Introduction
Architectural rendering has emerged as an indispensable tool in the design and construction process, providing a visual language that bridges the gap between conceptual ideas and tangible outcomes. As stakeholders increasingly demand clarity and precision, the importance of high-quality renderings cannot be overstated.
This article delves into the multifaceted world of architectural rendering, exploring its:
1. Definition
2. Significance
3. Best practices necessary for achieving accuracy
It highlights the transformative impact of technology on rendering processes, including the integration of AI and real-time rendering capabilities, which enhance communication and streamline workflows. Furthermore, the discussion addresses common pitfalls that architects must avoid to ensure their visualizations effectively convey design intent.
By examining future trends and the evolving landscape of architectural visualization, this article equips lead architects with the knowledge necessary to leverage these advancements, ultimately fostering innovation and client satisfaction in their projects.
Understanding Architectural Rendering: Definition and Importance
Architectural visualization, emphasizing architectural rendering accuracy, includes the creation of both two-dimensional and three-dimensional images that vividly depict the features and aesthetics of proposed architectural concepts. This process is crucial as it enables stakeholders—architects, clients, and decision-makers—to visualize the end product prior to construction, thereby enhancing collaborative communication. Establishing the suitable degree of detail in illustrations is crucial for homeowners and businesses alike, as it promotes a clearer comprehension of purpose and functionality.
Top-notch visuals not only express creative intent but also ensure architectural rendering accuracy, promoting improved contractor communication and greatly minimizing the likelihood of conceptual misunderstandings. Additionally, they enable the early detection of design problems, resulting in cost savings in project design development through timely adjustments from stakeholders. The role of pre-sales visualization cannot be overstated; our illustrations serve as a bridge between concept and reality, instilling confidence in projects and generating investment before physical construction begins.
Significantly, over 70% of customers prioritize personalized reports that align with their specific needs, underscoring the importance of tailored visualizations in the design process. Furthermore, the economic landscape of the profession highlights the need for architects to master effective visualization techniques to remain competitive, especially given the average income of $85,968 for male architects and $79,033 for female architects. The case study titled ‘3D Visualization Finally Reaches Mainstream Use: History & Benefits’ illustrates the evolution and growing acceptance of 3D visualization, showcasing how its integration into building design not only enhances client understanding but also positions architects to better navigate the competitive landscape, ultimately driving project success and client satisfaction.
Best Practices for Achieving Accuracy in Architectural Renderings
Achieving architectural rendering accuracy starts with meticulous attention to measurements and scale. Every element, from furniture to structural components, must be modeled to precise specifications to maintain architectural rendering accuracy, as inaccuracies at this stage can lead to significant misrepresentations in the final output. Implementing measurement practices is crucial for establishing a valuable data architecture, ensuring that the architectural rendering accuracy reflects true dimensions and proportions.
Furthermore, for both interior and exterior projects, utilizing high-quality textures and materials that closely mimic real-world surfaces is imperative. Understanding the interactions between materials and light—such as glossiness and reflectivity—enables more authentic representations. Lighting plays a pivotal role in creating realism; simulating natural light according to geographical location and time of day is essential, while artificial lighting must align with the intended design aesthetics.
Regularly reviewing and recalibrating these elements not only mitigates inaccuracies but also enriches the overall realism of the renderings. Significantly, as reported by The Architect’s Newspaper, there are presently 35,621 candidates actively pursuing licensure, highlighting the competitive nature of the profession and the necessity for precision in design practices. By following these best practices and utilizing advanced simulation software, architects can significantly improve architectural rendering accuracy, ultimately aiding in more effective communication of project intent and customer expectations.
The use of tools such as Adobe Creative Suite/Cloud further supports the creation of high-quality textures and materials, which reinforces the critical importance of architectural rendering accuracy in architectural visualizations. Furthermore, the minute elements in illustrations help convey a captivating narrative regarding the design, encapsulating its essence and encouraging customers to imagine the final result. Our extensive experience in producing high-quality visuals across various sectors further ensures that we meet and surpass customer expectations.
Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Rendering Accuracy
Recent advancements in visualization technologies have fundamentally transformed the landscape of architectural representations, significantly enhancing contractor communication, client understanding, and architectural rendering accuracy. High-quality visuals truly give your contractors a break, as they eliminate guesswork and provide clarity in design. Leading software like Lumion, V-Ray, and Enscape now provide advanced features such as real-time visualization and ray tracing capabilities, empowering architects to create high-fidelity images with remarkable speed and architectural rendering accuracy.
These tools utilize intricate algorithms to simulate light behavior in virtual environments, which enhances architectural rendering accuracy for shadows and reflections while facilitating detailed 3D visualizations for client evaluation. A recent case study titled ‘Future of Architectural Visualization’ highlights that the industry is increasingly shifting towards real-time visualization and AI tools, with 50% of respondents expecting more intuitive tools and 37% planning to invest more in AI. Moreover, as project complexity and scale increase, the need for architectural rendering accuracy rises, leading to escalated visualization time and resource requirements, which makes high-quality visuals even more essential for informed decision-making and building excitement about what’s to come.
