Introduction
The evolution of architectural rendering has become a cornerstone in the communication of design concepts, bridging the gap between vision and realization. As architects strive to convey their ideas with precision, understanding the nuances of various rendering techniques is essential. This article delves into the key methodologies that underlie effective architectural visualization, including:
- The intricate details of ray tracing
- The expediency of rasterization
It also explores the transformative impact of emerging technologies such as:
- Artificial intelligence
- Virtual reality
These technologies are reshaping the rendering landscape. By examining best practices and sustainable approaches, this discussion aims to equip architects with the knowledge necessary to enhance their rendering capabilities, ultimately fostering clearer stakeholder communication and more impactful project outcomes.
Understanding Architectural Rendering: Key Concepts and Techniques
Architectural rendering technology serves as a vital conduit between design concepts and their visual representation, enabling architects to communicate ideas effectively and ensuring clarity among stakeholders. Among the most prominent techniques are:
Ray Tracing: This advanced imaging method meticulously simulates the behavior of light as it interacts with various surfaces, yielding images of remarkable realism. Its ability to produce intricate reflections, shadows, and refractions enhances client understanding and satisfaction, making it ideal for high-stakes presentations and detailed project proposals.
Rasterization: In contrast, rasterization is a more expedient method that transforms 3D models into 2D images. While it allows for fast processing suitable for real-time applications, it often sacrifices detail and accuracy compared to ray tracing. This technique is particularly effective in scenarios where speed is essential, such as interactive evaluations, helping to eliminate misunderstandings during contractor communications.
Photorealistic vs. Non-Photorealistic Rendering: Understanding the distinction between these two approaches is crucial. Photorealistic depiction strives to produce imagery that closely mimics real-life scenarios, making it invaluable for client presentations and marketing materials. Non-photorealistic visual representation, however, serves a different purpose, allowing for artistic interpretations and conceptual illustrations that can effectively convey ideas in a more abstract manner.
When creating structures’ visualizations, it is essential to consider the appropriate levels of detail, which can vary based on the assignment’s stage and audience. For example, initial conceptual sketches may gain from reduced detail to stimulate creative contributions, while final presentations necessitate extensive levels of detail to ensure clarity and build confidence among stakeholders.
Integrating these methods into architectural rendering technology is crucial for achieving the desired effect in various architectural endeavors. Recent trends indicate a growing preference for ray tracing as a component of architectural rendering technology, due to its unparalleled detail and realism, aligning with the industry’s push towards higher-quality visual outputs. Additionally, as 62% of architecture firms use cloud-based collaboration tools, there is a chance for improved visualization processes and task coordination.
A recent case study emphasized that 70% of companies are intending to invest more in technology, especially in management and design software, highlighting the emphasis on improving visualization techniques. Keeping updated on these advancements will be crucial for lead architects looking to improve their visualization skills and maintain design heritage. The integration of 3D visualizations not only enhances client understanding but also significantly improves stakeholder communication, ultimately boosting confidence and investment.
Innovations in Architectural Rendering: AI, VR, and Beyond
Recent progress in architectural rendering technology is fundamentally altering the landscape of building visualization practices.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): The integration of AI algorithms is redefining visualization processes by optimizing processing times and enhancing image quality through pattern recognition from prior projects. Noteworthy tools such as DALL-E and Midjourney exemplify AI-driven innovations that expedite the creation of high-quality visuals, allowing architects to focus on creative solutions rather than technical constraints.
This shift underscores the notion that the journey of AI integration is about enhancing creativity, not replacing it. The growth of AI technologies is reflected in broader trends, such as the approval of 139 AI-related medical devices by the FDA in 2022, highlighting increasing acceptance and integration of AI across various fields. Furthermore, AI plays a pivotal role in creating lifelike CG humans for architectural rendering technology, effectively bridging the uncanny valley and enhancing the realism of architectural visualizations.
Virtual Reality (VR): The application of VR technology enables architects to immerse clients within their creations, offering an unparalleled perspective that surpasses traditional renderings. This interactive experience facilitates more informed choices and significantly boosts client satisfaction. As architects embrace VR, they are equipped to create empathetic solutions that resonate more deeply with users. Understanding public opinion on AI is vital in anticipating its societal impacts, as it may influence how architects integrate these technologies into their practices. Moreover, the collaborative journey fostered by VR allows for shared insights among stakeholders, enhancing the overall development process.
