Introduction
In the realm of architectural rendering, the selection of an appropriate graphics card is not merely a technical decision; it is a pivotal factor that can significantly influence the quality and efficiency of visualizations. With the increasing complexity of architectural projects demanding higher levels of detail and realism, understanding the essential characteristics of graphics cards becomes paramount.
This article delves into the critical aspects to consider when choosing a graphics card, including:
- VRAM capacity
- CUDA core count
- Architectural advancements
While also providing recommendations for optimal performance in rendering tasks. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of benchmarks and maintenance practices to ensure sustained performance, ultimately guiding professionals in making informed decisions that enhance their workflows and project outcomes.
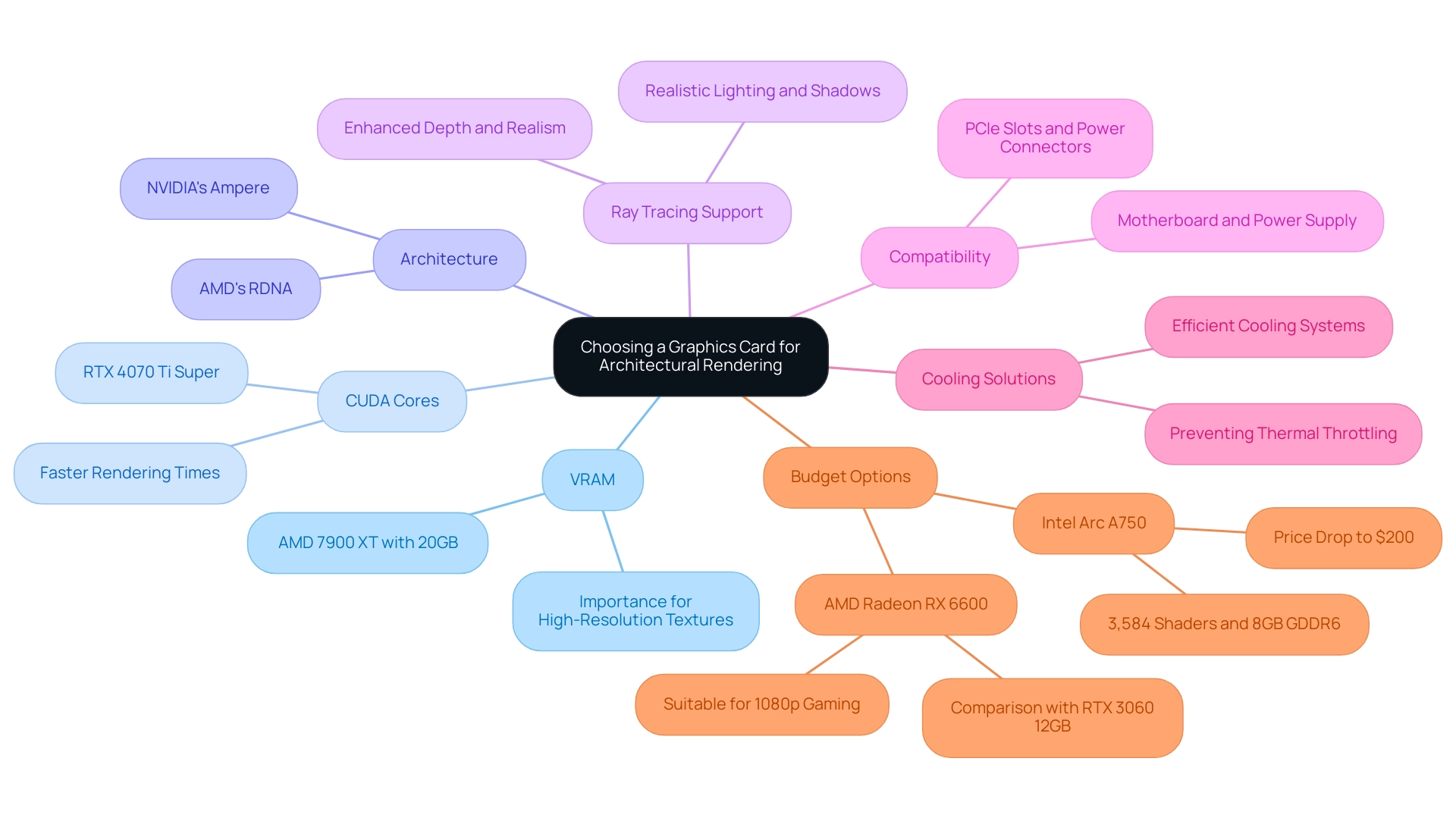
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Graphics Card for Architectural Rendering
When choosing a graphics component for building design rendering, it is essential to take into account several key factors that directly influence performance and efficiency:
VRAM (Video RAM): For architectural visualization, the ability to manage high-resolution textures and complex models is paramount. To handle larger projects effectively, it is essential to choose the best graphics card for architectural rendering, which should be equipped with at least 8GB of VRAM. For instance, the AMD 7900 XT features a substantial 20GB of VRAM, making it particularly suited for high-poly scenes and intricate visualizations. As AMD states, ‘This GPU is priced competitively against the more exorbitant Nvidia GeForce RTX 4080, with the RX 7900 XTX showing the edge in testing, in most of the games we ran it on.’ The level of detail supported by such hardware not only enhances realism but also imbues projects with an emotional impact, making them feel more tangible and engaging.
