Overview:
The article focuses on comparing the best software for 3D architectural visualization while addressing the challenges faced in this field. It highlights various software options like Autodesk 3ds Max, SketchUp, and Lumion, noting their unique features, and discusses key challenges such as processing time and integration issues, offering solutions like cloud rendering and improved communication to enhance workflow efficiency and output quality.
Introduction
The realm of 3D architectural visualization is witnessing a significant transformation, driven by technological advancements and an increasing demand for high-quality visual representations. As architects strive to communicate their designs more effectively, a plethora of software options have emerged, each offering unique capabilities that cater to various project needs.
From enhancing contractor collaboration to reducing design misunderstandings, these tools are not merely accessories but essential components in the modern architectural workflow. This article delves into the leading software solutions, explores the challenges faced in 3D rendering, compares rendering techniques, and examines the transformative role of virtual reality, while also highlighting the future trends that architects must embrace to stay ahead in an evolving industry.
Top Software Options for 3D Architectural Visualization
In the rapidly evolving field of 3D architectural visualization, several software options stand out through their robust capabilities and user-friendly interfaces, significantly enhancing contractor communication and reducing misunderstandings. High-quality visualizations serve as essential tools for design development, allowing architects to craft detailed 3D representations that facilitate client evaluation and design experimentation. These depictions serve as a ‘window into the future’ of your project, offering clarity that is essential for informed decision-making and generating enthusiasm about what lies ahead.
The visualization and simulation segment is expected to grow significantly due to trends in new-age technologies like machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR). Among the most notable contenders are:
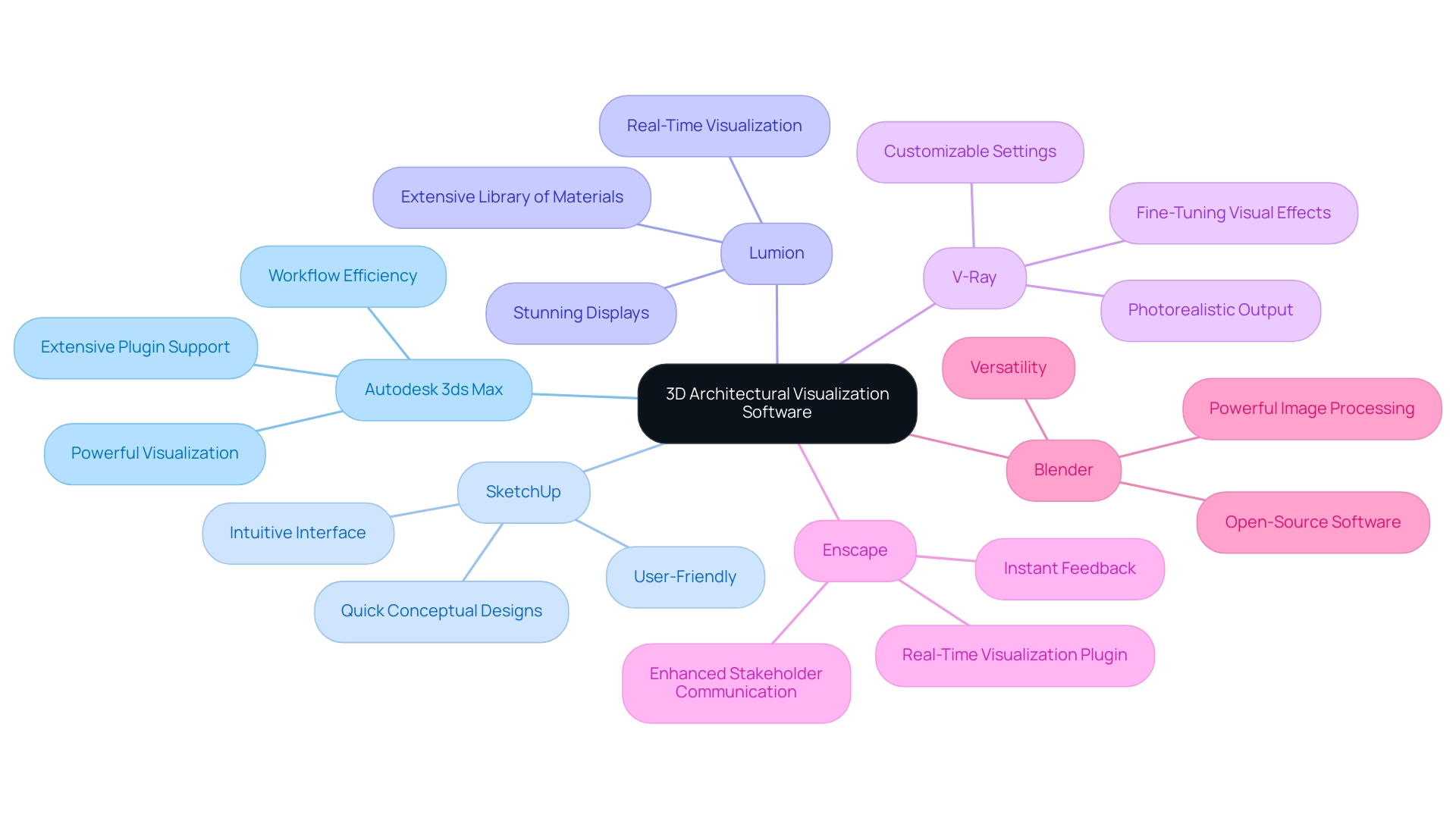
Autodesk 3ds Max: Esteemed for its powerful visualization capabilities and extensive plugin support, Autodesk 3ds Max remains a leading choice among professionals seeking to produce high-quality visualizations.