Architectural Rendering Technology: Technologies such as Unreal Engine enable architects to visualize and adapt concepts in real-time, thereby enhancing collaboration and the decision-making process. This capability not only streamlines workflows but also fosters interdisciplinary collaborations, essential for addressing complex design challenges. The future envisions a collaborative ecosystem where various stakeholders leverage AI and VR for holistic solutions, as highlighted in the case study titled ‘Collaborative AI Ecosystems.’ This illustrates the profound influence of architectural rendering technology on structure visualization, emphasizing the significance of teamwork in overcoming design challenges and instilling confidence in pre-sales imagery, which is essential for attracting investments.
Lighting Techniques: Furthermore, the role of lighting in visualizations must not be overlooked. Differentiating between artificial lighting in interiors and natural sunlight in exteriors greatly influences the perception of space and can enhance the overall effectiveness of 3D visualizations. By thoughtfully evaluating these lighting techniques, architects can further enhance the quality of their visual representations, ensuring they resonate well with potential investors during the pre-sales phase.
Best Practices for High-Quality Architectural Renderings
Achieving high-quality architectural visualizations necessitates the use of architectural rendering technology and adherence to several best practices that elevate the final output. With the architecture industry experiencing a growth rate of 1.6% CAGR between 2019 and 2024, the significance of these practices cannot be overstated:
- Attention to Detail: Each element within the visualization must be crafted with precision, from the intricate textures of materials to the nuanced effects of lighting. These subtle details not only enhance the visual appeal of residential architecture but also contribute to the storytelling aspect, capturing the essence of the structure and conveying a compelling narrative about the space.
- Lighting and Shadows: Strategic use of both natural and artificial light sources is vital in creating depth and atmosphere. By experimenting with various times of day, architects can observe how lighting alters the perception of a space, thus enhancing its visual narrative and market differentiation.
- Post-Processing: Utilizing software like Photoshop for post-rendering adjustments is crucial. Enhancing colors, contrast, and sharpness during this phase can significantly elevate the quality of the visual presentation, ensuring it resonates with viewers and meets client expectations. Furthermore, software applications like Lumion or V-Ray can be utilized to produce realistic visuals that further enhance the storytelling through visual detail.
- Feedback Loop: Establishing a continuous feedback loop involving clients and colleagues throughout the visualization process is essential. This cooperative method permits enhancements and aesthetic advancements, ultimately resulting in a more successful project outcome and highlighting the significance of client collaboration in attaining desired results.
As emphasized by Malgo Widaj, founder of RNDR, the field of architecture is evolving towards an inclusive and tech-driven approach that values meaningful beauty creation. By implementing these best practices and considering outsourcing for architectural rendering technology, professionals can enhance business efficiency and quality, ensuring that they meet modern market demands. Outsourcing can enable teams to concentrate on essential design tasks while utilizing specialized visual services for impactful imagery.
For instance, selecting the appropriate resolution for each project is critical for achieving stunning visuals that align with specific needs. This consideration, along with the previously mentioned best practices, ensures that the final outputs are both impactful and aligned with the industry’s growth trajectory.
Sustainable Practices in Architectural Rendering
Achieving sustainability in architectural rendering involves implementing several best practices while also embracing architectural visualization’s transformative potential:
Use of Eco-Friendly Materials: Accurately representing sustainable building materials in renderings is crucial. This practice not only encourages the use of eco-friendly materials in real-life endeavors but also informs clients about their advantages. For instance, materials like bamboo, recycled steel, and low-VOC paints are excellent choices that architects can showcase to influence stakeholders to prioritize sustainability in their creations.
Immersive Visualization: Architectural visualization offers an experience that transforms prospects into participants in shaping their future homes. This immersive approach fosters a deeper connection between the initiative and its potential residents, setting the foundation for a strong community from the outset. By engaging future homeowners in the visualization process, architects can cultivate a sense of belonging and investment in the community.
Energy Efficiency: Renderings should effectively illustrate concepts that maximize natural light and minimize energy consumption. Demonstrating how a building will function sustainably enhances the overall impact of the project while showcasing the architect’s commitment to environmentally responsible planning.
