Overview
The article titled “Best Practices for Using CGI Software: Tips from Industry Experts” focuses on effective strategies for utilizing CGI software to enhance visual content creation. It emphasizes the importance of starting with a well-defined concept, utilizing advanced techniques like proxies for efficiency, and engaging with professional communities to share insights, which collectively lead to improved outcomes in CGI projects.
Introduction
The realm of computer-generated imagery (CGI) has undergone a remarkable transformation, evolving from simple 2D representations to sophisticated 3D animations that redefine visual storytelling. This article delves into the intricacies of CGI animation, exploring its foundational techniques such as:
- Modeling
- Texturing
- Rendering
which are essential for creating compelling visual narratives. As the demand for high-quality visual content surges, particularly in industries like architecture and entertainment, understanding the tools and practices that drive this evolution becomes paramount. From the pivotal role of advanced software to the historical milestones that have shaped the industry, this exploration provides valuable insights for professionals seeking to enhance their CGI expertise. Furthermore, it anticipates future trends, including the integration of artificial intelligence and immersive technologies, which promise to further revolutionize the landscape of CGI. By examining these elements, practitioners can better navigate the complexities of CGI and leverage its potential to captivate audiences and foster meaningful connections within their projects.
Understanding CGI Animation: Basics and Functionality
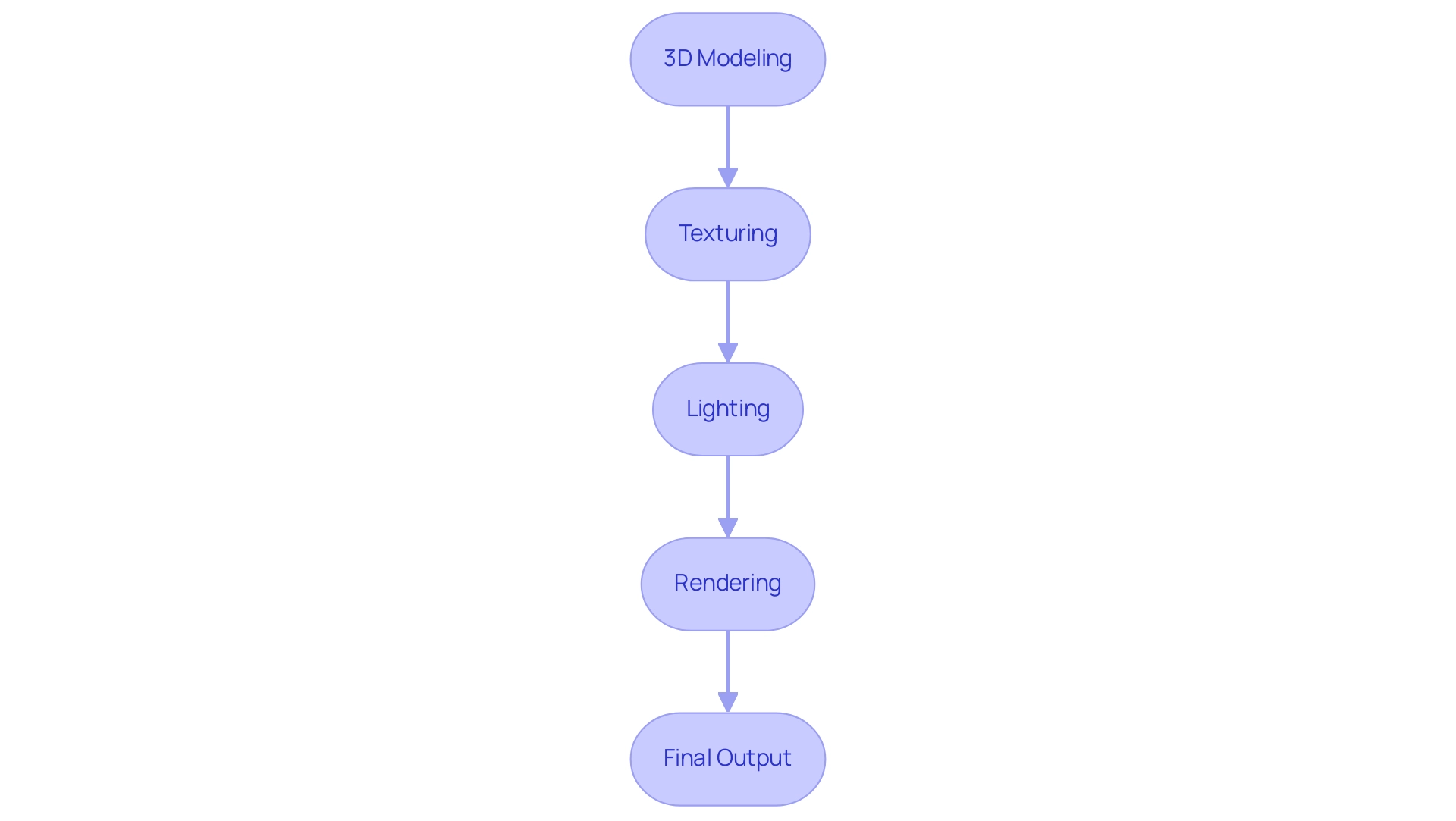
Computer-generated imagery (CGI) represents a pivotal advancement in visual content creation, involving the generation of still or animated imagery through sophisticated CGI software. CGI visuals consist of a varied range of methods, notably featuring:
- 3D modeling
- Texturing
- Lighting
Mastery of these processes is crucial for leveraging CGI software capabilities effectively.
