Overview:
Virtual reality (VR) enhances architectural presentations by transforming how clients engage with designs, allowing for immersive experiences that improve understanding of space and design intent. The article supports this by detailing how VR fosters deeper client involvement, facilitates real-time feedback during design reviews, and serves as a powerful marketing tool, ultimately leading to more informed decision-making and enhanced satisfaction.
Introduction
The integration of virtual reality (VR) into architectural presentations marks a significant paradigm shift in how architects engage with clients and stakeholders. By transcending traditional 2D and 3D models, VR facilitates an immersive experience that allows clients to navigate and interact with designs in a virtual environment. This transformative approach not only enhances understanding of spatial relationships and design intent but also fosters a collaborative atmosphere where real-time feedback can be seamlessly integrated.
As the architectural landscape continues to evolve, the adoption of VR technology emerges as a critical strategy for professionals seeking to elevate client engagement and satisfaction, ultimately driving the success of their projects. The following exploration delves into the practical applications, benefits, and future trends of VR in architecture, illustrating its profound impact on the industry.
The Transformative Role of Virtual Reality in Architectural Presentations
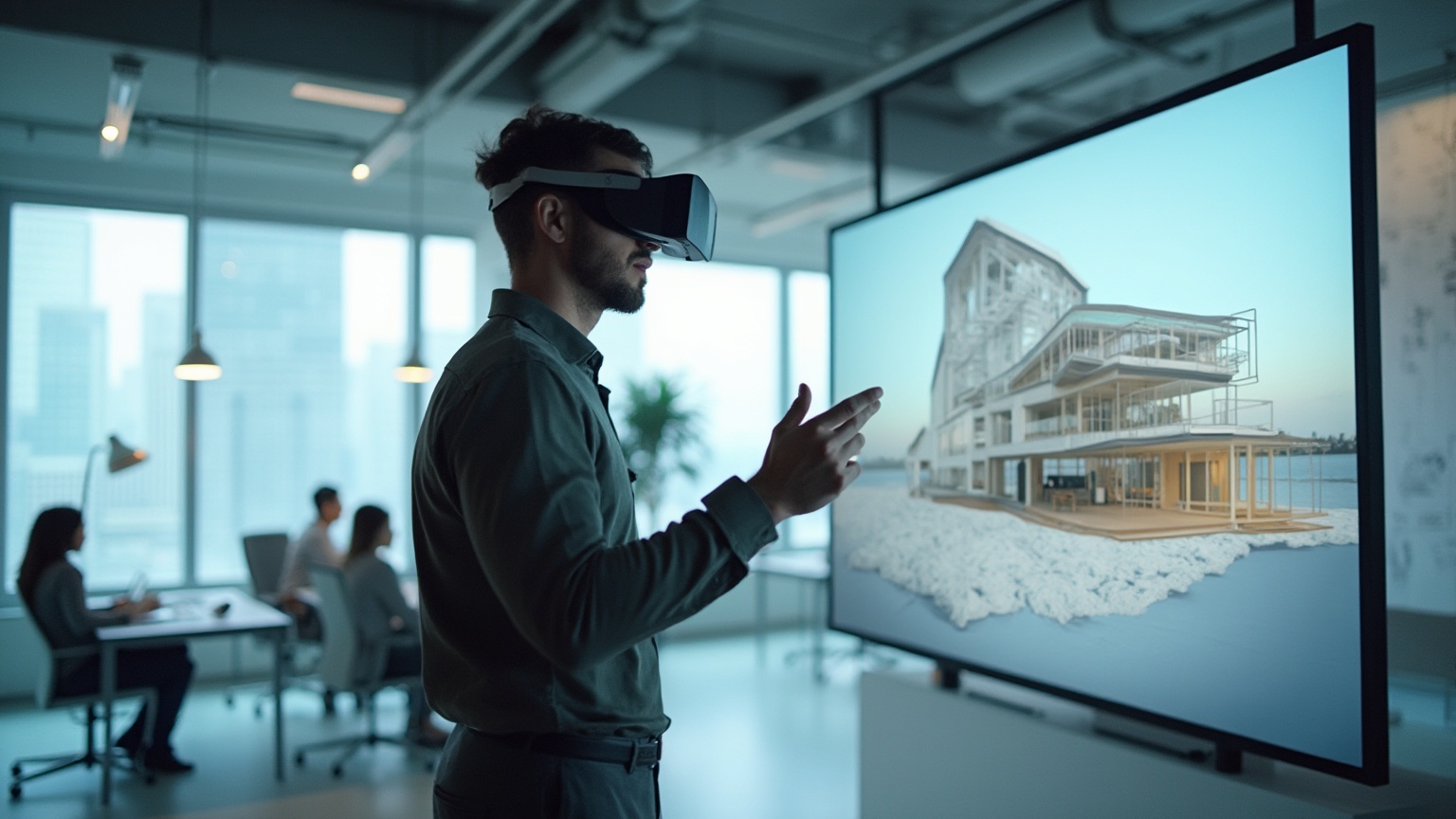
Virtual reality serves as a guide to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations by fundamentally changing how presentations in construction are delivered, allowing clients to immerse themselves in concepts as if they were physically navigating the space. This evolution from traditional 2D renderings and even 3D models viewed on screens to an interactive environment enhances stakeholder engagement with the project at an unprecedented level. Clients can better grasp scale, proportion, and spatial relationships, leading to more nuanced feedback and informed decision-making.
