Overview:
The article focuses on best practices for effectively integrating virtual reality (VR) into architectural presentations to enhance user engagement and communication. It emphasizes the importance of investing in quality VR technology, optimizing 3D models, and utilizing storytelling techniques, all of which significantly improve client satisfaction and project outcomes by allowing for immersive, interactive experiences that clarify design intent and foster collaboration.
Introduction
The integration of virtual reality (VR) into architectural presentations marks a transformative shift in the industry, moving beyond traditional methods to create immersive experiences that resonate deeply with clients. This innovative approach not only enhances client engagement by allowing them to navigate projects before construction begins but also fosters a clearer understanding of design elements such as scale and spatial relationships. As architecture firms increasingly prioritize sustainable design and embrace advanced technologies, the role of VR becomes paramount in aligning client expectations and driving investment.
The following exploration delves into practical strategies for successful VR implementation, the creation of compelling content, and the overcoming of inherent challenges, while also forecasting future trends that will shape the architectural landscape. By harnessing the full potential of VR, architects can elevate their presentations, ensuring that they not only meet but exceed client aspirations in a rapidly evolving digital environment.
Transforming Architectural Presentations with Virtual Reality
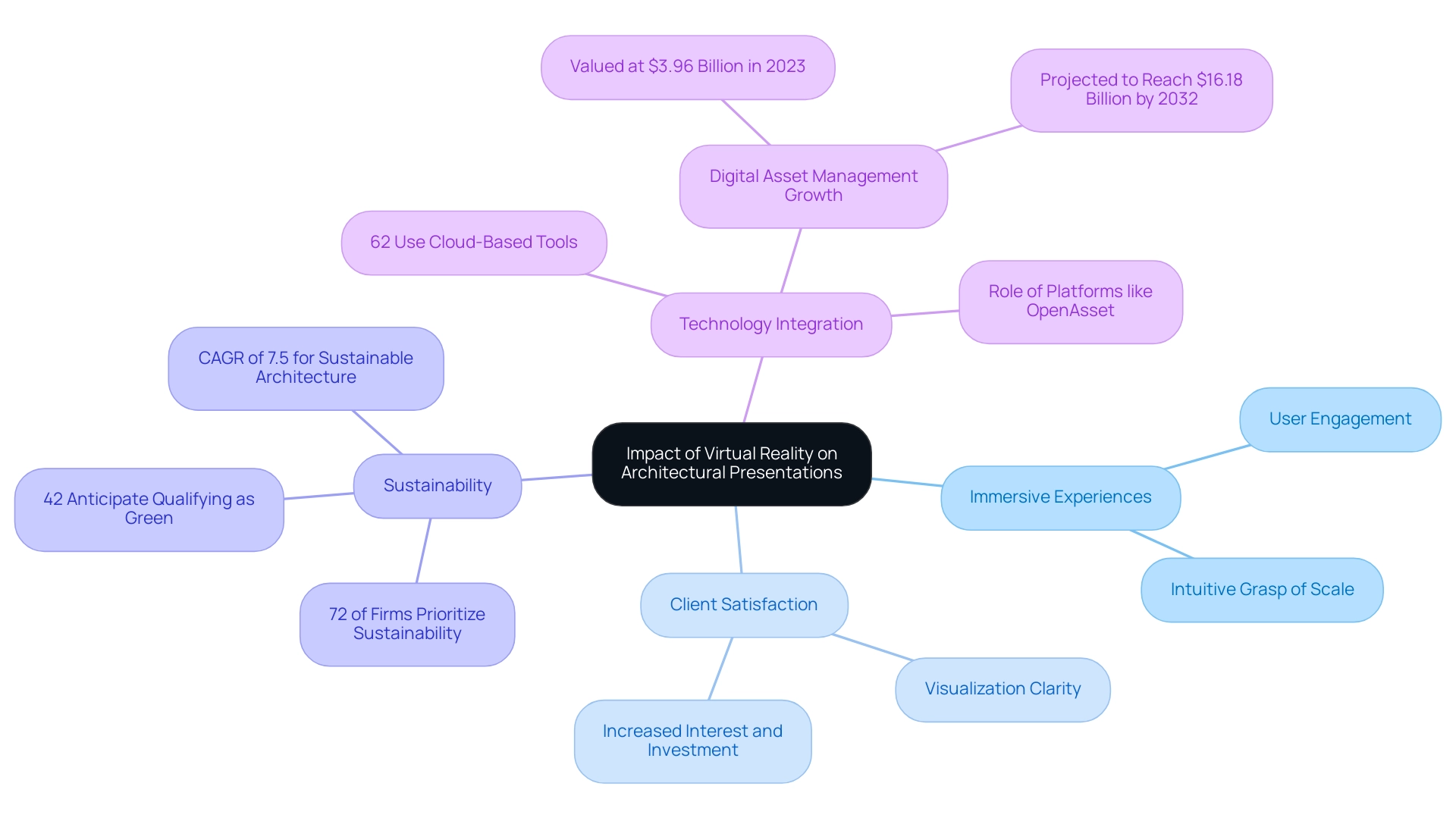
The best impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations is that it has fundamentally transformed the field, transcending traditional 2D drawings and static images to offer immersive experiences that involve users at a profound level. The best impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations is achieved by allowing users to explore a virtual environment before construction, which promotes an intuitive grasp of scale, proportion, and spatial relationships. This pre-sales visualization not only instills confidence in the project but also serves as a powerful tool for generating interest and investment, as our renderings act as tangible assets that ignite enthusiasm and drive early financial commitments.
