Overview
The article provides a comprehensive tutorial on drafting drawing techniques, covering essential tools, fundamental methods, and advanced practices necessary for success in architectural design. It emphasizes the importance of precision tools, various drawing styles, and advanced technologies like 3D modeling and VR, which together enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of architectural visualizations and presentations.
Introduction
In the world of architectural design, the tools and techniques employed can significantly influence the quality and effectiveness of drafts. From the essential drafting instruments that lay the groundwork for precision to advanced 3D visualization methods that bring ideas to life, mastering these elements is crucial for aspiring architects and designers.
This article delves into the fundamental tools, techniques, and styles that are pivotal in the drafting process, exploring everything from the basics of line weights and hatching to the innovative applications of virtual reality and 3D modeling software.
By understanding and implementing these practices, designers can enhance their creativity, improve communication with clients and contractors, and ultimately elevate their architectural presentations to new heights.
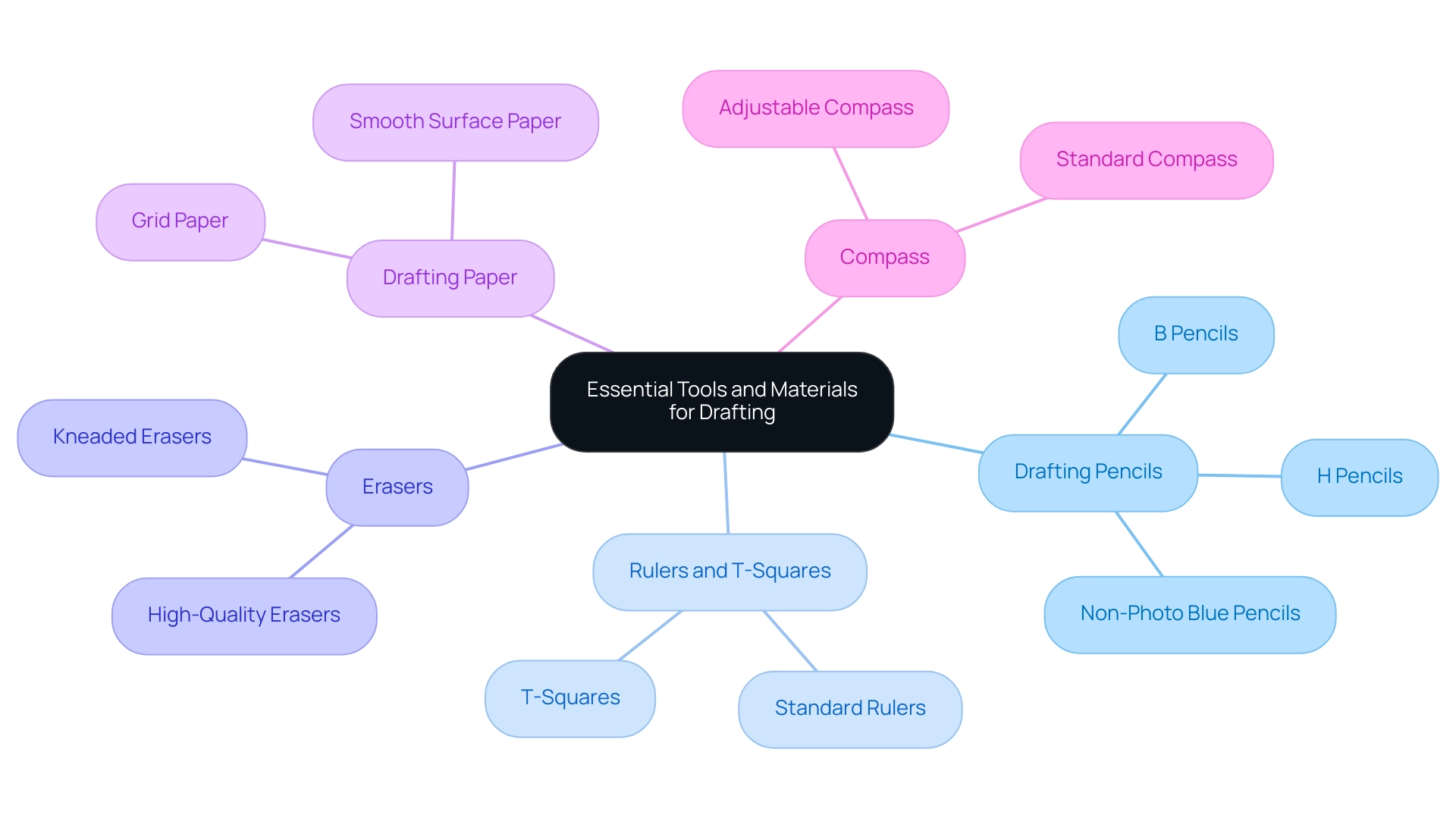
Essential Tools and Materials for Drafting
To embark on your drafting journey, it’s crucial to equip yourself with the following essential tools that will enhance both your precision and creativity:
- Drafting Pencils: A variety of pencils, including H for fine lines and B for darker lines, are essential for creating clear and precise sketches. The appropriate pencil selection greatly influences the quality of your artwork.