Furthermore, the role of pre-sales visualization is paramount; our renderings serve as a bridge between concept and reality, instilling confidence in projects and attracting investment long before construction begins. This process not only produces essential income but also maintains historical legacy by honoring creativity through detailed 3D interior renderings.
The integration of VR enhances the architect-client relationship, fostering a deeper understanding of design intent and addressing potential concerns early in the process. As VR technology continues to advance, the guide to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations will illustrate how its applications in architectural presentations will expand, making it imperative for architects to adopt and refine this innovative approach. Our commitment to building lasting partnerships is reflected in the honest feedback we receive from customers, such as one individual who stated, ‘The VR experience allowed us to visualize our project in a way we never thought possible, making us feel confident in our investment.’
These testimonials underscore our emphasis on dependable service and creative problem-solving, further aligning customer vision with expert execution. The effective application of such technology not only enhances the experience but also satisfies the increasing demands of customers for immersive involvement, marking a crucial transformation in communication strategies within the field.
A notable example is the successful use of VR technology in the creation of the VR Star Theme Park in China, which opened in 2018 and featured over 40 VR rides. This case demonstrates the potential for VR to improve user engagement and satisfaction, which aligns with the guide to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations by emphasizing the significance of incorporating such technologies into design.
Practical Applications and Benefits of VR in Architecture
Virtual reality (VR) serves as a guide to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations by transforming numerous phases of architectural projects and offering inventive solutions that improve both planning processes and customer interactions. Key applications include:
Design Review: Utilizing VR for design reviews transforms the feedback process.
Architects can involve customers in immersive environments where real-time modifications are not only possible but encouraged. This collaborative approach fosters communication and serves as a guide to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, aligning closely with the immersive impact of architectural visualization and allowing for a deeper connection between potential residents and their future homes. By actively participating in shaping their living spaces, individuals contribute to a sense of ownership and community, setting the foundation for strong community ties.Customer Involvement: The use of VR significantly improves customer interaction during demonstrations.
The guide to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations demonstrates that by allowing users to navigate and explore virtual spaces, the feedback received is considerably more detailed and insightful than traditional presentation methods can elicit. This corresponds with the advantages of 3D visualizations in architecture, providing a guide to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, as immersive experiences enhance customer satisfaction and engagement throughout the development process.
The precision and detail captured in exterior renderings not only help individuals visualize the design essence but also create an emotional connection to the project, reinforcing their sense of belonging within the community. The guide to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations highlights how VR serves as a potent marketing tool, allowing prospective customers to experience projects before their physical realization. This capability is particularly impactful in real estate developments, where immersive walkthroughs can generate substantial interest and drive sales.
Statistics show that the Asia Pacific region accounted for 40% of the VR revenue share in 2021, reflecting the growing demand for such applications in the industry. The detailed renderings act as a guide to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, supporting effective storytelling, enhancing the marketing narrative, and assisting customers in envisioning their future within the community.
- Training and Education: VR also plays a pivotal role in training and education for architects and students alike.
It offers a regulated setting for investigating intricate structures and comprehending spatial dynamics, essential for cultivating proficiency in building practices. The focus on accuracy and intricacy during the training stage reflects the meticulous creation of 3D visualizations, guaranteeing that future architects are proficient in both the technical and emotional dimensions of creation.