Its seamless integration with other Autodesk products significantly enhances workflow efficiency, making it a staple in architectural firms and ensuring that stakeholders have a clear vision of the project.SketchUp: Recognized for its intuitive interface, SketchUp is particularly well-suited for quick conceptual designs. Although it may not compete with the processing capabilities of more advanced software, its ease of use has earned it a dedicated following among architects and designers, allowing for swift project iterations that improve user comprehension.
Lumion: This software excels in real-time visualization, enabling users to create stunning displays with remarkable speed. Lumion’s extensive library of materials and objects aids in crafting lifelike environments, making it an excellent choice for impactful presentations that can excite clients about the potential of a project.
V-Ray: As a visualization engine that integrates seamlessly with various 3D modeling software, V-Ray is celebrated for its photorealistic output.
It provides a wide range of customizable settings, enabling designers to fine-tune visual effects to meet project specifications precisely, which is crucial for informed decision-making.Enscape: This real-time visualization plugin is compatible with popular creation tools such as Revit and SketchUp. Enscape enables designers to visualize their creations instantaneously, facilitating immediate feedback and informed decision-making throughout the design process, crucial for enhancing stakeholder communication.
Blender: An open-source software that has surged in popularity due to its versatility and powerful image processing capabilities. With a vibrant community and an abundance of tutorials, Blender provides an excellent solution for designers seeking cost-effective yet sophisticated visualization tools, emphasizing the significance of investing in quality visualizations for unique projects.
Each of these software options offers distinct features tailored to various aspects of architectural visualization. As the architecture business sector expands—with 73,313 architecture businesses in the U.S. and a projected CAGR of 1.6% from 2019 to 2024—architects must navigate the challenges in best software for 3D architectural visualization to make informed software selections. Additionally, a significant 28% of architects, engineers, contractors, owners, and investors report that most of their building projects qualify as green, with 42% anticipating reaching that level within the next three years, reflecting a growing trend towards sustainable design.