- Rulers and T-Squares: These tools are fundamental for creating straight lines and ensuring accurate measurements. Their reliability contributes to the overall professionalism of your drafting drawing.
- Erasers: A high-quality eraser is vital for correcting mistakes without damaging your paper, allowing for clean revisions in your work.
- Drafting Paper: Choosing the suitable paper is essential; grid paper helps in accuracy, while smoother surfaces are perfect for intricate illustrations. The choice of paper can influence the final presentation of your designs.
- Compass: An essential instrument for creating circles and arcs, a compass enables accuracy in forming geometric shapes.
In total, there are 24 common instruments that professionals frequently employ, which highlights the variety available to improve your design practice. One notable instrument is the non-photo blue pencil, which is especially helpful for sketching and creating preliminary drawings; its blue lines are not captured by photocopiers or scanners. This allows architects to sketch freely without interfering with final presentations.
Equipped with these resources, you will establish a strong foundation for your drafting drawing practice, enabling you to concentrate on refining your techniques and unleashing your creativity. As highlighted by the Institute of Data, “This ongoing support ensures you gain long-term benefits from your education, giving you the tools and connections needed for success.” Such foundational skills not only enhance your immediate capabilities but also provide long-term benefits essential for your success in architectural design.
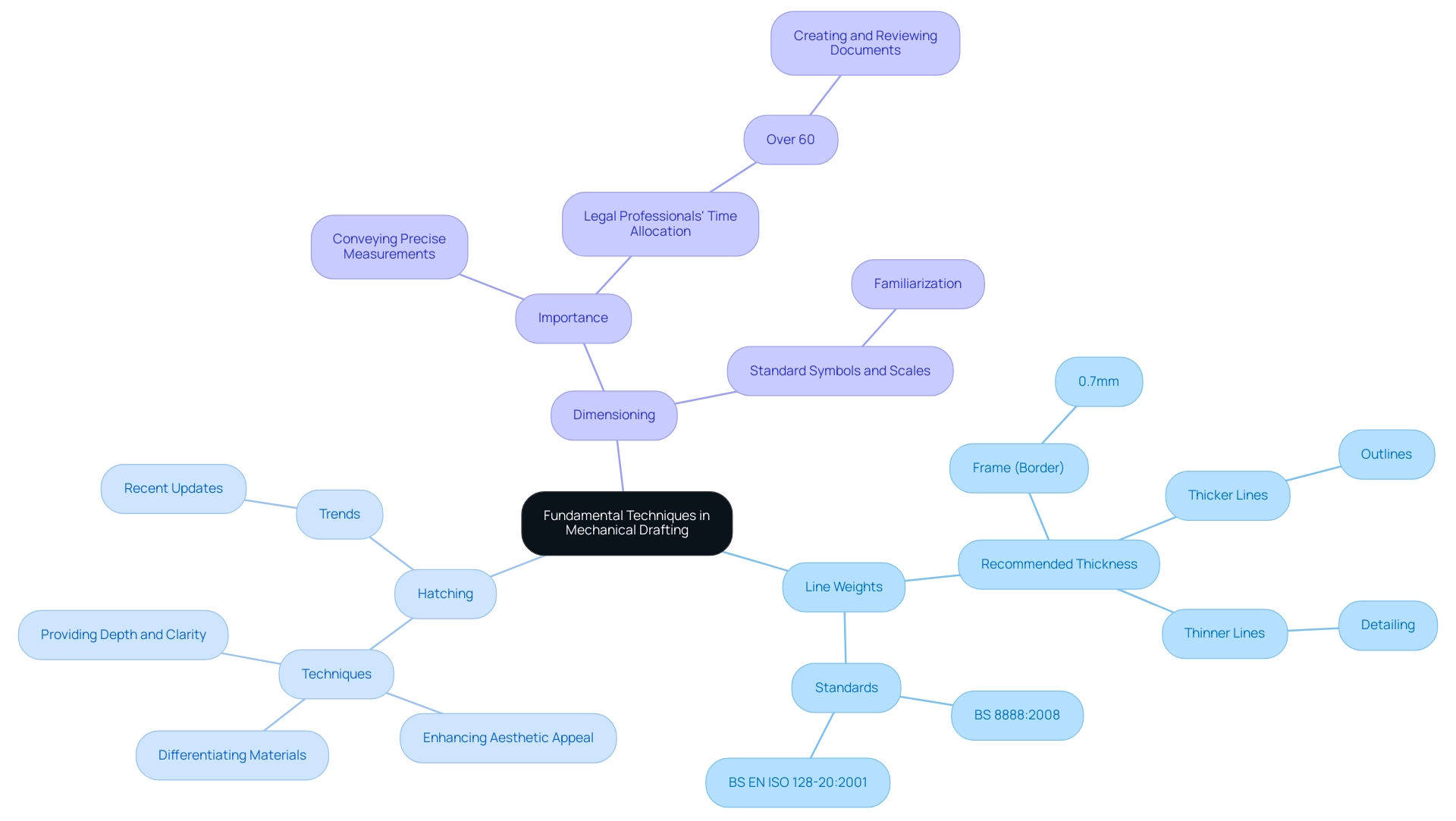
Fundamental Techniques in Mechanical Drafting
To elevate your mechanical drafting skills, it’s crucial to master several essential techniques:
- Line Weights: Utilizing varying line weights is fundamental to distinguishing different elements within your illustrations. According to Paul Munford, the recommended line weight for the frame (border) in engineering documents is 0.7mm. Thicker lines typically denote outlines, while thinner lines are reserved for detailing, providing clarity and focus in your creations. Adhering to standards such as BS 8888:2008 and BS EN ISO 128-20:2001 ensures that your drawings maintain industry compliance and professionalism.
- Hatching: Implementing hatching techniques effectively differentiates materials or sections in your drawings. This not only enhances the aesthetic appeal but also provides depth and clarity, allowing viewers to quickly interpret the design elements. Staying updated with recent trends in hatching techniques can further enhance your drawing skills.
- Dimensioning: Accurate dimensioning is vital for conveying precise measurements. Familiarize yourself with standard symbols and scales to ensure that all measurements are clear and understandable. This practice is vital, particularly given that legal professionals allocate over 60% of their time creating and reviewing documents. This statistic underscores the critical nature of precision in any technical illustration, reinforcing the need for meticulous attention to detail.
By focusing on these fundamental techniques and adhering to established standards, you will significantly enhance the quality of your drafting drawing. Furthermore, as emphasized in the case study on bias prevention in GenAI content, ensuring accuracy and reliability in your drafting processes is crucial for producing trustworthy and effective outputs, paving the way for more advanced methods in mechanical drafting.