Incorporating VR into building workflows serves as a guide to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, offering considerable advantages such as improved customer satisfaction, a decrease in modifications, and heightened precision. As articulated by Jasmine Katatikarn, founder of the Academy of Animated Art, who brings over 20 years of experience in feature animation and VFX, the application of VR technologies is crucial for future architectural practices. Her insights serve as a guide to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, showcasing how VR improves collaborative creation processes and customer involvement.
Furthermore, case studies such as Boeing’s implementation of mixed-reality solutions demonstrate tangible outcomes, including a 20% decrease in maintenance time and a 15% increase in operational efficiency. Furthermore, emerging technologies such as the wearable soft technologies for haptic sensing and feedback, studied by Yin et al., enhance VR’s capabilities, offering architects innovative tools for improved experience. As architects increasingly embrace VR technology, they will find a guide to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, revealing capabilities that go well beyond simple showcases and fundamentally altering the creative process while nurturing a collaborative spirit that aligns closely with customer visions.
Integrating VR into Your Workflow
Integrating Virtual Reality (VR) into your architectural workflow requires a structured approach, which can be found in the guide to The impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, complemented by the expertise of J. Scott Smith Visual Designs. Here are the essential steps to achieve this integration effectively:
Assess Your Needs: Conduct a thorough evaluation of your projects to identify where VR can offer the most value. Examine aspects such as client showcases, review sessions, and marketing initiatives in the guide to The impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, where immersive visualization can improve engagement and comprehension. Partnering with J. Scott Smith Visual Designs can help visualize and validate your concepts from the outset.
Select Appropriate Software: Choose VR software that is compatible with your existing design tools and workflows. Leading options include:
- Autodesk Revit paired with Enscape for photorealistic renderings
- SketchUp integrated with V-Ray for enhanced visualization
Unreal Engine for creating fully immersive environments
Each of these platforms offers unique features that can significantly enhance your displays, drawing on the detail-driven 3D architectural visualizations provided by our team.Invest in Suitable Hardware: Acquire the necessary VR hardware to facilitate seamless integration. High-performance VR headsets, such as the Oculus Rift and HTC Vive, should be complemented by computers equipped with robust graphics processing units (GPUs) capable of handling complex 3D rendering tasks without latency.
Develop VR Content: Begin the process of creating VR content by exporting your 3D models into your chosen VR software. Familiarize yourself with the specific tools and settings of the software to ensure optimal performance and visual fidelity in the VR environment. Our preliminary renderings can serve as a foundation for this content development.
Test and Iterate: Before showcasing to stakeholders, perform thorough testing of your VR outputs with internal teams. Solicit constructive feedback and implement necessary modifications to refine the user experience. This iterative process will ensure that your displays are refined and impactful, improving stakeholder engagement and clarity.
Leverage Real-Time Monitoring: Utilize VR for real-time monitoring of projects, which helps identify discrepancies early, allowing for prompt corrective actions. This proactive method, in conjunction with iterative renderings based on customer feedback, can significantly enhance project outcomes.
Explore Case Studies: Referencing case studies, such as “Architecture and Ethnography,” can illustrate the relationships between architecture and VR, showcasing how ethnographic perspectives can enhance architectural presentations and the integration of VR technology. Storytelling through our 3D renderings translates your vision into clear visuals, fostering stronger relationships.
By following the guide to The impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations and working together with J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, architects can effectively incorporate VR into their workflows, significantly enhancing both creative processes and client interactions. Contact us today to arrange a consultation and discover how we can assist in bringing your concepts to life.
Future Trends in Architectural Visualization with VR
As virtual reality technology advances, several pivotal trends are set to redefine architectural visualization:
Enhanced Interactivity: Future applications of virtual reality are set to provide unparalleled levels of interactivity, enabling users to alter layouts in real-time during presentations. This capability not only boosts engagement but also cultivates a deeper sense of personalization in the creation process, reflecting our dedication to a collaborative rendering approach at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, which encompasses initial communication and project briefs to fully comprehend user needs.
Integration of Augmented Reality: The synergy of virtual reality with augmented reality (AR) will empower architects to seamlessly overlay digital models onto real-world environments. This innovative method provides customers a unique viewpoint, demonstrating how suggested concepts blend with current environments and improving spatial awareness, which is essential for effective communication and detail modeling in our projects.