Key Challenges in 3D Architectural Rendering and Solutions
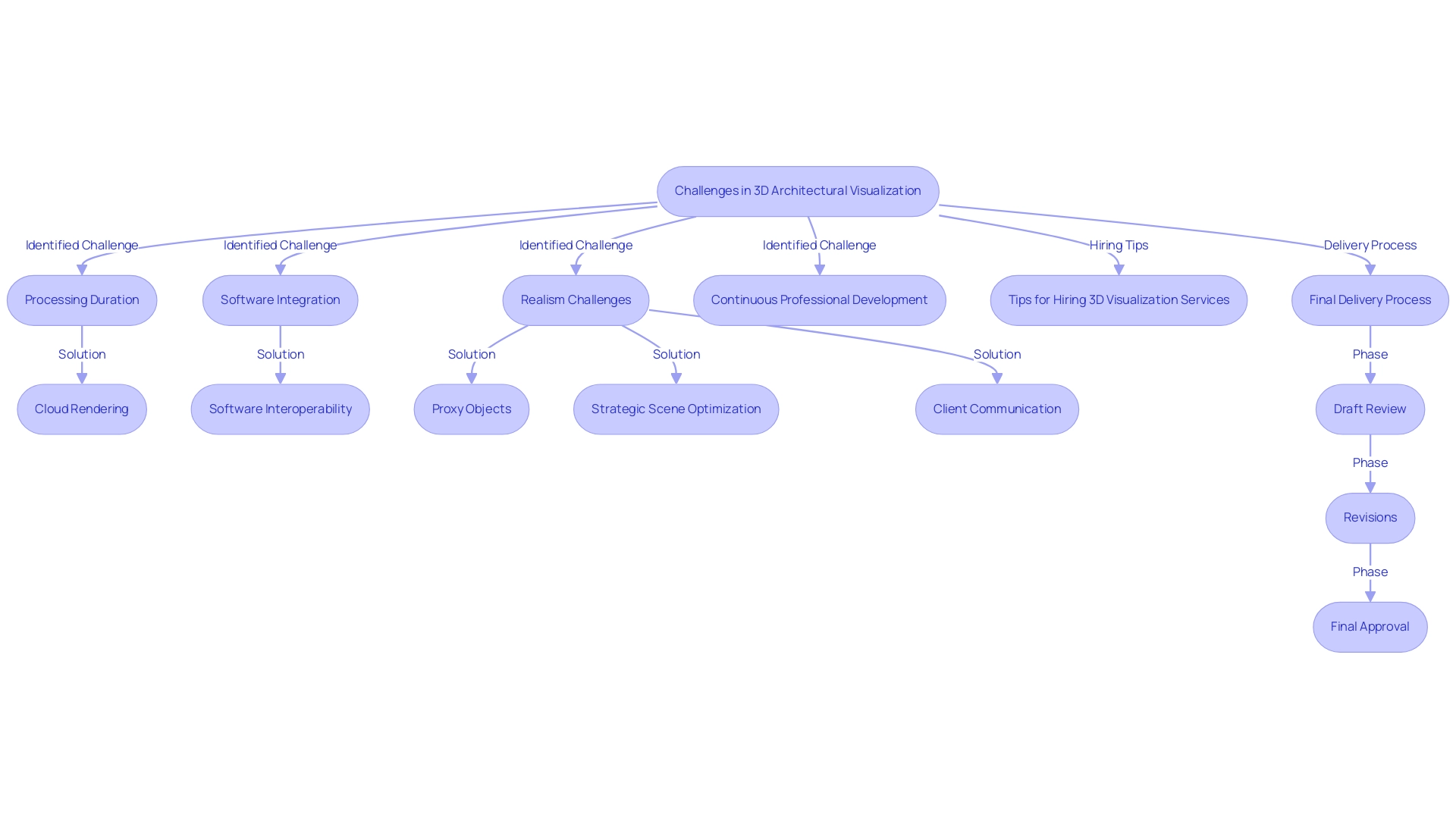
The challenges in Best software for 3D architectural visualization encompass a variety of issues that can impede workflow efficiency and compromise output quality. Key challenges in Best software for 3D architectural visualization identified in the industry include:
Processing Duration: High-quality images can require extensive processing time, particularly for intricate scenes.
Solution: Utilizing cloud rendering services can drastically diminish rendering times, enabling designers to focus on critical project components. This approach not only enhances productivity but also aligns with the growing trend of technology investment, as approximately 70% of architecture firms are planning to invest more in technology over the next year.The integration of diverse software tools often presents challenges in Best software for 3D architectural visualization, resulting in workflow disruptions.
Solution: Opting for software that prioritizes interoperability or utilizing commonly accepted file formats can effectively alleviate these complications. Additionally, ensuring that validation fields are included in software tools enhances proper form submission and overall workflow efficiency.The discussion on realism includes challenges in Best software for 3D architectural visualization.
Performance: Achieving a balance between photorealistic results and optimal performance highlights the challenges in Best software for 3D architectural visualization.
Solution: The use of proxy objects and strategic scene optimization allows designers to manage performance effectively without sacrificing the quality of visual outputs. Elevated customer expectations for visual representations can create challenges in Best software for 3D architectural visualization for designers.
Solution: Establishing transparent communication channels and providing customers with preliminary drafts fosters collaborative feedback, helping to align expectations and reduce stress on the architect’s workflow. Encouraging client input at every stage ensures that the final results reflect the client’s vision, enhancing satisfaction and project outcomes. The rapid pace of advancements in visualization technologies presents challenges in Best software for 3D architectural visualization that can be daunting.