CUDA Cores: The count of CUDA cores in a GPU is a significant indicator of performance in graphics. A higher core count generally correlates with faster rendering times, allowing for more efficient workflows. In the current landscape, the RTX 4070 Ti Super has emerged as the best graphics card for architectural rendering in the $600-$800 range, effectively addressing earlier concerns regarding memory specifications while boasting impressive CUDA core capabilities. The enhanced processing power from these cores allows for more complex calculations, which can lead to more realistic lighting and shadow effects, further deepening the emotional resonance of the visualizations.
Architecture: Opting for the latest GPU architectures, such as NVIDIA’s Ampere or AMD’s RDNA, ensures improved performance and efficiency. These advancements not only improve visualization capabilities but also ensure that you invest in the best graphics card for architectural rendering, offering a degree of future-proofing for your hardware and allowing you to capture intricate details that elevate the overall quality of your projects.
Ray Tracing Support: For projects that require realistic lighting and shadow effects, selecting a graphics card with robust ray tracing support is imperative. This technology can dramatically elevate the quality of renderings, making them more lifelike and visually compelling, which is essential for creating a resonant emotional experience for viewers. By accurately simulating how light interacts with surfaces, ray tracing enhances the depth and realism of architectural visualizations, making them more impactful.
Compatibility: It is vital to ensure that your chosen graphics card is compatible with your workstation’s motherboard and power supply. Verify the availability of sufficient PCIe slots and power connectors to avoid installation issues.
Cooling Solutions: Given that graphical processes can generate significant heat, choosing a GPU with an efficient cooling system is essential. This will assist in sustaining peak functionality under load and avert thermal throttling, which can impede efficiency.
Budget Options: For those seeking more budget-friendly alternatives, the Intel Arc A750 is a viable option and is considered one of the best graphics cards for architectural rendering, offering competitive performance against the RX 6600 with 3,584 shaders and 8 GB of GDDR6 memory. Despite facing some driver issues, it has recently seen a significant price drop to around $200, making it a recommended choice for budget-conscious users. Furthermore, the AMD Radeon RX 6600 is appropriate for contemporary 1080p gaming and ought to be evaluated against Nvidia’s RTX 3060 12GB for improved value.
By thoughtfully weighing these aspects, including the complex elements that can amplify the emotional effect and realism of your visualizations, you can choose a graphics solution that fulfills the rigorous needs of design visualization, ultimately improving your workflow and project results.
