Overview
Building your dream home using house 3D printing involves a structured process that includes designing a model, preparing the site, selecting materials, printing the structure, and finishing the interior. The article emphasizes that this innovative method not only enhances design flexibility and reduces construction time and costs significantly but also aligns with sustainability goals by minimizing waste and resource use.
Introduction
As the construction industry stands on the brink of a technological revolution, 3D printing emerges as a transformative force reshaping how homes are built. This innovative method leverages additive manufacturing to create building components with unmatched precision and efficiency, significantly reducing construction time and material waste.
With the ability to craft complex designs that traditional methods often struggle to achieve, 3D printing offers architects and builders unprecedented creative freedom while promising substantial cost savings.
As professionals in the field begin to harness this technology, understanding its applications, advantages, and the challenges it presents becomes essential for navigating the future of home construction.
From sustainable practices to the integration of smart technology, the potential of 3D printing in residential building is vast, paving the way for a more efficient and environmentally friendly industry.
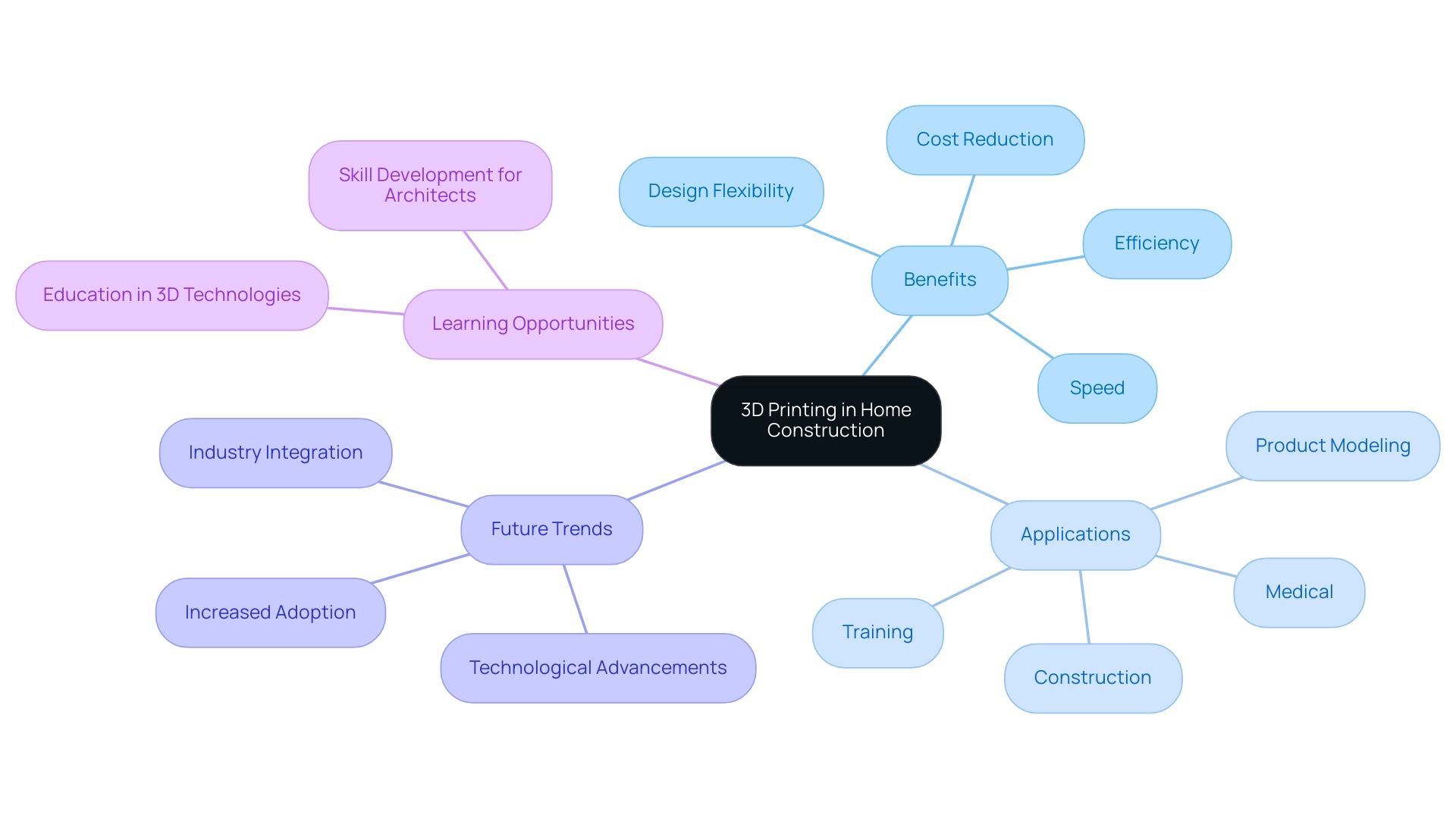
Introduction to 3D Printing in Home Construction
3D printing in home development represents a groundbreaking shift in how building components are created, utilizing additive manufacturing technology to layer materials with precision and efficiency. This method not only speeds up project timelines but also reduces waste, addressing critical concerns in the industry. Furthermore, the ability to create intricate designs that traditional building methods often struggle to achieve is a game changer.
As the construction sector increasingly adopts this technology, it is vital for professionals, especially lead architects, to understand its myriad applications and benefits, which include enhanced design flexibility and the potential for significant cost reductions. Recent advancements in 3D fabrication are paving the way for a more integrated industry chain, fostering collaboration and streamlining production processes. Chris Connery, Global VP of Analysis at CONTEXT, noted,
A challenging 2023 has set the stage for a rebound, and 3D printer shipments look to accelerate in the years to come.