Solution: Engaging in continuous professional development through workshops and online courses ensures architects remain informed about the latest tools and techniques, facilitating adaptation to new technologies. With 70% of animators possessing a bachelor’s degree, it underscores the importance of skilled professionals in achieving high-quality visualizations.
Tips for Hiring 3D Architectural Visualization Services
When looking for quality 3D architectural visualization services, consider the following tips:
- Review Portfolios: Examine previous work to gauge the quality and style of visuals.
- Check References: Speak to previous customers to understand their experiences and satisfaction levels.
- Evaluate Communication: Ensure the service provider maintains clear and open communication, which is crucial for aligning with your vision.
- Discuss Timelines: Inquire about their turnaround times and ensure they can meet your project deadlines.
- Understand Pricing: Get a detailed breakdown of costs to avoid unexpected expenses.
Final Delivery Process
The final delivery of architectural visuals should be a collaborative process. It generally includes several phases, such as:
- Draft Review: Customers receive initial drafts for feedback, ensuring alignment with their vision.
- Revisions: Based on customer input, necessary adjustments are made to improve the visuals.
- Final Approval: Once the customer is satisfied, the final high-resolution images are delivered, often accompanied by a detailed explanation of the design elements.
By systematically addressing the challenges in Best software for 3D architectural visualization with strategic solutions and incorporating actionable hiring tips and a clear delivery process, architects can significantly enhance their 3D visualization processes. This ultimately leads to delivering exceptional visualizations that meet and exceed client demands. As Nick Martin aptly notes,
Make sure the product is the focus of the image,
a principle that becomes especially crucial in an era where the architecture sector is expanding, reflecting a steady increase in the number of firms operating in the industry.
Comparing Rendering Techniques: Rasterization vs. Ray Tracing
In the realm of architectural visualization, the choice between rasterization and ray tracing highlights the challenges in Best software for 3D architectural visualization, as both techniques offer distinct advantages. Moreover, the incorporation of initial conceptual visuals can significantly affect the visualization process and overall project results.
