Overview
The article explores the transformative benefits of architectural visualization technology by highlighting its impact on communication, marketing, design validation, customer engagement, and education in real projects. It supports this by providing evidence of improved client understanding through 3D renderings, increased sales from pre-sales visualizations, and successful case studies demonstrating enhanced project outcomes, thereby underscoring the critical role of such technologies in modern architectural practice.
Introduction
The integration of 3D visualization technologies has emerged as a transformative force within the architectural landscape, offering architects unprecedented tools to communicate their designs with clarity and precision. This article delves into the myriad benefits of 3D visualization, including:
- Enhancing client engagement
- Streamlining project approvals
- Bolstering marketing efforts
- Facilitating educational applications
As the industry evolves, the incorporation of artificial intelligence and real-time rendering is set to further revolutionize architectural practices, enabling professionals to create immersive experiences that resonate with clients and stakeholders alike. Through a series of compelling case studies, the article illustrates successful implementations of these technologies, while also addressing the challenges that firms may encounter during adoption. By exploring the future trends shaping architectural visualization, this discussion underscores the critical importance of embracing innovation to remain competitive in an ever-evolving market.
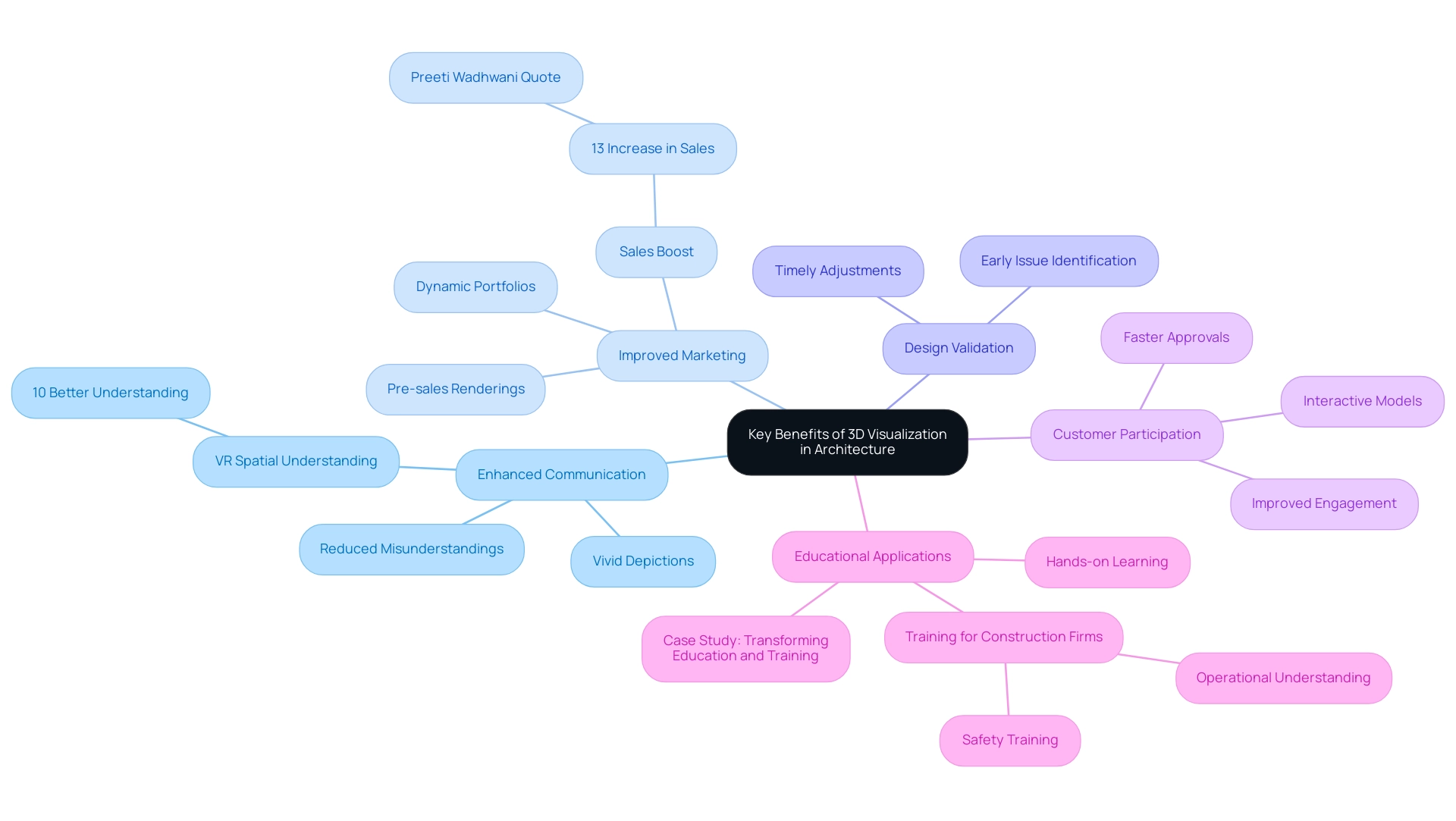
Unlocking the Potential: Key Benefits of 3D Visualization in Architecture
The advent of 3D visualization technology has fundamentally transformed how architects present their designs, yielding several key benefits that enhance both client communication and project outcomes:
Enhanced Communication: 3D renderings offer a vivid and accurate depiction of designs, enabling architects to articulate their concepts more effectively to clients and stakeholders. This clarity significantly reduces potential misunderstandings, ensuring that all parties share a common vision for the project. By offering contractors detailed representations, including interactive elements and comprehensive details, architects can eliminate guesswork, as what you see truly is what you get. Notably, participants who explored space in VR exhibited a 10% better spatial understanding than those who only viewed 2D floor plans, highlighting the effectiveness of immersive technologies in design comprehension.
