Introduction
Architectural rendering stands as a pivotal element in the design process, transforming abstract concepts into vivid visual narratives that facilitate communication between architects, clients, and stakeholders. This intricate process involves the generation of two-dimensional images or animations from three-dimensional models, necessitating a deep understanding of several core principles.
Mastery of perspective, lighting, materials, and composition is essential for producing renderings that not only convey the intended design but also evoke an emotional response from the viewer. As the architectural landscape evolves, so too does the technology and methodologies employed in rendering, with advancements such as virtual reality and artificial intelligence reshaping the field.
This article delves into key concepts, best practices, and innovative techniques that architects must embrace to enhance their rendering capabilities and meet the growing demands of a competitive market.
Understanding Architectural Rendering: Key Concepts and Techniques
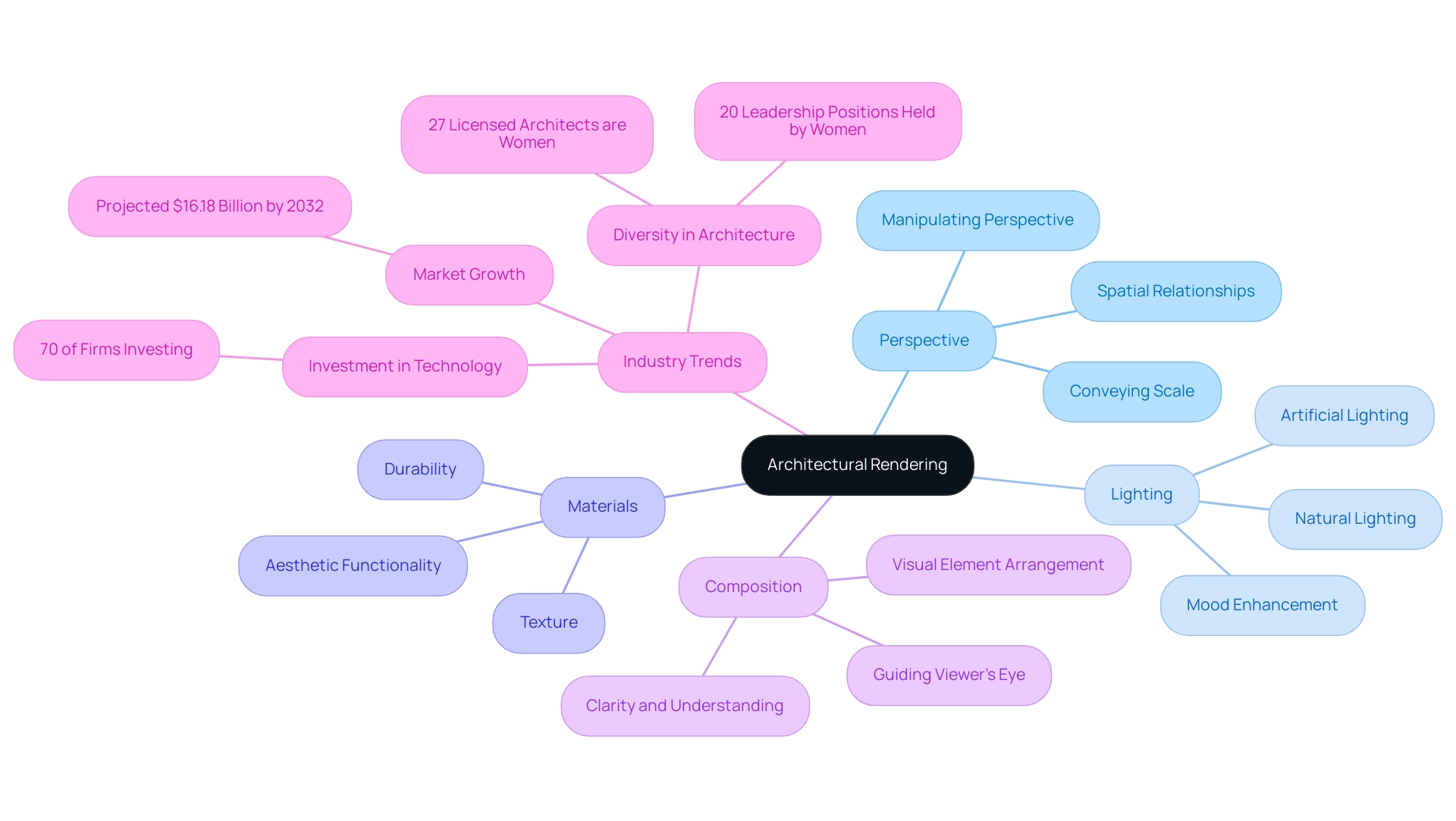
Architectural visualization is the process of generating two-dimensional images or animations from three-dimensional models, serving as a crucial tool for visualizing designs. Mastery of several key concepts is essential for creating high-quality visuals:
- Perspective: A critical skill is the ability to manipulate perspective effectively, as this creates a sense of depth and realism within the visuals. This technique allows architects to convey scale and spatial relationships accurately, which is vital for both homeowners and businesses in understanding the potential of their spaces. For homeowners, a more intimate perspective may be beneficial, while businesses might require broader views to showcase entire developments.
