Overview:
The article focuses on how to effectively analyze case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, emphasizing a structured approach that includes identifying purpose, examining composition, evaluating lighting, and assessing materiality, among other steps. This method is supported by the article’s detailed breakdown of each analytical step and its significance in enhancing communication, reducing costs, and improving design outcomes in architectural practices.
Introduction
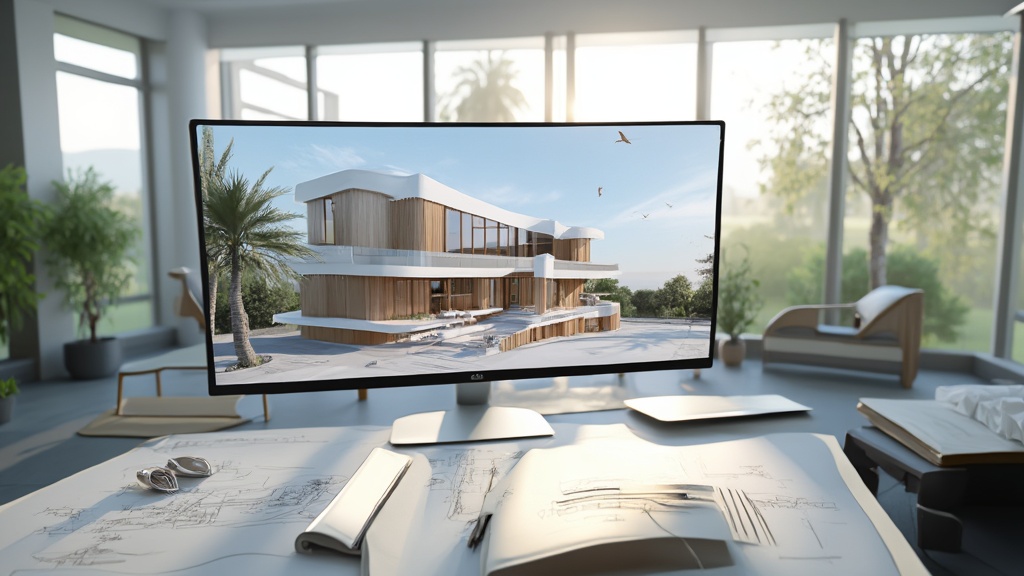
In the dynamic world of architecture, the integration of 3D rendering technology has revolutionized the way designs are conceptualized, communicated, and realized. By producing photorealistic images and animations, architects can vividly convey their visions, allowing clients and stakeholders to engage with projects on a deeper level.
This article delves into the multifaceted role of 3D rendering in architectural practice, exploring its significance in enhancing design understanding, facilitating stakeholder collaboration, and driving investment through compelling visual narratives. Through case studies and practical insights, the discussion will illuminate the essential tools and methodologies that architects can leverage to refine their visualization skills and adapt to emerging trends in the industry.
As the architectural landscape continues to evolve, understanding and utilizing these rendering techniques will be paramount for creating spaces that resonate with communities and foster lasting connections.
