Overview
3D modeling and rendering are essential processes that help transform your ideas into visual representations. These techniques find applications in various fields, including architecture, gaming, and medical imaging. We understand that mastering these skills can feel overwhelming, especially as technology advances and market demands grow. It’s crucial for effective communication and decision-making.\n\nImagine the challenges you might face when trying to convey your vision. The fear of potential design flaws can be daunting. However, embracing these techniques can be a solution, offering you the ability to visualize concepts clearly and accurately. By honing your skills in this area, you not only enhance your professional capabilities but also foster better collaboration with others.\n\nAs you navigate this journey, remember that you are not alone. Many professionals share similar concerns, and together, we can address these challenges. The growing need for skilled professionals in this field is a testament to the importance of your development. With the right support and resources, you can master these techniques and unlock new opportunities for success.
Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of design, we understand that the challenges of visualization can be daunting. Architects, game developers, and product designers often grapple with the complexities of bringing their imaginative ideas to life. It’s not just about creating visuals; it’s about effectively communicating those concepts and making informed decisions with stakeholders. As the demand for immersive and realistic visualizations grows, we recognize how vital it is to grasp the nuances of 3D modeling and rendering.
This article seeks to explore the core concepts and diverse applications of these processes across various industries. We will also highlight the latest technological advancements that are propelling this field forward. Our goal is to equip you with the insights needed to navigate the evolving landscape of digital design.
Imagine mastering best practices while also addressing the common challenges that arise in your projects. The journey into 3D modeling and rendering is not merely technical; it is a pathway to unlocking your creativity and fostering innovation in every endeavor. Together, let’s embrace this adventure and discover how collaboration can lead to remarkable outcomes.
Defining 3D Modeling and Rendering: Core Concepts
Navigating the world of 3D modeling and rendering can be daunting. Many face challenges in visualizing their ideas accurately, which can lead to frustration and uncertainty. This is where specialized software comes into play, creating a mathematical representation of three-dimensional objects. It helps define an object’s shape, structure, and surface characteristics, making the design process more manageable and less intimidating.
Rendering then takes this 3D model and transforms it into a two-dimensional image, mimicking the way light interacts with surfaces. This process is vital in producing realistic visuals that resonate with clients and stakeholders alike. Whether in architecture, gaming, or product development, these technologies are essential for creating compelling visual representations that truly capture the essence of a project.
Consider the many ways 3D visualization can alleviate concerns:
- In architecture, it brings concepts to life, ensuring client satisfaction.
- In medical imaging, it enhances diagnostic accuracy.
- In training simulations, it provides realistic practice scenarios.
- In product prototyping, it allows for rapid iterations.
- In graphic creation, it enriches visual storytelling.
With the market for 3D modeling and rendering projected to grow at an impressive CAGR of 16% from 2024 to 2032, the demand for skilled professionals in this field is on the rise. Mastering these techniques is not just beneficial; it’s becoming increasingly essential for effective communication and decision-making.
When it comes to architectural illustrations, determining the right level of detail is crucial for conveying intent accurately. Utilizing keyboard shortcuts and custom brushes on drawing tablets can significantly enhance efficiency, allowing designers to complete tasks more swiftly while fostering creativity. Recent advancements from major companies like Autodesk and Adobe are continually improving the capabilities of 3D visualization tools, providing designers with the resources they need to succeed.
Moreover, strategic partnerships—like the collaboration between Ecopia AI and Nearmap—are paving the way for innovative 3D mapping products and enhanced data accuracy. These developments reflect a competitive landscape where major players are forming alliances to improve their offerings. Staying informed about these trends is vital for any design professional who wants to harness the full potential of 3D modeling and rendering.
In this evolving landscape, remember that you are not alone in your journey. Embracing these technologies can lead to enhanced visualization, improved decision-making, and effective communication. Together, we can navigate these challenges and unlock the full potential of your creative visions.
Applications of 3D Modeling and Rendering in Various Industries
3D modeling and rendering are vital in architecture, enhancing creativity and functionality while addressing the concerns of both architects and clients. These methods empower architects to create detailed visualizations, which serve as essential tools during the pre-sales phase. They instill confidence in projects and attract investment through persuasive imagery. In today’s competitive landscape, where U.S. architecture firms invested over $2.8 billion in software and technology in 2020, this becomes even more crucial.