Improved Marketing: High-quality visualizations have emerged as indispensable marketing tools, allowing architects to display their work dynamically within portfolios and presentations. As highlighted by Preeti Wadhwani in the UNCTAD Digital Economy Report 2021, the deployment of 3D virtualization can boost product sales by 13%, underscoring its effectiveness in attracting clients and investors. Furthermore, pre-sales renderings serve as a bridge between concept and reality, empowering developers to generate crucial revenue long before the physical realization of the endeavor. For example, a recent project showcased in our case studies demonstrated how pre-sales renderings successfully attracted significant investment, validating the project’s viability before construction began.
Design Validation: Using 3D representation allows architects to identify possible structural issues early in the development process. This proactive approach facilitates timely adjustments, ensuring that the final product aligns closely with the original vision and customer expectations. The clarity offered by these visual representations assists in creating intricate plans that can be assessed by customers efficiently.
Customer Participation: The incorporation of interactive 3D models enables customers to examine concepts in real-time, improving their engagement in the project. This level of engagement fosters satisfaction and can lead to quicker approvals, ultimately strengthening relationships. By removing the guesswork from creation, architects can ensure that clients are fully aware of what to expect.
Educational Applications: A significant case study named “Transforming Education and Training” illustrates how 3D representation tools offer practical learning experiences for students in architecture and design. These tools also function as training mechanisms for construction firms, improving safety training and operational comprehension, which further demonstrates the extensive uses of 3D representation in the field.
In summary, the strategic implementation of 3D representation not only streamlines communication with clients but also enhances marketing strategies and educational outcomes, validating its position as a critical component in modern architectural practice.