This perspective reflects a broader trend where the highest expected potential for 3D printing impact is observed in sectors like medical applications, with 77% of respondents recognizing this potential. This statistic highlights the transformative potential of this technology across various areas, including residential building and architectural design. Additionally, the case study titled ‘Technological Advancements in 3D Printing’ illustrates how rapid advancements are enabling faster and more efficient building methods for house 3D printing, enhancing material options and design capabilities, ultimately leading to lower production costs and increased adoption of 3D printed homes.
Beyond building, 3D rendering finds applications in medical imaging, training simulations, and product modeling, highlighting its diverse importance. As demand for skilled professionals in these areas grows, learning opportunities in 3D rendering technologies become increasingly crucial for architects looking to stay competitive in the evolving job market.
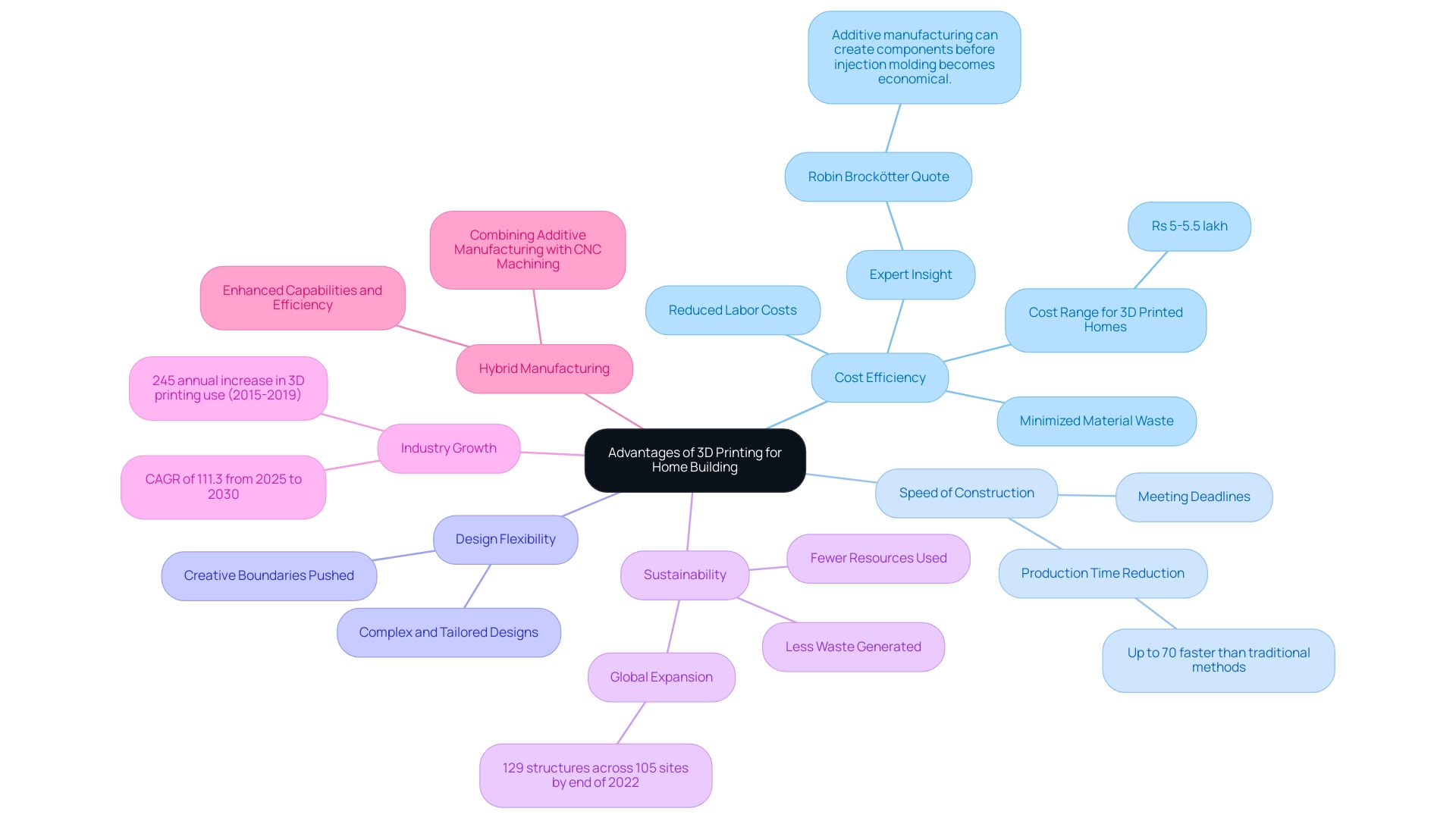
Advantages of 3D Printing for Home Building
The benefits of 3D fabrication in residential construction are compelling and transformative:
- Cost Efficiency: By significantly reducing labor costs and minimizing material waste, 3D fabrication can lead to substantial savings in construction budgets. The cost to build a 3D printed home typically ranges from Rs 5-5.5 lakh, making it an economically viable option for many builders. Specialists such as Robin Brockötter, a supply chain manager at Protolabs Network, stress that,
additive manufacturing can now begin creating an increasing number of components before injection molding becomes more economical, underscoring the developing cost efficiency of this innovation in construction. - Speed of Construction: Dwellings can be produced in only a few days, representing a significant advancement over conventional building practices. With the potential to decrease building time by as much as 70%, this innovation enables contractors to adhere to deadlines more effectively.