For instance, 3D modeling entails the construction of a digital representation of an object, which serves as the foundational step for any CGI project. Texturing, the subsequent stage, applies surface details and color to these models, enhancing their realism. Lighting techniques are employed to simulate the interaction of light with objects, critically influencing the mood and visibility of the scene.
Ultimately, rendering is the process that transforms these complex 3D models into 2D images or visuals, resulting in the final visual product. Architectural visualization offers more than just an image; it provides an immersive experience that fosters connections between future homeowners and their potential communities, setting the foundation for strong community ties. Notably, the TV production sector has been growing by 4% year-over-year since 2020, reflecting the increasing relevance and demand for CGI in the industry.
As Ma Li, President of the China Animation Association, stated, ‘The total output value of China’s creative industry is projected to surpass 300 billion yuan ($41.2 billion) in 2023,’ underscoring the significance of CGI within this expanding landscape. Furthermore, collage animation exemplifies an artistic approach within CGI techniques, utilizing various materials and textures to create visually compelling narratives. This method is popular for conveying nuanced messages, making it a favored choice for social and cultural commentaries in short films and music videos.
By familiarizing oneself with these essential concepts, practitioners can significantly enhance their proficiency with CGI software and improve the overall quality of their outputs.
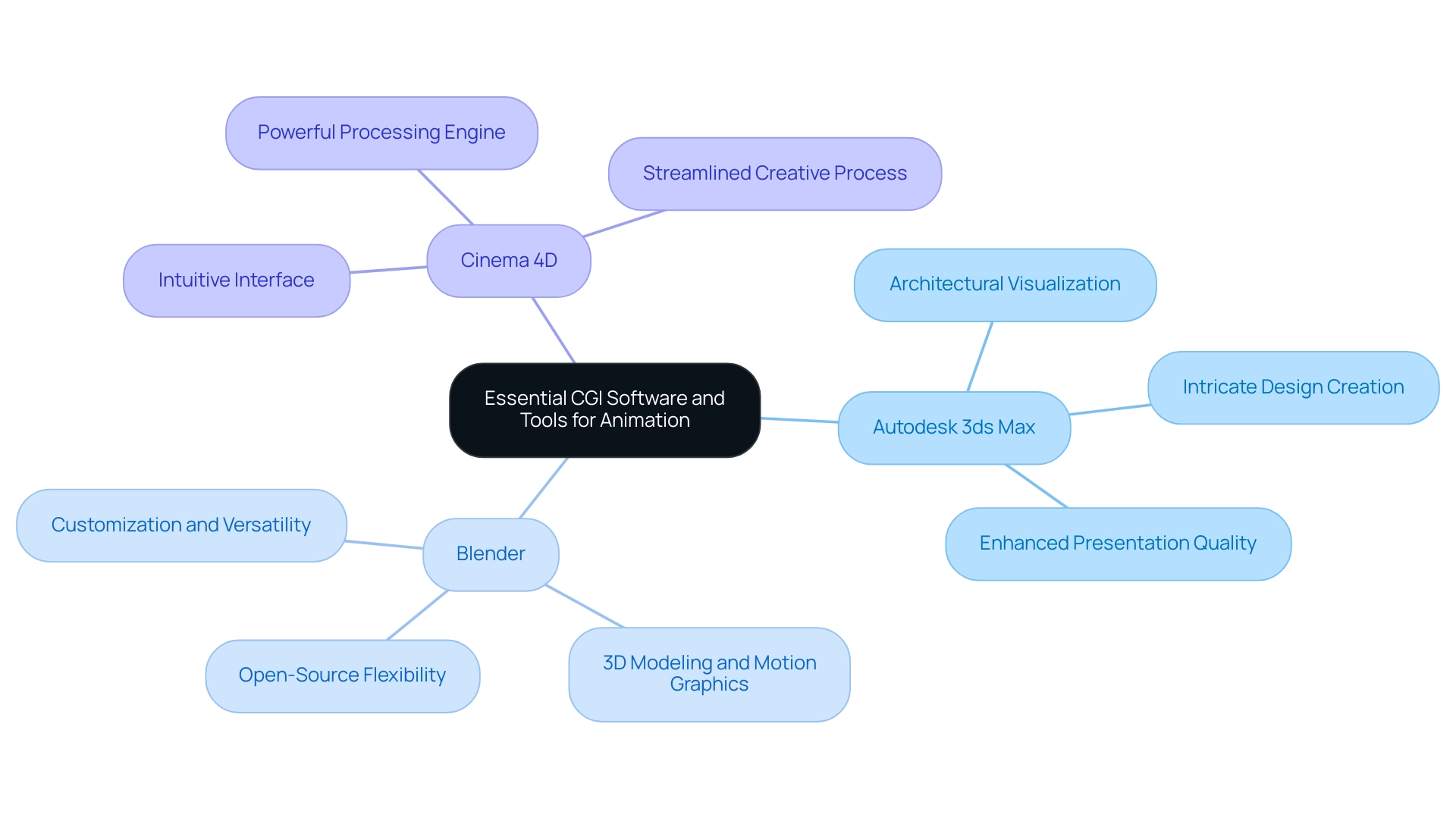
Essential CGI Software and Tools for Effective Animation
Experts in the CGI domain depend on several essential CGI software tools, each addressing specific requirements. Autodesk 3ds Max is notable for its advanced modeling and visualizing capabilities, establishing it as a top selection for architectural visualization. Its robust capabilities facilitate the creation of intricate designs, thus enhancing presentation quality for architectural works.