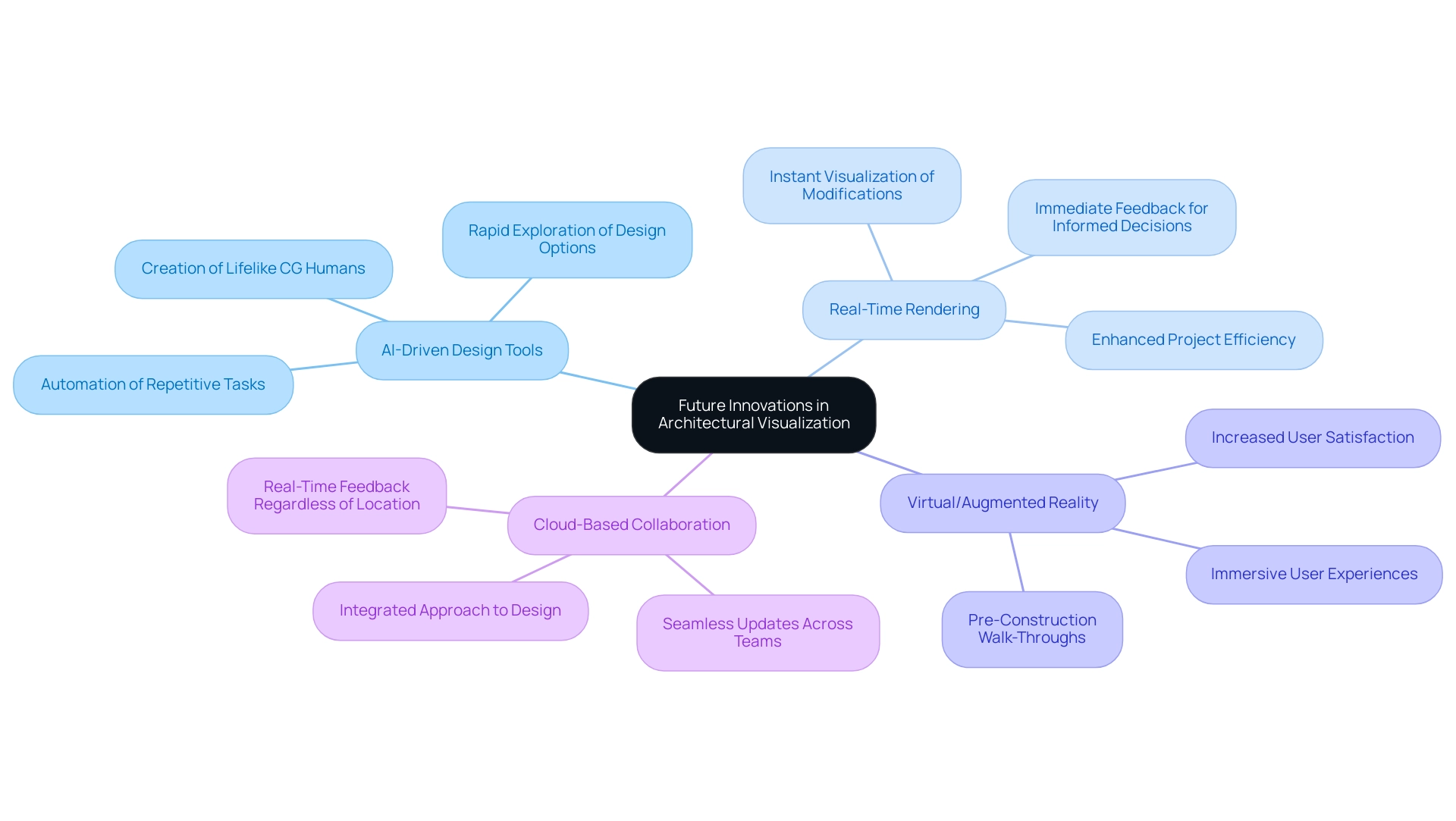
Future Innovations: The Role of AI and Real-Time Rendering in Architectural Visualization
The landscape of architectural representation is poised for remarkable evolution, showcasing the benefits of the future of architectural visualization technology, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence and real-time rendering technologies. Several key trends are emerging:
- AI-Driven Design Tools: Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the visualization process by automating repetitive tasks, notably in the creation of lifelike CG humans, which are essential for bridging the uncanny valley in architectural renderings.
This shift allows architects to concentrate on the creative aspects of their work while AI manages technical details. For instance, sophisticated AI algorithms can swiftly generate multiple variations based on predefined parameters, facilitating rapid exploration and refinement of options.
- Real-Time Rendering: This cutting-edge technology empowers architects to visualize modifications instantly, providing immediate feedback throughout the design process.
As a result, architects can make informed decisions on the fly, significantly minimizing the time needed for revisions and enhancing overall project efficiency.
Virtual and Augmented Reality: The integration of virtual and augmented reality into architectural visualization is transforming user engagement. These immersive technologies enable users to experience ‘walk-throughs’ of designs before construction, significantly enhancing their understanding and satisfaction with the final outcomes.
Cloud-Based Collaboration: Looking ahead, innovations in cloud-based platforms are expected to further facilitate collaboration among architects, engineers, and clients. These advancements will enable seamless updates and real-time feedback across teams, regardless of geographic location, fostering a more integrated approach to architectural design.