- Design Flexibility: The abilities of house 3D fabrication support complex and tailored designs that are often unreachable with traditional building methods. This flexibility enables architects and builders to push the boundaries of creativity in home design.
- Sustainability: Utilizing fewer resources and generating less waste, 3D fabrication contributes to more eco-friendly building practices. As the market for house 3D fabricated structures expands—evidenced by the 129 structures across 105 building sites worldwide by the end of 2022—this innovation aligns with the growing demand for sustainable development solutions.
Additionally, the percentage of respondents indicating they created more than 1,000 parts rose from 4.7% in 2022 to 6.2% in 2023, reflecting the increasing adoption of 3D fabrication in the industry. Moreover, the trend of hybrid manufacturing, which combines additive manufacturing with CNC machining, is pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved in construction, further enhancing the capabilities and efficiency of house 3D fabrication technology. As the sector expects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 111.3% from 2025 to 2030, the advantages of house 3D technology in residential construction are poised to become even more evident.
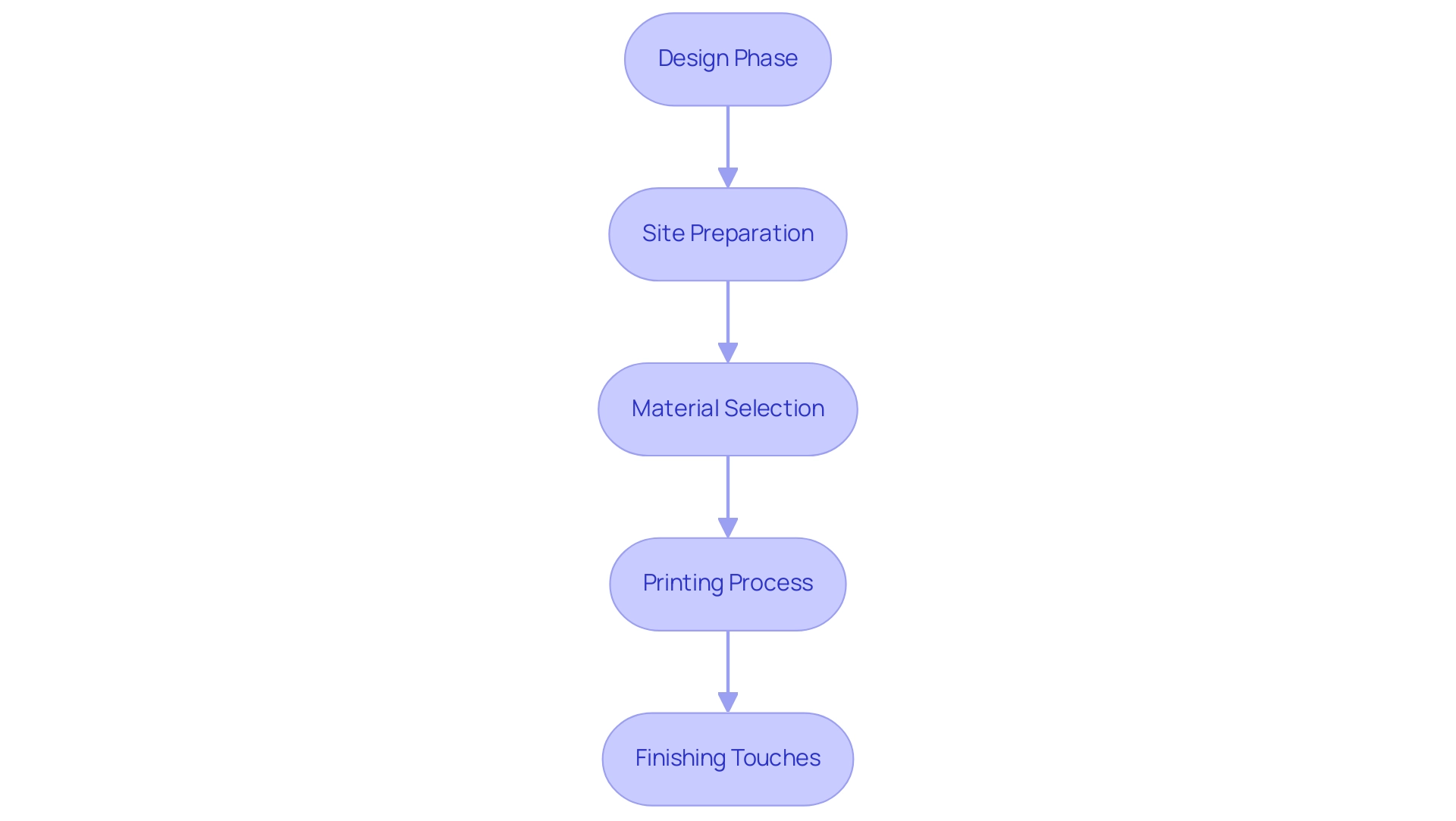
Step-by-Step Process of 3D Printing Your Home
The procedure of 3D fabrication of a residence is organized around several key steps that guarantee efficiency and quality:
- Design Phase: Begin by collaborating with an architect or designer to create a detailed house 3D model of your home. Delivering clear and prompt information during this phase is essential as it acts as the blueprint for the entire building process, enabling complex designs that utilize the features of 3D technology. For instance, specifying the desired layout, materials, and any unique features early on can prevent costly changes later. Thoughtful design decisions, as noted by architect Igolkina, are essential in optimizing both time and cost in this innovative process.