- Lighting: Both natural and artificial lighting play pivotal roles in visualization. Understanding how to utilize lighting not only enhances the mood but also adds realism to the final product, influencing the viewer’s emotional response. This is particularly important when contrasting artificial lighting in interiors with natural sunlight in exteriors, which can significantly affect the perception of a space. For instance, interior visualizations may focus on how light interacts with furniture and finishes, while exterior images emphasize the impact of sunlight on the building’s facade.
- Materials: The selection and application of textures that closely mimic real-world surfaces are paramount. This attention to detail helps to convey the intended aesthetic and functionality of the design, emphasizing the durability and texture of materials, which is crucial for stakeholder communication and decision-making. Homeowners might prioritize materials that reflect personal style, while businesses may focus on durability and cost-effectiveness.
- Composition: Thoughtful composition involves arranging visual elements to guide the viewer’s eye strategically, accentuating the structural features and narrative of the design. This plays a key role in enhancing clarity and understanding for all stakeholders involved. Various compositions might be utilized for residential compared to commercial projects to emphasize distinct characteristics pertinent to each audience.
Understanding these fundamental concepts creates a solid basis for architectural rendering engaging visual representations. As the market for digital asset management is projected to reach $16.18 billion by 2032, and with 70% of architecture firms planning to invest more in technology within the next 12 months, mastering these visualization techniques is more significant than ever. Furthermore, with 35,621 candidates actively working on licensure, as reported by The Architect’s Newspaper, the profession in architecture is witnessing considerable growth, underscoring the importance of these skills.
Interacting with these trends not only improves the technical quality of visualizations but also corresponds with the changing expectations within the design sector. Additionally, it is essential to recognize the ongoing disparities in the architecture industry; while women make up 27% of licensed U.S. architects, they hold only 20% of leadership positions in architecture firms, highlighting the need for diversity and inclusion in this evolving landscape.
