Introduction
Architectural rendering stands at the intersection of artistry and technology, serving as a vital conduit between abstract design concepts and tangible visual experiences. In an era where digital advancements continuously reshape the architectural landscape, the ability to create compelling visualizations is paramount. This article delves into the multifaceted world of architectural rendering, exploring its significance in communication, the transformative impact of AI, and the essential tools that facilitate this intricate process.
From the initial stages of conceptualization to the final polish of photorealistic images, understanding the nuances of rendering not only enhances client engagement but also elevates the overall quality of architectural practice. As the industry evolves, so too must the techniques and technologies employed, ensuring that architects remain at the forefront of innovation and creativity in their visual storytelling.
Understanding Architectural Rendering: An Overview
An architectural rendering sketch in architecture represents both an art and a science, crafting two-dimensional images or animations that vividly showcase the attributes of proposed designs. This practice is essential for effective communication, as it enables architects and clients to visualize spaces using an architectural rendering sketch prior to the commencement of construction. In today’s digital landscape, AI is revolutionizing this field by creating lifelike CG humans that help bridge the uncanny valley, significantly enhancing architectural visualizations.
For instance, these realistic representations can evoke emotional responses from viewers, making the visualizations more relatable and impactful. Moreover, the role of lighting cannot be overstated; contrasting artificial interior lighting with natural sunlight in exteriors not only improves realism but also enhances the overall story of the endeavor. Pre-sales visualization acts as a strong instrument for building trust in an initiative, enabling developers to showcase images as concrete assets that can spark interest and funding even prior to construction starting.
Detailed interior visuals showcase functionality and aesthetics, directly contributing to client satisfaction and effective marketing strategies. Significantly, a case study on Digital Asset Management (DAM) demonstrates that numerous architecture firms are employing cloud-based collaboration tools for task coordination, connecting the significance of visualization techniques to wider industry practices. With 35,621 candidates actively pursuing licensure, it is clear that design visualization plays a crucial role in the professional advancement of architects and the industry’s growth.