- Site Preparation: Proper site preparation is crucial. Clear the area and ensure the site meets all necessary requirements for 3D printing, such as stable ground and adequate space for the printer. This step is essential for a successful build and minimizes potential delays, further emphasizing the importance of early planning.
- Material Selection: Choose suitable materials for construction. Options like concrete or thermoplastics should be selected based on the design specifications and budget considerations. These materials are integral to the structural integrity and aesthetic of the completed house 3D project. Notably, Europe’s largest house 3D manufactured building, which measures approximately 54m long, 11m wide, and 9m high, showcases the scale and capabilities of modern 3D technology in construction.
- Printing Process: With the design finalized and materials selected, utilize a house 3D printer to construct the home layer by layer. It’s crucial to oversee the production process closely to uphold quality control and resolve any problems that may occur during assembly. This meticulous attention to detail ensures accuracy in renderings and enhances client collaboration.
- Finishing Touches: After the main structure is printed, complete the interior and exterior finishes. This includes installing plumbing, electrical systems, and other aesthetic elements that transform the printed shell into a livable space. The use of house 3D design visualization allows for proactive adjustments during this phase, resulting in significant cost savings by making changes before the final build. Additionally, the advancements in house 3D printing technology have made this process increasingly viable, with over 70% of businesses in the sector discovering new applications by 2019. This method not only improves design adaptability but also aids in minimizing waste and on-demand manufacturing, making house 3D printed residences a sustainable option for contemporary building.
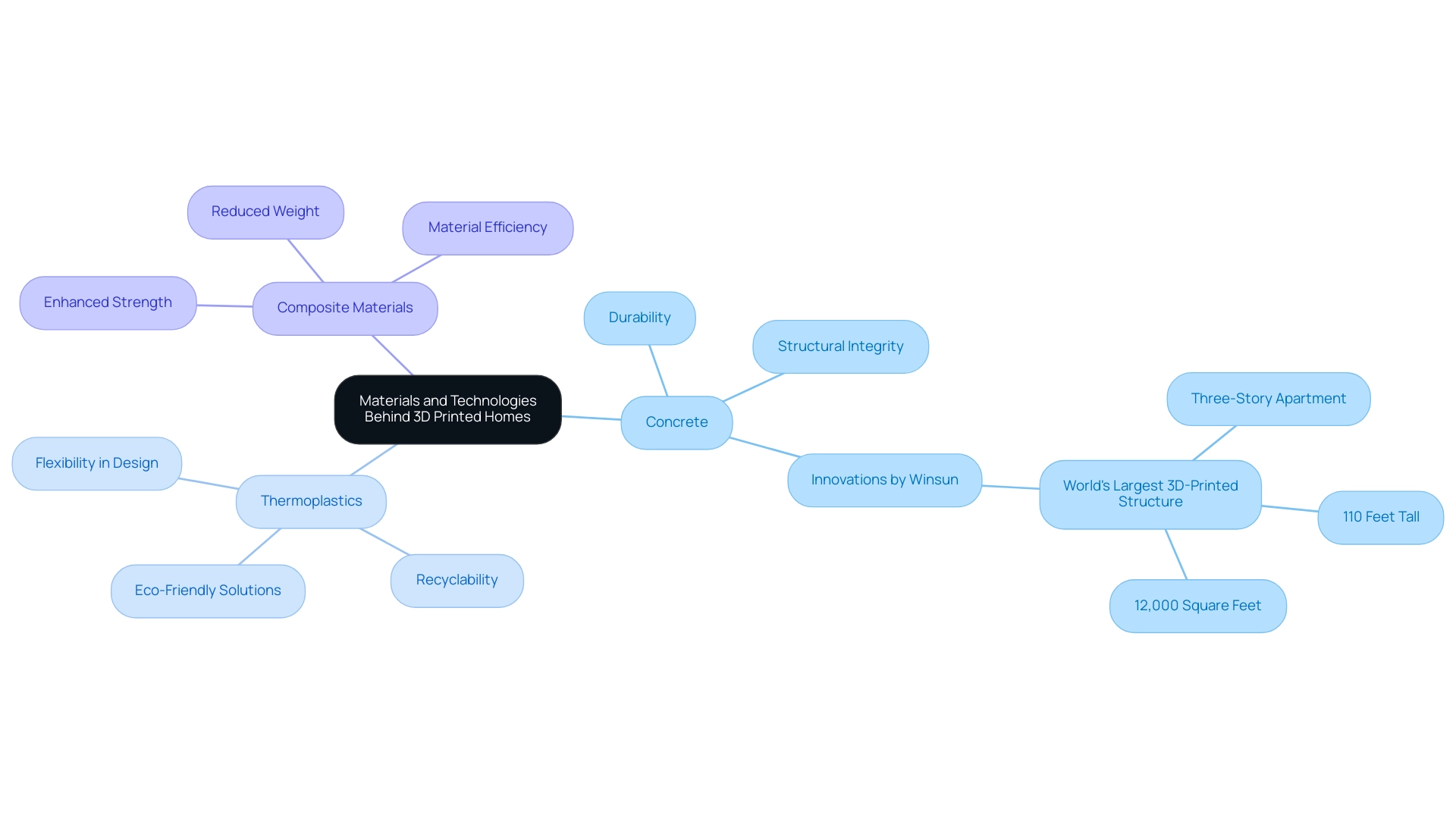
Materials and Technologies Behind 3D Printed Homes
In the realm of house 3D printed homes, various materials are at the forefront, each contributing to the efficiency and sustainability of building processes. The most commonly used materials include:
Concrete: High-strength concrete mixtures are favored for their exceptional durability and structural integrity. Innovations in concrete formulations are being driven by companies like Winsun, which recently completed the world’s largest 3D-printed concrete structure—a three-story apartment building measuring 110 feet tall and covering an area of 12,000 square feet—showcasing the material’s capabilities in large-scale applications. Francois Minec, a specialist in materials science, observes, “The progress in concrete innovation is crucial for the future of sustainable building.”
