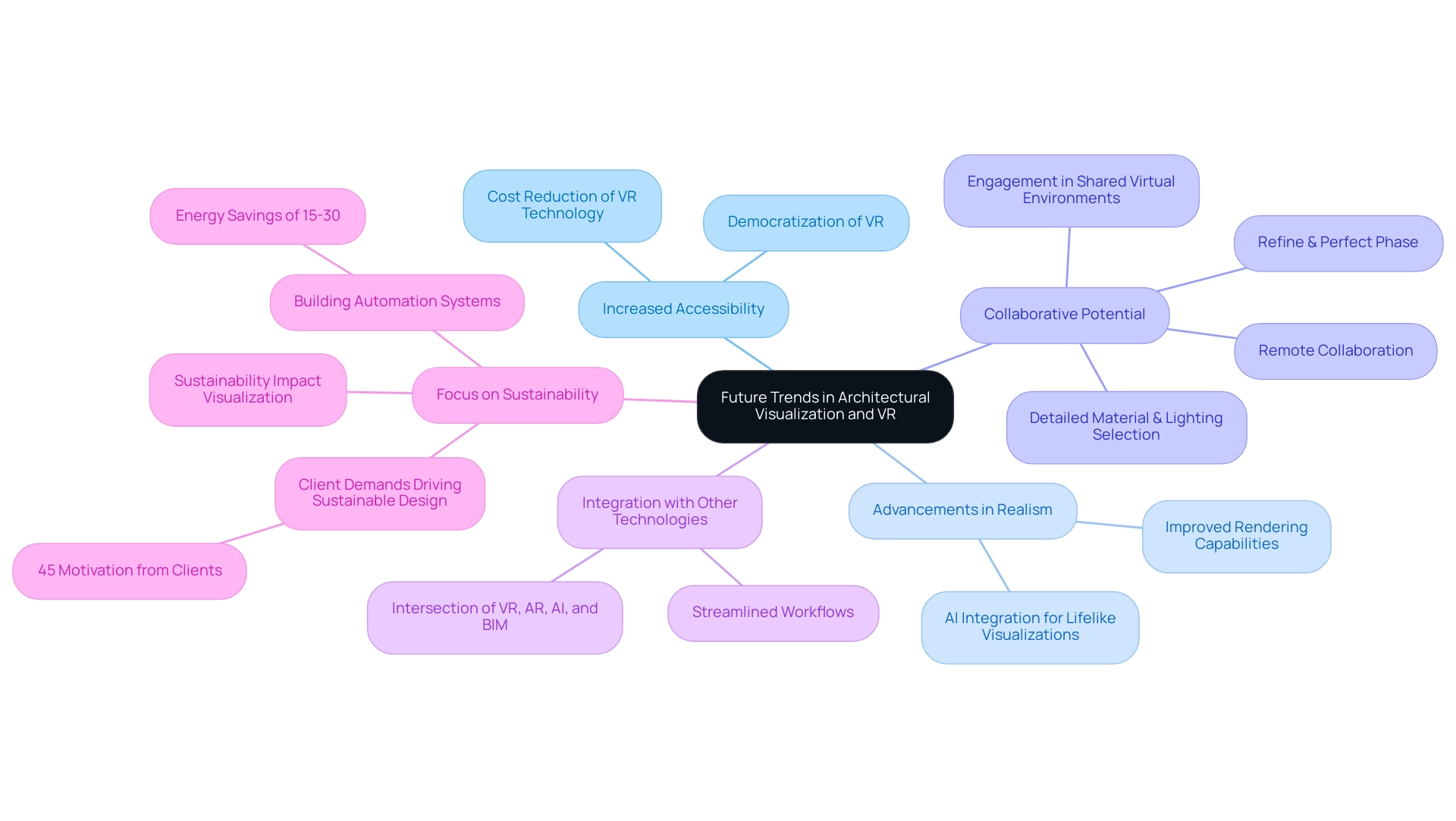
Future Trends in Architectural Visualization and VR
The future of architectural visualization is closely linked to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, which is poised for transformative advancements that will reshape the industry landscape. Several key trends are emerging:
- Increased Accessibility: The decreasing cost of VR technology is making immersive experiences more attainable for architects, broadening its application within the field.
This democratization of VR provides insights on how to understand the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, enabling a wider range of professionals to leverage these powerful tools in their creative processes.
Advancements in Realism: Continuous improvements in rendering capabilities, including the integration of artificial intelligence to create lifelike CG humans, are anticipated to yield even more realistic visualizations. These advancements not only help bridge the uncanny valley but also improve understanding and engagement, fostering more effective communication of design concepts.
Collaborative Potential: The collaborative potential of virtual reality highlights how to understand the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations. It allows architects, customers, and stakeholders to engage seamlessly in a shared virtual environment, irrespective of geographical barriers. This remote collaboration is increasingly essential, particularly as the percentage of companies working remotely has significantly dropped to only 9.9% this year, highlighting how to understand the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations to maintain effective communication and development.
Key steps in our collaborative rendering process include:
– Detailed Material & Lighting Selection, where we meticulously create materials that reflect project intent.
– The Refine & Perfect phase, where we provide progress renderings for client feedback, ensuring satisfaction and alignment with project goals.
Integration with Other Technologies: The intersection of VR with augmented reality (AR), artificial intelligence (AI), and building information modeling (BIM) is creating comprehensive creation and presentation tools. This convergence will streamline workflows and enhance the overall quality of architectural outputs, ensuring that intricate details are captured to enhance realism and emotional impact.
Focus on Sustainability: As sustainability becomes a primary concern in architectural planning, it is important to understand how to assess the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations as a valuable tool for visualizing the environmental impact of various projects. This capability assists architects in making informed choices that align with contemporary sustainability objectives, further influenced by customer demands, which account for 45% of the motivation toward sustainable design. For instance, building automation systems can lead to energy savings of up to 15-30%, showcasing the importance of integrating such technologies in achieving sustainability targets in architecture.
As these trends develop, the architectural landscape will increasingly reflect the profound influence of technology, emphasizing the need for professionals to adapt and innovate in their practices.
Our clients have consistently praised our collaborative approach, noting how our detailed renderings and attentive communication have exceeded their expectations, reinforcing the effectiveness of our services.
Conclusion
The integration of virtual reality into architectural presentations offers a transformative approach that enhances engagement, communication, and overall project outcomes. By immersing clients in lifelike environments, architects can convey design intentions with unprecedented clarity, fostering emotional connections that are vital for securing project approvals and investments. The ability to make real-time modifications during presentations not only streamlines the design process but also empowers clients to participate actively, ensuring their visions are accurately reflected.
However, the journey towards effective VR integration is not without its challenges. Architects must navigate initial communication barriers, technical limitations, and potential client resistance. By addressing these issues through thorough planning, robust training, and open dialogue about budget constraints, firms can successfully harness the power of VR to elevate their practice. The emphasis on collaboration, both in the design process and with clients, is crucial for maximizing the benefits of this technology.
Looking ahead, the future of architectural visualization is bright, with trends pointing towards increased accessibility, enhanced realism, and a strong focus on sustainability. As VR technology continues to evolve, architects who embrace these advancements will not only enhance their competitive edge but also contribute to a more sustainable and innovative industry. The ongoing commitment to ethical practices and responsible technology usage will further solidify the role of VR as an indispensable tool in modern architectural design.

0 Comments