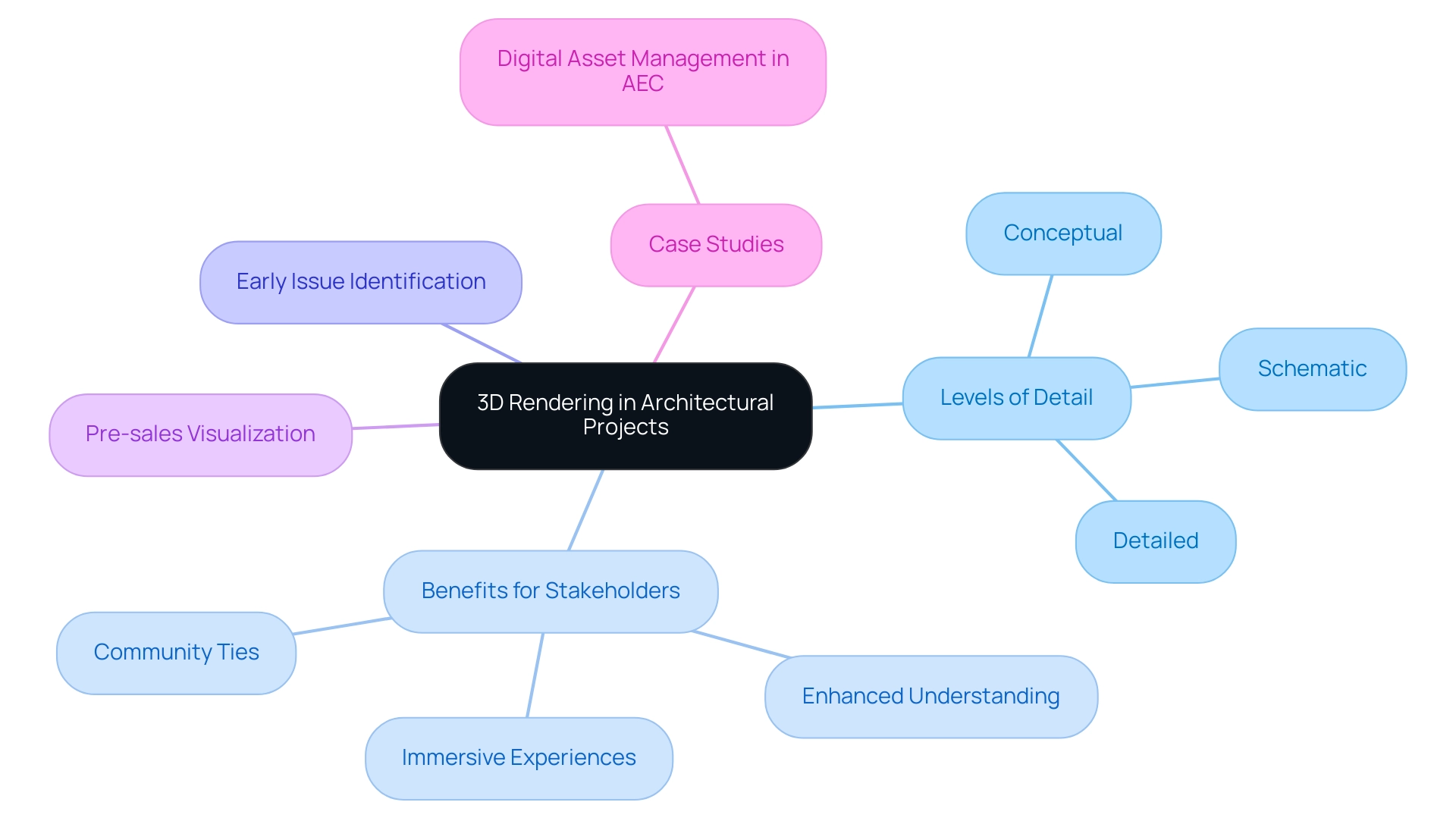
Understanding 3D Rendering in Architectural Projects
In contemporary architectural practice, 3D rendering plays a pivotal role by generating photorealistic images and animations that vividly depict architectural concepts at varying levels of detail, such as conceptual, schematic, and detailed renderings. This capability is particularly valuable for homeowners and businesses, as it not only enhances understanding of spatial relationships, material selections, and lighting dynamics but also fosters immersive experiences that connect potential residents with their future homes, thus laying the groundwork for strong community ties. By employing advanced software platforms, architects can produce intricate three-dimensional representations, facilitating improved communication with stakeholders and removing conceptual misunderstandings.
Furthermore, the use of 3D representations allows for the early identification of design issues, which can lead to significant cost savings in project development through timely client adjustments. The role of pre-sales visualization is crucial, empowering developers with tangible assets that instigate interest and investment long before a project’s physical manifestation. The case study titled ‘Digital Asset Management in AEC’ serves as a guide to case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, demonstrating that implementing such systems results in enhanced accessibility and organization in design practices, while highlighting the advantages of incorporating 3D visualization into digital workflows.
The evolution of 3D visualization technology underscores the importance of photorealistic imagery in architecture, serving as a cornerstone for effective communication and successful project realization, while enhancing the immersive experience that fosters community connections.