Thermoplastics: These materials are gaining traction due to their flexibility in design and potential for recycling, aligning with the growing demand for eco-friendly building solutions. Experts in materials science emphasize the benefits of thermoplastics in enhancing the sustainability of 3D printed structures.
Composite Materials: By combining various materials, builders can achieve enhanced strength while reducing overall weight, which is crucial for both structural performance and material efficiency.
The tools utilized in this groundbreaking building approach include a variety of systems, from gantry-style printers to sophisticated robotic arms. Significantly, novel robotic systems are appearing that facilitate large-format 3D fabrication, offering distinct benefits like enhanced speed and accuracy, rendering them perfect for diverse building uses. With 45% of builders showing confidence in house 3D fabrication for production volume, the adoption of these technologies is poised to change the environment of residential construction in 2024 and beyond.
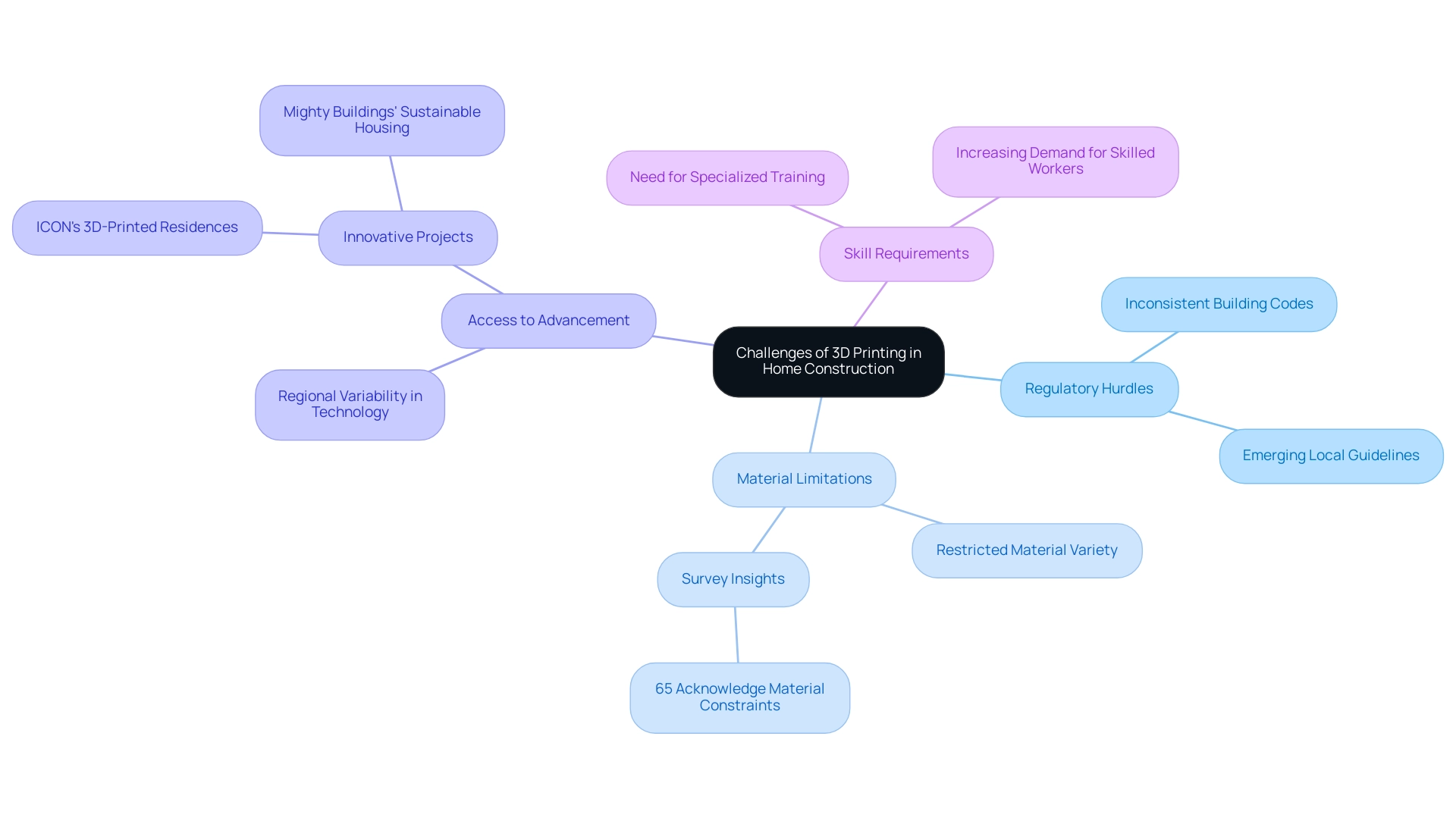
Challenges and Limitations of 3D Printing in Home Construction
Despite the transformative potential of 3D fabrication in building, several challenges must be navigated:
Regulatory Hurdles: The current landscape shows that many building codes and regulations have yet to adapt to the nuances of 3D manufactured structures. Local authorities are starting to formulate specific guidelines to tackle these distinctive building techniques, but inconsistencies continue to pose a major obstacle to broad acceptance.