Role of AI and Machine Learning: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning is likely to revolutionize architectural planning processes by automating repetitive tasks and providing intelligent recommendations customized to user preferences and current architectural trends. This evolution could streamline workflows, allowing architects to focus on more creative aspects of their projects, while also enhancing the lifelike quality of CG humans in visualizations to overcome the uncanny valley.
Cloud-Based VR Solutions: As cloud technology advances, architects will benefit from improved capabilities to share immersive VR experiences remotely with users. This advancement in accessibility will facilitate collaboration across geographic boundaries, enabling more inclusive design discussions, much like our approach to ensuring smooth communication throughout the rendering process, where we emphasize prompt feedback and a single point of contact for project representation.
Privacy Concerns: As immersive technologies become more prevalent, privacy concerns related to data collection and user tracking must be addressed. Transparent data usage policies are essential to maintain customer trust and ensure compliance with regulations.
By remaining attuned to these emerging trends, architects can harness the potential of innovative technologies, such as virtual reality, as a guide to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, ultimately delivering cutting-edge presentations that resonate profoundly with customers. The implementation of these technologies is already evident in various sectors, including architecture, where firms like Program-Ace have successfully completed over 900 projects, offering a guide to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations. With nearly 120,000 licensed architects across 55 U.S. jurisdictions, as reported by The Architect’s Newspaper, the relevance of these trends cannot be overstated.
Furthermore, the case study on Mixed Reality (MR) and Extended Reality (XR) illustrates how these technologies blend physical and digital realities, creating environments where physical and digital objects interact in real time, further enhancing visualization.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of VR in Architecture
Numerous architectural firms have effectively integrated virtual reality (VR) into their operational frameworks, producing remarkable outcomes that enhance both customer engagement and precision in creation.
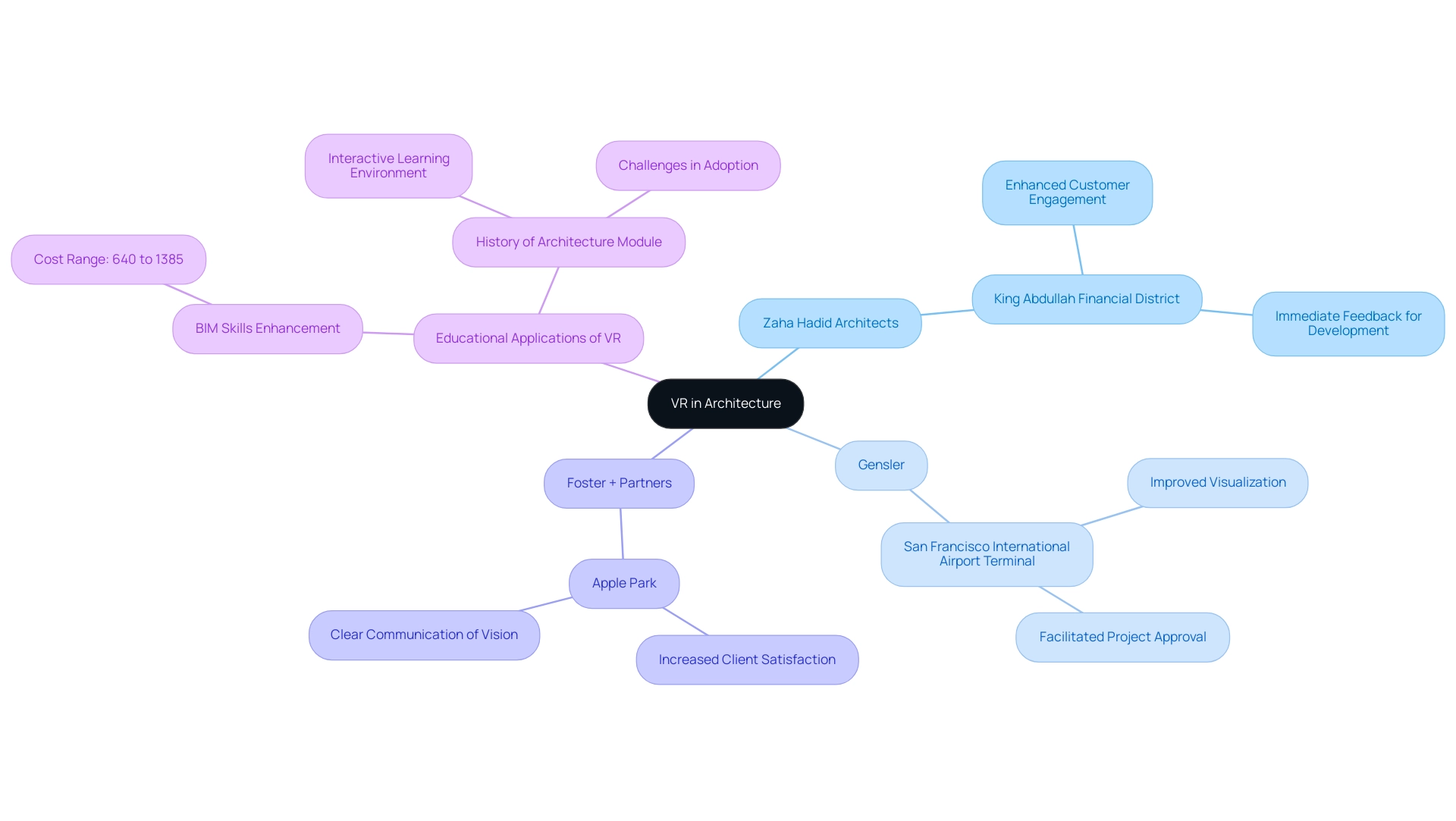
Zaha Hadid Architects: This firm harnessed the capabilities of VR in the presentation for the King Abdullah Financial District in Saudi Arabia. By enabling customers to explore the project in a virtual environment, the firm obtained immediate feedback that greatly impacted later development iterations.
Gensler: At Gensler, VR was crucial in the planning process for the new terminal at San Francisco International Airport. The immersive experience provided stakeholders with a clear visualization of the terminal’s flow and aesthetics, facilitating project approval through enhanced understanding and engagement.
Foster + Partners: This firm utilized VR to elevate presentations for Apple Park in Cupertino. By allowing patrons to explore the campus within a virtual setting, Foster + Partners effectively communicated the overarching vision and intent, leading to enhanced satisfaction and clarity.