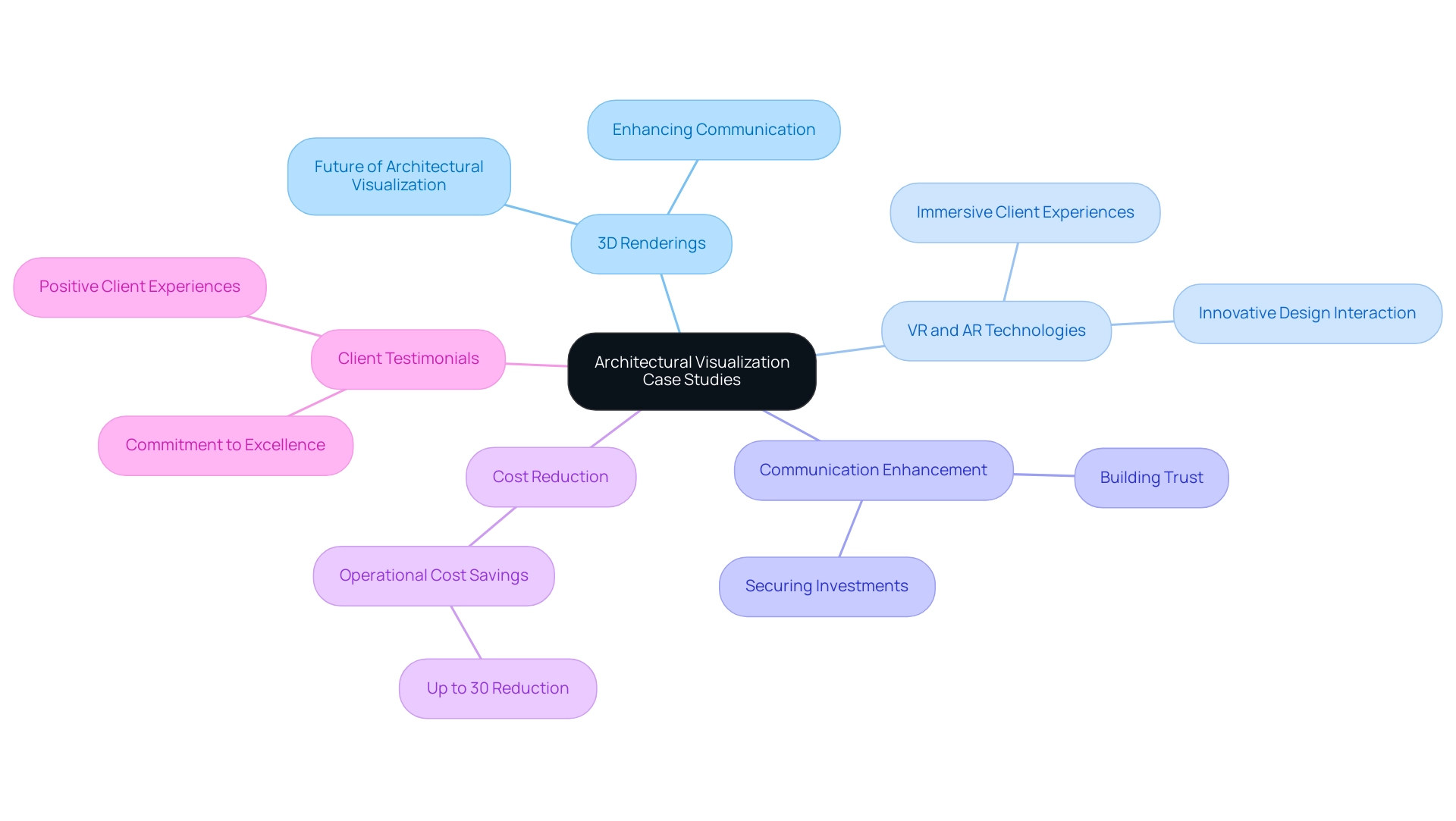
The Role of Case Studies in Architectural Visualization
The guide to case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects serves as pivotal examples demonstrating the use of 3D images across diverse projects. These studies illustrate how effective rendering techniques not only enhance communication of concepts but also bolster project confidence and secure investment. For instance, the case study titled ‘Future of Architectural Visualization’ highlights advancements through technologies like virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), offering immersive experiences that enable clients to interact with designs in unprecedented ways.