Material Limitations: The variety of materials appropriate for 3D fabrication in residential development is still restricted, which can limit design options. While innovative materials are being explored, many existing options do not meet the necessary structural or aesthetic requirements for residential applications. A recent survey involving over 700 professionals in the Protolabs Network revealed that 65% of respondents acknowledged these material constraints, significantly impacting their design processes.
Access to Advancement: Availability of advanced 3D printing methods varies significantly by region, which can hinder the implementation of these innovative building techniques. Companies like ICON and Mighty Buildings are leading the way with projects such as the 3D-printed residences in Austin, Texas, and the sustainable housing developments in California. These initiatives highlight progress in innovation and stress the need for improved access to state-of-the-art resources to guarantee fair development across various sectors.
Skill Requirements: The operation of 3D printers and the management of the building process require a specialized skill set. This need for expertise can present challenges, particularly in markets where training and resources are scarce. As Chris Connery, Global VP of Analysis, noted,
A challenging 2023 has set the stage for a rebound and 3D printer shipments look to accelerate in the years to come.
This expected rise in deliveries highlights the urgent requirement for skilled workers to efficiently utilize this innovation and satisfy the increasing demand in the sector.
Tackling these obstacles is essential for the successful incorporation of 3D fabrication into residential building, particularly as the industry braces for the projected expansion in this creative field.
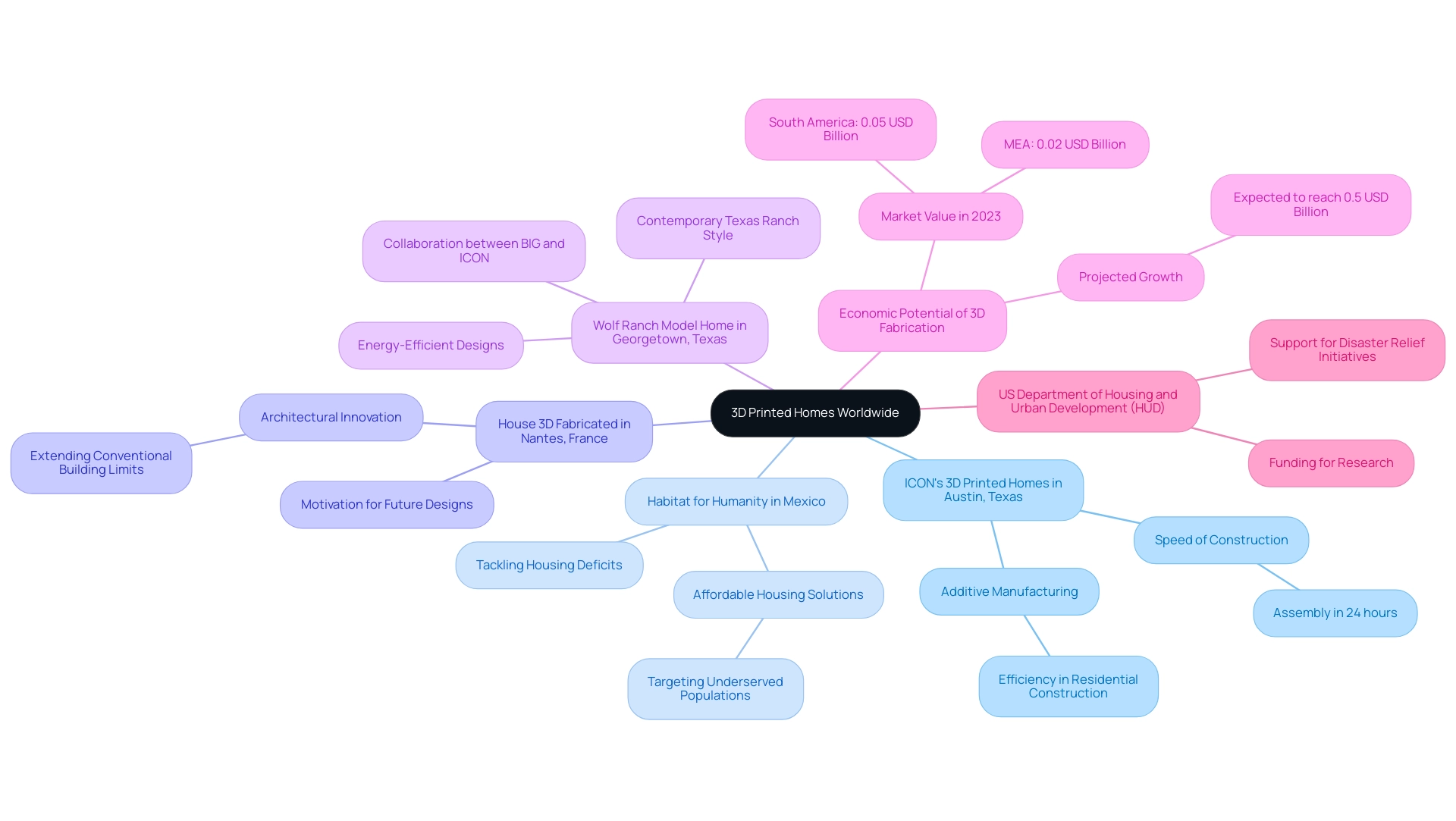
Case Studies: Successful 3D Printed Homes Around the World
The emergence of 3D fabricated residences is transforming the housing environment globally, with several remarkable projects demonstrating the method’s potential:
- ICON’s 3D Printed Homes in Austin, Texas: These innovative dwellings are a testament to the speed and efficiency of 3D fabrication, with assembly completed in as little as 24 hours. This quick turnaround not only fulfills housing needs but also showcases the effectiveness of additive manufacturing in residential construction.
