Understanding Design Development
Definition and Place in the Architectural Process
Design Development is the third phase in the typical architectural process, following Schematic Design and preceding Construction Documents. While Schematic Design establishes the general direction of the project, Design Development refines and develops these ideas into a more detailed and coherent design.
During this phase, architects work closely with clients, engineers, and consultants to make critical decisions about materials, systems, and equipment. The goal is to create a comprehensive design that not only meets aesthetic expectations but also addresses functional requirements, budget constraints, and regulatory standards.
Key Objectives of Design Development
- Refine the architectural vision established in Schematic Design
- Determine specific materials, systems, and equipment
- Develop detailed floor plans, elevations, and sections
- Coordinate with engineering disciplines (structural, mechanical, electrical, plumbing)
- Produce more accurate cost estimates
- Ensure compliance with building codes and regulations
The Design Development Process
Initial Review and Goal Setting
The Design Development phase typically begins with a thorough review of the Schematic Design documents. This review ensures that the project’s fundamental goals and requirements are still being met as the design evolves. Key stakeholders should reaffirm or adjust project objectives, considering any new insights gained during the Schematic Design phase.
Detailed Design Refinement
With goals established, the design team delves into the details of the project. This involves:
- Space Planning: Refining room layouts, circulation paths, and spatial relationships.
- Building Systems Integration: Working with engineers to integrate structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems into the design.
- Material Selection: Choosing specific materials for both exterior and interior elements, considering aesthetics, durability, cost, and sustainability.
- Building Envelope Design: Developing details for walls, roofs, and foundations, focusing on energy efficiency and weather resistance.
- Interior Design Development: Refining interior layouts, selecting finishes, and planning for furniture and equipment.
Coordination and Collaboration
Effective coordination between various design disciplines is crucial during this phase. Regular meetings and communication channels should be established to ensure that:
- Architectural designs align with engineering requirements
- Specialty consultants (like lighting designers or acousticians) can provide input
- Client feedback is incorporated promptly into the evolving design
3D Modeling and Visualization
As the design becomes more detailed, 3D modeling plays an increasingly important role. Advanced visualization techniques help in:
- Communicating design intent to clients and stakeholders
- Identifying and resolving spatial conflicts
- Studying lighting and shadow effects
- Evaluating material choices and color schemes
Cost Estimation and Value Engineering
Throughout Design Development, cost estimates become increasingly accurate. This allows for:
- Regular budget reviews to ensure the project remains financially viable
- Value engineering exercises to optimize cost without sacrificing quality or functionality
- Informed decision-making when choosing between design alternatives
Analysis of Materials and Systems
A significant portion of Design Development is dedicated to analyzing and selecting materials and systems. This involves:
- Exterior Materials: Evaluating options for facade materials, roofing, windows, and doors.
- Interior Finishes: Selecting flooring, wall finishes, ceilings, and cabinetry.
- Mechanical Systems: Determining HVAC strategies, considering energy efficiency and comfort.
- Electrical Systems: Planning lighting layouts, power distribution, and low-voltage systems.
- Plumbing Systems: Designing water supply, waste management, and specialty plumbing needs.
- Technology Integration: Planning for telecommunications, security systems, and audiovisual needs.
- Vertical Transportation: Designing elevator systems and staircases.
For each option, architects provide:
- Initial cost estimates
- Life cycle cost analyses
- Performance characteristics
- Aesthetic considerations
- Sustainability metrics
Site Design and Landscape Architecture
Design Development also addresses the building’s relationship with its site:
- Refining site layout and grading plans
- Developing landscape design concepts
- Planning for parking and site circulation
- Addressing stormwater management and site utilities
Regulatory Compliance and Permitting
Ensuring compliance with building codes and regulations is a critical aspect of Design Development:
- Conducting code analyses to verify compliance
- Initiating discussions with local authorities having jurisdiction
- Preparing documentation for zoning approvals or variances, if needed
- Beginning the process of applying for building permits
Client Involvement and Decision-Making
Time Commitment and Meeting Structure
Clients should expect to be actively involved throughout the Design Development phase:
- Weekly or bi-weekly meetings with the design team
- Regular review of design progress and options
- Timely decision-making to keep the project on schedule
It’s recommended to have a core group of decision-makers to streamline the process, typically including:
- Key stakeholders from the client organization
- Project manager or owner’s representative
- Facilities management representatives (for larger projects)
Making Informed Decisions
To facilitate effective decision-making:
- Architects should provide clear, comprehensive information on each option
- Clients should establish internal processes for evaluating and approving design decisions
- Decisions should be documented and communicated clearly to the entire project team
Balancing Desires with Constraints
Clients often face challenging decisions during Design Development, balancing:
- Aesthetic preferences
- Functional requirements
- Budget constraints
- Long-term operational considerations
It’s crucial to keep the project’s core goals in mind when making these decisions, prioritizing elements that align with the overall vision and objectives.