As the architectural industry navigates these technological transformations, the projected market growth—expected to expand from $4.59 billion in 2024 to $16.18 billion by 2032—underscores the critical role of these advancements in shaping future practices. According to industry insights, the highest concentration of architect jobs is currently in the District of Columbia, where the mean annual wage stands at $115,230, indicating a robust demand for skilled professionals adept in these emerging technologies.
As highlighted by ArchDaily, ‘When creating unique architecture, visionary ideas aren’t always enough. A unique look demands character, courage, and distinctive materials.’ This sentiment reflects the growing emphasis on innovation and unique materials in architectural design.
Moreover, the significance of intricate details in architectural renderings enhances realism and emotional impact, making each creation feel more authentic and relatable. High-quality renderings highlight the benefits of the future of architectural visualization technology, acting as a ‘window into the future’ that is crucial for informed decision-making and generating enthusiasm about what’s to come. The case study on regional demographics reveals that architects are most in demand in Atlanta, GA, with Virginia being the best state for architects to live in, further emphasizing the importance of adapting to these emerging technologies.
The architectural sector is also experiencing substantial transformations, driven by technological advancements and an emphasis on sustainability initiatives, which are becoming more pertinent in contemporary creation processes.
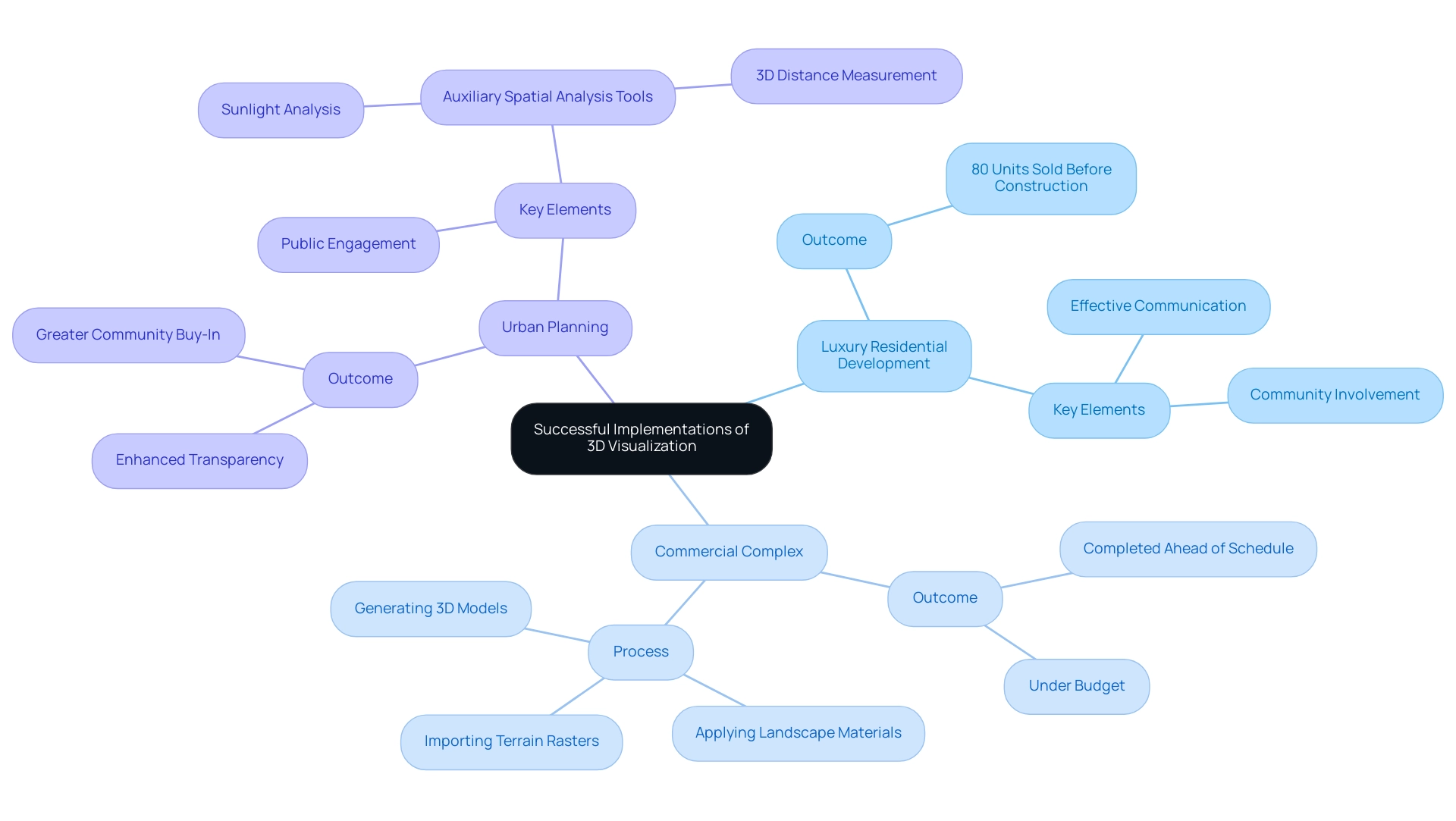
Case Studies: Successful Implementations of 3D Visualization
Numerous prominent architectural endeavors have effectively utilized 3D representation, yielding remarkable outcomes. For example:
- Luxury Residential Development: A prominent architectural firm employed cutting-edge 3D rendering to showcase a luxury residential endeavor in Michigan that combined traditional charm with modern design.