At J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, our collaborative rendering process reflects these successful strategies. From initial communication and detailed project briefs, we establish a strong foundation for understanding customer needs and design specifics. Our skilled artists meticulously create detailed 3D models, ensuring high levels of accuracy and flexibility throughout the rendering process.
This encompasses the meticulous choice of materials and lighting, which are essential in attaining a realistic visual experience that corresponds with the vision of the customer. By actively engaging customers in feedback cycles with clay renderings and progress updates, we cultivate a collaborative atmosphere that highlights customer involvement and satisfaction.
As Jonghoon Kim points out, VR’s economic feasibility in design, engineering, and construction education is considerable, emphasizing its potential to change not only customer showcases but also educational approaches. Furthermore, statistics show that collaborative VR for enhancing Building Information Modeling (BIM) skills in construction management classrooms has total costs ranging from 640 to 1385, illustrating the financial implications of adopting this technology. Additionally, the case study on the History of Architecture module demonstrates how VR can foster interactive learning environments, moving beyond user engagement to enhance educational experiences.
This underscores the transformative power of VR in architectural presentations and education, which serves as a guide to the impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations by demonstrating its ability to enhance client interactions and lead to superior design outcomes. As VR technology continues to evolve, its applications in architecture are poised to expand further, promising even greater advancements in the field.
Conclusion
The integration of virtual reality (VR) into architectural presentations represents a profound shift in how architects communicate and collaborate with clients. By moving beyond traditional 2D and 3D models, VR provides an immersive platform that enhances client engagement and facilitates a deeper understanding of design intent. The article outlines the myriad applications of VR, from design reviews and client interactions to marketing initiatives, illustrating how this technology not only streamlines workflows but also fosters a collaborative atmosphere that aligns closely with client visions.
The benefits of VR extend beyond mere visualization; they encompass improved client satisfaction, reduced design revisions, and increased accuracy in project execution. As highlighted through case studies of leading firms such as Zaha Hadid Architects and Gensler, the successful implementation of VR can significantly influence design outcomes and enhance stakeholder engagement. Additionally, the future trends discussed—such as enhanced interactivity, the integration of augmented reality, and the role of AI—indicate that the potential of VR in architecture is still expanding.
As architects look to elevate their practice, adopting VR technology becomes an imperative strategy. This innovative approach not only meets the growing expectations of clients for immersive experiences but also positions firms at the forefront of architectural communication and collaboration. Embracing these advancements will undoubtedly lead to more successful projects and stronger client relationships, ultimately redefining the architectural landscape for years to come.

0 Comments