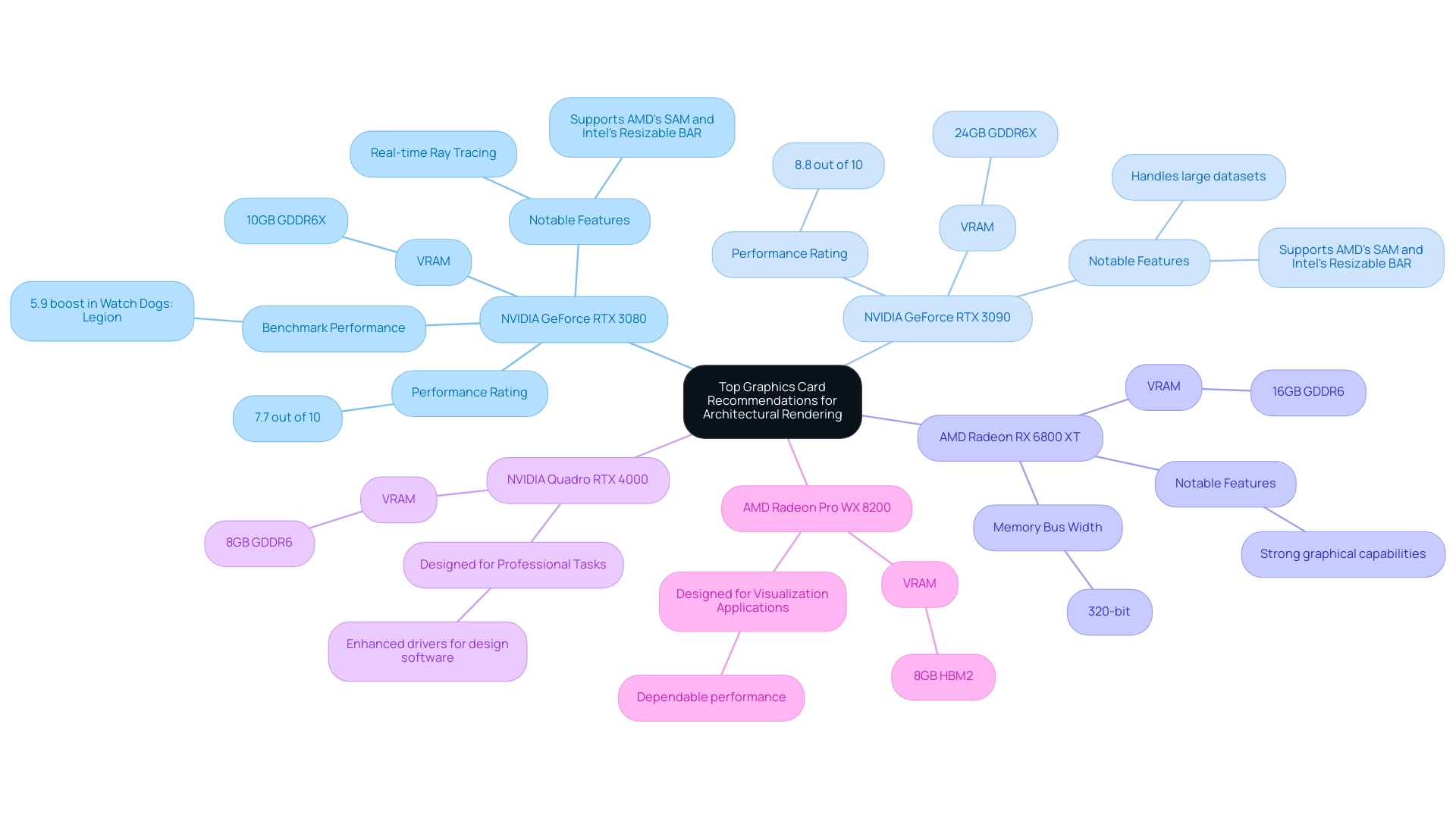
Top Graphics Card Recommendations for Optimal Architectural Rendering
Choosing the best graphics card for architectural rendering is essential for attaining high-quality visual representation, especially considering the project’s complexity and scale. High-quality renderings serve as a window into the future of your project, allowing everyone involved to visualize the potential and understand the vision behind the blueprints. Here are some of the top recommendations for 2024:
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080: Equipped with 10GB of GDDR6X VRAM, the RTX 3080 excels in real-time ray tracing, making it suitable for a wide range of architectural projects. Recent benchmarks indicate a boost of 5.9% in Watch Dogs: Legion at Full HD Ultra Preset, showcasing its capabilities in demanding scenarios. Additionally, it supports AMD’s Smart Access Memory (SAM) and Intel’s Resizable BAR, boosting efficiency further.