ArchiCAD stands out as the most popular software in this realm, with Revit following closely, holding a 33.2% market share. This showcases the industry’s reliance on advanced visualization tools. Moreover, 3D interior design visuals play a significant role in preserving architectural legacy and celebrating creativity. They not only highlight functionality and aesthetics but also enhance client satisfaction and marketing effectiveness.
Testimonials from clients at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs underscore the importance of trust, reliability, and shared vision in achieving successful outcomes. One client shared, ‘The visuals created by J. Scott Smith Visual Designs not only realized our vision but also drew considerable investment before the endeavor even started.’ Such authentic experiences illustrate how detailed interior visuals contribute to maintaining schedules and budgets while providing personalized services and innovative problem-solving.
The applications of 3D modeling and rendering extend far beyond architecture. In gaming, it creates immersive environments, and in film, it crafts realistic visual effects that engage audiences. The medical field also benefits, as 3D modeling produces precise anatomical models for education and surgical planning. As we witness advancements in architectural technology—like the completion of the Southern Hemisphere’s first 3D-printed multi-storey home in Melbourne—it becomes evident that 3D modeling and rendering not only enhance complexity but also foster innovation in practical applications.
Understanding the Differences: 3D Modeling vs. 3D Rendering
In the world of digital design, 3D modeling and rendering are interconnected yet serve different purposes, each with its own set of challenges that can feel overwhelming at times.
3D Modeling focuses on building the structure and form of an object. This phase uses various techniques, such as polygonal modeling and sculpting, to create intricate details and textures that enhance the object’s surface. For instance, many prefer polygonal modeling for its accuracy and control, while sculpting allows for more organic shapes and elaborate details. Each method meets distinct needs, and this careful approach is vital for capturing the essence of the design, ultimately enhancing the appeal and uniqueness of architectural projects.
On the other hand, 3D rendering transforms the completed model into a visually captivating image or animation. This process involves defining lighting, materials, and camera angles, all essential for achieving a high level of realism. The importance of mastering these elements cannot be overstated, especially with the rapid advancements in visualization technologies. As Yufei Lin from Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications highlights, this article delves into several key aspects of computer graphics, showcasing significant progress in ray tracing, visualization techniques, algorithm optimization, data processing, and real-time visualization. These innovations remind us how crucial it is for designers to stay updated with the latest techniques in 3D modeling and rendering, ensuring precision through meticulous detail, collaboration, and advanced software.
Our commitment extends to providing high-quality renderings for both interior and exterior architectural projects, encompassing detailed visualizations and comprehensive site documentation. We also leverage technology to effectively document existing spaces, ensuring that our clients gain a thorough understanding of their tasks.
Explore our portfolio to see a selection of our work that highlights these capabilities.
The emergence of cloud technology has significantly changed the landscape for studios and freelancers, empowering them to tackle projects that might otherwise be limited by local resources. This innovation enables designers to harness powerful remote servers for 3D modeling and rendering, greatly reducing render times and enhancing project scalability.
Research into accelerated ray tracing technologies is also crucial, particularly for depicting gradient media. These advancements facilitate physically accurate visualization in real-time, addressing challenges that were once difficult to overcome with traditional methods. A practical example can be found in the case study titled “Real-Time Visualization of Gradient Media,” which explores the complexities of simulating gradient media in real-time.
The authors developed a technique using accelerated ray tracing systems that allows for the accurate depiction of scenes with gradient media in real-time, demonstrated through test images and animations using NVIDIA OptiX.
Understanding these unique roles is vital for professionals engaged in 3D modeling and rendering, as it fosters teamwork and ensures that projects meet both aesthetic and functional goals. As we approach 2024, grasping the differences between modeling and visualization will be crucial for leveraging new technologies and optimizing outcomes in creative endeavors, while maximizing the value of detailed visuals in enhancing residential architecture concepts.
Best Practices and Techniques for Effective 3D Modeling and Rendering
Achieving outstanding quality in 3D modeling and visualization, particularly in capturing the essence of your architectural concepts, can be quite challenging. It’s important to recognize these hurdles and address them thoughtfully. Here are some best practices that can help you navigate this journey:
Plan Your Workflow: Start by sketching your initial concepts. This preparatory work not only clarifies your vision but also streamlines your modeling process. By outlining your steps, you ensure precision in your renderings, allowing your ideas to shine through.
Use Reference Images: Collect a variety of real-world images that align with your creative intentions. These images act as essential guides, helping you maintain accuracy in proportions and intricate details. They are crucial for rendering compelling and realistic final outputs that truly reflect the soul of your design.