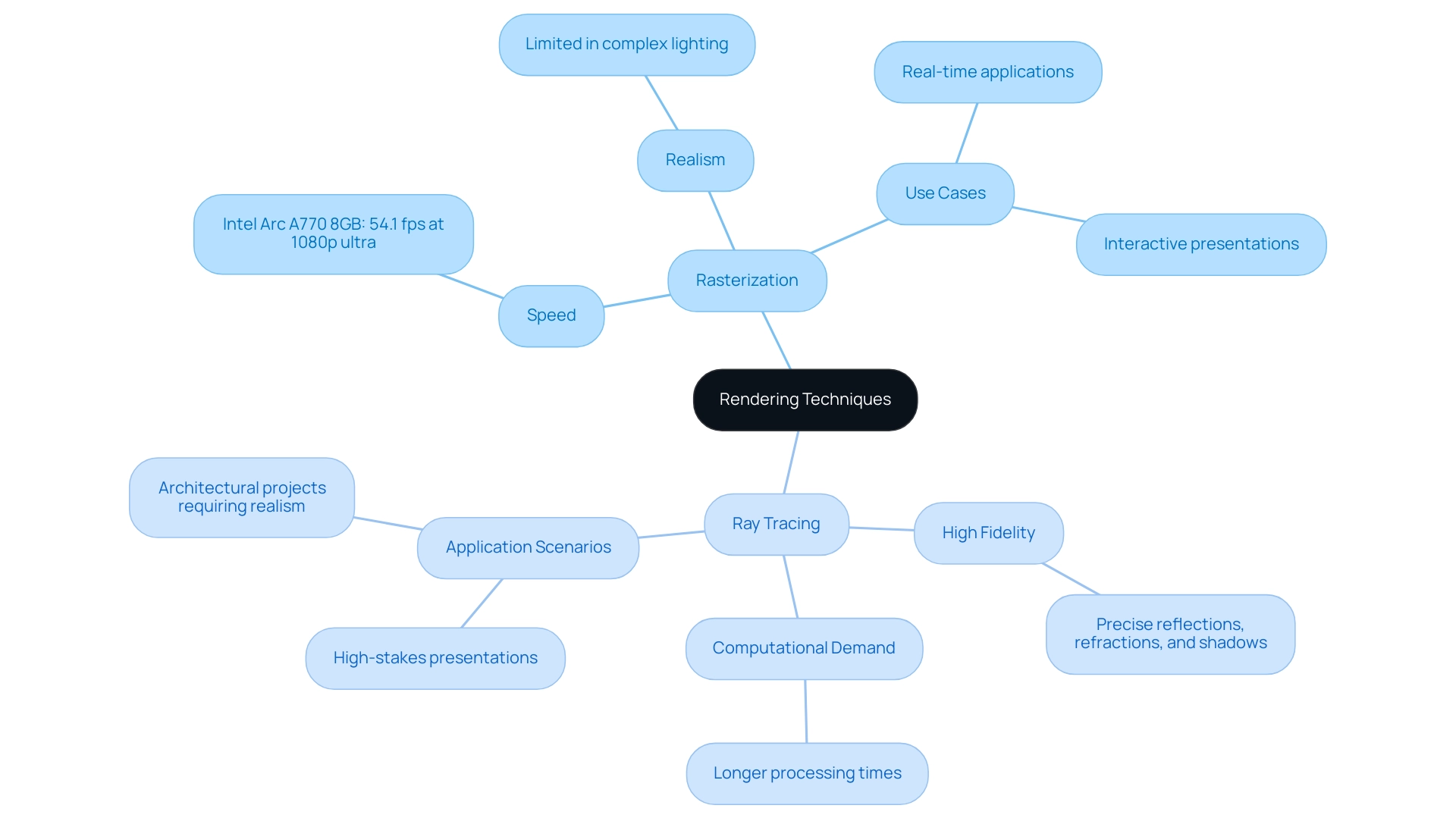
Rasterization: This method translates 3D models into 2D images through the projection of geometry onto a display surface.
Renowned for its speed, rasterization excels in real-time applications such as video games and interactive presentations, where immediate feedback is crucial. For instance, the Intel Arc A770 8GB achieves 54.1 fps at 1080p ultra, showcasing its capability in delivering rapid visualizations. Despite its efficiency, rasterization often falls short in accurately simulating complex light interactions, leading to images that may lack the desired realism.
This limitation can be particularly noticeable in scenarios demanding intricate lighting effects.
- Ray Tracing: Conversely, ray tracing provides a more sophisticated approach by simulating the behavior of light as it interacts with objects in a scene. This technique meticulously tracks the paths of rays, producing highly realistic images that feature precise reflections, refractions, and shadows.
However, this level of detail comes at a cost; ray tracing is computationally intensive and typically leads to longer processing times. For example, the Arc A580 is recognized for providing excellent value for ray tracing performance, illustrating its effectiveness in high-fidelity projects. As architectural projects increasingly demand high fidelity, the challenges in Best software for 3D architectural visualization associated with ray tracing become critical considerations.
Inquiries regarding ray tracing with OpenGL add to the challenges in Best software for 3D architectural visualization, as architects must maneuver through these intricacies.
Integrating initial conceptual images into the creation process improves swift visualization, offering architects a budget-friendly method to investigate concepts before investing considerable resources. These representations facilitate effective communication among stakeholders, ensuring everyone is aligned with the project’s direction. The cost-effectiveness of preliminary renderings facilitates early-stage decision-making, enabling stakeholders to assess options without substantial financial commitments.
Architects must evaluate these techniques based on their specific project demands. For rapid visualizations, rasterization may be adequate, offering the speed necessary for iterative creation processes. In contrast, for high-stakes presentations where realism is essential, ray tracing emerges as the superior choice, delivering unparalleled visual quality.