- Habitat for Humanity’s initiative featuring house 3D technology in Mexico: This initiative exemplifies how 3D technology can serve as a vital tool in providing affordable housing solutions to underserved populations. By utilizing this innovation, Habitat for Humanity has made notable progress in tackling housing deficits in economically disadvantaged regions.
- The House 3D Fabricated in Nantes, France: A groundbreaking demonstration that investigates the architectural potentials of 3D fabrication, this project extends the limits of conventional building methods. It acts as a motivation for upcoming designs and innovations in home construction.
- Wolf Ranch Model Home in Georgetown, Texas: This full-sized model home represents a collaboration between BIG and ICON, showcasing contemporary Texas ranch style and energy-efficient designs, illustrating the potential of additive construction.
Additionally, recent developments in the field highlight the increasing economic potential of house 3D fabrication in housing. In 2023, the South America and MEA regions were valued at 0.05 USD Billion and 0.02 USD Billion, respectively, with expectations to grow to 0.5 USD Billion. Significantly, Larsen and Toubro, in partnership with ITT Madras, finished a 3D printed structure in Bengaluru, India, in only 44 days for about $27,500—roughly 40% less than conventional building approaches, with minimal noise reported during the process.
The US Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) has acknowledged the importance of this innovation by funding research on house 3D building techniques and supporting the creation of house 3D printed homes aimed at disaster relief initiatives. Instances like these demonstrate the significant influence that 3D fabrication can exert on economical housing solutions, paving the way for more sustainable and efficient construction methods globally.
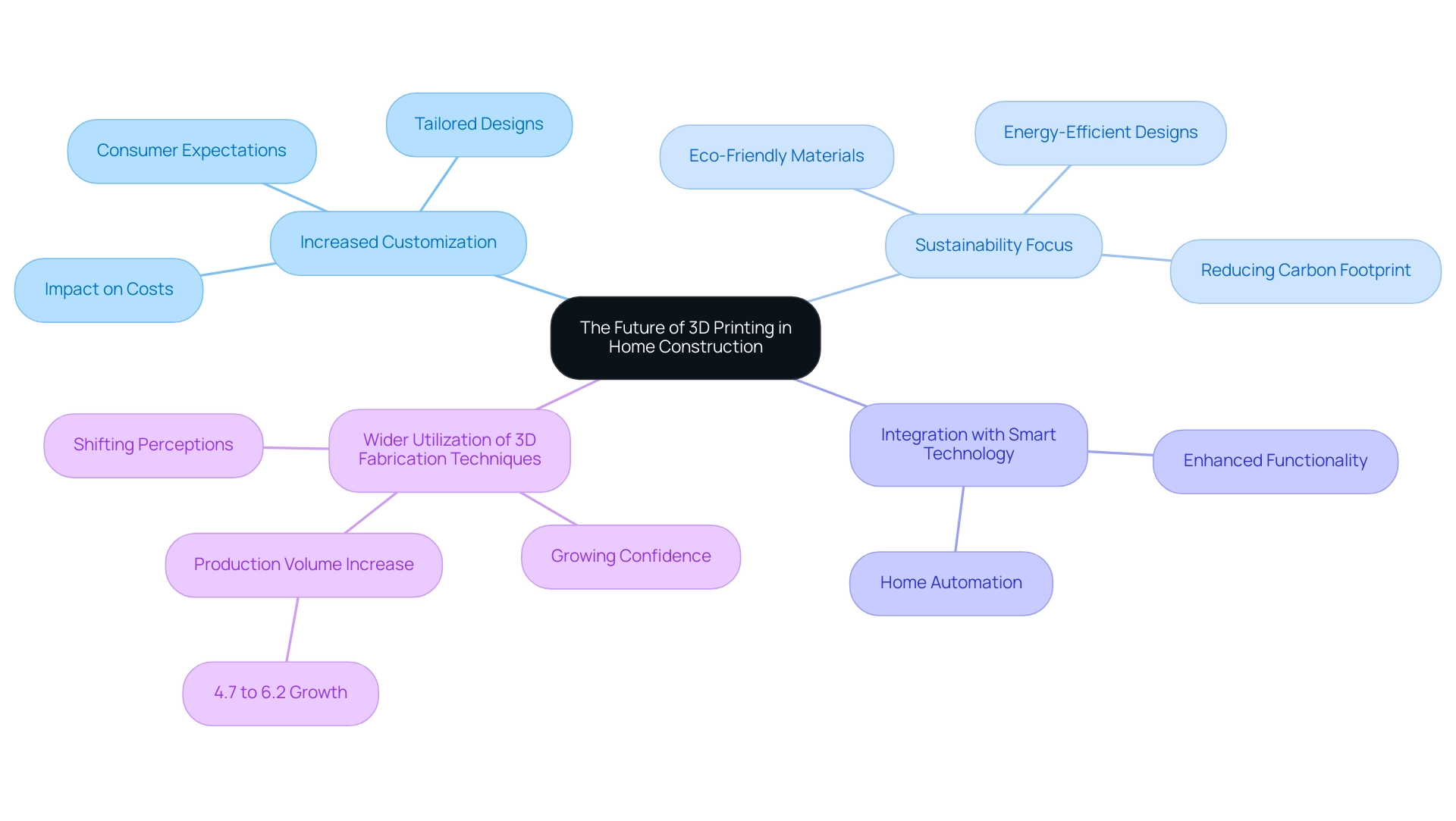
The Future of 3D Printing in Home Construction
The future of 3D printing in residential construction is exceptionally promising, marked by several key trends that are set to redefine the industry landscape. One of the most notable trends is increased customization, which plays a crucial role in determining the overall investment in rendering projects. With advancements in technology, homeowners can tailor designs more than ever before, offering a spectrum of options that cater to individual preferences.