The rise of cloud-based processing services allows professionals to offload resource-intensive tasks, granting architects the freedom to focus on creativity and design while achieving stunning visual results. Additionally, 40% of firms that meet or exceed their goals plan to invest in project management software next year, underscoring the broader trend of increasing technology investment in the architecture sector. Staying abreast of these advancements is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge, as 70% of architecture firms are expected to enhance their technology investments in the coming year.
This change signifies a wider trend towards incorporating sophisticated visualization methods into design workflows that enhance architectural rendering accuracy, ultimately promoting more creative and effective practices.
Avoiding Common Mistakes in Architectural Rendering
Common errors in design can severely undermine the architectural rendering accuracy, affecting the quality and effectiveness of the final output. A prevalent error is the failure to ensure architectural rendering accuracy when accounting for scale, which can lead to unrealistic proportions that misrepresent the design and mislead clients. For instance, a minor oversight in scale can create a visual that appears either overwhelmingly large or insignificantly small, resulting in a disconnect with the intended architectural vision.
Moreover, the intricate details—from the way sunlight dances off the windows to the texture of the bricks—play a crucial role in enhancing the architectural rendering accuracy and the emotional impact of visual representations. Neglecting to fine-tune lighting settings can yield flat, uninspiring images; effective lighting is crucial for ensuring architectural rendering accuracy in conveying depth and atmosphere. An over-reliance on default settings within visualization software often compromises architectural rendering accuracy, generating generic results that lack the nuance required for high-quality presentations.
Adjusting these settings to the specific context of the project is essential for achieving architectural rendering accuracy and more impactful outcomes. A practical suggestion for lead architects is to elevate the camera height to 25 or 30 feet to improve clarity in visuals. Regular peer reviews and feedback loops are invaluable, as they facilitate the early identification of issues, enabling timely adjustments that enhance overall outcomes.
Following software guidelines is critical, as different 3D modeling software have varying functionalities; understanding these can prevent errors that arise from manual adjustments. As Paul Keskeys, Editor in Chief at Architizer, aptly states, ‘If a diagram, sketch, or physical model can communicate your concept better than a polished visual, you should steer clear of the uncanny valley in favor of clarity.’ This principle strengthens the necessity for precision and intentionality in design illustration, similar to the instructions found in user manuals that highlight detail for effective communication.
Furthermore, Boeri Studio’s ‘Bosco Verticale’ project illustrates the difficulties of incorporating trees into building concepts, highlighting the vital function of intricate visuals in depicting and improving residential architecture. By diving deeper into these details, we can see how they contribute to a project feeling real, lived-in, and ready to be built.
Future Trends in Architectural Rendering: AI and Real-Time Technologies
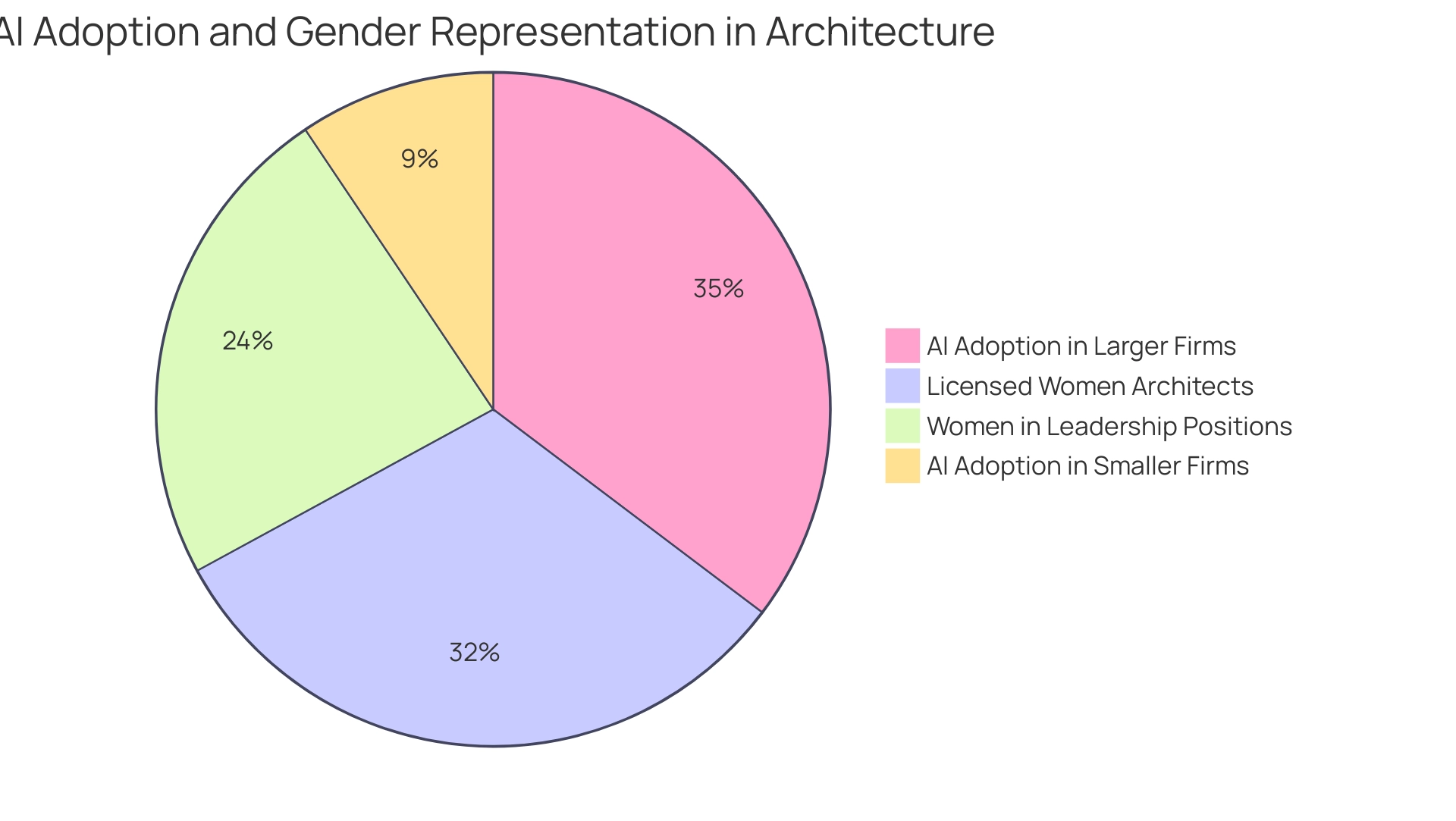
The design visualization field is on the verge of a substantial change, primarily driven by advancements in architectural rendering accuracy, artificial intelligence (AI), and real-time imaging technologies. Premium visuals, characterized by architectural rendering accuracy, act as a ‘gateway to the future of your project,’ enabling stakeholders to envision possible results and grasp the fundamental concept behind the creations. Current statistics indicate that over 30% of larger architectural firms are integrating AI solutions, a stark contrast to the mere 8% adoption rate among smaller firms with five employees or fewer.