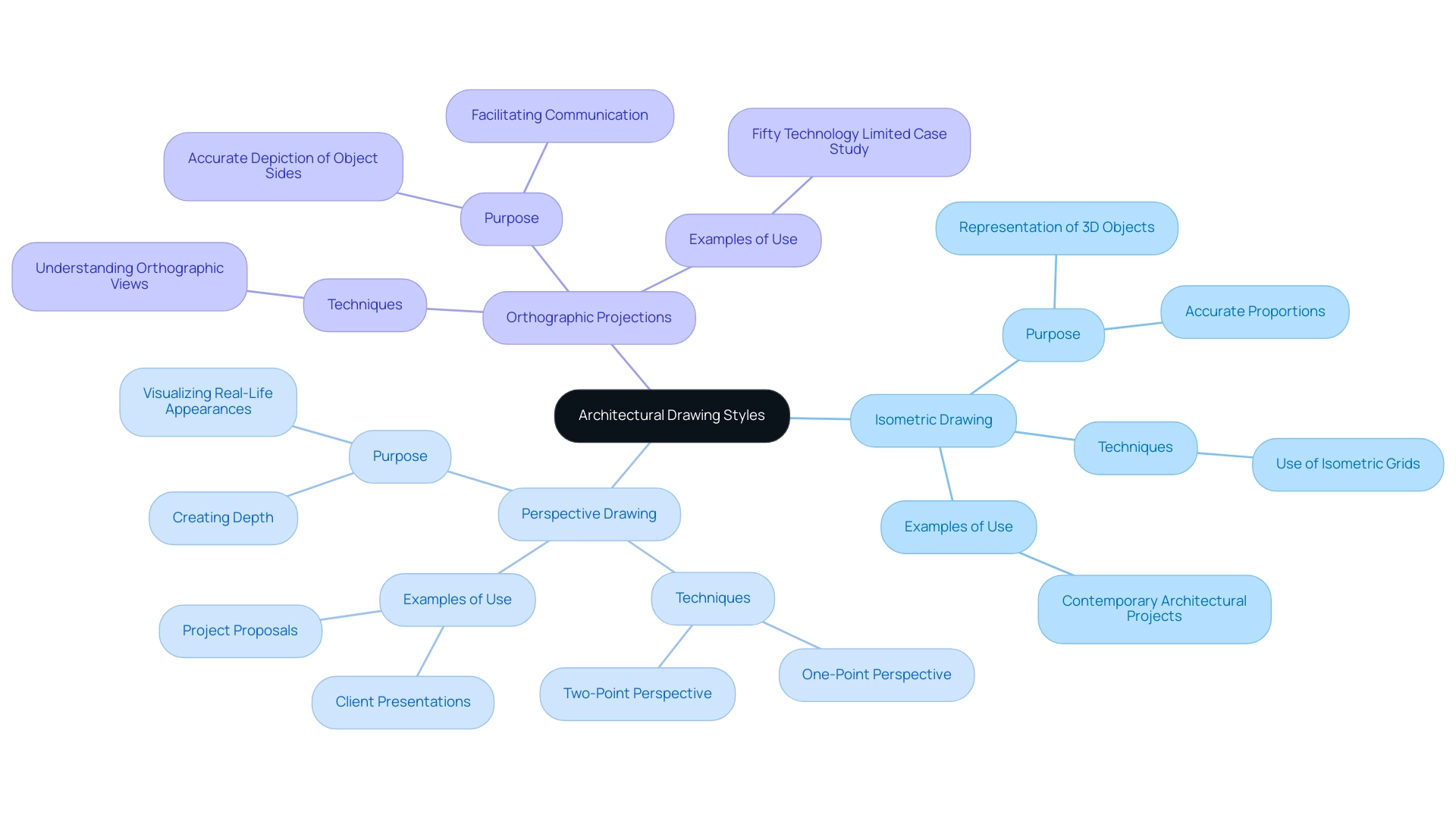
Exploring Different Drawing Styles: Isometric and Beyond
To excel in architectural design, it is crucial to become proficient in various drawing styles, each serving a distinct purpose in visual communication:
- Isometric Drawing: This technique enables the representation of three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional surface without distortion. By practicing with isometric grids, architects can ensure accurate proportions and relationships between components. Recent statistics indicate that isometric representation methods are utilized extensively in projects, with a significant percentage of architects reporting their use in contemporary work. This highlights their relevance in modern architecture and their role in enhancing clarity in architectural visualizations.
- Perspective Drawing: Mastering the principles of one-point and two-point perspective is essential for creating depth in architectural illustrations. These techniques, such as drafting drawing, allow designers to visualize how their creations will appear in real life, making them invaluable for client presentations and project proposals. As trends emphasize the growing demand for realistic representations, perspective drawing significantly contributes to this need. Yasser El-Gammal, in “Architecture and Fashion—Something in Common,” explores the parallels between these fields, underscoring the importance of perspective in effectively communicating architectural visions.