A comprehensive understanding of different styles, from architectural rendering sketches to highly photorealistic images, empowers architects to select the most suitable approach for each project. As the terrain of building visualization evolves, adopting these techniques is essential for providing engaging visual stories that connect with stakeholders, ultimately improving the design experience.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Stunning Architectural Renderings
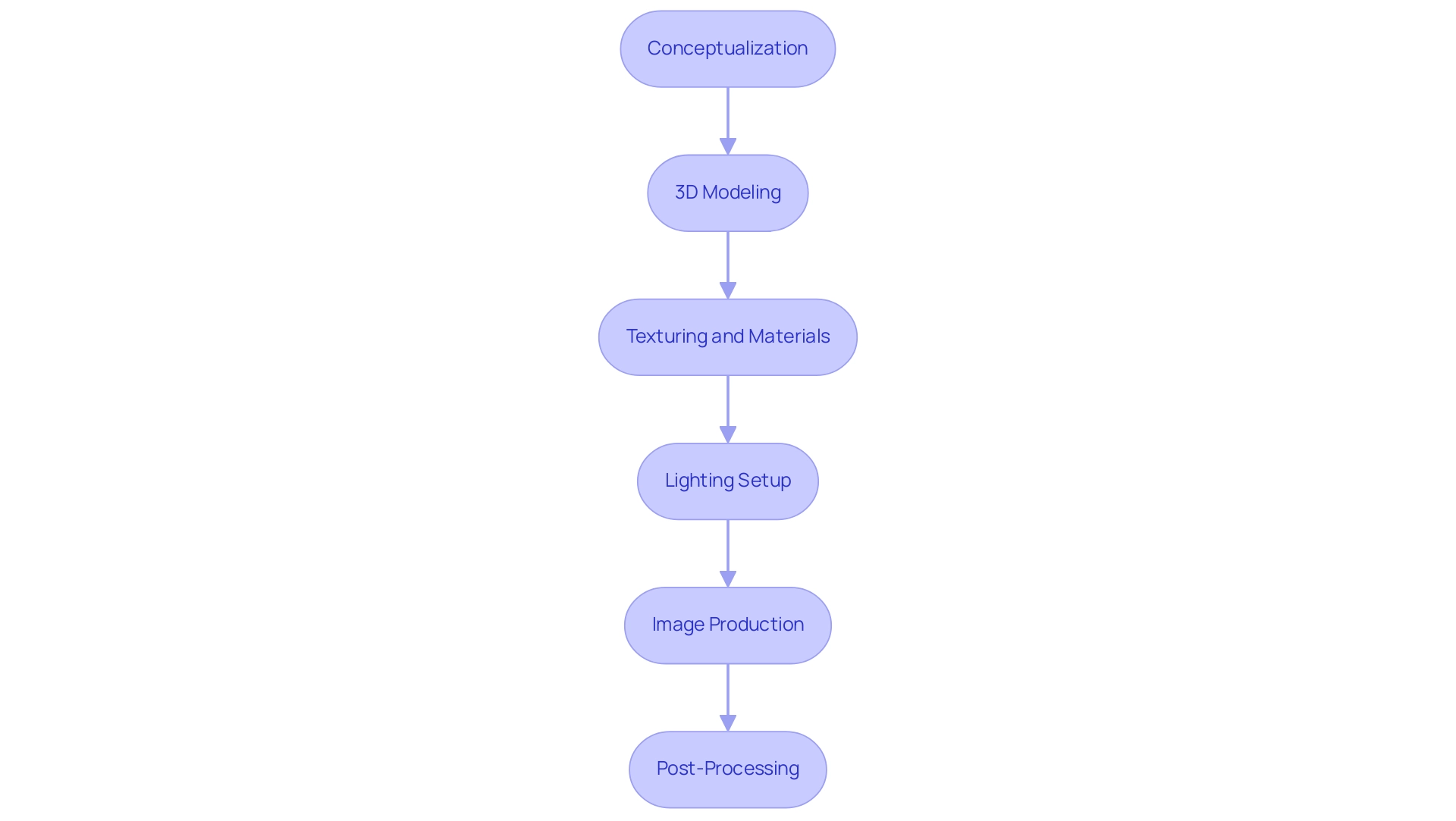
Conceptualization: The rendering process starts with thorough information collection, which includes floor plans, creative intentions, and stakeholder requirements. Initial sketches should be created to explore various layout options, ensuring a foundation for informed decision-making that captures the essence of the design.
3D Modeling: Utilizing advanced software such as SketchUp or Revit, architects can construct a precise 3D representation of the project. Attention to detail is crucial at this stage; dimensions and proportions must be meticulously verified to maintain architectural integrity and ensure accuracy in renderings.
Texturing and Materials: The application of textures and materials to the 3D model is vital for achieving realism. Choosing finishes that precisely represent the final vision fosters a more engaging and credible representation, enhancing client understanding and improving stakeholder communication. Tiny details in textures and materials play a significant role in telling the story of the design, adding depth and character to the visual output.
Lighting Setup: Proper lighting is essential for enhancing the mood and atmosphere of the visualization. Consideration should be given to both artificial and natural light sources, analyzing how they interact with the architectural elements to create a dynamic visual experience that aligns with the client’s vision.
High-quality images are produced using powerful visualization software, including V-Ray and Lumion. Adjusting settings for detail and realism is paramount, as these final outputs serve as critical tools for client presentations and marketing, facilitating communication and ensuring all stakeholders are on the same page. The level of detail displayed in these illustrations should be tailored to the audience’s needs, ensuring clarity and effective visualization of the design.