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090: With an impressive 24GB of VRAM, the RTX 3090 is engineered to handle extremely detailed scenes and large datasets, positioning it as the premier choice for high-end architectural visualization. Reliability ratings have shown an 8.8 out of 10 score based on user feedback, underscoring its user satisfaction compared to the 7.7 rating for the RTX 3080. As Abde Manaf, a Comparisons Expert, notes, “He is always eager to learn more and is constantly seeking new challenges to improve his skills,” reflecting the ongoing advancements in graphics technology.
AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT: This card includes 16GB of GDDR6 VRAM and provides strong capabilities in graphical applications. Its competitive benchmarks make it a viable alternative for architects who prefer the best graphics card for architectural rendering from AMD solutions. The memory bus width of 320-bit enhances data handling, making it effective for graphical tasks.
NVIDIA Quadro RTX 4000: Designed for professional tasks, the Quadro series is enhanced with drivers specifically developed for design software, ensuring both stability and high efficiency in demanding activities, which is crucial for experts in the industry.
AMD Radeon Pro WX 8200: Providing 8GB of HBM2 memory, this workstation device is tailored for visualization applications, making it a strong option for design professionals seeking dependable performance.
When selecting the best graphics card for architectural rendering, it is essential to evaluate your particular processing needs, budget limitations, and the software applications you plan to employ. These suggestions are focused on assisting you in attaining outstanding outcomes in your visualization projects, making certain that you are well-prepared to confront the challenges of contemporary design while improving client involvement through high-quality visual representations that evoke emotional reactions and a sense of realism.
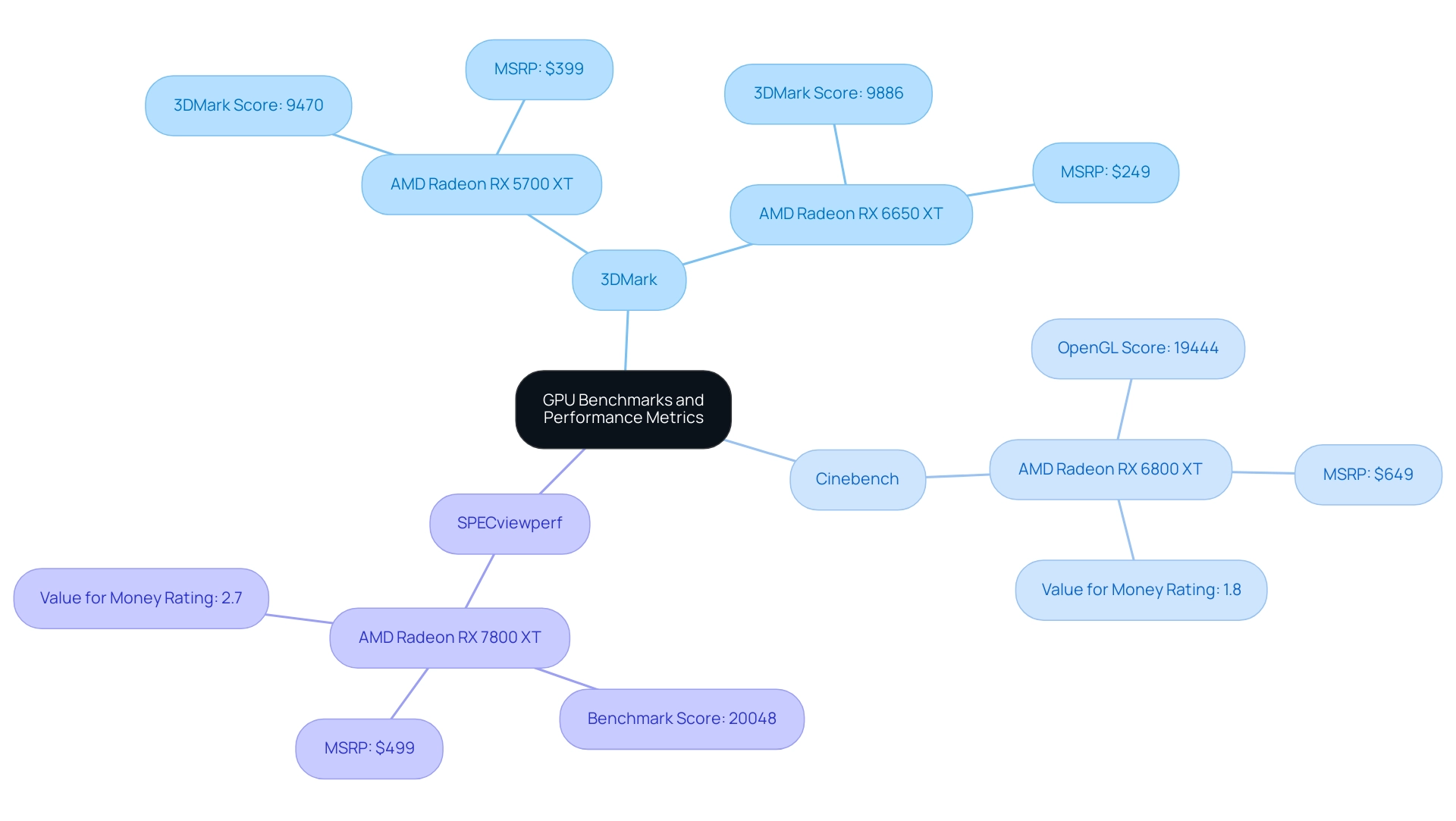
Understanding GPU Benchmarks and Performance Metrics
When assessing the best graphics card for architectural rendering, it is crucial to take into account a range of benchmarks and capability metrics that precisely represent their abilities. Providing clear and timely information during the selection process can significantly optimize both time and costs in your projects. To achieve this, ensure you send us detailed specifications, including project scope, intended software usage, and visualization requirements early in the process:
- 3DMark: Renowned for its thorough assessment of GPU capabilities across varying rendering scenarios, 3DMark offers critical insights through its Time Spy and Fire Strike tests. For example, the AMD Radeon RX 5700 XT boasts a 3DMark Graphics Score of 9470, providing a baseline for assessing capability. Additionally, the AMD Radeon RX 6650 XT, with an MSRP of $249, achieves a score of 9886, showcasing its competitive capability at a lower price point.
Cinebench: While primarily known for CPU benchmarking, Cinebench also evaluates GPU performance during graphical tasks. The OpenGL scores are especially crucial, as they demonstrate how effectively a GPU can handle workload management. The AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT, for instance, achieves a score of 19444, indicating robust rendering capabilities that can significantly impact workflow. Notably, the AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT has an MSRP of $649 and a value for money rating of 1.8, suggesting a higher cost relative to its performance.
- SPECviewperf: This benchmark emphasizes the capabilities of the best graphics card for architectural rendering in professional applications, including popular architectural visualization software. Higher SPECviewperf scores correlate with superior results in practical tasks, making this a critical evaluation tool for architects.
Render Time: It is crucial to assess the average render times for specific projects or scenes when reviewing benchmarks. A GPU that excels in render time can notably enhance workflow efficiency, allowing architects to optimize their productivity and meet project deadlines.
Real-World Example: The AMD Radeon RX 7800 XT, priced at $499, supports DirectX 12.0 and boasts an impressive benchmark score of 20048, with a value for money rating of 2.7. This illustrates a compelling example of capability versus cost, reinforcing the importance of considering both metrics in the selection process.
Understanding these benchmarks and metrics empowers architects to make informed, data-driven decisions when selecting the best graphics card for architectural rendering that meets their specific needs. Additionally, as Jarred Walton, a senior editor at Tom’s Hardware, emphasizes, keeping up with the latest graphics trends is essential for optimizing performance in design applications. Collaborating with a dedicated 3D visualization specialist can further improve the clarity and effectiveness of your visualizations, contributing to the overall success of your projects.