Reports indicate that firms implementing VR have experienced the best impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, as clients are able to visualize the final product with unprecedented clarity, leading to significant increases in client satisfaction. A significant statistic shows that:
- 72% of architecture firms now prioritize sustainable practices, aligning with the increasing demand for green buildings and the projected 7.5% CAGR for sustainable architecture from 2021 to 2028.
- 42% of firms anticipate qualifying as green within the next three years, highlighting the industry’s shift towards sustainability.
Furthermore, the best impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations enhances communication among stakeholders by providing a shared platform for discussion, effectively reducing misunderstandings and aligning expectations during the early stages of the design process. Notably, 62% of architecture firms utilize cloud-based collaboration tools for coordination, reflecting the technological integration in architectural practices. As the global digital asset management market continues to expand, projected to reach $16.18 billion by 2032, the integration of platforms like OpenAsset will further streamline the management of digital assets within VR environments, solidifying the role of virtual reality in modern architectural practice.
As The Architect’s Newspaper notes, there were 35,621 candidates actively working on licensure, underscoring the growing workforce engaged in innovative practices, including VR adoption. Ultimately, this immersive approach demonstrates the best impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, as it not only enhances user engagement but also fosters a deeper connection between the projects and their future residents, laying the groundwork for strong community ties from the outset.