- Orthographic Projections: Understanding orthographic views is fundamental for accurately depicting different sides of an object without distortion. This method offers a clear and precise representation, facilitating better communication of intentions among project stakeholders. A case study involving Fifty Technology Limited illustrates how effective communication through orthographic projections can enhance user interaction and clarity, especially in projects requiring thorough data collection and analysis.
Moreover, investing in high-quality visual renderings and drafting drawing, whether for interior or exterior designs, serves as a crucial tool for architects. These renderings not only highlight the potential of concepts but also clarify the vision behind the blueprints, aiding in informed decision-making and generating excitement about upcoming projects.
When differentiating between interior and exterior renderings, it is essential to consider the technical differences in lighting, materials, and environments. For instance, interior renderings often utilize softer lighting to create a warm and inviting atmosphere, while exterior renderings may employ harsher, more dynamic lighting to highlight architectural features against natural backdrops. Additionally, materials used in interiors, such as textiles and finishes, require careful representation to convey texture and color accurately, whereas exterior materials like brick or stone must be depicted with attention to their interaction with the surrounding environment.
By mastering these illustration styles and understanding these technical differences, architects can significantly improve the impact of their visual presentations.
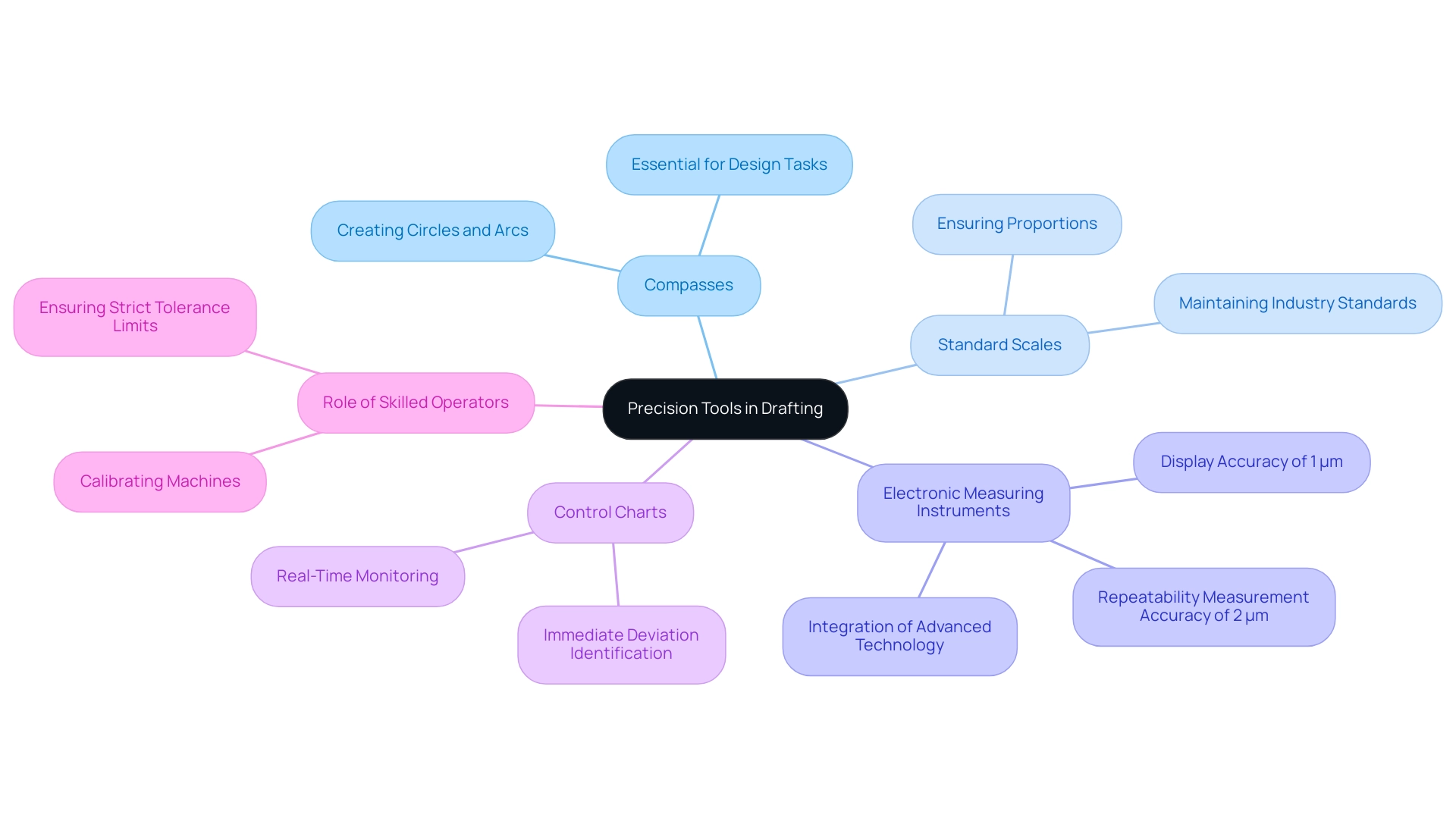
The Role of Precision Tools in Achieving Accurate Drafts
Employing precise instruments is crucial for drafting drawing accuracy and achieving professional outcomes in construction.