Leveraging advanced architectural rendering technology and software tools that evaluate the environmental impact of materials and designs is essential for sustainability. These tools provide architects with data-driven insights, allowing them to create more sustainable designs that resonate with contemporary environmental standards.
- Promoting Sustainable Design: Through engaging visuals, architects can showcase innovative sustainable practices that may influence clients and stakeholders. This visual depiction acts as an important instrument in promoting eco-friendly choices, in accordance with the increasing movement towards sustainability in building initiatives. The investment in high-quality visualizations is not just about aesthetics; it is a strategic approach that enhances clarity and excitement, ultimately leading to informed decision-making.
In light of recent studies from the Harvard School of Public Health, it is evident that working in green environments can significantly enhance cognitive performance. Research shows that these environments lead to a 97% higher score in crisis response, a 183% increase in strategic thinking, and a 172% boost in information usage compared to non-green environments. Moreover, taking into account the case study titled ‘Impact of Buildings on Air Pollution,’ which emphasizes that the World Health Organization estimates 7 million premature deaths annually are associated with air pollution—with buildings playing a significant role in emissions—it is evident that incorporating these principles into design is not only advantageous but crucial.
By doing so, professionals can contribute to a more sustainable future while simultaneously enhancing outcomes.
The Future of Architectural Rendering: Trends and Predictions
Looking ahead, several key trends are set to transform the landscape of architectural visualization:
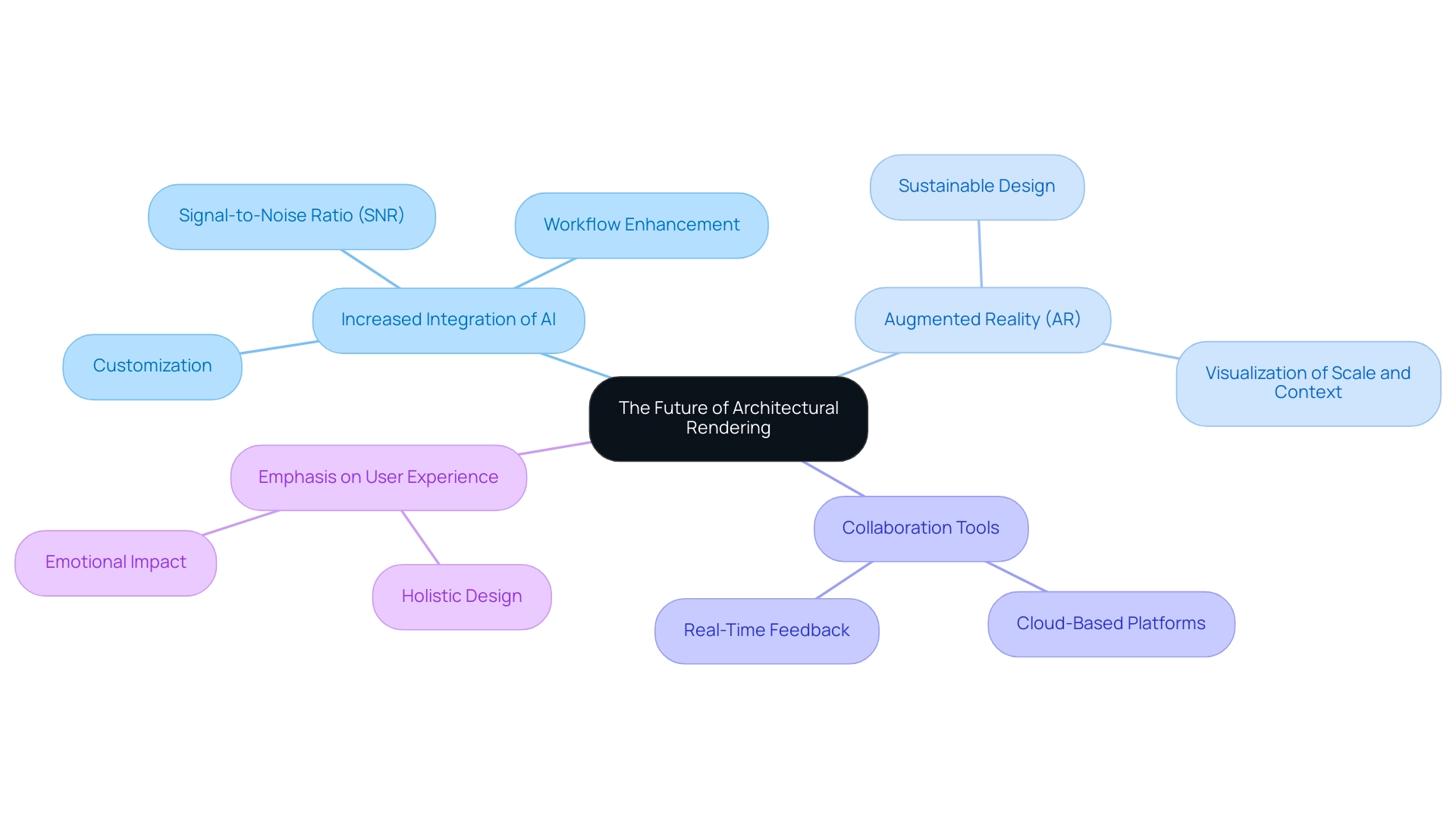
Increased Integration of AI: The incorporation of artificial intelligence is expected to expand significantly, automating various tasks and thereby enhancing the creative process. Ai’s abilities will enable customized creations suited to client preferences, enhancing workflows and elevating results. As mentioned in discussions on performance, grasping essential concepts like the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) can further enhance reliability in processing.
Augmented Reality (AR): Building upon the advancements in virtual reality, augmented reality will become a vital tool for architects, allowing them to project digital creations onto real-world environments. This architectural rendering technology aids in visualizing concepts and provides clients with a tangible sense of scale and context, facilitating informed decision-making. Additionally, with 42% of architects anticipating their plans will qualify as green within the next three years, AR can play a vital role in showcasing sustainable design practices effectively.