The realistic renderings not only captured the unique spirit of the locale but also facilitated clear communication with potential homeowners, significantly reducing miscommunication about the vision. This led to 80% of the units being sold before construction, illustrating how effective imagery boosts confidence in developments and involves the community, making it an essential element of real estate marketing tactics.
Commercial Complex: In a recent commercial development, 3D representations provided stakeholders with a comprehensive view of the initiative, facilitating a streamlined approval process. This proactive approach led to the project’s completion ahead of schedule and under budget, underscoring the critical role of effective communication in driving project success. The representation process involved multiple steps, including importing terrain rasters, applying landscape materials, and generating detailed 3D models, highlighting the complexity behind effective representations.
Urban Planning: A municipal planning department incorporated 3D representations into community engagement initiatives, enabling residents to see proposed developments. This integration not only enhanced transparency but also fostered greater community buy-in, leading to smoother project approvals.
As Huayi Zheng remarks,
Auxiliary spatial analysis tools are integrated to help end users perform ‘professional’ tasks such as sunlight analysis and 3D distance measurement.
Such tools are essential in maximizing the utility of 3D models, further enriching the architectural representation process. Furthermore, the challenges related to large-scale GIS data representation, as discussed in the case study titled ‘Challenges in Large-Scale GIS Data Visualization,’ highlight the necessity for advanced computational resources to effectively manage and depict extensive datasets.
Overall, these examples highlight the considerable influence that 3D representation has on improving the efficiency and effectiveness of various architectural projects, emphasizing the benefits of the future of architectural visualization technology and the significance of customer testimonials in demonstrating the value of our work at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs. We prioritize establishing enduring partnerships with those we serve, ensuring that their expectations are not just met but surpassed, which is central to our commitment to excellence.