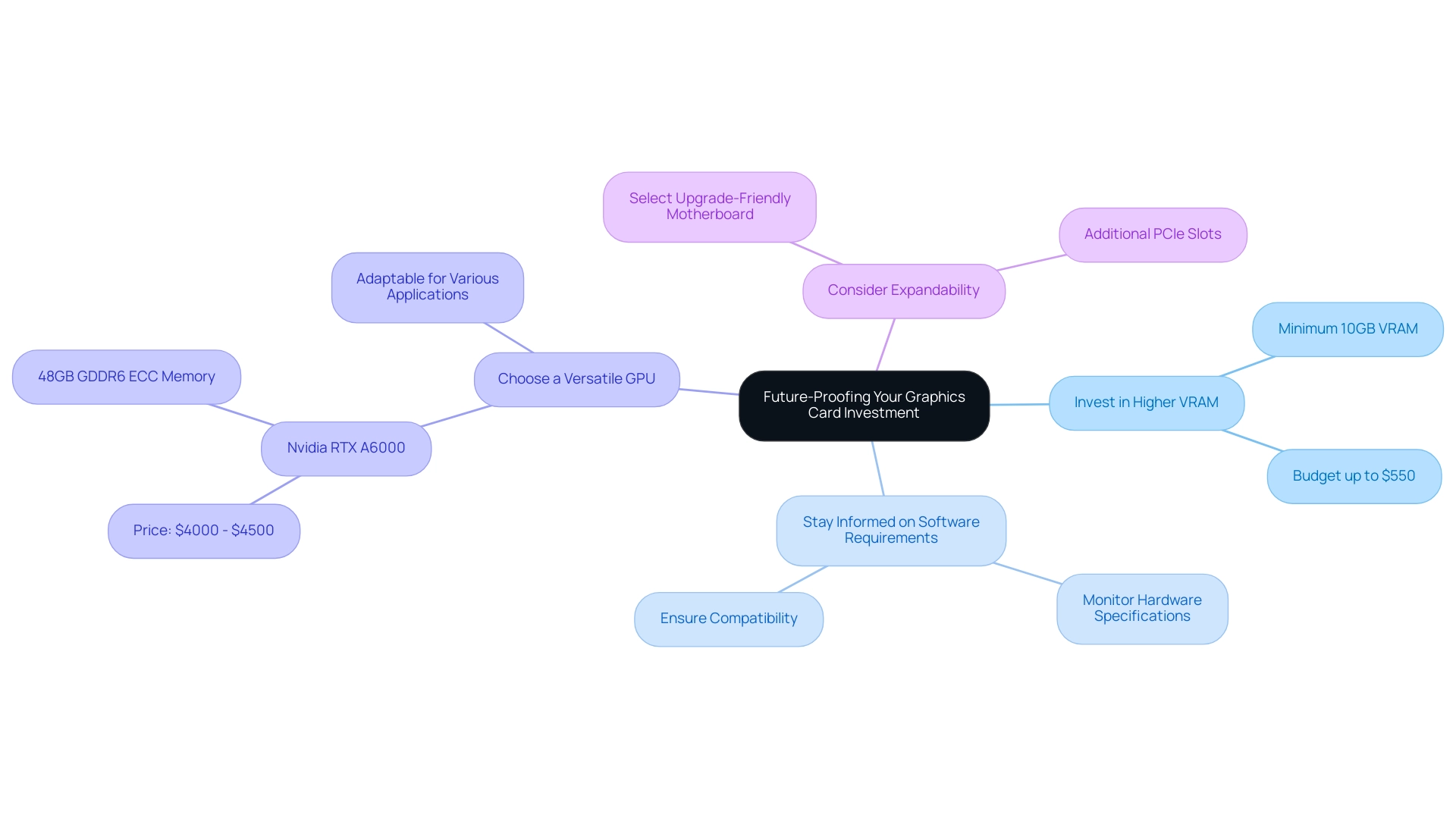
Future-Proofing Your Graphics Card Investment
To effectively future-proof your graphics unit investment, consider implementing the following strategies, particularly in light of the critical role that high-quality 3D visualizations play in building projects:
Invest in Higher VRAM: As the complexity of architectural projects continues to escalate, a higher VRAM capacity becomes essential. A graphics card with at least 10GB of VRAM is the best graphics card for architectural rendering, as it will better accommodate larger textures and intricate models, enabling the creation of detailed 3D visualizations that enhance client understanding and foster better decision-making. For those operating on a budget, aim to spend no more than $550 to secure a capable GPU without overspending.
Stay Informed on Software Requirements: Architectural visualization tools frequently update to utilize the latest advancements in display technology. It is critical to monitor the minimum and recommended hardware specifications for your software to ensure ongoing compatibility and optimal performance, ultimately supporting effective stakeholder communication during the design process.