These considerations are further underscored by the latest advancements in ray tracing technology, which continue to enhance its viability in architectural applications. As Basemark aptly notes,
Only time will tell if these trends hold or if new limits are going to be broken…
The Role of Virtual Reality in Architectural Visualization
Virtual reality (VR) is fundamentally transforming architectural visualization, offering immersive experiences that allow individuals to engage deeply with their future spaces through a three-dimensional environment. The integration of VR into architectural practices yields several key benefits:
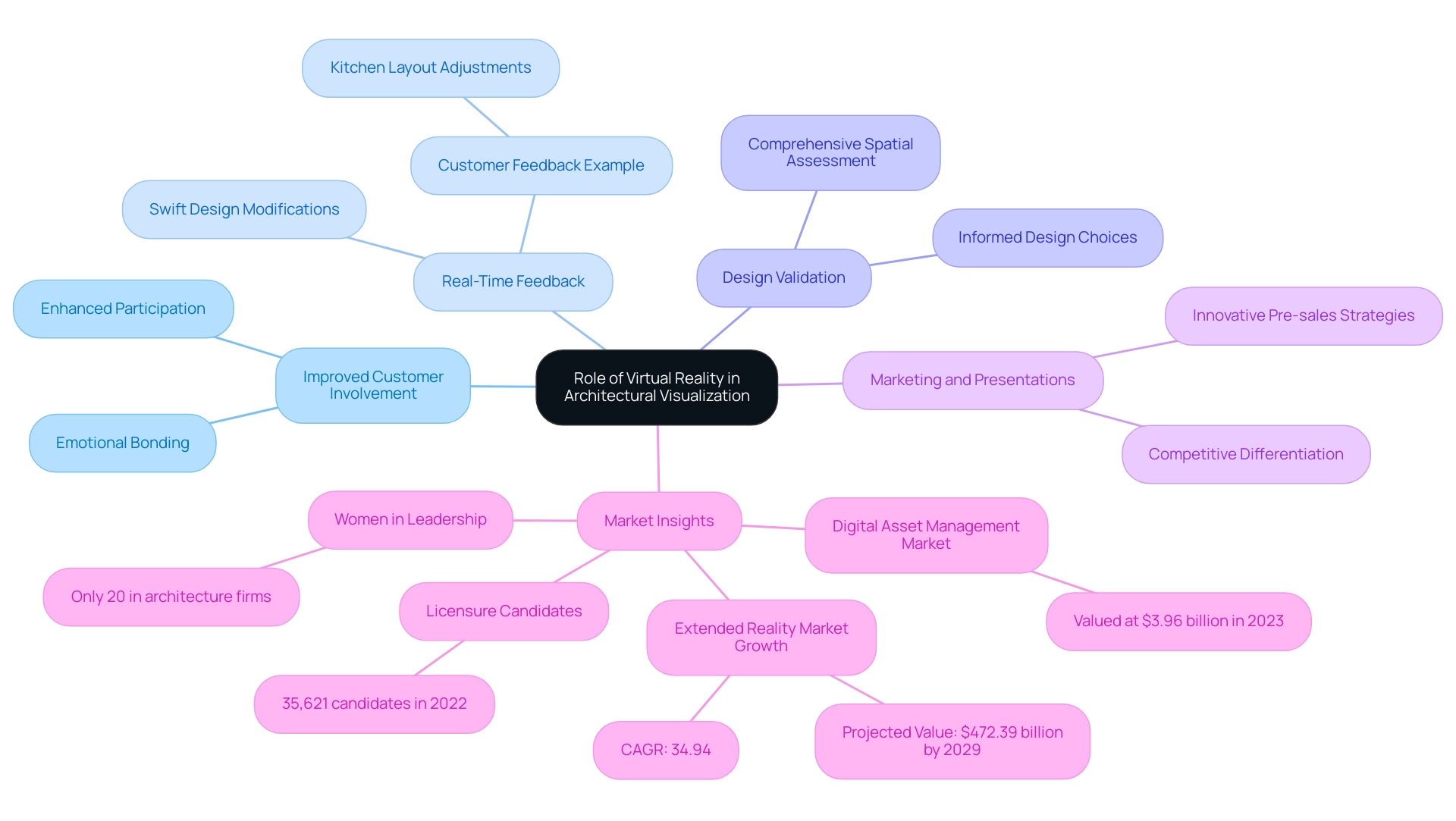
Improved Customer Involvement: By enabling customers to virtually experience their potential surroundings, VR cultivates a deep emotional bond with the concept, greatly boosting their participation in the process, similar to the early collaborative planning stages highlighted in interior visualization projects.
Real-Time Feedback: During VR walkthroughs, architects can swiftly modify designs based on feedback, effectively streamlining the design process while enhancing overall satisfaction. This iterative feedback loop reflects the detailed conversations conducted during the planning of renovation designs, ensuring that customer visions are accurately captured. For instance, in a recent project, customer feedback during a VR session led to significant adjustments in the kitchen layout, aligning it more closely with their vision for an open and innovative space.
Design Validation: Unlike traditional renderings, VR facilitates a comprehensive assessment of spatial relationships and creative elements, empowering architects to make more informed choices that better align with customer expectations, similar to the meticulous planning stages that lead to tailored project proposals.
Marketing and Presentations: Incorporating VR into presentations not only distinguishes companies in a competitive environment but also captures customer interest, demonstrating an innovative approach that is essential for successful pre-sales and marketing strategies.