- Compasses: A compass is invaluable for creating consistent circles and arcs, which are essential to many design tasks. Mastery of this tool allows for the creation of precise curves vital for architectural and engineering applications, especially in drafting drawing.
Utilizing a standard scale not only ensures that correct proportions are maintained in your drafting drawing but also aligns with industry standards, enhancing overall project quality. It guarantees that angle measurements are exact, which is crucial for the structural integrity of designs. As mentioned by Ronan Ye, a Rapid Prototyping and Rapid Manufacturing Specialist,
To attain high accuracy, it’s crucial to assess the measurement system utilized during machining,
emphasizing the significance of precise instruments in the design process.
Integrating these instruments into your drafting drawing practice not only enhances the accuracy of your work but also elevates your professionalism in the industry. Furthermore, the integration of advanced precision tools, such as the electronic camera-based measuring instruments developed by Tianjin University, featuring a display accuracy of 1 μm and repeatability measurement accuracy of 2 μm, exemplifies how technology continues to evolve and improve the accuracy of drafting drawing. Visual renderings play a critical role in strengthening communication with contractors by clearly conveying intentions, thereby eliminating misunderstandings.
This aligns with the principle that ‘traditional’ means different things to everyone; showing a rendering removes all doubt. Therefore, offering your contractors a break by supplying clear visual aids can significantly improve their comprehension of your creations. Additionally, control charts can monitor machining performance in real time, allowing for immediate identification of deviations that may affect accuracy.
Case studies demonstrate that skilled operators play a critical role in calibrating these machines, ensuring adherence to strict tolerance limits, which is essential for maintaining precision in drafting drawing. By understanding and applying these techniques, you can significantly enhance the accuracy and reliability of your creations, ultimately influencing broader industry trends in construction. The storytelling aspect of 3D visualizations also adds depth, capturing the essence of your design and presenting a compelling narrative of what the future holds for a building or home.