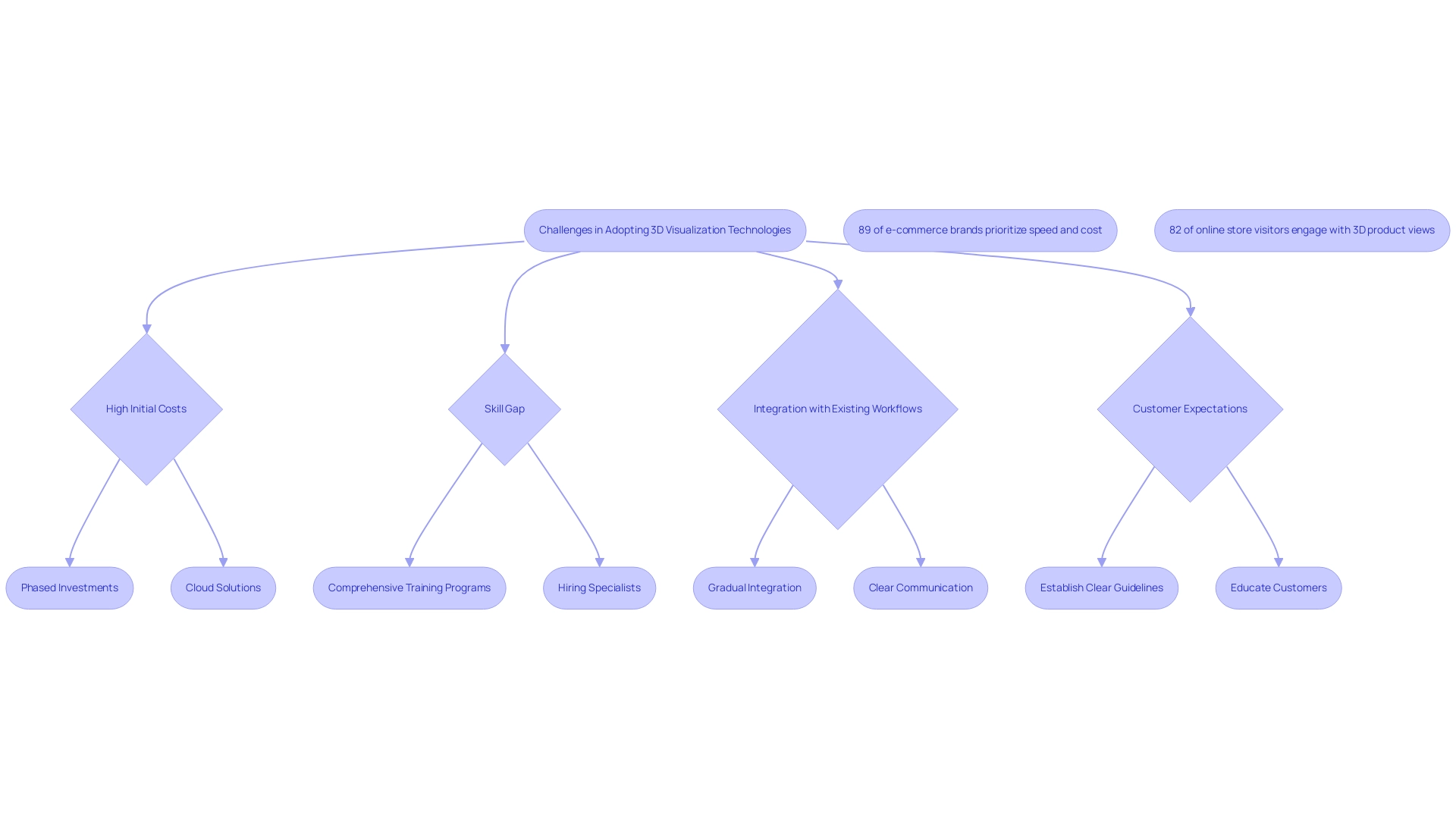
Challenges and Solutions in Adopting 3D Visualization Technologies
Despite the significant advantages of 3D imaging technologies, several challenges may emerge during the adoption phase:
- High Initial Costs: The investment in advanced software and hardware can pose a barrier, particularly for smaller firms. To address this issue, companies might explore phased investments or leverage cloud-based solutions, which can significantly reduce upfront costs while still providing access to cutting-edge tools. Involving reliable 3D architectural rendering service providers can further optimize this investment by delivering high-quality outputs that enhance client engagement.
- Skill Gap: A notable deficiency in the necessary skills to effectively utilize advanced representation tools exists among many professionals in the field. To bridge this gap, firms should prioritize investing in comprehensive training programs or consider hiring specialists with expertise in 3D imaging technologies. This not only enhances internal capabilities but also bolsters communication with customers, improving the overall development process.
- Integration with Existing Workflows: The incorporation of new technologies into established workflows can present substantial challenges. A gradual integration approach, complemented by clear communication among team members, can facilitate smoother transitions and enhance overall productivity. Employing 3D representations early in the design phase can assist in addressing design problems, thereby optimizing project workflows.
- Customer Expectations: Unrealistic customer expectations regarding the abilities of 3D representations can result in misunderstandings and dissatisfaction. Establishing clear guidelines and proactively educating customers about the visualization process is essential for managing these expectations effectively. This is vital in fostering strong client relationships, as effective storytelling through 3D renderings translates architect visions into clear visuals.
In light of these challenges, here are some tips for hiring quality 3D architectural rendering services:
- Assess Portfolio: Review the provider’s past work to ensure their style aligns with your vision and standards.