Practical Tips for Successful VR Integration in Architecture
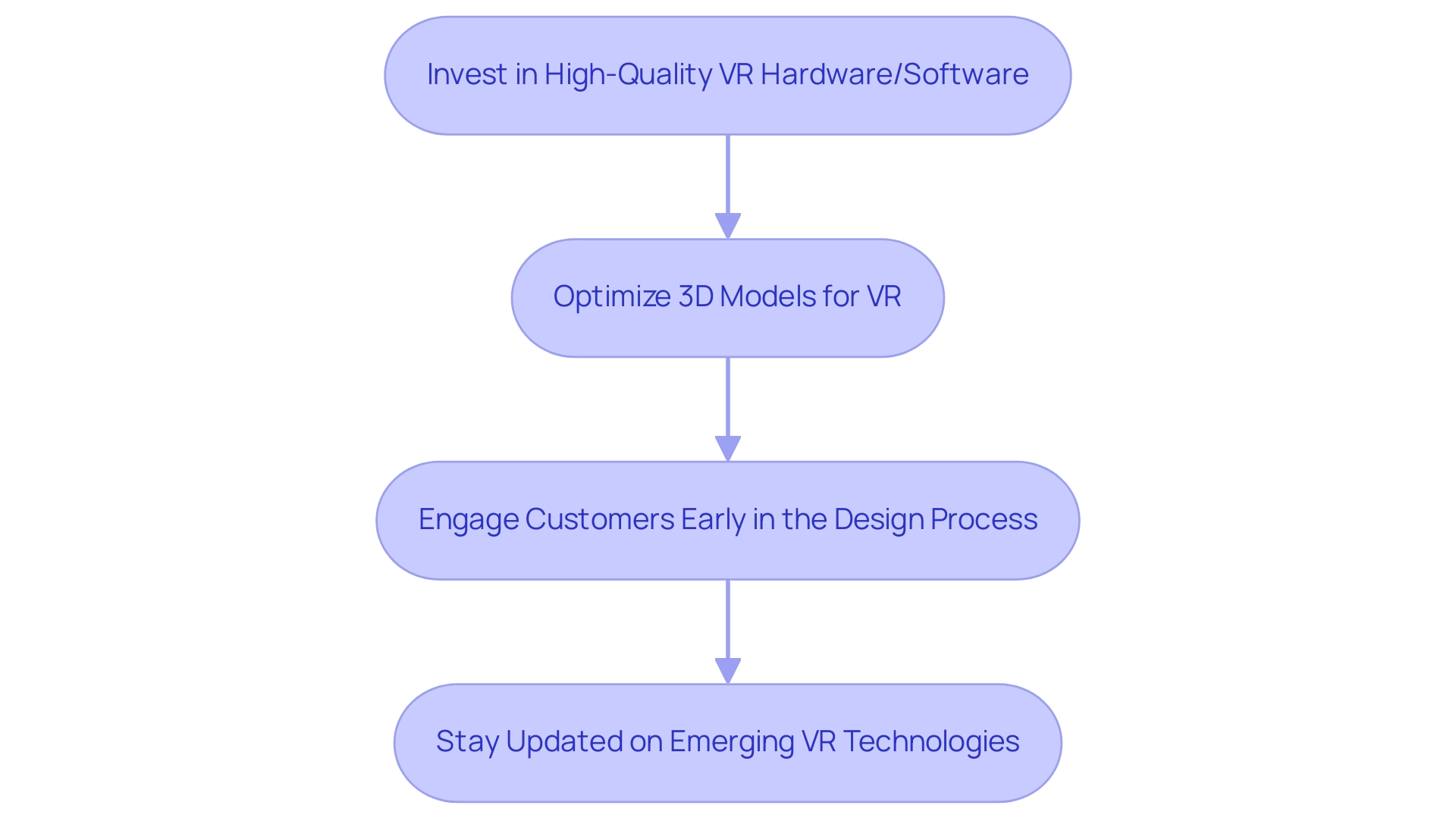
To effectively incorporate the best impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, several best practices should be followed. Firstly, invest in high-quality VR hardware and software that facilitates seamless visualization. The Meta Quest 3S, for example, offers a resolution of 1832 x 1920 per eye, making it a budget-friendly option for immersive experiences; however, it does have limitations in controller tracking and audio options.
In contrast, the HTC Vive Cosmos Elite is priced at £692 and is lower priced compared to other high-end models, though it requires additional accessories.
Secondly, optimizing your 3D models for VR is crucial; this involves simplifying geometry while ensuring that textures are of high-quality yet not overly complex to maintain performance. Engaging customers early in the design process through VR enhances satisfaction and fosters a collaborative environment where feedback can be integrated proactively.
This aligns with the collaborative rendering process at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, which includes:
- Initial communication to understand goals
- Detailed modeling
- Ongoing feedback loops to ensure that client visions are accurately captured
Lastly, remain vigilant regarding emerging VR technologies and trends. As Devindra Hardawar remarked, ‘For all of its complexity, however, the Bigscreen Beyond provides the most immersive PC VR experience I’ve ever encountered,’ emphasizing the rapid advancements in the field that can improve architectural displays.
By following these practices, architects can leverage the full potential of VR to transform their display strategies, showcasing the best impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, which plays an essential role in project development and decision-making.