Preparing for Design Development
To make the most of the Design Development phase, clients should:
- Review and reaffirm project goals and priorities
- Establish a clear decision-making process within their organization
- Appoint a point person to communicate with the project manager
- Prepare to make timely decisions to keep the project on schedule
- Be open to creative solutions proposed by the design team
- Consider long-term operational needs, not just initial construction costs
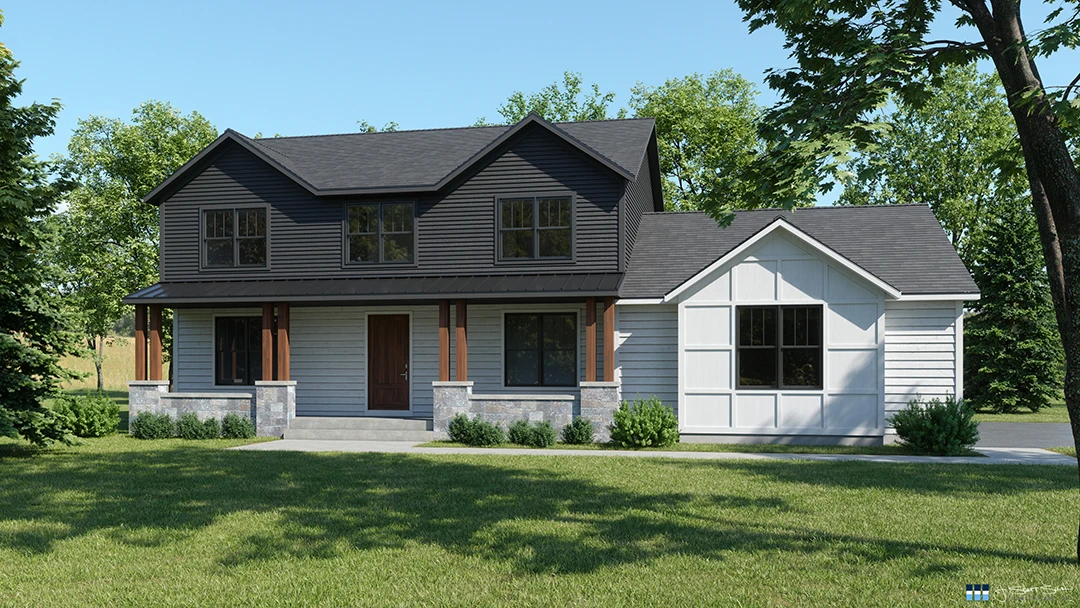
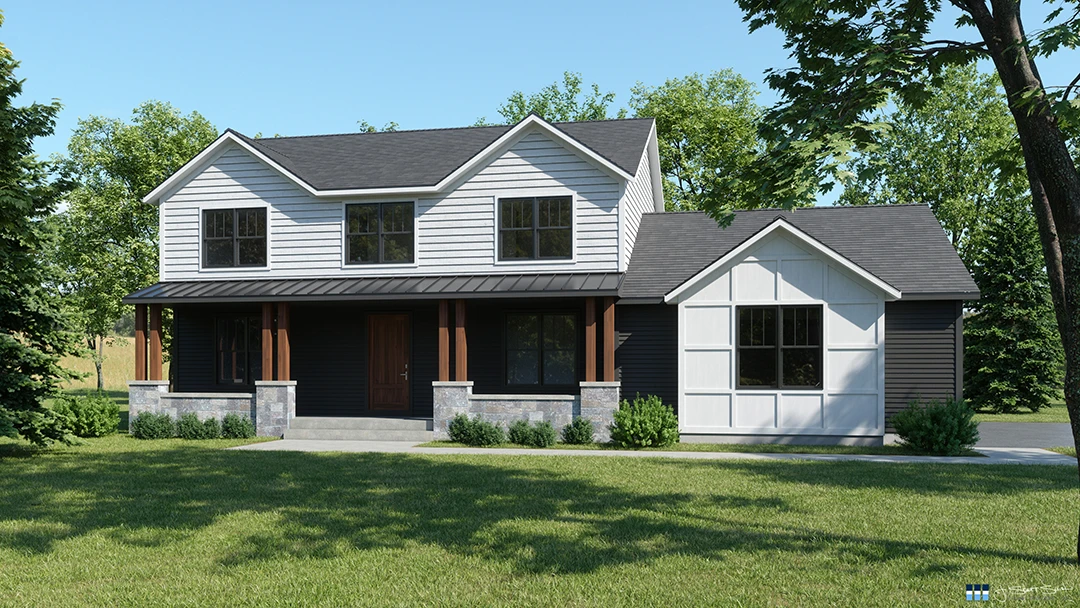


Building Information Modeling (BIM)
BIM has revolutionized the Design Development process by:
- Allowing for better coordination between disciplines
- Providing more accurate 3D representations of the design
- Facilitating clash detection and problem-solving
- Enabling data-driven decision-making
Virtual and Augmented Reality
Advanced visualization technologies are increasingly used in Design Development to:
- Provide immersive experiences of the proposed design
- Allow clients to “walk through” spaces before they’re built
- Test different design options in real-time
- Enhance understanding of spatial relationships and scale
Parametric Design Tools
These tools allow architects to:
- Quickly generate and evaluate multiple design options
- Optimize designs for specific performance criteria
- Respond more flexibly to changes in project requirements
Deliverables of the Design Development Phase
By the end of Design Development, the project team typically produces:
- Refined floor plans, elevations, and sections
- Updated 3D models and renderings
- Outline specifications for major building components
- Updated cost estimates
- Preliminary engineering drawings (structural, mechanical, electrical, plumbing)
- Initial material and finish selections
- Preliminary furniture layouts
- Updated project schedule
These deliverables form the basis for the Construction Documents phase, where the design will be further detailed for bidding and construction.
Conclusion: Setting the Stage for Success
The Design Development phase is a critical juncture in the architectural process, where vision begins to align with reality. By thoroughly developing the design, making informed decisions, and leveraging modern technologies, project teams can set a strong foundation for successful project execution.