- Check References: Speak with previous clients to gauge their satisfaction and the provider’s reliability.
- Evaluate Communication: Ensure the provider can clearly articulate their process and is responsive to your needs.
- Consider Technical Expertise: Look for firms that utilize the latest technologies and software to ensure high-quality outputs.
It’s noteworthy that 89% of e-commerce brands prioritize speed and cost when selecting 3D content providers and editing tools. This highlights the importance of not only adopting the right technologies but also ensuring that they align with practical business needs. Furthermore, as CASTOR recently announced a feature that transforms 2D models into 3D parts, it illustrates the ongoing advancements in the industry that can help overcome barriers to adoption. Additionally, with 82% of online store visitors engaging with 3D product views, the benefits of these technologies are evident, enhancing user experience and reducing return rates by providing a clearer understanding of products. Insights from the case study titled ‘Application Analysis of 3D Rendering Solutions’ reveal that the AEC sector’s demand for product design and modeling led to its dominance in 2022, emphasizing the importance of 3D imaging technologies in overcoming existing challenges. Addressing these challenges through targeted solutions will be vital for architects seeking to harness the full potential of emerging imaging technologies.
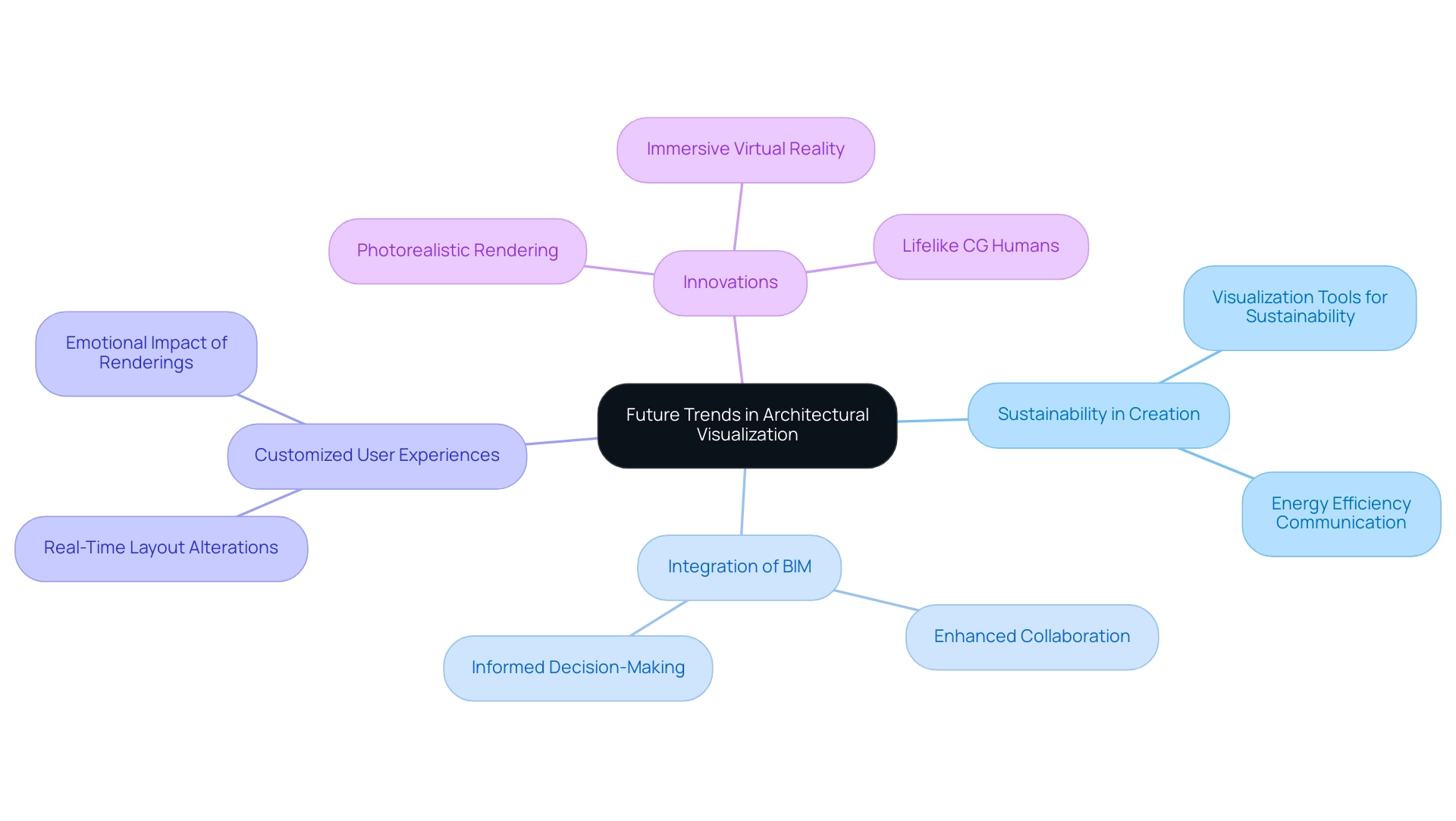
The Future Landscape: Trends to Watch in Architectural Visualization
The landscape of architectural representation is undergoing a significant transformation, with several emerging trends highlighting the benefits of the future of architectural visualization technology that promise to redefine the practice.