Post-Processing: The final step involves refining the rendered images using editing software such as Photoshop. This stage allows for enhancements in color, contrast, and the inclusion of additional elements, ultimately culminating in a polished visual that effectively communicates the design’s essence. Successful design visualization projects demonstrate a commitment to quality at each of these stages. As Hetherington Newman observed, they were pleased with the intermediate results, so we proceeded with the design process, highlighting the significance of iterative feedback and client collaboration in achieving desired outcomes. Moreover, Matterport Virtual Staging services begin at $25.00, demonstrating the cost-efficiency of design visualization. A relevant case study is the Salt Art Gallery in Turkey, which employs unique designs created by different designers every four months to enhance its visual identity and client engagement. This strategic method illustrates how presentation design section depiction can create a memorable brand voice and foster client satisfaction.
Essential Tools and Software for Architectural Rendering
Producing breathtaking architectural rendering sketches necessitates an adept combination of software and hardware tailored to the demands of the profession. With 64% of staff architects majoring in architecture, the importance of these tools for professionals in the field cannot be overstated. Superior visual representations, such as an architectural rendering sketch, play a vital role in development, offering essential clarity that supports informed decision-making and amplifies emotional impact through intricate details.
These architectural rendering sketches provide a glimpse into the future of your project, enabling stakeholders to envision the result and connect emotionally with the concept. The subsequent categories are crucial to the creation process:
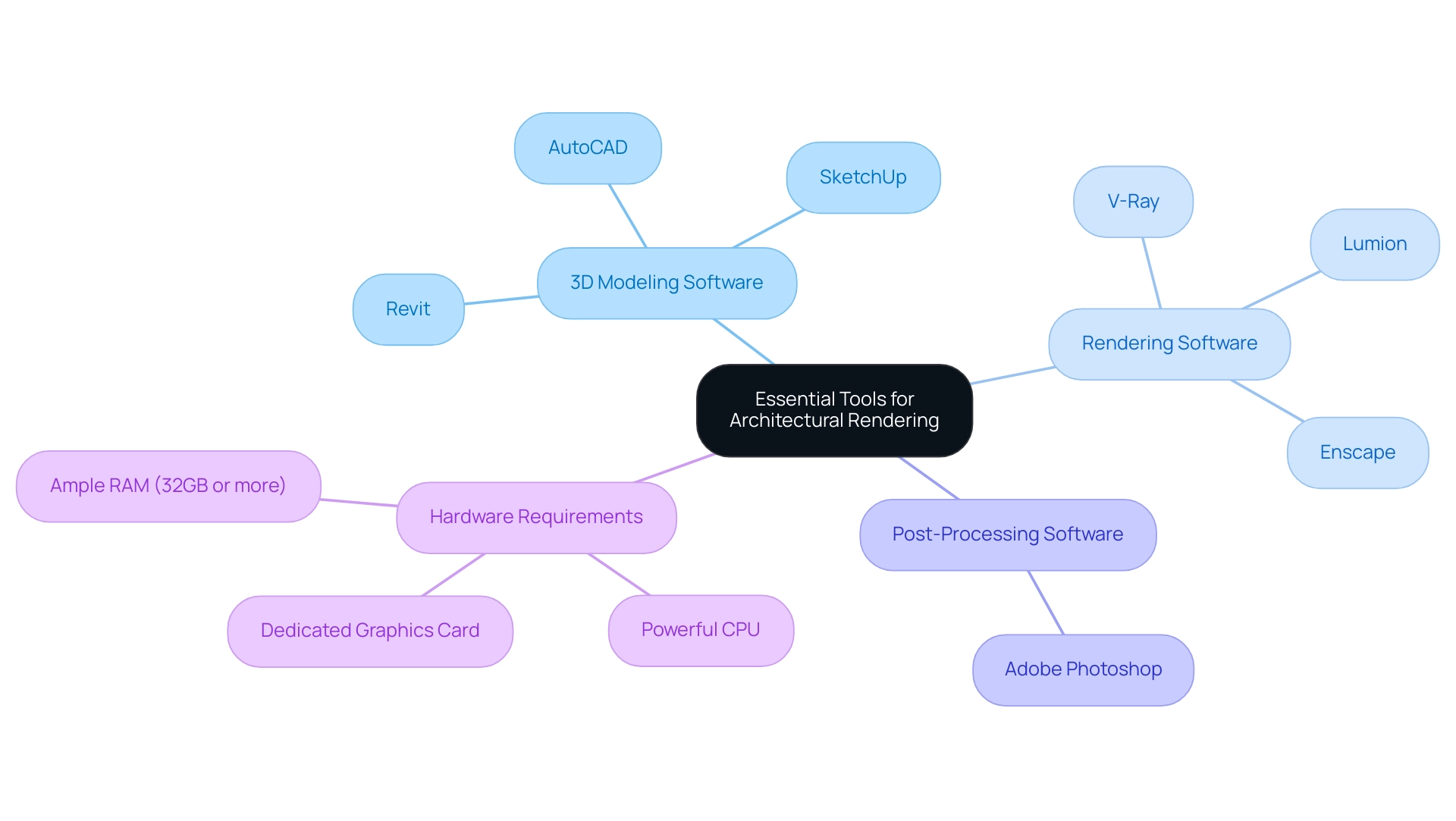
- 3D Modeling Software: Essential tools such as AutoCAD, SketchUp, and Revit are foundational for crafting accurate building models. These applications enable architects to visualize their creations in a three-dimensional space, facilitating better spatial understanding and accuracy.