As Catherine Paul, a content writer and editor at ArchiCGI, observes, ‘The future of architectural representation is not just about aesthetics; it’s about creating experiences that resonate with clients.’ Moreover, the effectiveness of pre-sales displays is clear in how our images create interest and income well ahead of construction starting, making them vital resources for developers. The guide to case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects enables architects to examine successful strategies and recognize common pitfalls, such as miscommunication or underutilization of technology, while exploring innovative approaches in the field.
Each case study presents a distinctive viewpoint on the fusion of technology and aesthetics, offering invaluable insights that are crucial for architects aiming to refine their visualization skills. Moreover, utilizing detailed interior visualizations throughout a building’s lifecycle can lead to a potential reduction in facility operation costs by as much as 30%, underscoring the practical benefits of these visualization techniques. This reduction is directly connected to the improved functionality and aesthetics offered by detailed visualizations, which can assist in making informed design choices.
As the architectural landscape evolves, these case studies will serve as a guide to case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, remaining crucial resources for architects aspiring to elevate their practice through effective visualization. Additionally, client testimonials play a significant role in building trust and reliability, reflecting our commitment to excellence and innovation, and showcasing the positive experiences our clients have had with our services.
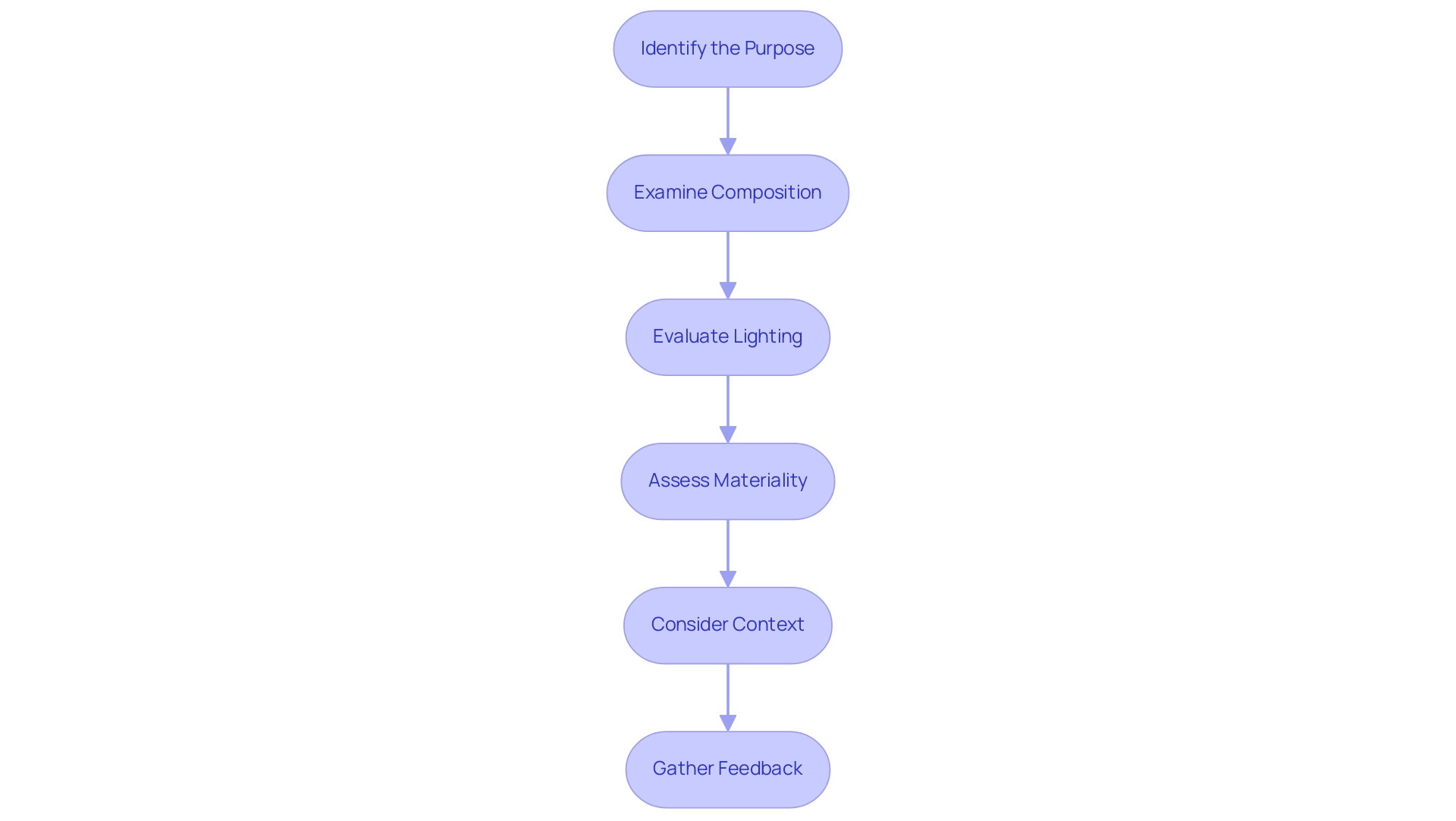
Step-by-Step Guide to Analyzing 3D Renderings
To effectively analyze 3D images, adhere to the following structured approach:
Identify the Purpose:
Begin by understanding the intent behind the representation. Determine whether it is intended for client presentation, marketing strategies, or validation, as clarity in purpose sets the foundation for effective communication.Examine Composition:
Assess the arrangement of elements within the depiction. Effective composition is essential, directing the viewer’s eye and highlighting key architectural features that resonate with the essence of the work.Evaluate Lighting:
Analyze the lighting techniques employed. Consider whether the lighting is natural or artificial and how it influences the mood and spatial perception within the visualization.
Recent insights indicate that appropriate lighting is fundamental in showcasing intentions, enhancing overall visual appeal.
Assess Materiality:
Review the textures and materials employed in the depiction. Examine their realism and appropriateness concerning the overall design vision. High-quality material representation can significantly impact audience perception, reflecting the meticulous detail necessary for accurate project documentation.Consider Context:
Evaluate how the depiction situates the structure within its environment. A depiction should respect and complement the surrounding context, enhancing its integration into the landscape. The function of detailed representations is crucial in visualizing and improving residential architecture designs, serving as a guide to case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, which can result in higher property value through market differentiation.Gather Feedback:
Engage in discussions with peers or clients to obtain diverse perspectives on the effectiveness of the visual presentation. This dialogue can reveal insights that may not be immediately apparent during the initial analysis.
Furthermore, our knowledge enables us to produce top-notch images for both interior and exterior projects, guaranteeing a thorough representation experience. Utilizing this thorough approach will enhance your skill to critically assess 3D visualizations, in line with the substantial expansion of the visualization and 3D graphics software market, anticipated at a CAGR of 30.6% from 2023 to 2030. Key market segments encompass software components, organization size, operating systems, applications, end-use industries, and regions, which are essential for understanding the broader context of 3D visualization.
As emphasized by Apple, advancements in software capabilities, such as those in MacOS Sonoma, enhance the visualization experience, making such evaluations increasingly relevant. Additionally, the Windows operating system maintains a dominant share in the 3D visualization market due to its compatibility with powerful graphics hardware and software, further emphasizing the importance of evaluating different software platforms in your analysis. Remember, the small elements in your illustrations contribute to a captivating narrative that embodies the essence of your creation.