Creating Engaging VR Content for Presentations
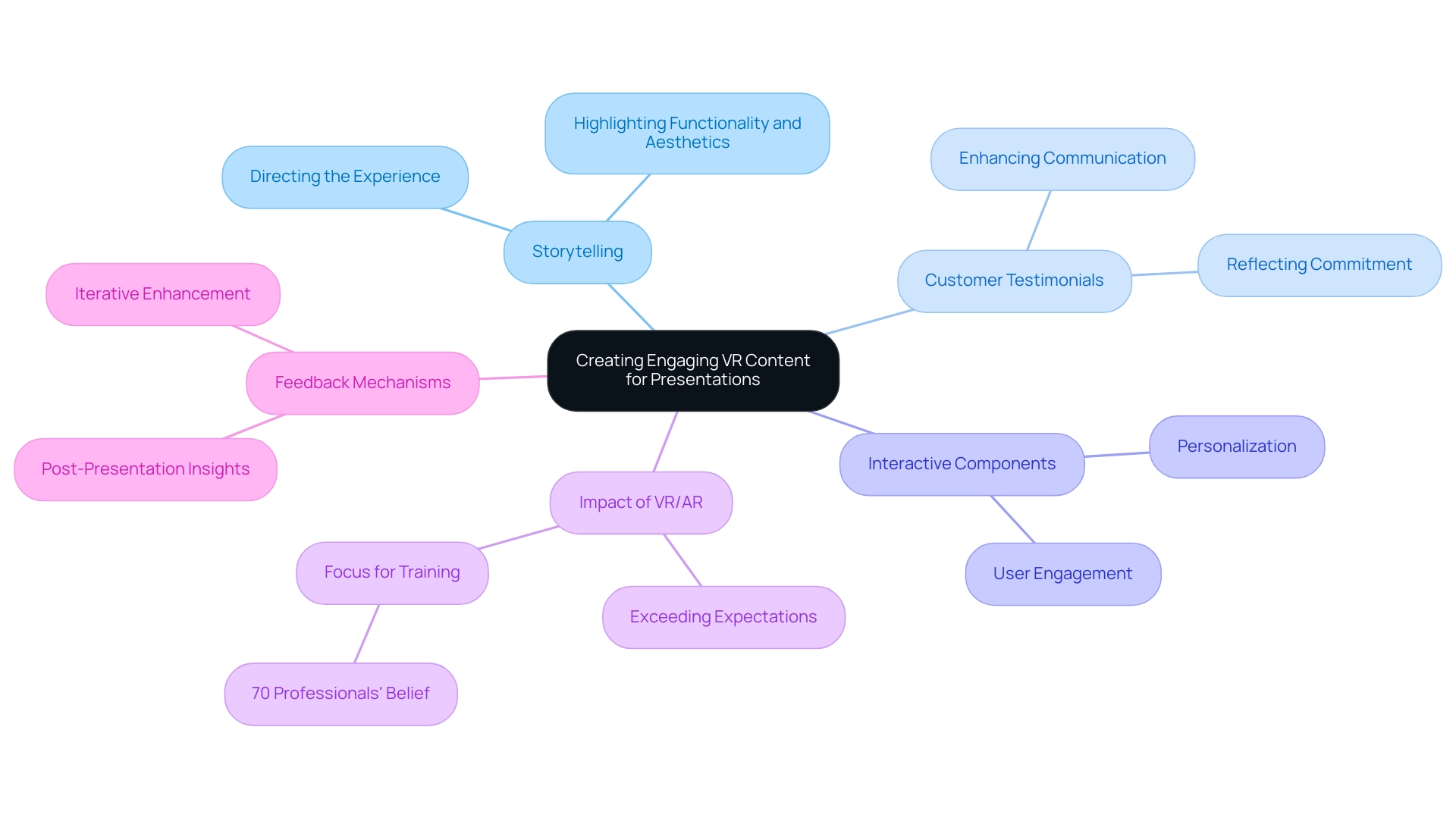
To craft compelling VR content for architectural presentations, it is essential to weave storytelling elements throughout the experience. Employing storytelling methods effectively directs individuals through the creation process, highlighting essential aspects that enhance both functionality and aesthetics. At J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, we recognize that customer testimonials are not just endorsements; they reflect our commitment to enhancing contractor communication and eliminating design misunderstandings through clear visual renderings.
For instance, one customer noted, ‘The visual renderings provided clarity that we had not experienced before, allowing us to communicate our vision to the contractors without confusion.’ Companies utilizing AR/VR indicate that the advantages surpass expectations (Capgemini), demonstrating the best impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations. Additionally, a significant 70% of professionals believed that VR/AR for training would be a focus for 2021, highlighting the growing importance of this technology in the industry.
The integration of interactive components allows users to personalize aspects of the design—such as materials and layouts—thereby fostering a sense of ownership and deeper investment in the project. Moreover, realistic lighting and environmental settings demonstrate the best impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations by enhancing the immersive quality and significantly influencing viewers’ perceptions of the proposed space. The experiences of those we serve, as shared in testimonials across platforms like Google, Facebook, and Houzz, illustrate how our approach helps identify design issues early and improves stakeholder communication.
We actively seek feedback from customers post-presentation, utilizing their insights to refine our VR content continually. This practice not only aligns the delivery with client expectations but also facilitates the iterative enhancement of our VR storytelling techniques, ensuring that each showcase resonates more effectively with its audience.