- Rendering Software: For impressive visual outputs, V-Ray, Lumion, and Enscape stand out as leading choices. These visualization engines are famous for their capacity to create architectural rendering sketches that showcase realistic lighting, textures, and materials, bringing design concepts to life. Notably, 28% of architects, engineers, contractors, owners, and investors report that most of their building projects qualify as green, with 42% anticipating reaching that level within the next three years, emphasizing the need for tools that can effectively showcase sustainable designs.
- Post-Processing Software: Adobe Photoshop remains a staple in the architectural visualization field, widely used for final enhancements. Its capabilities in color correction, detail refinement, and image compositing are invaluable for achieving polished, professional results. The incorporation of crucial software for AEC marketing, as showcased in case studies, illustrates how these tools improve the quality and effectiveness of architectural rendering sketches and marketing materials in architecture firms.
- Hardware Requirements: A robust workstation is vital for managing intricate visualization tasks efficiently. Key specifications include a powerful CPU, ample RAM (ideally 32GB or more), and a dedicated graphics card, which collectively ensure smooth operation during intensive processing tasks. This hardware setup enables designers to manage complex models and high-resolution visuals without sacrificing performance.
As the market for design visualization continues to develop, remaining updated on architectural rendering sketch tools and their specifications is essential for any lead designer aiming to provide impactful presentations and enhance business efficiency through informed outsourcing choices. Outsourcing 3D design visualization can offer access to specialized skills, shorten timelines, and enable architects to concentrate on core design tasks, ultimately improving overall efficiency.