Best Practices for Creating Photorealistic Architectural Renderings
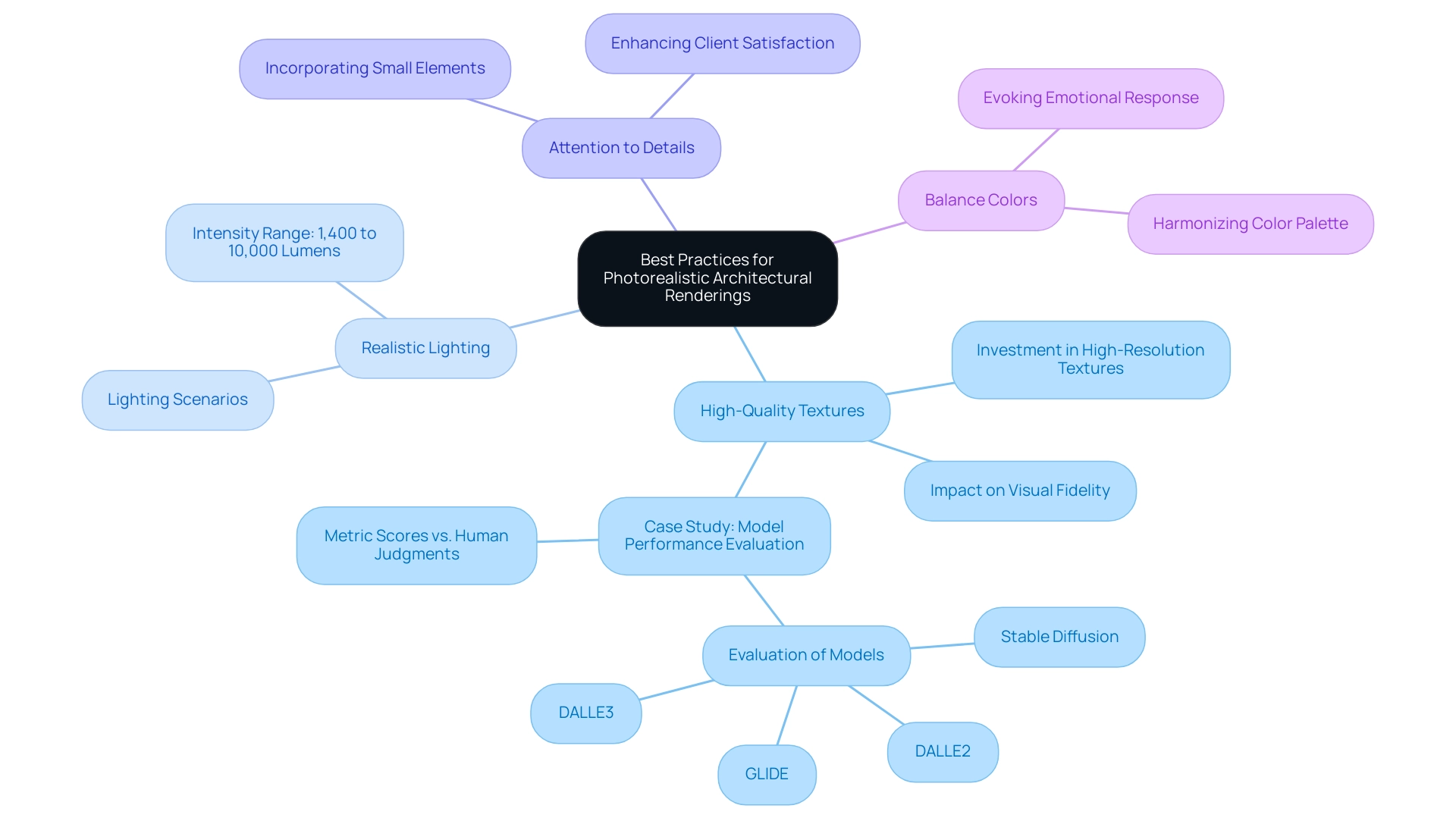
Achieving photorealistic results in architectural renderings necessitates adherence to several best practices that refine both quality and realism:
- Use High-Quality Textures: Prioritize investment in high-resolution textures that accurately depict real-world materials. The effects of high-quality textures on visual outcomes cannot be overstated, as they significantly enhance visual fidelity and realism. Case studies, such as the Model Performance Evaluation, highlight varying levels of agreement between metric scores and human judgments, underscoring the importance of texture quality in achieving realistic renders and in influencing pricing decisions.
- Implement Realistic Lighting: Explore a range of lighting scenarios, including variations in time of day and weather conditions. Proper lighting is essential for achieving the desired atmospheric quality in your visualizations, with intensity uniformly sampled between 1,400 and 10,000 lumens. This quantitative foundation not only bolsters the discussion but also highlights the role of lighting in enhancing realism and fostering buyer confidence during pre-sales phases.