Conversely, Blender, as an open-source option, offers an extensive toolkit for 3D modeling and motion graphics. It is perfect for both beginners and experienced animators, allowing for extensive customization and versatility in various animation endeavors. Cinema 4D is especially praised in the field of motion graphics, thanks to its intuitive interface and powerful processing engine, which streamline the creative process.
Each of these tools possesses unique strengths that cater to specific applications, underscoring the importance of selecting the right software based on the task’s unique demands. High-quality visual representations, similar to a glimpse into the future of an initiative, are essential for making informed choices and generating enthusiasm among stakeholders. They play a pivotal role in pre-sales visualization, enhancing confidence and generating investment even before the physical realization of the endeavor.
For instance, the case study titled ‘The Power of Pre-Sales Visualization’ illustrates how effective renderings can ignite interest and investment long before construction begins. As the CGI software market evolves, spurred by a 30% increase in demand for skilled visual effects professionals since 2018, understanding CGI software tools becomes increasingly essential for successful project outcomes. Notably, the global visual entertainment market was valued at $394.6 billion in 2022 and is anticipated to expand to $528.8 billion by 2030, reflecting a CAGR of 5.00%.
This growth is supported by the findings of the case study titled ‘Market Drivers for CGI Software,’ which highlights the rising need for advanced visual content using CGI software in film production, advertising, and gaming. According to Lionel Sujay Vailshery, a research expert covering cloud computing and emerging tech industries, get in touch with us now to learn more about leveraging these tools effectively.