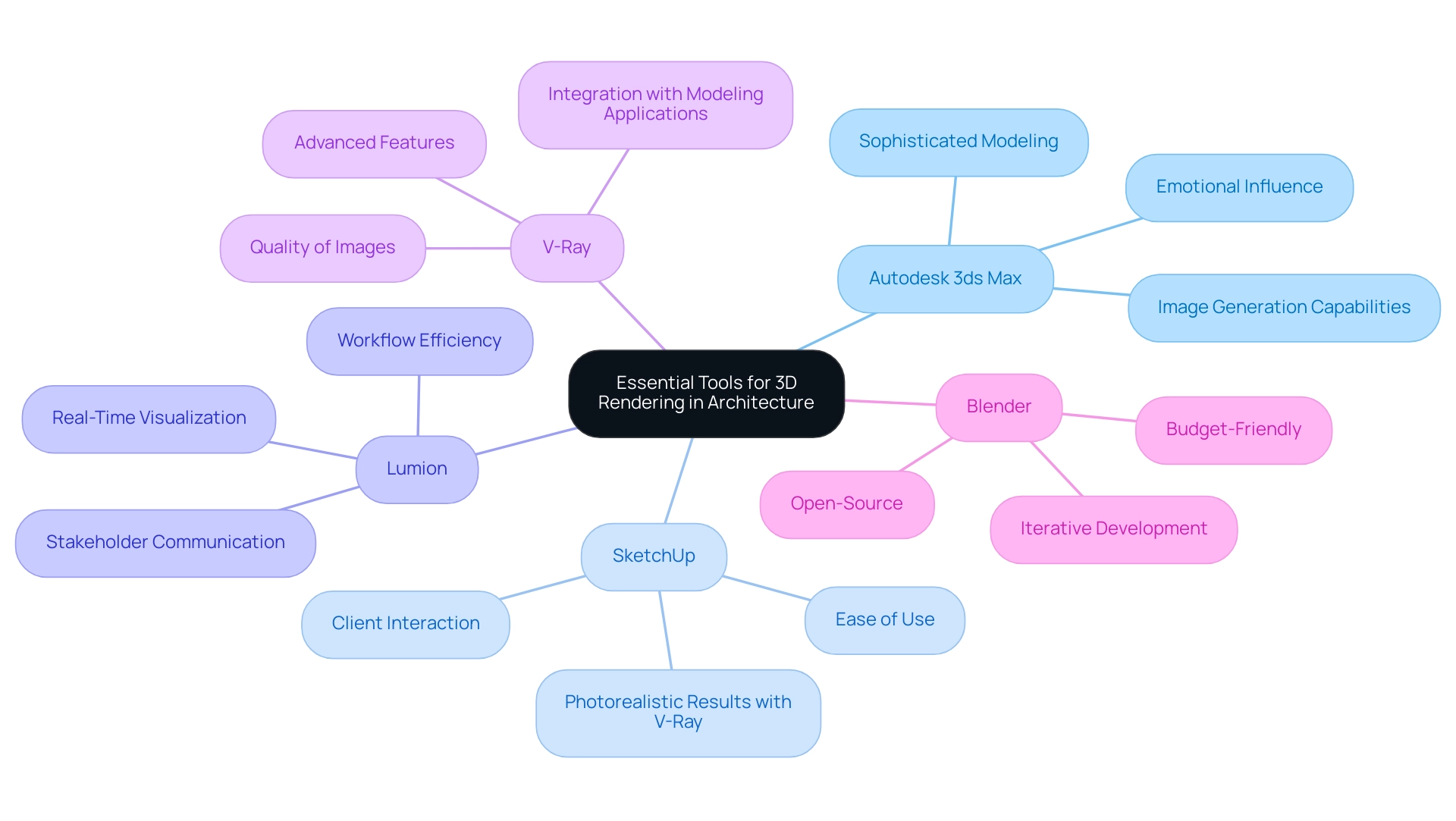
Essential Tools and Software for 3D Rendering
In the field of 3D depiction for architecture, several key software tools serve as a guide to case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, highlighting their capabilities and influence on presentation projects.
Autodesk 3ds Max: Renowned for its sophisticated modeling and image generation capabilities, Autodesk 3ds Max is a fundamental component in the architectural presentation toolkit, allowing architects to craft intricate designs with accuracy, thus amplifying the emotional influence of their projects.
SketchUp: This intuitive software is favored for its ease of use in generating 3D models. When paired with visualization plugins like V-Ray, it produces photorealistic results that are essential for impactful presentations and significant client interaction.
Lumion: Acknowledged for its real-time visualization capabilities, Lumion enables architects to create engaging representations rapidly, thereby enhancing workflow efficiency and promoting improved communication with stakeholders.
V-Ray: As a highly regarded visualization engine, V-Ray integrates seamlessly with various modeling applications, providing advanced features that elevate the quality of produced images, vital for informed decision-making.
Blender: This open-source software is perfect for budget-sensitive projects, providing powerful modeling and visualization tools that address a wide variety of design requirements while facilitating iterative development processes.