The Role of Photorealism in Architectural Renderings
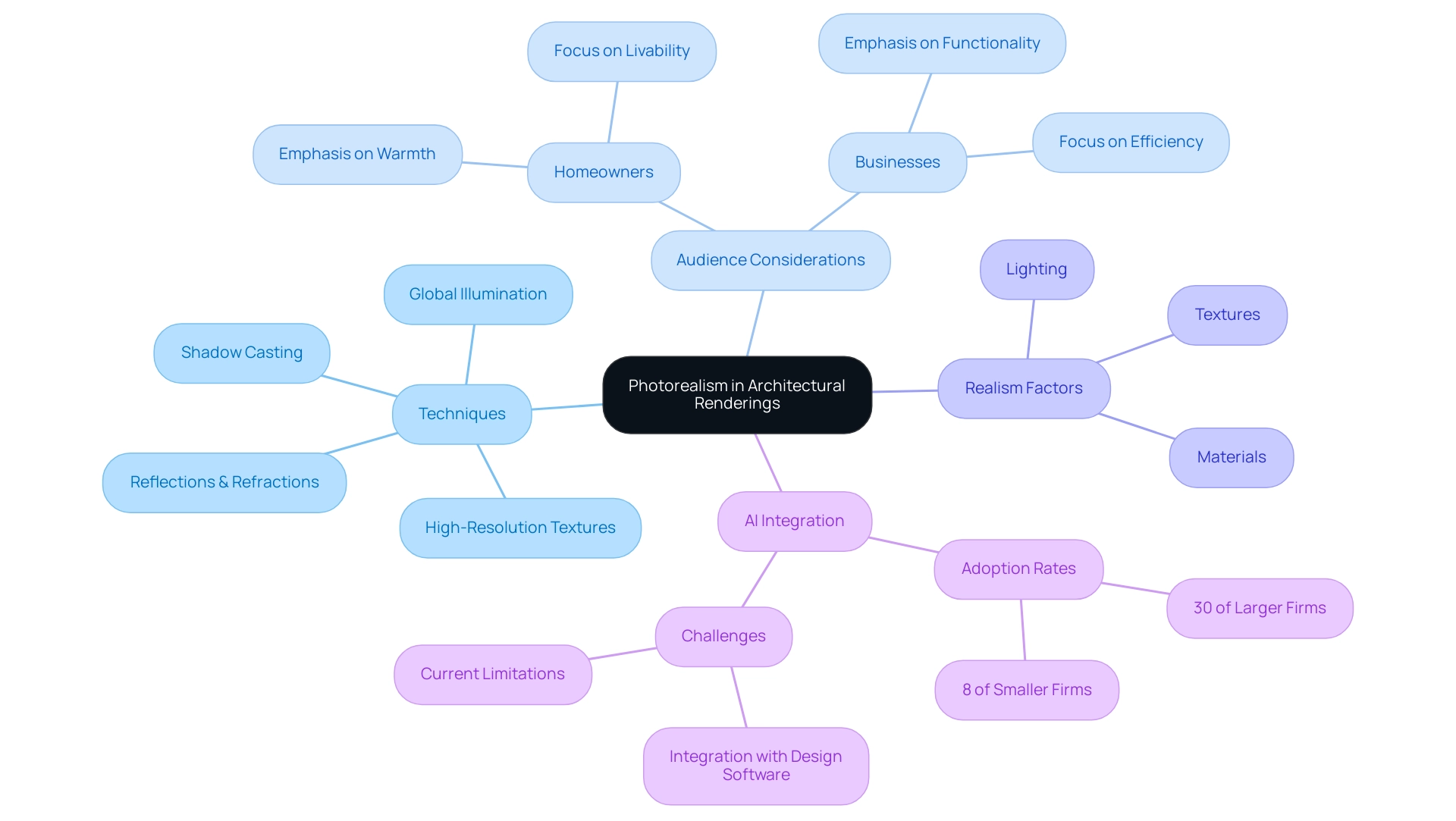
Photorealism in architectural rendering sketch aims to create images that closely mimic real-life photographs, which is an increasingly crucial standard in the architectural field. Achieving such lifelike detail necessitates meticulous attention to various elements, including lighting, materials, and textures. Advanced techniques such as global illumination enhance realism by simulating natural light, while accurate shadow casting adds depth and dimension to the scene.
The use of high-resolution textures ensures that surfaces appear authentic and tactile. Furthermore, intricate details—from the way sunlight dances off windows to the subtle texture of bricks—play a pivotal role in enhancing realism and emotional impact, making a project feel lived-in and ready to be built. It is crucial to identify the suitable level of detail according to the target audience; for homeowners, visuals should emphasize the warmth and livability of areas, whereas for businesses, an emphasis on functionality and efficiency may be more pertinent.
Incorporating complex elements like reflections and refractions significantly boosts the overall realism of the rendering. By mastering these photorealistic techniques, architects can produce an architectural rendering sketch that conveys their intentions with clarity, ultimately fostering confidence in clients and stakeholders. As Kalina Prelikj, Editorial Assistant at Architizer, observes, the capacity to honor outstanding creations is grounded in the accuracy of visual representation, highlighting the significance of photorealism in accomplishing this aim.