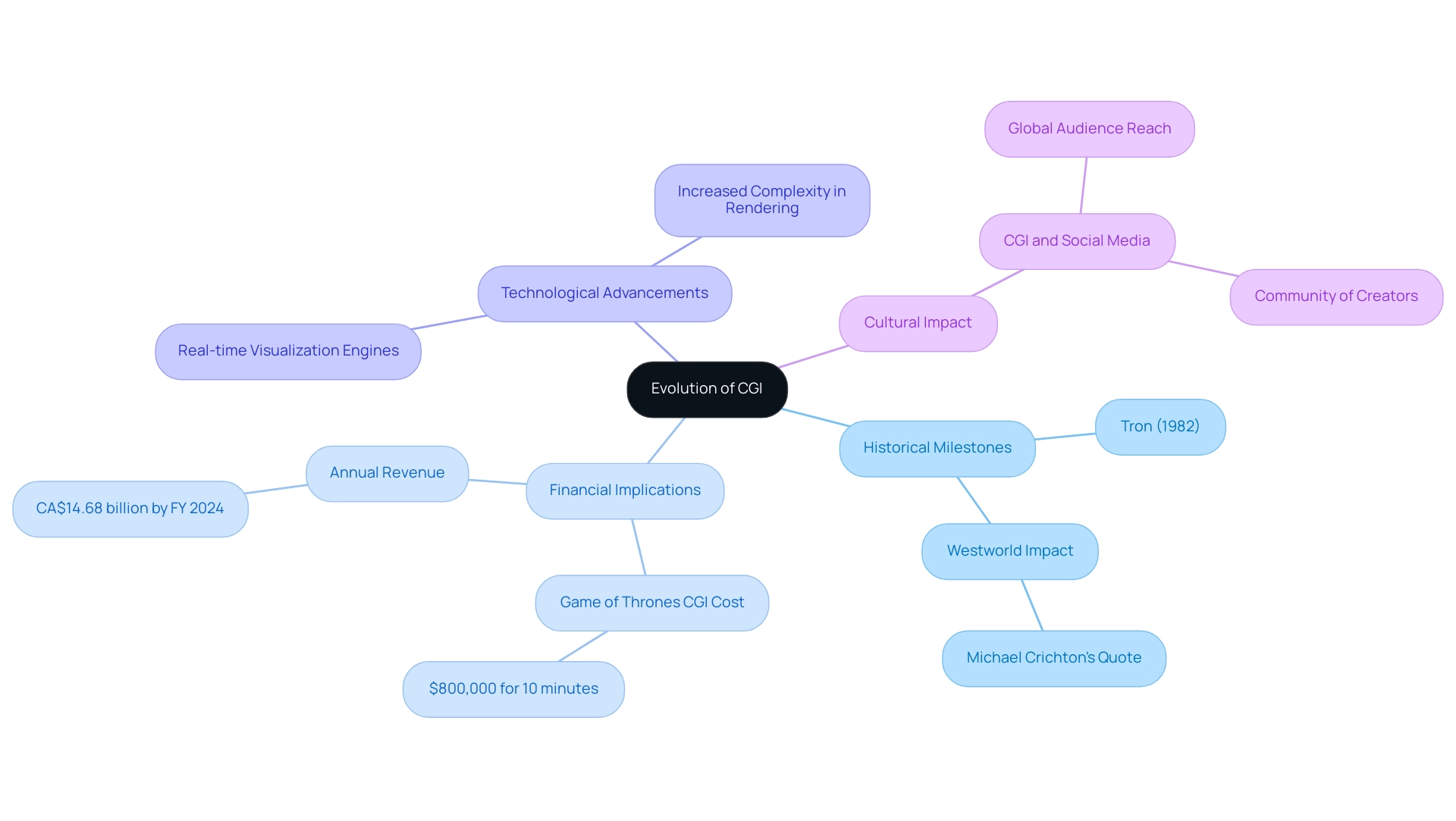
The Evolution of CGI: Lessons from the Past
The evolution of computer-generated imagery (CGI) represents a significant journey from the rudimentary 2D graphics of the early days to the intricate 3D visuals we see today. A pivotal moment in this evolution occurred with the release of ‘Tron’ in 1982, a film that not only showcased the groundbreaking potential of CGI but also set the stage for its widespread adoption in the cinematic landscape. As hardware capabilities expanded and CGI software became more sophisticated, the industry witnessed a dramatic increase in the realism and complexity of CGI animations.
Notably, an episode of ‘Game of Thrones’ featuring just 10 minutes of CGI cost $800,000, underscoring the financial implications of CGI production that architects must consider when managing budgets. The advent of real-time visualization engines has further revolutionized this field, enabling artists to produce high-quality visuals with unprecedented speed and efficiency. High-quality representations serve as a vital glimpse into the future of architectural endeavors, enabling stakeholders to visualize concepts and make informed choices that generate enthusiasm.
Additionally, the complexity and scale of an undertaking can significantly affect rendering time and resource requirements; for example, the intricacies involved in rendering an entire community versus a single-car garage require different levels of investment. A detailed analysis reveals that large-scale undertakings can incur costs that are several times greater than smaller ones, making it essential for architects to budget accordingly.