Comprehending these tools is crucial for grasping the complexities involved in the guide to case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects.
The level of detail in architectural illustrations plays a crucial role in helping homeowners and businesses visualize their projects accurately, fostering emotional connections and informed decision-making. For example, the collaboration between TechViz and Lenovo ThinkReality illustrates how sophisticated graphics tools can improve data display in AR, enabling users to shift from CAD applications to 3D representations effortlessly.
Furthermore, major trends in the visualization and 3D modeling software market indicate that technological advancements are driving innovation, critical for addressing challenges such as the economic losses from extreme weather—estimated at US$140 billion—highlighted by NVIDIA’s Earth-2 climate digital twin cloud platform.
This context underscores the integral role of these tools in contemporary design practices, their importance in fostering community connections, and enhancing contractor communication through immersive experiences.
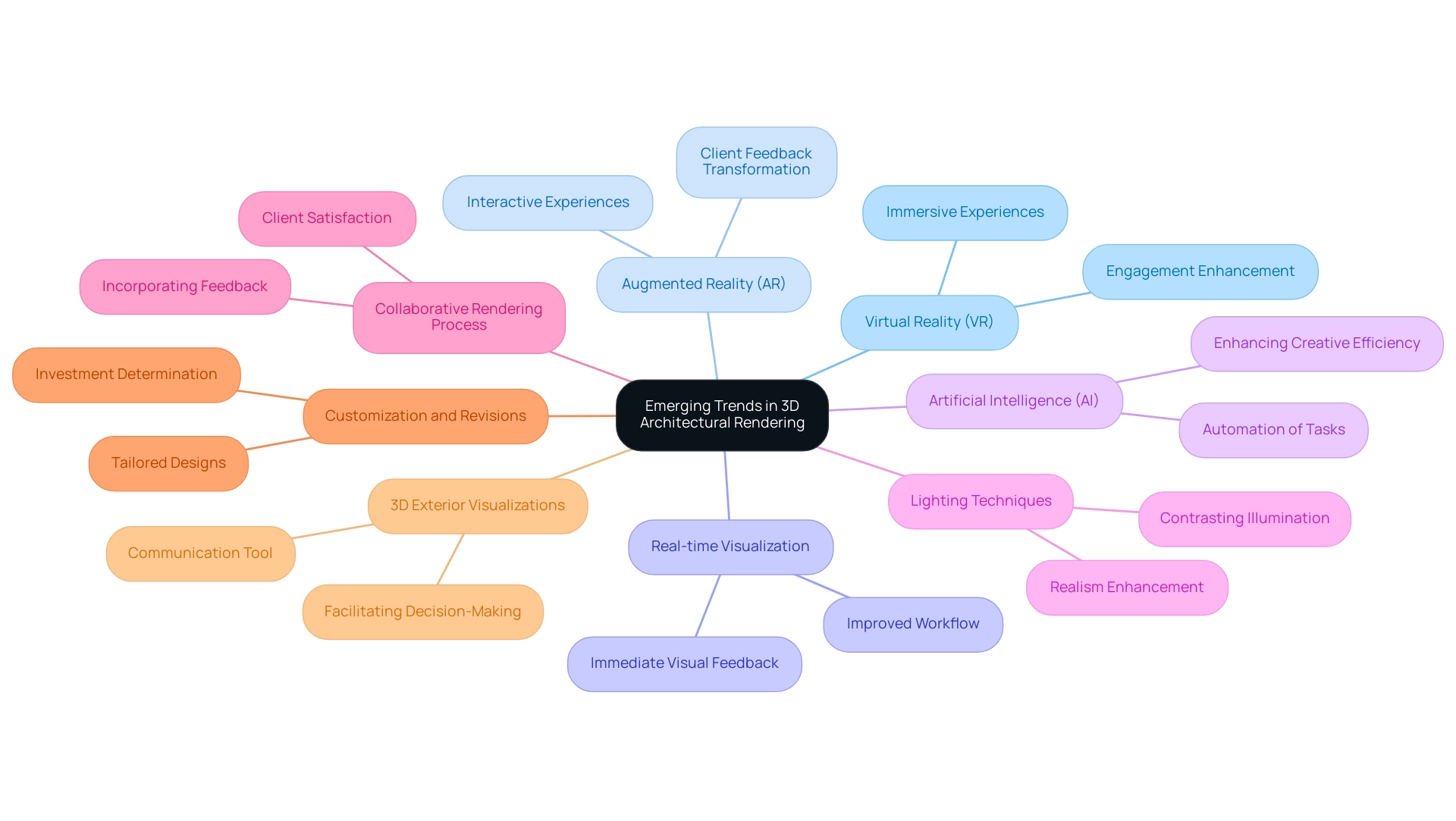
Emerging Trends in 3D Architectural Rendering
The landscape of 3D building rendering is rapidly evolving, which is detailed in the guide to Case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, characterized by several key trends that architects should closely monitor.