Collaboration Tools: The ongoing shift towards remote work underscores the necessity for robust cloud-based collaboration tools. These platforms will become essential for sharing visuals, enabling real-time feedback from clients and teams, and ensuring that objectives remain aligned despite geographic distances. The collaborative visualization process at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs exemplifies this approach; from initial communication and project briefs to detailed 3D models and client satisfaction, every step is designed to engage clients and integrate their specifications into the final product. Key stages such as detailed modeling and material selection are essential in this process, ensuring that every aspect of the creation reflects the client’s vision.
Emphasis on User Experience: Future visualizations will increasingly prioritize user experience. The focus will extend beyond mere aesthetics, delving into how spaces function and the emotional impact they have on occupants. This holistic approach recognizes that successful designs must cater to the needs and experiences of those who inhabit them, paving the way for more thoughtful and responsive architectural solutions. The crucial function of high-quality visuals in development and decision-making will remain vital, driving the demand for architectural rendering technology that enhances realism and emotional impact through intricate details. By utilizing advanced software for modeling and rendering, J. Scott Smith Visual Designs ensures that every project not only meets but exceeds client expectations.
Conclusion
The exploration of architectural rendering techniques reveals their critical role in enhancing design communication and stakeholder engagement. By thoroughly understanding methodologies such as ray tracing and rasterization, architects can select the most appropriate approach for their projects, balancing detail with expediency. The distinction between photorealistic and non-photorealistic rendering further emphasizes the importance of tailoring visualizations to the specific needs of clients and stages of design.
Emerging technologies, including artificial intelligence and virtual reality, are set to revolutionize the rendering landscape. The integration of AI not only optimizes rendering processes but also enhances the creative potential of architects, allowing them to focus on innovative solutions. Meanwhile, virtual reality offers immersive experiences that deepen client engagement, fostering a collaborative environment that leads to more informed design decisions.
Incorporating best practices, such as meticulous attention to detail, effective lighting techniques, and a robust feedback loop, is essential for producing high-quality renderings. These practices not only elevate the aesthetic appeal of projects but also ensure that they resonate with stakeholders, ultimately fostering confidence and investment in the designs presented.
As sustainability becomes increasingly vital in architectural practices, leveraging eco-friendly materials and digital tools to visualize sustainable designs will not only promote environmental responsibility but also enhance project outcomes. The future of architectural rendering lies in the seamless integration of advanced technologies and collaborative approaches, paving the way for innovative solutions that prioritize user experience and environmental stewardship. Embracing these trends will be essential for architects aiming to thrive in an evolving industry landscape.

0 Comments