Michael Crichton once remarked, ‘Moving on a few years, computer graphics continued to be used in various experimental short films but finally hit it big on the silver screen in the sci-fi Western thriller Westworld.’
This quote provides authoritative insight into the evolution of CGI, enhancing the credibility of our understanding. Furthermore, analyzing the case study titled ‘CGI and Social Media’ reveals how platforms like Twitter and YouTube have transformed the dissemination of CGI software content, allowing creators to reach global audiences and fostering a community of fans and creators who share ideas and collaborate. By examining these historical milestones and contemporary developments, professionals can glean essential insights that inform current best practices and drive innovation within CGI software initiatives, while also understanding the trajectory of CGI’s role in film and beyond.
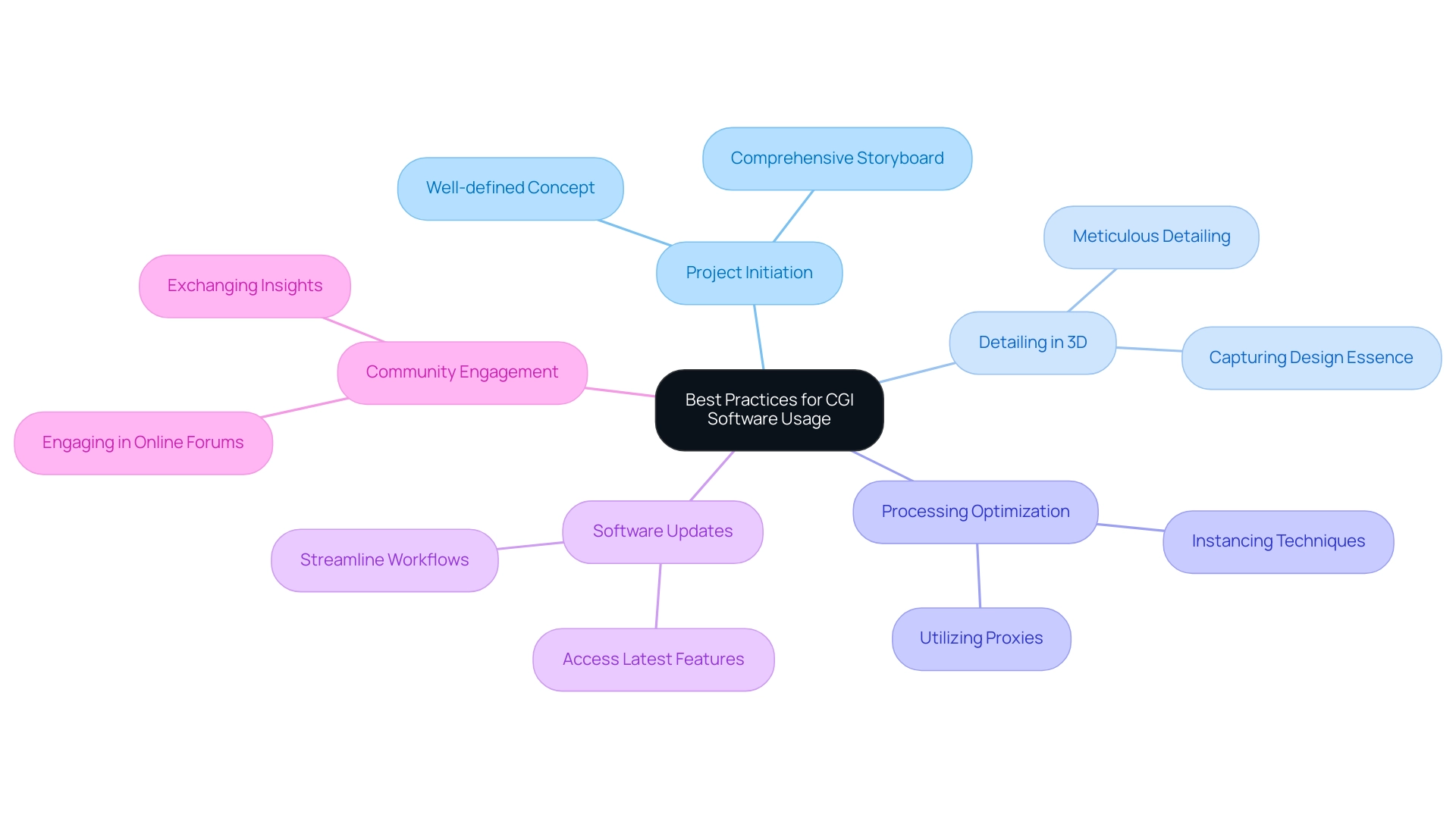
Expert Tips and Best Practices for CGI Software Usage
To optimize the effectiveness of cgi software, practitioners must adhere to several best practices that emphasize precision and detail. Initiating each project with a well-defined concept and comprehensive storyboard is critical, as these foundational steps ensure that the animation process is directed and focused, significantly reducing the likelihood of extensive revisions later in the project lifecycle. The significance of capturing the essence of design through meticulous detailing is crucial in 3D exterior representations, as these tiny details contribute to a compelling narrative about the future of the building or home.