Overcoming Challenges in VR Implementation
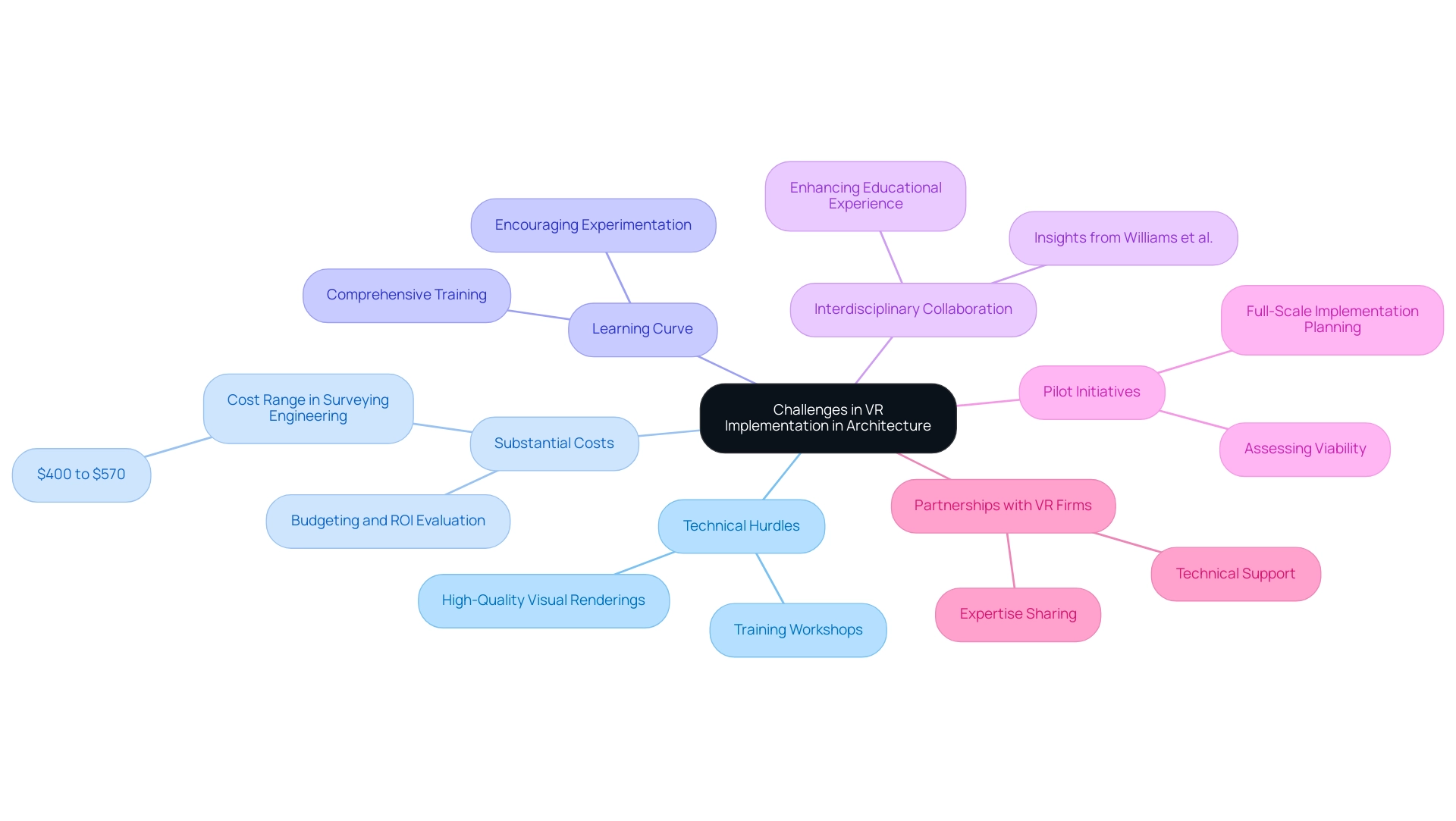
The adoption of virtual reality on architectural presentations presents a series of challenges, including technical hurdles, substantial costs, and a significant learning curve. To effectively navigate these obstacles, it is crucial to invest in comprehensive training for your creative teams. Conducting workshops focused on VR software and hardware can ensure that all team members are proficient and comfortable with the technology.