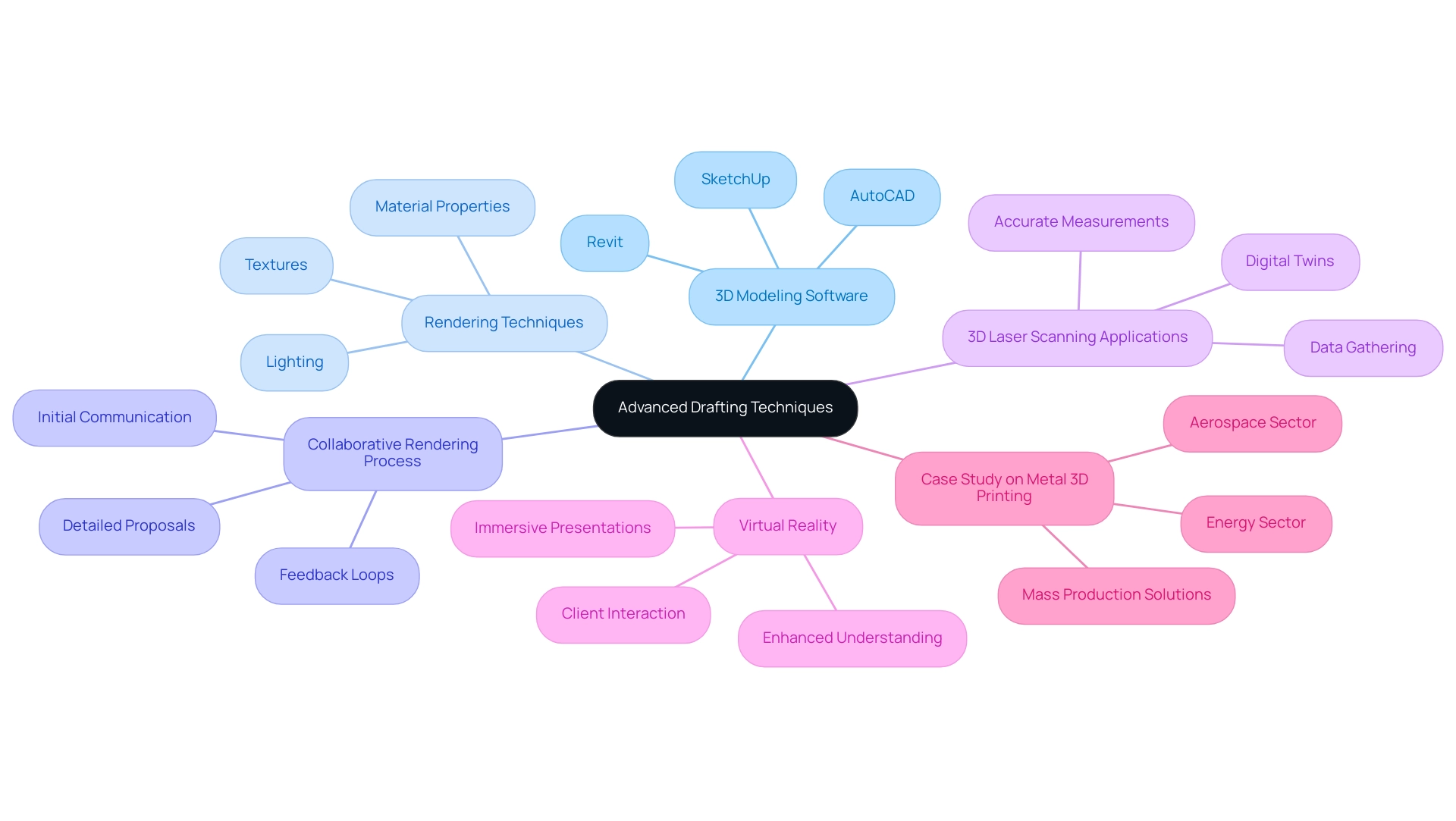
Advanced Drafting Techniques: 3D Visualization and Rendering
To excel in advanced drafting drawing techniques, consider focusing on the following key areas:
3D Modeling Software: It’s essential to become proficient with leading software applications such as AutoCAD, SketchUp, and Revit. These tools are fundamental for generating intricate 3D models that can be transformed into realistic renderings. As the retail technology revenues in the U.S. are projected to reach USD 485 billion in 2023, the demand for skilled professionals adept in these programs continues to rise.
Rendering Techniques: Mastering rendering software is crucial for creating high-quality visualizations of your architectural concepts. A deep understanding of lighting, textures, and material properties will enable you to produce lifelike representations that convey your vision effectively. High-quality renderings serve as a window into the future of your project, allowing stakeholders to see potential and understand the vision behind the drafting drawing, which is vital for making informed decisions and generating excitement. Major players like Autodesk and ESRI are enhancing their products, reflecting the industry’s commitment to elevating architectural visualization.
Collaborative Rendering Process: The path to successful renderings starts with initial communication. Understanding your project goals and specific needs through a detailed proposal helps establish a clear vision. This collaborative method, from drafting drawing basic projects to refining intricate 3D representations, ensures that the final product captures your vision while exceeding client expectations. For example, feedback loops during the rendering process allow for adjustments based on client preferences, which is crucial for achieving satisfaction.
3D Laser Scanning Applications: Incorporating 3D laser scanning into your workflow can significantly enhance the accuracy of your models. This technology enables accurate measurements and data gathering, which are essential in the development of digital twins and asset visualization solutions, resulting in informed decision-making in construction projects.