With the rise of interactive 3D content driven by advancements in faster processors and improved graphics capabilities, this approach is more relevant than ever. Furthermore, utilizing proxies and instancing techniques can greatly enhance processing times, particularly in complex scenes where high detail levels may hinder performance. Regularly updating software is also vital; access to the latest features and enhancements can streamline workflows and improve overall output quality.
Engaging with online forums and professional communities allows practitioners to exchange insights, address challenges, and learn from the collective experiences of peers in the field. When searching for quality 3D architectural visualization services, take into account the following suggestions:
- Assess the provider’s portfolio for quality and style.
- Look for testimonials or reviews from past clients.
- Confirm they comprehend your requirements and vision.
Successful examples of CGI software in marketing, such as virtual product demonstrations and interactive storytelling experiences, showcase the practical applications of these best practices.
Implementing these practices not only contributes to more polished and professional results but also enhances the collaborative spirit essential for success in CGI.
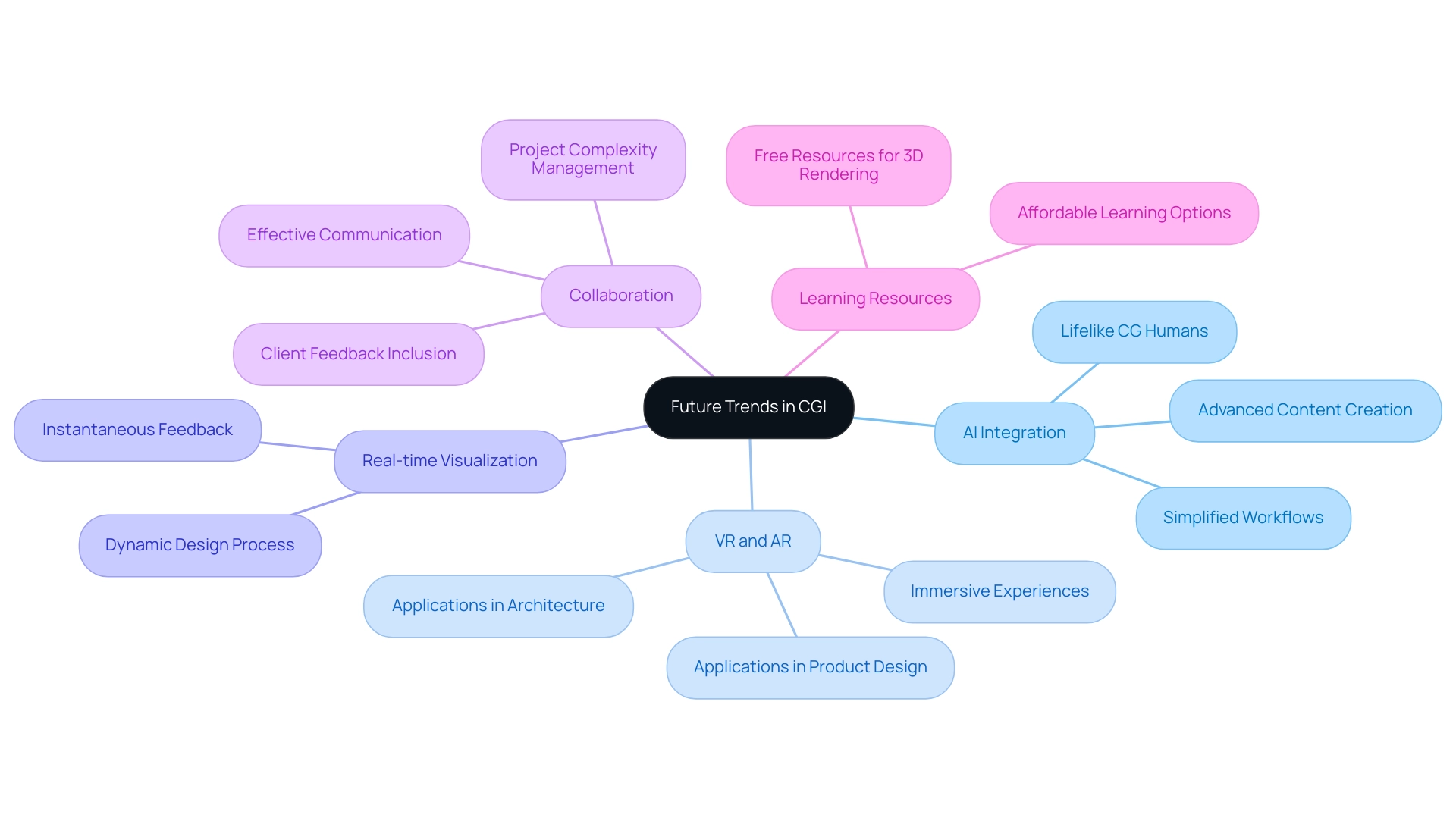
Future Trends in CGI: What to Expect and Prepare For
As the landscape of CGI software technology evolves, several pivotal trends are emerging that professionals must closely monitor. A notable trend is the increasing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) within CGI processes, specifically in creating lifelike CG humans for architectural visualizations, effectively bridging the uncanny valley. This improvement not only simplifies workflows but also brings advanced features in content creation, allowing the production of high-quality visual outputs crucial for development and decision-making.
Furthermore, the rise of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) is revolutionizing CGI, facilitating the development of immersive experiences that captivate users and expand applications across architecture, real estate, and product design. The demand for real-time visualization is gaining momentum, allowing creators to receive instantaneous feedback during the design process, thus promoting a more dynamic and iterative approach to development. To stay competitive in this rapidly changing environment, professionals should actively explore these technologies and adapt their workflows accordingly, ensuring they remain at the forefront of innovation in CGI applications.