- Pay Attention to Details: Incorporating small elements such as furniture, landscaping, and human figures can vitalize your renderings. Their presence adds depth and context, transforming a static image into a dynamic visual narrative that effectively showcases functionality and aesthetics, enhancing client satisfaction and marketing effectiveness. Tiny details, in particular, contribute to storytelling by providing a glimpse into the lifestyle and environment that the design aims to create.
- Balance Colors: Utilize a well-considered color palette that harmonizes with the design, evoking the intended emotional response from the viewer.
As Patrick Hanrahan pointed out, “In this paper, we examine the current work and propose avenues for future research,” it is evident that the design visualization domain is continuously evolving. By rigorously applying these practices, your presentations will not only stand out but will also effectively convey the design intent, reflecting a high level of professionalism in visual representation and reinforcing the confidence necessary to attract investment and generate revenue.
Choosing the Right Software for Architectural Rendering
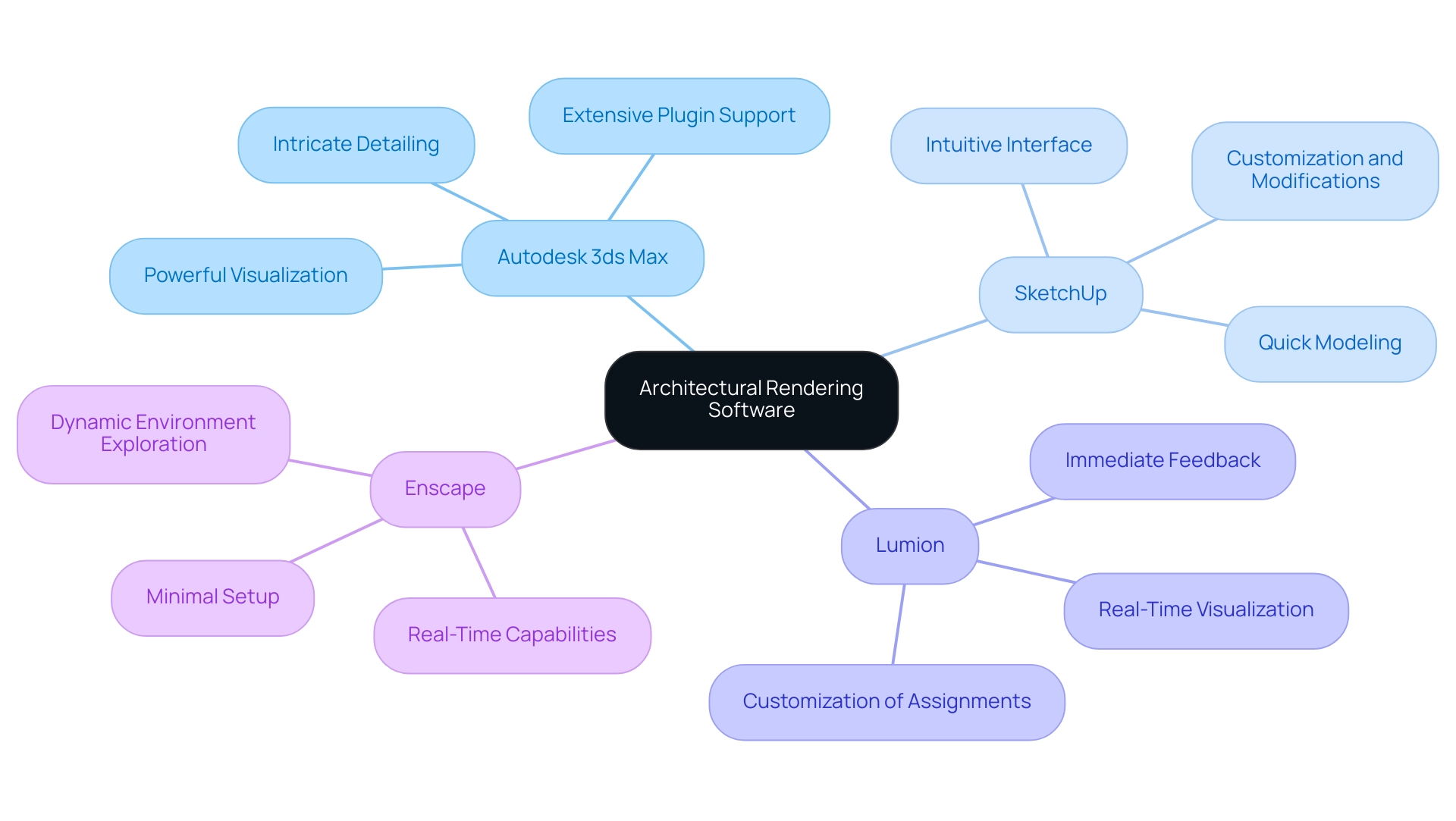
When choosing software for design visualization, it is crucial to evaluate several top alternatives that address diverse assignment needs:
- Autodesk 3ds Max: Celebrated for its powerful visualization capabilities, Autodesk 3ds Max provides extensive plugin support, making it a preferred option among experts aiming for high-quality results. Its versatility enables intricate detailing, crucial for architectural rendering engaging visualizations, thus enhancing the realism and emotional effect of works by evoking engagement through thoughtful design.