Virtual Reality (VR): The incorporation of VR technology in architectural visualization is altering how clients engage with concepts, enabling immersive experiences that allow them to navigate spaces as if they were physically present. A relevant case study, “Managing Student Distractions in Virtual Reality Learning,” highlights how VR tools can enhance engagement by establishing guidelines that maintain student focus.
Augmented Reality (AR): By enhancing real-world environments with digital overlays, AR provides interactive experiences that are transforming client engagement and feedback throughout the creation process.
Real-time Visualization: The need for tools that enable real-time visualization is increasing, as they provide immediate visual feedback, greatly improving the workflow and boosting collaborative efforts.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being utilized to automate routine visualization tasks, particularly in creating lifelike CG humans, thereby enhancing creative efficiency and allowing architects to concentrate on more intricate artistic aspects. This technology is also pivotal in bridging the uncanny valley, ensuring that visualizations resonate more effectively with clients.
Lighting Techniques: The importance of lighting in architectural illustrations cannot be overstated; contrasting artificial illumination in interiors with natural sunlight in exteriors enhances realism and conveys intent effectively, serving as a guide to Case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects.
Collaborative Rendering Process: At J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, our collaborative process—from initial communication to detailed 3D modeling—ensures client satisfaction by incorporating feedback at each stage.
Customization and Revisions: The focus on customization and the readiness to adjust designs play a crucial role in determining the investment required for unique projects. Tailoring designs to meet specific client needs serves as a guide to case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, as it not only enhances satisfaction but also ensures that the final product aligns with their vision.
3D Exterior Visualizations: These visuals serve as a vital tool for enhancing communication between homeowners and builders, providing a clear visual representation that facilitates discussions and decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
Investing in Quality: Ultimately, investing in impressive 3D renderings is essential for articulating your architectural vision, as they significantly enhance communication between homeowners and builders.
As the industry shifts towards eco-friendly architecture, visualizing sustainable design practices aligns with client expectations and reflects broader environmental considerations. Remaining informed about these developments empowers architects to leverage cutting-edge technologies and innovative approaches, ultimately enhancing the quality and impact of their work.
Conclusion
The integration of 3D rendering technology in architecture has fundamentally transformed the design process, enhancing visualization, communication, and stakeholder engagement. The ability to generate photorealistic images and animations not only aids in conveying complex design ideas but also fosters deeper connections between clients and their future spaces. This article has explored the essential role of 3D rendering, highlighting its significance in facilitating understanding of spatial relationships, materiality, and lighting dynamics while also serving as a valuable tool for pre-sales visualization.
Case studies have illustrated the practical applications of these rendering techniques, demonstrating their capacity to build confidence among stakeholders and attract investment. The advancements in virtual and augmented reality further emphasize the need for architects to embrace emerging technologies that enhance user experience and interaction. By employing a structured approach to analyzing 3D renderings, architects can refine their visualization skills and ensure that their designs resonate effectively with clients.
Moreover, staying informed about the latest tools and trends in 3D rendering is crucial for architects aiming to maintain a competitive edge in an evolving landscape. The emphasis on customization, real-time rendering, and the integration of artificial intelligence underscores the importance of innovation in architectural practices. Ultimately, leveraging these advancements will not only elevate the quality of architectural visualization but also contribute to creating spaces that foster community connections and reflect the aspirations of clients. Embracing 3D rendering technology is not just an enhancement of the design process; it is an essential strategy for architects committed to excellence and impactful storytelling in their work.

0 Comments