Choose a versatile GPU, as it is the best graphics card for architectural rendering, excelling in various applications such as visualization, modeling, and simulation. The Nvidia RTX A6000, for example, is a top-tier choice priced between $4000 and $4500, featuring 48GB of GDDR6 ECC memory. This versatility ensures that your investment in the best graphics card for architectural rendering remains advantageous as your workflow adjusts to new needs and approaches, particularly in producing high-quality visual outputs that are essential for project development.
Consider Expandability: For those constructing a workstation, select a motherboard designed for future upgrades, featuring additional PCIe slots for potential GPU expansions. This foresight will enable you to adjust your system as display technologies advance and as the needs for intricate building visualizations grow.
By following these strategies, you can ensure that your investment in the best graphics card for architectural rendering remains relevant and efficient for years to come, especially as innovations like real-time ray tracing and AI acceleration transform the structural landscape. Jane Doe, an architect, underscores this shift in workflow by stating, “The ability to render in real-time has transformed our creative process; it allows for immediate iteration and client engagement that traditional methods simply cannot match.” Moreover, high-quality visuals act as a glimpse into the future of your projects, making it essential to plan for rising VRAM requirements in upcoming design endeavors.
This preparation not only enhances client understanding but also leads to significant cost savings by allowing for early identification of design issues, ultimately ensuring project success.
Maintenance Tips for Your Graphics Card
To ensure your graphics card operates at peak performance and maintains reliability in architectural rendering, implement the following maintenance best practices:
Regular Dusting: Accumulation of dust can significantly hinder cooling efficiency. Utilize compressed air to thoroughly clean the GPU and its cooling fans, ideally conducting this maintenance every few months to prevent overheating issues. Consistent dusting is vital, as it aids in sustaining optimal thermal efficiency, which is important for processing tasks.
Temperature Monitoring: Employ advanced software tools to consistently monitor your GPU temperatures during rendering operations. If temperatures frequently exceed safe thresholds, it may be necessary to enhance system ventilation or consider an upgrade to your cooling solution. Monitoring GPU metrics such as memory usage and thermal efficiency is essential for maintaining optimal function. As mentioned in the case study ‘Importance of GPU Metrics for Administrators,’ effective monitoring assists in enhancing efficiency and supports data-driven decisions regarding resource allocation.
Driver Updates: Maintaining your GPU drivers current is essential for utilizing enhancements and fixing issues. Frequent updates can enhance compatibility with display software and significantly boost overall efficiency, ensuring that you are utilizing the latest optimizations. This practice is crucial, particularly given that the RTX engine often utilizes more VRAM than the CUDA engine, which can affect efficiency in visuals.
Power Supply Assessment: Verify that your power supply unit (PSU) delivers sufficient power to your GPU, particularly after any upgrades. Insufficient power supply can lead to quality decline and system instability, undermining your rendering capabilities.
Benchmark Testing: Conduct regular benchmark tests to assess your GPU’s metrics. This proactive approach allows you to detect any performance declines early, enabling you to address potential issues before they impact your workflow.
Additionally, for those seeking further guidance, as Mohan Atreya suggests, “Sign up for a free Org if you want to try this yourself with our get started guides.” By adhering to these maintenance strategies, you will ensure that the best graphics card for architectural rendering remains efficient and capable of meeting the demanding requirements, ultimately supporting your design objectives for years to come.
Conclusion
Selecting the right graphics card for architectural rendering is a critical decision that encompasses various technical specifications and performance metrics. Key factors such as VRAM capacity, CUDA core count, and architectural advancements directly influence the quality and efficiency of visualizations. As architectural projects become increasingly complex, the necessity for a robust graphics card equipped with features like ray tracing support and efficient cooling solutions becomes paramount.
The recommendations outlined for 2024 highlight the importance of choosing a graphics card that not only meets current rendering demands but also offers future-proofing capabilities. Options such as the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 and AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT stand out for their exceptional performance, ensuring that professionals can deliver high-quality renderings that resonate with clients and stakeholders.
Moreover, understanding GPU benchmarks and maintaining optimal performance through regular maintenance practices ensures that the graphics card operates efficiently over time. By investing in the right hardware and adhering to best practices, architects can significantly enhance their workflows and project outcomes, ultimately leading to more engaging and emotionally impactful visualizations. In a field where precision and detail are paramount, the careful selection and upkeep of graphics cards will undoubtedly shape the future of architectural rendering.

0 Comments