- SketchUp: This software is particularly appreciated for its intuitive interface, facilitating quick modeling. When paired with visualization plugins like V-Ray, it transforms into a powerful instrument for crafting visually attractive presentations without extensive technical know-how, accommodating tasks of varying complexity and scale while enabling easy customization and modifications that can impact investment choices.
- Lumion: A leader in the domain of real-time visualization, Lumion enables architects to make quick adjustments and receive immediate feedback, significantly improving the design process and interactions with stakeholders, particularly for intricate tasks where time is critical. Its capabilities support the customization of assignments, ensuring that unique design characteristics are effectively showcased.
- Enscape: Popular among architects for its real-time visualization capabilities, Enscape requires minimal setup and seamlessly integrates with existing workflows, enabling quick explorations of design options in a dynamic environment. This flexibility aids in personalization and modifications, which are crucial for addressing particular customer requirements and enhancing architectural rendering engaging.
As the architectural visualization market is expected to expand from $4.59 billion in 2024 to $16.18 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.0%, it is essential to assess your specific requirements—such as the intricacy of tasks and the desired output quality—to choose the most appropriate software. Each of these choices provides distinct benefits that can greatly influence project efficiency and visual quality, particularly in terms of intricate details that enhance architectural rendering engaging customer engagement and project specifications.
Additionally, advancements in visualization technology, such as the launch of the next generation AI text-to-3D generator by Meta Platforms, Inc. in July 2024, emphasize the significance of remaining current with the latest tools that can enhance visualization capabilities. Considering the diverse market segments, including various software types and organizational sizes, can also influence your software choice. For example, the incorporation of AI and machine learning in 3D visualization technology has demonstrated an improvement in performance and automation of processes, as shown in the case study on AI and Machine Learning in 3D Visualization.
This implementation is expected to improve production efficiency and image quality, pushing the boundaries of realism and creativity in digital media.