Virtual Reality: The incorporation of Virtual Reality (VR) in architectural presentations is transforming how concepts are conveyed. This immersive technology allows clients to interact with concepts in a captivating environment, significantly enhancing their understanding and appreciation of the project. As noted by SAP SE, approximately 70% of organizations in the U.K. are planning to adopt new technologies to tackle various challenges in manufacturing and development, indicating a strong shift towards innovative solutions.
Case Study on Metal 3D Printing: The trend of adopting metal 3D printing for end-use parts production in the aerospace and energy sectors illustrates the practical applications of drafting drawing techniques. This case study reflects how industries leverage new printing solutions designed for mass production, thereby accelerating workflows and enhancing productivity.
By honing your expertise in 3D visualization, rendering techniques, and understanding the latest industry trends, you will be well-prepared to present your designs in a compelling and professional manner, meeting the evolving expectations of clients in an increasingly competitive market. Additionally, incorporating testimonials from satisfied clients can further validate the effectiveness of your rendering process and its impact on project success.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of architectural drafting involves a comprehensive understanding of various essential tools, techniques, and styles that collectively enhance both creativity and precision. From the foundational drafting instruments, such as pencils and rulers, to the advanced capabilities offered by 3D modeling software and virtual reality, each element plays a critical role in the drafting process. The effective use of line weights, hatching, and dimensioning not only elevates the quality of drafts but also ensures compliance with industry standards, fostering professionalism.
The exploration of diverse drawing styles, including isometric and perspective drawing, further enriches visual communication, allowing architects to convey their design intentions clearly and effectively. Implementing precision tools, such as compasses and drafting scales, is vital for achieving accuracy, while advanced techniques like rendering and 3D visualization facilitate compelling presentations that resonate with clients and stakeholders alike.
Ultimately, the integration of these drafting practices empowers architects and designers to push the boundaries of their creativity while enhancing project clarity and communication. By embracing both traditional and innovative techniques, architectural professionals can elevate their presentations and, in turn, their impact on the industry. The continuous evolution of drafting tools and technologies promises a future where creativity and precision go hand in hand, paving the way for groundbreaking architectural designs that inspire and transform.
Frequently Asked Questions
What essential tools are needed for drafting?
Essential tools for drafting include drafting pencils (H for fine lines and B for darker lines), rulers and T-squares for straight lines and accurate measurements, high-quality erasers for clean corrections, suitable drafting paper (grid paper for accuracy and smoother surfaces for intricate illustrations), and a compass for creating circles and arcs.
Why is the choice of drafting pencils important?
The choice of drafting pencils is important because different pencils (H for fine lines and B for darker lines) greatly influence the clarity and quality of sketches in your artwork.
How do rulers and T-squares contribute to drafting?
Rulers and T-squares are fundamental tools for creating straight lines and ensuring accurate measurements, which contribute to the professionalism and reliability of drafting drawings.
What role do erasers play in the drafting process?
High-quality erasers are vital for correcting mistakes without damaging the paper, allowing for clean revisions and maintaining the integrity of the artwork.
How does the type of drafting paper affect the final presentation?
The type of drafting paper affects the final presentation by influencing accuracy and detail; grid paper helps with precision, while smoother surfaces are ideal for intricate illustrations.
What is the purpose of a compass in drafting?
A compass is essential for creating circles and arcs, enabling accuracy in forming geometric shapes within your designs.
What is a non-photo blue pencil and why is it useful?
A non-photo blue pencil is particularly useful for sketching and creating preliminary drawings because its blue lines are not captured by photocopiers or scanners, allowing architects to sketch freely without interfering with final presentations.
What are some key techniques to master for mechanical drafting?
Key techniques for mechanical drafting include using varying line weights to distinguish elements, implementing hatching techniques for material differentiation, and ensuring accurate dimensioning for clear measurements.
Why is dimensioning important in drafting?
Dimensioning is important because it conveys precise measurements, which is critical for clarity and understanding in technical illustrations.
How can adhering to established standards improve drafting quality?
Adhering to established standards, such as BS 8888:2008 and BS EN ISO 128-20:2001, ensures that drawings maintain industry compliance and professionalism, significantly enhancing the quality of drafting work.

0 Comments