Optimize Geometry: Strive for a balanced polygon count. Keeping it manageable is vital for ensuring smooth performance during your modeling and rendering processes. This is especially important when working with complex scenes or animations, as it enhances communication with stakeholders and fosters better understanding.
Utilize High-Quality Textures: The choice of textures can greatly influence the realism of your work. Opt for high-resolution textures that elevate the visual appeal of your model. Avoid overly simplistic designs that may detract from the quality and detail necessary for effective client evaluations.
Master Lighting Techniques: Experimenting with various lighting setups can create mood and depth within your renders. Proper lighting transforms a scene, highlighting essential features and guiding the viewer’s eye. This is vital for visualizing residential architecture designs that resonate emotionally.
Regularly Save and Backup Work: To protect against data loss, implement consistent saving practices throughout your work. Regular backups are crucial, especially as tasks become more complex. This ensures that all your meticulous details are preserved, allowing you to focus on your creative process.
Consider Animation Basics: If your project involves animation, incorporating basic animations or rigs early on can be beneficial. Testing movement and deformation at this stage allows for modifications before final output, ensuring a seamless animation process and contributing to the overall design development.
Monitor Performance Metrics: Keep an eye on crucial parameters like screen size, anti-aliasing level, memory usage, and the number of passes. Being aware of these metrics helps you understand CPU overhead and optimize performance, maintaining efficiency as you navigate the evolving best practices in 3D modeling and rendering for architectural visualizations.
Determine the Appropriate Level of Detail: It’s essential to consider your audience when presenting your illustrations. Different stakeholders, such as homeowners and businesses, may require varying levels of detail in their projects. Customizing your visual presentations to meet these expectations can enhance communication and comprehension, ensuring that the story of your creation is effectively conveyed.
Emphasize Tiny Details for Storytelling: Remember, the small elements in your creations significantly contribute to the overall narrative of your design. These details not only enhance realism but also engage viewers, allowing them to connect emotionally with your work. By focusing on these aspects, you can create a richer narrative that resonates deeply with your audience.
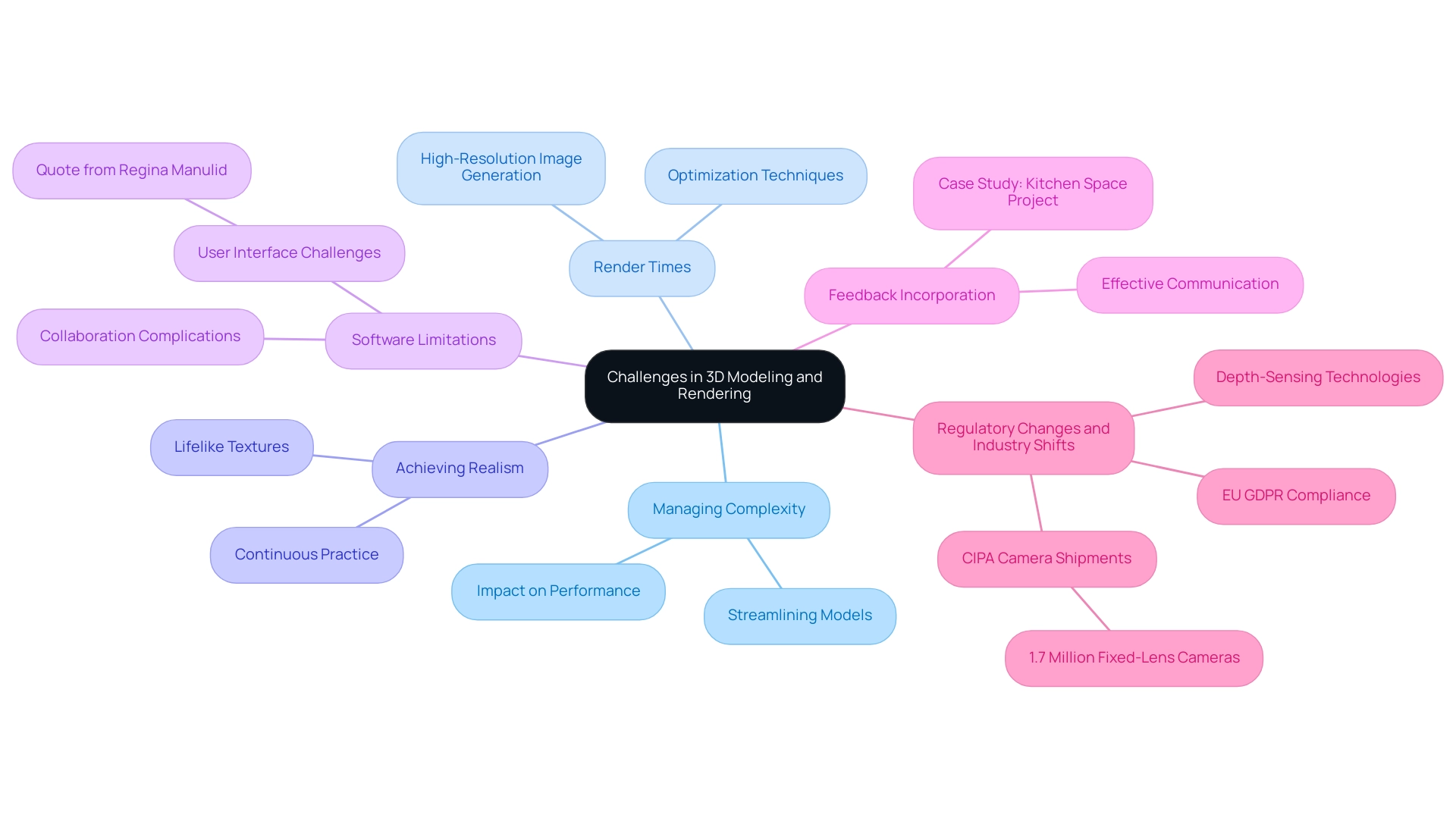
Navigating Challenges in 3D Modeling and Rendering
In the realm of 3D modeling and visual representation, professionals often grapple with significant challenges that can feel overwhelming.
Managing Complexity: High levels of detail in models can severely impact performance, causing frustration. Streamlining models through 3D modeling and rendering without sacrificing quality is vital for upholding efficiency. The complexities of an architectural endeavor can influence processing time and resource needs, leaving professionals feeling stressed and under pressure.