For clients, understanding and actively participating in this phase is key to ensuring that the final building not only meets aesthetic expectations but also functions efficiently, complies with regulations, and aligns with long-term organizational goals. While the process can be demanding, the rewards of a well-executed Design Development phase are evident in the quality, efficiency, and satisfaction derived from the completed project.
As architecture continues to evolve, embracing new technologies and sustainable practices, the Design Development phase will remain a crucial period for innovation, problem-solving, and collaboration. It’s here that the true potential of a project is realized, setting the stage for the creation of buildings that not only serve their immediate purpose but also contribute positively to their environment and community for years to come.
FAQs
What is design development in architecture?
Design development is a stage in the architectural process where detailed 3D visualizations are created to help clients understand and evaluate the design. This phase allows for experimentation with design changes, material selection, and other elements to ensure client satisfaction.
How do 3D visualizations help in the design process?
3D visualizations provide a realistic view of the project, making it easier for clients to understand and make informed decisions. They enhance communication between architects, clients, and contractors, and help identify potential issues early, saving time and money.
Do you use Photoshop for creating 3D renderings?
While “photoshopping” has become a common term, we primarily use advanced 3D modeling software and render engines to create our visualizations. Photoshop may be used minimally in our process to enhance and refine the final images.
How can design development save money on a project?
By visualizing the design in 3D, potential issues can be identified and resolved early in the process, preventing costly changes during construction. Clients can make adjustments during the design phase, leading to more accurate and efficient project execution.
How do I get started with your design development services?
Contact us today to schedule a consultation. We will discuss your project’s vision and requirements, and guide you through our process to create stunning 3D visualizations that will bring your architectural ideas to life.
0 Comments