Furthermore, interdisciplinary collaboration is essential in developing effective VR applications for AEC education, as it enhances the overall educational experience. A systematic review titled ‘Cost Analysis of VR Applications in AEC Education’ sheds light on the financial implications, indicating that costs for VR technologies can range significantly—between $400 and $570 in surveying engineering—highlighting the necessity for careful budgeting and evaluation of return on investment (ROI). Integrating insights from Williams et al. on the incorporation of VR in architectural education can provide a broader perspective on the benefits and challenges of this technology.
Initiating a pilot initiative serves as an effective strategy to assess the viability of VR in your practice before a full-scale implementation. Moreover, the use of high-quality visual renderings and 3D visualizations can significantly enhance communication and idea conveyance, helping designers and developers resolve potential design issues early, ultimately streamlining workflows.
Additionally, forging partnerships with specialized VR firms can provide invaluable expertise and support, helping mitigate technical issues that may arise. To address the steep learning curve, cultivating an environment that encourages experimentation is essential. Allowing team members to explore the capabilities of VR without the pressure of immediate outcomes fosters innovation and creativity, ultimately showcasing the best impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations.
Jasmine Katatikarn’s insights into consumer enthusiasm for VR, particularly within gaming—where 64% express excitement—underscore the potential for similar engagement within architecture, making it all the more critical to overcome these initial challenges. By incorporating intricate details in architectural renderings, you can enhance realism and emotional impact, making your designs feel real, lived-in, and ready to be built. Furthermore, it is essential to consider the financial implications of VR technologies and the importance of forming partnerships with specialized VR firms to provide technical support and expertise, which can help mitigate challenges during implementation.
Future Trends in VR for Architecture
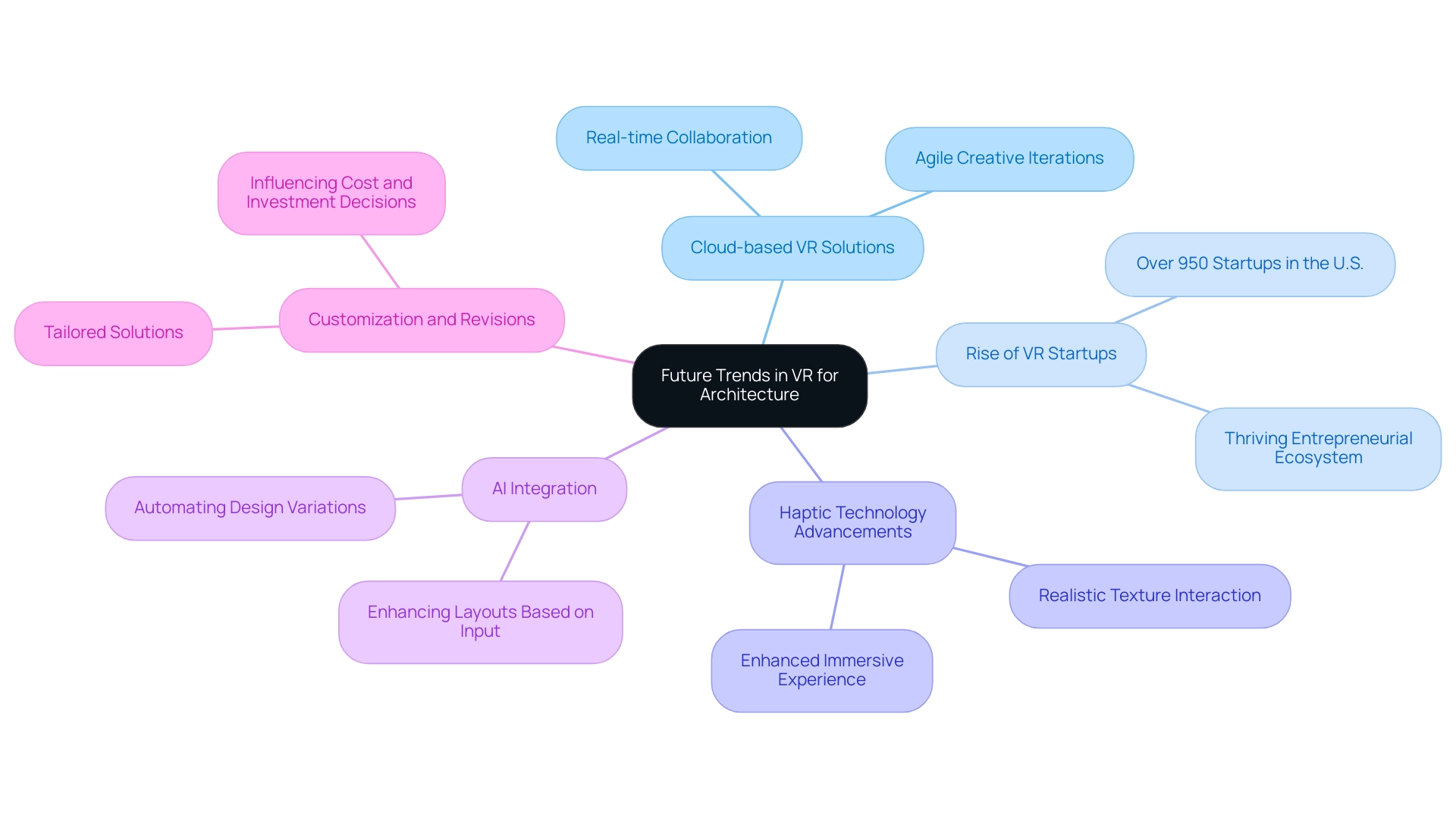
As we look to the future, several pivotal trends are set to shape the integration of virtual reality (VR) in architecture, particularly through the lens of AI-driven advancements. A key development is the emergence of cloud-based VR solutions, which revolutionize collaboration and accessibility for project stakeholders by enabling real-time updates and feedback. This fosters agile creative iterations that align closely with client preferences, enhancing the collaborative rendering process at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs.
Moreover, the rise in VR-related startups—over 950 in the U.S. alone—highlights an expanding entrepreneurial ecosystem and a robust interest in VR technologies. According to Fortune Business Insights, the global digital asset management (DAM) market was valued at $3.96 billion in 2023, underscoring the growing importance of digital solutions across industries.
Advancements in haptic technology are further elevating the immersive experience by allowing users to ‘feel’ textures and materials within virtual environments, significantly enhancing the realism of architectural presentations and emphasizing the texture and durability of interior and exterior materials. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) is expected to simplify the creation process, automating tasks like producing variations and enhancing layouts based on user input, which is essential in establishing the funding for distinctive rendering endeavors.