In a landscape where approximately 86% of architects express confidence in AI’s transformative potential, mastering photorealism becomes not just an artistic endeavor but a strategic necessity to secure approvals and align with evolving professional standards. However, challenges persist, especially concerning the integration of AI with design modeling software, which architects must navigate to fully utilize the advantages of these advanced visualization techniques. Our passion for capturing these details ensures that every element contributes to a larger picture, making the project not only visually appealing but also emotionally resonant.
Overcoming Challenges in Architectural Rendering
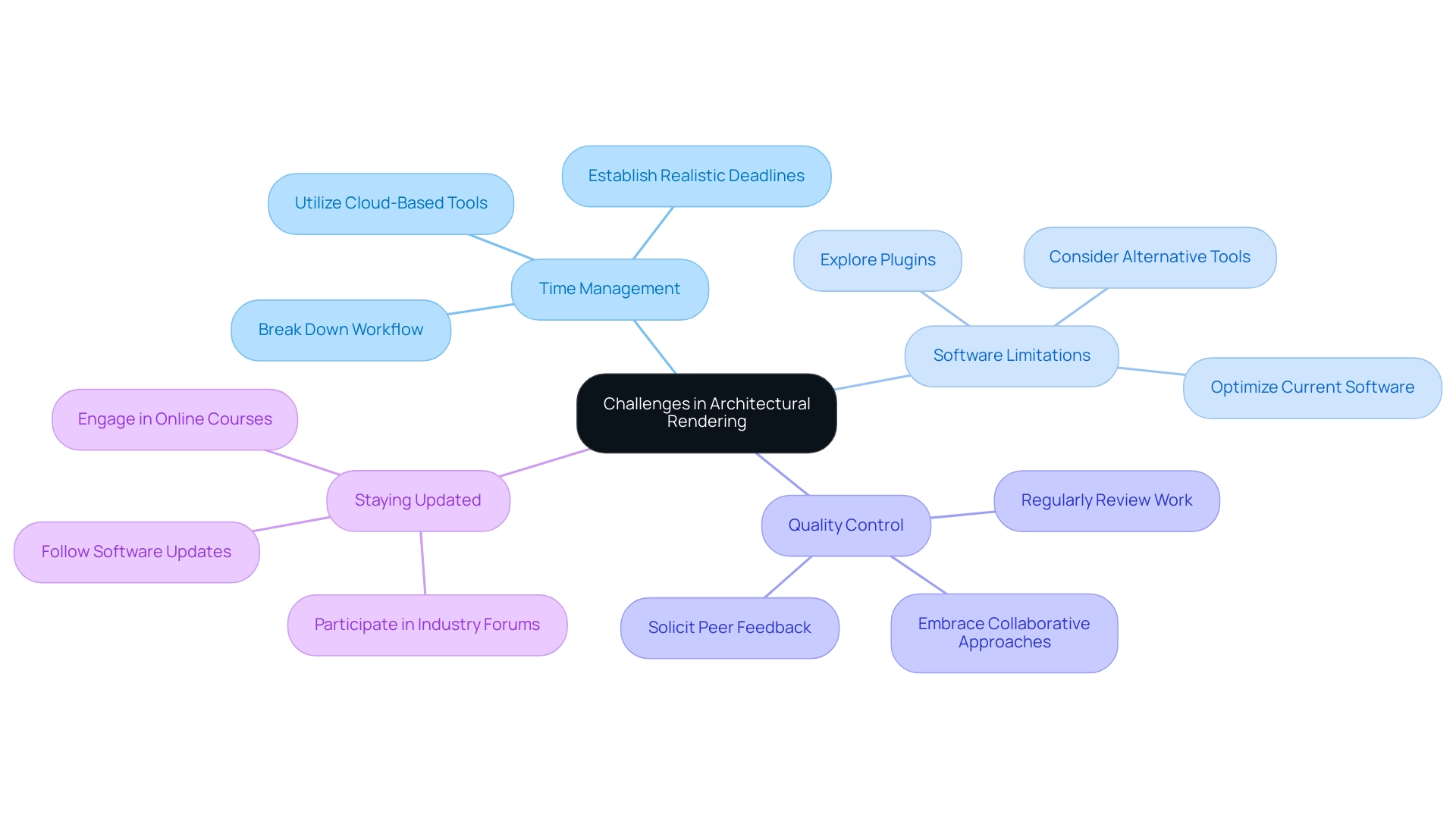
The challenges presented by architectural visualization can be addressed through strategic approaches, particularly in creating an architectural rendering sketch. Key issues include:
Time Management: The rendering process often demands considerable time investment. To enhance efficiency, break down the workflow into manageable tasks and establish realistic deadlines. Utilizing 3D visualizations facilitates clearer communication between designers and clients, leading to quicker buy-in and significantly reducing costly changes later. Statistics reveal that effective time management can enhance outcomes, making this a crucial focus area for architects. In fact, cloud-based collaboration tools are utilized by 62% of architecture firms for project coordination, underscoring the importance of technology in managing design projects.
Software Limitations: Understanding the capabilities and limitations of your processing software is vital for optimizing your workflow. Explore different plugins or alternative tools that could enhance your current software, thereby broadening your creative capabilities and boosting productivity. Top-notch architectural rendering sketches can assist in simplifying the creation process and ensure projects progress seamlessly from idea to finalization.
Quality Control: Ensuring the accuracy and detail of your visuals is essential. Regularly review your work and solicit feedback from peers to identify areas for enhancement. This collaborative approach not only fosters continuous improvement but also aligns with the benefits of early design issue resolution, ultimately elevating the overall quality of your designs. As Kalina Prelikj notes, embracing a multifaceted approach to architecture can enhance creative outputs, making collaboration even more valuable. The intricate details captured in architectural rendering sketches, from sunlight reflections to textural nuances, enhance realism and emotional impact, making projects feel ready to be constructed.