Collaboration is essential in this environment; as highlighted in the joint creation process at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, effective communication and the inclusion of client feedback throughout the phases—including initial discussions, briefs, and ongoing updates—are vital for attaining satisfaction and success. Furthermore, the complexity and scale of projects greatly affect processing times and resource needs, making it crucial to comprehend these elements when deciding on investment in distinctive visualization projects. Notably, the animation industry has seen a growth of 4% year-over-year since 2020, underscoring the increasing relevance of CGI software.
Real-world applications, such as resolving client technical issues through active listening and clear instructions, highlight the importance of effective communication and support in CGI processes, resonating with the practical guidance needed by lead architects. For those looking to enhance their skills, there are numerous affordable and free resources available for learning 3D rendering, which can significantly benefit professionals aiming to excel in this field.
Conclusion
The exploration of computer-generated imagery (CGI) animation reveals its profound impact on visual storytelling and project visualization across various industries. By understanding the foundational techniques of modeling, texturing, lighting, and rendering, professionals can elevate their CGI projects to new heights, ensuring that they effectively convey their intended narratives. The importance of selecting the appropriate software tools, such as Autodesk 3ds Max, Blender, and Cinema 4D, cannot be overstated; each offers unique capabilities tailored to specific project needs, ultimately influencing the quality and effectiveness of the visual output.
Reflecting on the historical advancements in CGI provides valuable context for current practices and future innovations. The evolution from basic 2D graphics to complex 3D animations illustrates the technological strides that have reshaped the industry. As CGI continues to grow—evidenced by the significant market expansion and the integration of real-time rendering and AI—professionals must remain vigilant in adapting to these developments. The case studies and expert insights shared throughout this discussion serve to reinforce the necessity of best practices and continuous learning in this ever-evolving field.
Looking ahead, embracing emerging trends such as virtual reality and the increasing role of AI will be critical for maintaining a competitive edge. As the demand for high-quality, immersive visual content surges, architects and CGI practitioners alike must leverage these advancements to create compelling and impactful visual narratives. By fostering collaboration and honing technical skills, professionals can not only enhance their project outcomes but also contribute to the broader evolution of CGI as a powerful tool for communication and connection in the architectural realm.

0 Comments