Advanced Techniques and Innovations in Architectural Rendering
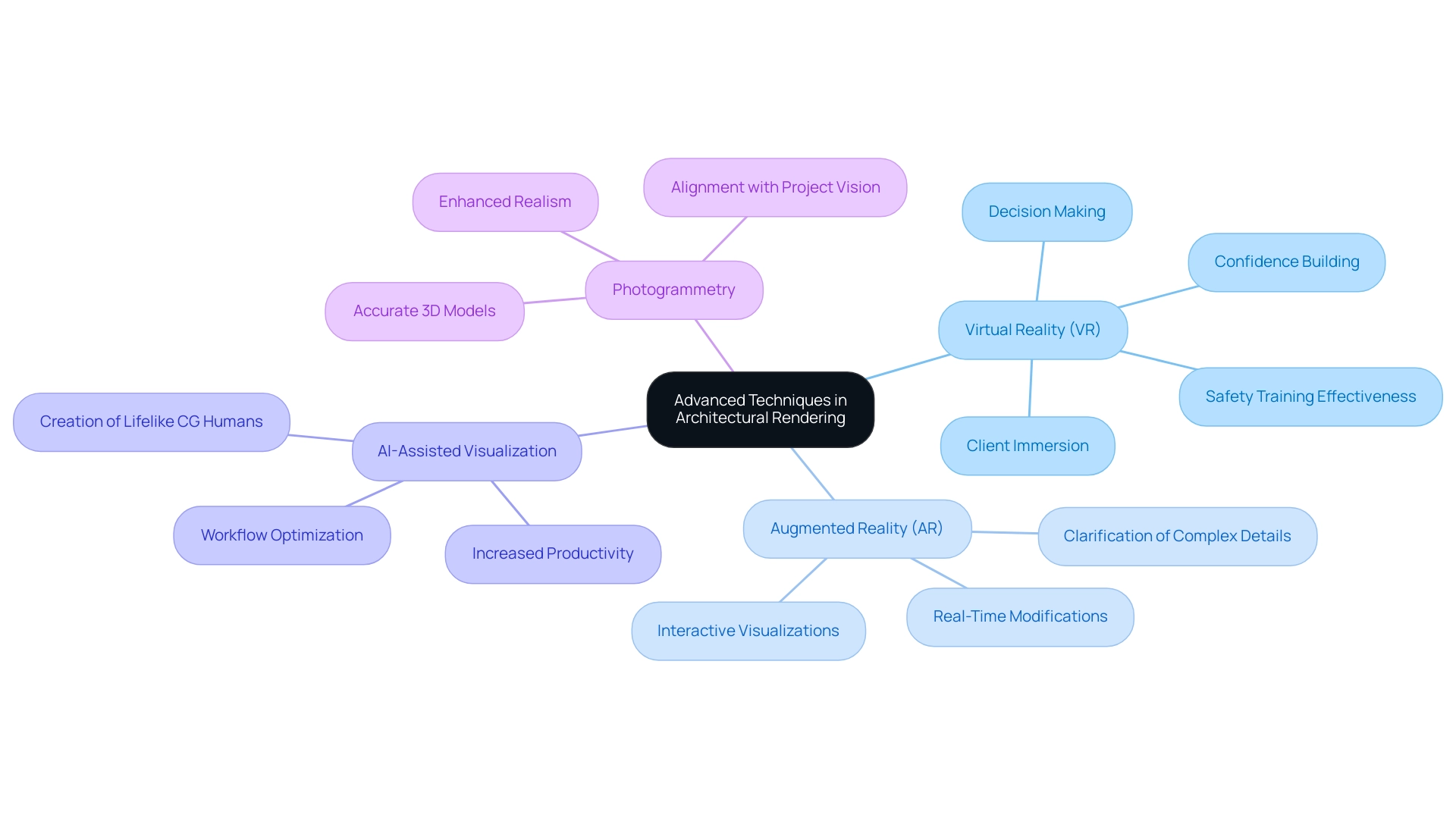
In the ever-evolving landscape of architectural rendering, several advanced techniques and innovations are essential for architects to consider:
Virtual Reality (VR): This technology immerses clients in a fully interactive environment, significantly enhancing their understanding and engagement with proposed designs. By offering a realistic perspective of the initiative, VR not only enhances customer confidence but also assists in decision-making, ensuring that stakeholders feel connected to the vision. Recent statistical analyses indicate a notable increase in confidence regarding VR technologies among professionals within the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry, reflecting a growing trend in its adoption.
Augmented Reality (AR): AR creates interactive visualizations that seamlessly integrate digital models with real-world environments. This capability enhances presentations and facilitates real-time modifications during the design process, allowing for greater adaptability based on feedback. The immediate visual feedback helps clarify complex project details, making it easier for customers to make informed decisions.
AI-Assisted Visualization: Artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in optimizing workflows by automating repetitive tasks, thereby increasing overall efficiency. Moreover, AI contributes to creating lifelike CG humans, bridging the gap between realism and the uncanny valley, which enhances the emotional connection clients have with the visualizations. Experts predict significant expansion in AI-supported methods within building visualization, especially as companies aim to improve both productivity and accuracy in providing high-quality visual results.