As the extended reality market is anticipated to reach $472.39 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 34.94%, the momentum behind VR technology will only accelerate. Additionally, Fortune Business Insights notes that the digital asset management (DAM) market was valued at $3.96 billion in 2023, highlighting the growing importance of digital tools in architecture. Architectural companies must consider integrating VR into their workflows to tackle the challenges in best software for 3D architectural visualization and maintain competitiveness while fulfilling the evolving expectations of those they serve.
In 2024, with 35,621 candidates actively pursuing licensure, the expected rise in VR utilization within architecture highlights the need for professionals to leverage this technology, thereby improving customer interaction and refining architectural creation processes. Moreover, with women occupying only 20% of leadership roles in architecture firms, leveraging diverse viewpoints in creation will be crucial for fostering inclusive client engagement and innovation.
Ready to explore the potential of your architectural concepts? Partner with J. Scott Smith Visual Designs to visualize and validate your ideas with our preliminary renderings. Reach out to us today to arrange a consultation and discover how we can assist in realizing your concepts.
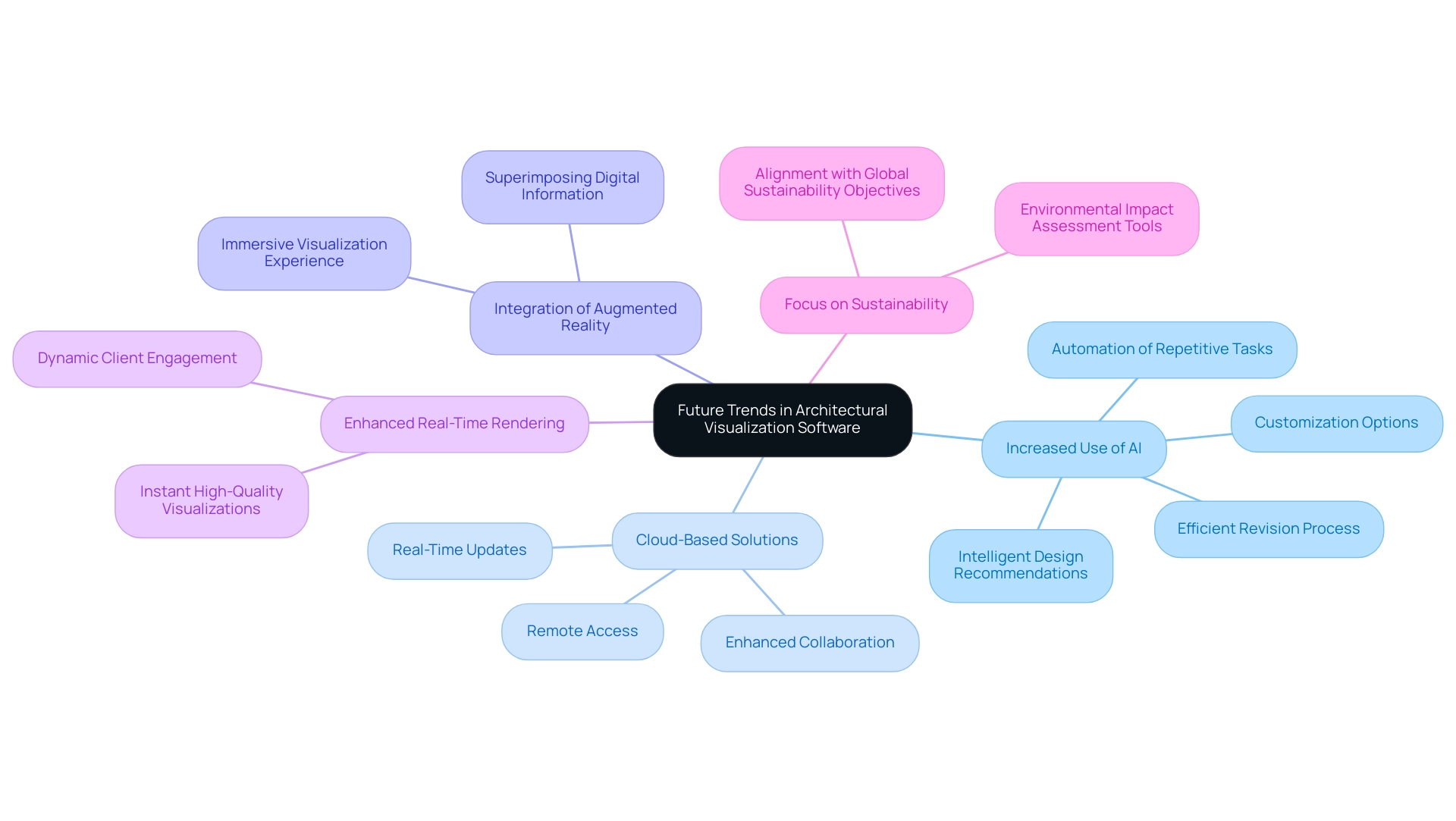
Future Trends in Architectural Visualization Software
The landscape of architectural visualization software is undergoing a transformative evolution, with several pivotal trends emerging that architects must monitor closely:
- Increased Use of Artificial Intelligence: Artificial intelligence is significantly enhancing the architectural design process by automating repetitive tasks, accelerating visualization speeds, and providing intelligent design recommendations. Notably, AI is bridging the uncanny valley by creating lifelike CG humans that enhance the realism of architectural visualizations.