Customization and revisions play a vital role in this process, as they allow for tailored solutions that meet specific needs, ultimately influencing the overall cost and investment decisions.
These trends not only signify a shift in how architecture is presented but also highlight the best impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, indicating a broader movement towards more interactive and personalized engagement. High-quality visual renderings are essential in development and decision-making, highlighting the best impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations as they effectively communicate design intent and leave a lasting impression. They can significantly impact client perceptions and decisions, highlighting the best impact of virtual reality on architectural presentations, as evidenced by studies showing that projects with high-quality renderings are more likely to receive approvals and funding.
With 64% of staff architects majoring in architecture, architects aiming to fully leverage the potential of VR in their presentations will find it essential to stay attuned to these developments. Virtual reality is rapidly growing and may soon become a daily habit at home or work, ultimately helping them maintain a competitive edge in the evolving architectural landscape.
Conclusion
The integration of virtual reality (VR) into architectural presentations signifies a pivotal advancement in the industry, transforming traditional methods into immersive experiences that profoundly engage clients. By allowing clients to navigate virtual spaces prior to construction, VR enhances understanding of design elements such as scale and spatial relationships, fostering greater confidence and investment in projects. The growing emphasis on sustainable design within architecture further amplifies the importance of VR, aligning client expectations with innovative, eco-friendly practices.
Successful VR implementation hinges on a series of best practices, including:
- Investing in high-quality hardware
- Optimizing 3D models
- Actively engaging clients throughout the design process
The creation of compelling VR content, enriched with storytelling elements and interactivity, serves to deepen client connections and enhance satisfaction. Challenges such as technical hurdles and substantial costs can be navigated through comprehensive training and interdisciplinary collaboration, ensuring that design teams are well-equipped to leverage VR effectively.
Looking ahead, emerging trends such as:
- Cloud-based VR solutions
- Advancements in haptic technology
- The incorporation of artificial intelligence
are poised to reshape architectural presentations. These innovations promise to enhance collaboration, streamline design processes, and provide a more interactive experience for clients. As the architectural landscape continues to evolve, staying attuned to these developments will be crucial for firms aiming to maintain a competitive edge while delivering high-quality visual renderings that resonate with clients and stakeholders alike. Embracing VR not only elevates the architectural presentation but also lays the groundwork for stronger community ties and sustainable practices in the industry.

0 Comments