Staying Updated: The realm of architectural visualization is in constant flux, with new techniques and software updates emerging regularly. To maintain a competitive edge, engage in online courses and participate in industry forums that discuss recent advancements. This commitment to lifelong learning will empower you to leverage the latest innovations effectively. The case study titled “Understanding the Concept of 3D Visualization and its Role in Modern Design” illustrates how 3D visualization is a critical component of contemporary design practices, influencing how architects and designers operate, leading to greater efficiency and creativity in design processes.
Confronting these challenges head-on is pivotal for architects aiming to refine their rendering practices and achieve superior project outcomes.
Conclusion
Architectural rendering is an indispensable tool that merges artistic vision with technological precision, facilitating clear communication between architects and their clients. The exploration of rendering techniques, from initial conceptual sketches to the refinement of photorealistic images, underscores the importance of this discipline in enhancing client engagement and elevating architectural practices. The integration of advanced software and AI-driven solutions not only streamlines the rendering process but also empowers architects to create compelling visual narratives that resonate with stakeholders.
As the architectural landscape continues to evolve, mastering the intricacies of rendering becomes essential for professionals striving to remain at the forefront of innovation. By overcoming challenges such as:
- Time management
- Software limitations
- The need for quality control
architects can refine their rendering practices and deliver superior outcomes. Continuous learning and adaptation to new technologies will further enhance the efficacy of architectural renderings, ensuring that they not only meet but exceed the expectations of clients and the market.
Ultimately, the ability to produce stunning architectural visualizations is not merely a reflection of technical skill but a strategic imperative that influences project success and stakeholder confidence. Embracing the full spectrum of rendering techniques and tools will empower architects to tell their design stories with clarity and impact, solidifying their role as leaders in an ever-evolving industry.

0 Comments