This integration is essential, as it enables companies to enhance workflow and concentrate on the creative elements of their projects while providing customization options that address specific requirements. AI also facilitates the revision process, enabling designers to make adjustments quickly and efficiently, ensuring that the final renderings align with the evolving vision of the project.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: As remote work becomes more prevalent, cloud-based software solutions are emerging as essential tools for fostering collaboration among project teams and clients.
These platforms enable real-time updates and facilitate access to projects from virtually anywhere, thus enhancing communication and productivity.
Integration of Augmented Reality: Augmented reality is poised to enhance virtual reality by enabling designers to superimpose digital information onto the physical environment. This capability enables a more immersive visualization experience, helping stakeholders better understand proposals in situ.
Enhanced Real-Time Rendering: With advancements in hardware technology, real-time rendering is becoming increasingly accessible, allowing architects to produce high-quality visualizations instantly. This shift is crucial for reviews and client presentations, fostering a more dynamic and interactive engagement with the project.
Focus on Sustainability: The architectural software landscape is increasingly prioritizing sustainability, with tools designed to assess the environmental impact of designs.
This trend aligns with global sustainability objectives and empowers designers to create more environmentally responsible structures.
By staying informed about these trends, designers can proactively adapt their practices and leverage innovative tools to enhance their visualization capabilities. High-quality renderings serve as a window into the future of projects, allowing all stakeholders to visualize potential outcomes and make informed decisions. The architectural industry is projected to experience steady growth, with a market value anticipated to reach $16.18 billion by 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate of 17.0% during the forecast period.
This growth reinforces the importance of embracing these emerging technologies and methodologies as a means of maintaining a competitive advantage. As Fortune Business Insights notes, the global digital asset management (DAM) market was valued at $3.96 billion in 2023, underscoring the increasing significance of technology in architecture. Additionally, with 40% of firms meeting their goals planning to invest in project management software, the adoption of new tools in architectural visualization is more crucial than ever.
Furthermore, with 73,313 architecture firms in the U.S. experiencing a growth rate of 1.6% CAGR from 2019 to 2024, the industry is poised for sustained development, highlighting the necessity for architects to adapt to these technological advancements.
Conclusion
The evolution of 3D architectural visualization is marked by significant technological advancements and an increasing demand for high-quality outputs. Architects now have access to a diverse array of software, from Autodesk 3ds Max to SketchUp, which enhances collaboration and supports sustainable design practices. Choosing the right tools is essential for effective project execution and client satisfaction.
However, challenges such as lengthy rendering times, software compatibility, and the need to balance realism with performance remain prevalent. Solutions like cloud rendering services and fostering transparent communication with clients can help mitigate these issues. Moreover, understanding the differences between rendering techniques—such as rasterization for speed and ray tracing for realism—enables architects to make informed decisions based on project requirements.
The incorporation of virtual reality into architectural visualization further enhances client engagement, allowing for immersive experiences that facilitate real-time feedback and informed design decisions. As the market continues to evolve, adopting virtual reality becomes crucial for modern architectural practices.
Looking ahead, trends including the rise of artificial intelligence, cloud-based solutions, and a commitment to sustainability are set to redefine architectural visualization. By embracing these innovations, architects can significantly improve their visualization capabilities, ensuring that high-quality renderings effectively communicate design intent and illuminate the future of their projects. As the architectural industry anticipates growth, adapting to emerging technologies will be vital for maintaining a competitive advantage.

0 Comments