Photogrammetry: This technique captures real-world environments to generate accurate 3D models, significantly enhancing the realism of architectural renderings. The precision afforded by photogrammetry allows architects to achieve architectural rendering engaging that conveys a more authentic representation of design intentions, which is critical for ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned with the project vision.
Staying abreast of these innovations is vital for architects aiming to make their architectural rendering engaging and push the boundaries of their visualizations. As Mojtaba Noghabaei noted, “Ultimately, the findings show a significant increase in AR/VR utilization in the AEC industry from 2017 to 2018,” a trend that is poised to continue over the next 5 to 10 years, especially in sectors such as healthcare. Furthermore, a case study on VR-based safety training demonstrated its marked effectiveness compared to traditional methods, highlighting the potential of VR in enhancing worker safety education.
Additionally, it is noteworthy that magnetic-based systems outperform image-based and infrared-based systems in construction scenarios, further illustrating advancements in the field. Embracing these advanced techniques not only enriches the user experience but also ensures that architectural rendering is engaging, positioning architects at the forefront of technological advancement in their field.
The Importance of Feedback and Iteration in Rendering
Incorporating feedback into your production process is crucial for continuous improvement and quality enhancement. To effectively collect and apply feedback, consider the following steps:
- Present Initial Versions: Share preliminary iterations of your designs with colleagues or clients to solicit their insights. This initial feedback can inform critical adjustments.
- Encourage Constructive Criticism: Cultivate an atmosphere where candid feedback is encouraged. Focus discussions on specific elements of the visuals to facilitate targeted improvements.
- Iterate Based on Feedback: Utilize the insights gained to refine your visuals. This iterative approach not only enhances the visual quality but also ensures that the design aligns with stakeholder expectations. Our collaborative process guarantees that client-requested revisions are addressed promptly, fostering a partnership aimed at excellence.
- Document Changes: Maintain a record of feedback and the modifications made. This documentation will provide valuable context, illuminating the evolution of your work over time.
Once the visuals meet your expectations, we proceed to the final delivery stage. Here, we refine the visuals, enhancing their quality and detail to ensure a polished, professional look. The finished architectural visuals are then provided in your preferred format, prepared for presentations, meetings with stakeholders, or further project development.
Valuing feedback and embracing an iterative design process can lead to significant advancements in the quality and effectiveness of your engaging architectural rendering visuals. As emphasized by our clients in various testimonials, including those on platforms like Google and Houzz, the user experience significantly improves when feedback is integrated. This collaborative effort results in architectural rendering engaging that not only meet but exceed expectations, similar to the success illustrated in the ‘Green Energy Planning App Success’ case study, which demonstrated enhanced user satisfaction through effective feedback implementation.
Such enhancements not only elevate the design’s aesthetic appeal but also optimize functionality, crucial for achieving project objectives.
Conclusion
Architectural rendering plays an indispensable role in the design process, serving as a bridge between conceptual ideas and tangible visual representations. Mastering key principles such as perspective, lighting, materials, and composition is essential for architects aiming to produce high-quality renderings that resonate with clients and stakeholders. The integration of advanced technologies, including virtual and augmented reality, as well as artificial intelligence, further enhances the capability to create immersive and realistic visualizations that align with contemporary market demands.
Implementing best practices, such as utilizing high-quality textures and realistic lighting, ensures that renderings not only meet aesthetic standards but also communicate the intended design effectively. The choice of appropriate software can significantly impact project efficiency and output quality, underscoring the importance of selecting tools that cater to specific project needs. As the architectural rendering industry continues to expand, staying abreast of innovations and advancements is paramount for architects to maintain a competitive edge.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of feedback and iteration within the rendering process enhances the quality and relevance of the visual outputs. By actively engaging clients and stakeholders throughout the process, architects can refine their renderings to better meet expectations, ultimately leading to more successful project outcomes. Embracing these principles and practices will not only elevate the standard of architectural visualization but also strengthen the overall design communication, paving the way for more informed decision-making and client satisfaction in an increasingly competitive landscape.

0 Comments