This level of personalization reflects a broader shift in consumer expectations towards unique, custom-built environments, underscoring the importance of quality and impressive 3D renderings in realizing architectural visions. Specific requests and revisions are integral to this process, as they can significantly influence the overall costs involved in each project, necessitating detailed estimates to align with client expectations.
Additionally, there is a significant sustainability focus emerging within the sector. The drive towards eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs is likely to become a hallmark of 3D printed residences, aligning with global efforts to reduce carbon footprints and enhance environmental responsibility. As builders embrace these materials, the impact on the overall sustainability of residential construction will be profound.
The potential for integration with intelligent systems is another exciting avenue for the future. As homes become increasingly connected, the seamless incorporation of smart technology into 3D printed structures will enhance functionality and convenience, marking a new era in home automation. Chris Connery, Global VP of Analysis at CONTEXT, notes, “A challenging 2023 has set the stage for a rebound and 3D printer shipments look to accelerate in the years to come,” highlighting the industry’s optimistic outlook.
Furthermore, wider utilization of 3D fabrication techniques is anticipated as awareness about its benefits continues to grow. A case study titled “Shifting Perceptions of 3D Printing for Production” illustrates this trend, showing a rise in the percentage of respondents producing over 1,000 parts from 4.7% in 2022 to 6.2% in 2023. This growing confidence in 3D fabrication for production volume signifies that more builders and homeowners are likely to explore this innovative approach to construction.
As each project is unique and may require specific customization, requests, and revisions, these trends collectively signal a transformative period for the industry, where 3D printing not only meets but exceeds the evolving demands of modern housing, leveraging additive manufacturing’s potential to improve product development through rapid prototyping and production.
Conclusion
The impact of 3D printing on home construction is profound and multifaceted, showcasing a transformative shift in how homes are designed and built. This innovative technology offers significant advantages, including:
- Remarkable cost efficiency
- Reduced construction time
- Enhanced design flexibility
All while promoting sustainable building practices. As the industry continues to evolve, the integration of advanced materials and technologies further enhances the potential of 3D printing, paving the way for a new era in residential construction.
Despite the challenges that remain, such as regulatory hurdles and material limitations, the momentum behind 3D printing is undeniable. Successful case studies from around the world illustrate its potential to address housing shortages and provide affordable solutions, making it a crucial tool in the fight against the global housing crisis. Moreover, as builders and architects increasingly embrace this technology, the future looks promising, with trends indicating a rise in:
- Customization
- Sustainability
- Smart technology integration
Ultimately, 3D printing is not just a passing trend; it represents a fundamental shift in the construction landscape that can redefine how homes are built and experienced. As the industry adapts to these changes, the possibilities for innovative, efficient, and environmentally friendly construction will continue to expand, creating a brighter future for homebuilding. Embracing this technology is essential for professionals aiming to stay competitive and meet the demands of a rapidly evolving market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 3D printing in home development?
3D printing in home development is a groundbreaking shift that utilizes additive manufacturing technology to layer materials precisely and efficiently, significantly speeding up project timelines and reducing waste.
What are the main benefits of 3D printing in construction?
The main benefits include cost efficiency, speed of construction, design flexibility, and sustainability. It reduces labor costs, minimizes material waste, allows for complex designs, and contributes to eco-friendly building practices.
How does 3D printing improve cost efficiency in construction?
3D printing significantly reduces labor costs and minimizes material waste, leading to substantial savings in construction budgets. Building a 3D printed home typically costs between Rs 5-5.5 lakh.
How quickly can 3D printed homes be constructed?
Dwellings can be produced in only a few days, potentially decreasing building time by as much as 70% compared to conventional building practices.
What design capabilities does 3D printing offer architects and builders?
3D printing supports complex and tailored designs that are often difficult to achieve with traditional methods, allowing for greater creativity in home design.
How does 3D printing contribute to sustainability in construction?
By utilizing fewer resources and generating less waste, 3D printing supports more eco-friendly building practices, aligning with the growing demand for sustainable development solutions.
What is the trend of hybrid manufacturing in construction?
Hybrid manufacturing combines additive manufacturing with CNC machining, enhancing the capabilities and efficiency of house 3D fabrication technology.
What is the expected growth rate of 3D printing in the construction sector?
The sector is expected to experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 111.3% from 2025 to 2030, indicating significant growth and adoption of 3D printing technology.
What other applications does 3D rendering have outside of construction?
3D rendering finds applications in medical imaging, training simulations, and product modeling, highlighting its diverse importance across various fields.
Why is it important for architects to learn about 3D rendering technologies?
As demand for skilled professionals in 3D rendering grows, learning about these technologies becomes crucial for architects to stay competitive in the evolving job market.

0 Comments