- Sustainability in Creation: As environmental factors progressively affect creative decisions, architects are anticipated to incorporate sustainable methods into their works.
Visualization tools that effectively communicate energy efficiency and environmental impact will become pivotal, allowing architects to showcase their commitment to sustainability.
- Integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM): The combination of BIM with advanced 3D visualization techniques is poised to transform collaboration and execution.
This integration enhances accuracy and facilitates informed decision-making throughout the development process, ultimately leading to more successful project outcomes.
- Customized User Experiences: With advancements in technology, there is a growing expectation for personalized user interactions during the creation process.
Adaptable visualization tools that enable users to alter layouts in real-time will gain traction, fostering a collaborative environment that aligns with user visions. The emotional impact of these personalized renderings can significantly improve client connection and satisfaction, as they see their ideas mirrored in the creations. Techniques such as incorporating intricate details and textures can evoke emotions and foster a deeper connection to the work.
- Innovations: Innovations such as photorealistic rendering, immersive virtual reality, and interactive presentations demonstrate the benefits of the future of architectural visualization technology by elevating the communication of architectural concepts.
These cutting-edge techniques will emphasize texture and durability in representations, making projects more engaging and accessible, thus enhancing client understanding and approval.
Moreover, lifelike CG humans are revolutionizing architectural representations, bridging the gap between realism and the uncanny valley, further enriching the presentation of designs. As architectural firms adjust to these trends, the focus on sustainability and innovative representation methods will not only meet current market demands but also establish architects as leaders in the changing built environment. Notably, architect fees typically range between $100 and $250 per hour, reflecting the financial implications of these emerging technologies.
Furthermore, as noted by Zippia, Virginia is recognized as the best state for architects to live in, further emphasizing the importance of location in the architectural profession. Additionally, with over 75% of firms producing architectural visualizations in-house, there is a clear shift towards greater autonomy and expertise in visualization techniques among architects. The precision and detail in exterior renderings play a crucial role in telling the story of a design, capturing its essence and ensuring that the vision is communicated effectively.
Conclusion
The transformative impact of 3D visualization technologies on the architectural landscape is both profound and multifaceted. As highlighted throughout the article, the integration of these tools enhances communication, streamlines project approvals, and bolsters marketing efforts, ultimately leading to improved client engagement and satisfaction. The case studies presented illustrate real-world applications that underscore the effectiveness of 3D visualization in driving project success, from luxury residential developments to urban planning initiatives.
Furthermore, the article emphasizes the impending advancements in artificial intelligence and real-time rendering, which promise to further revolutionize architectural practices. These innovations not only facilitate rapid design iterations but also enhance client experiences through immersive technologies such as virtual and augmented reality. As architects navigate these technological transformations, the anticipated growth of the architectural visualization market serves as a testament to the increasing importance of these tools in modern design processes.
In conclusion, embracing 3D visualization technologies is essential for architects seeking to remain competitive in an evolving industry. The challenges associated with their adoption can be mitigated through strategic investments in training, technology, and clear communication with clients. By leveraging these advancements, architects can not only enhance their design capabilities but also foster meaningful connections with clients, ultimately shaping the future of architecture in a sustainable and innovative manner.

0 Comments