AI’s ability to automate tedious tasks such as texture mapping and lighting adjustments not only streamlines workflows but also contributes to architectural rendering accuracy in the creation of lifelike CG humans, which is crucial for bridging the uncanny valley in visualizations. This progress enables architects to concentrate their efforts on the more imaginative elements of creation, ensuring that the architectural rendering accuracy in their 3D visuals aligns with both project specifications and customer expectations. Furthermore, real-time visualization technologies significantly improve architectural rendering accuracy, allowing architects to interact with their designs in highly immersive environments, which enhances client engagement and presentation quality.
The necessity of investing in high-quality visualizations, which directly impact architectural rendering accuracy, cannot be overstated, as it is essential for making informed decisions and building excitement about the final outcomes. Platforms like OpenAsset play an essential role in managing digital assets and streamlining complex projects, further enhancing efficiency in design workflows. As highlighted by industry specialists, the adoption of these innovative technologies is not merely a trend but a necessity for architects seeking to improve architectural rendering accuracy in their visualization processes.
Additionally, considering the diversity within the architecture industry, it is important to acknowledge that women represent 27% of licensed architects in the U.S. and hold only 20% of leadership positions, highlighting the ongoing challenges in representation. By staying informed about these developments and the industry’s landscape, which comprises approximately 73,313 businesses in architecture in the U.S., professionals can ensure they deliver state-of-the-art solutions that enhance architectural rendering accuracy and meet the evolving expectations of their clients, positioning themselves at the forefront of architectural innovation. The diverse applications of 3D rendering extend beyond architecture into fields such as medical imaging, training simulations, product prototyping, and graphic design, underscoring its importance across various sectors.
Conclusion
Architectural rendering is essential in the design and construction process, enhancing communication and clarity among stakeholders. High-quality renderings effectively bridge the gap between conceptual ideas and tangible outcomes, ensuring accurate representation of design intent. Precision in renderings is crucial, as it prevents costly misunderstandings and builds client confidence before construction begins.
To achieve realistic and impactful visualizations, architects must implement best practices, focusing on:
- Scale
- Detail
- The use of advanced rendering technologies
The integration of AI and real-time rendering capabilities is revolutionizing the industry, enabling architects to streamline workflows and enhance project fidelity. Staying updated on these technological advancements is vital for maintaining a competitive edge.
However, common pitfalls, such as inaccuracies in scale and lighting, can diminish the effectiveness of renderings. Addressing these challenges allows architects to improve their visualizations, ensuring they resonate with clients. The future of architectural rendering will continue to evolve, driven by innovation and a deeper understanding of client needs.
In summary, high-quality architectural rendering is fundamental for successful project outcomes. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies and adhering to best practices, architects can bring their visions to life, fostering innovation and excellence. This dedication to precision and creativity will not only enhance client satisfaction but also advance the architectural profession as a whole.

0 Comments