Render Times: Generating high-resolution images demands considerable processing power, leading to prolonged wait times that can test anyone’s patience. Average render times for such images can stretch into hours, depending on the complexity of the scene. However, by optimizing display settings and leveraging advanced techniques in 3D modeling and rendering, practitioners can significantly reduce these delays and enhance their overall workflow.
Achieving Realism: The quest for lifelike textures and materials can present considerable difficulties, often leaving designers feeling frustrated. The importance of intricate details—like the way sunlight dances off windows or the subtle texture of bricks—enhances the emotional effect of creations, making them feel real and lived-in. Continuous practice, experimentation, and the exploration of new tools are vital to mastering this aspect of 3D modeling and rendering.
Software Limitations: Understanding the constraints of visualization software related to 3D modeling and rendering is crucial for effective project planning and execution. As Regina Manulid notes, > Improving the user interface and experience of 3D rendering software is a challenge for software developers in particular <, highlighting the ongoing need for innovation in this area. These limitations can complicate the collaborative planning phase, as they may restrict the visualization of certain design elements in 3D modeling and rendering that the client envisions.
Feedback Incorporation: Integrating feedback from clients or team members can be challenging, yet effective communication is key to ensuring alignment and achieving objectives in 3D modeling and rendering projects. This process was exemplified in a recent project where early discussions with the client about their vision for an open and innovative kitchen space informed every subsequent decision. For instance, the client’s desire for a balance between showcasing the kitchen and the overall home led to strategic decisions about image selection and visualization styles, demonstrating the power of collaborative planning in refining the final output.
As we move into 2024, the introduction of EU GDPR-compliance measures and FCC regulations around the deployment of 3D imaging devices, which include aspects of 3D modeling and rendering, adds another layer of complexity. Moreover, with advancements in depth-sensing technologies on the horizon, professionals must remain adaptable. Emphasizing continuous learning and an iterative approach can empower animators and designers in 3D modeling and rendering to effectively stay abreast of these evolving challenges and optimize their workflows.
Additionally, it’s worth noting that in 2023, CIPA members shipped only 1.7 million fixed-lens cameras, reflecting a shift in the industry that may influence visualization practices. A relevant case study titled ‘Time and Resource Constraints’ illustrates how game development teams often face tight schedules and limited resources, forcing them to create high-quality animations without sacrificing quality or creativity. By prioritizing tasks based on deadlines and implementing agile methodologies, these teams can adapt quickly to project demands.
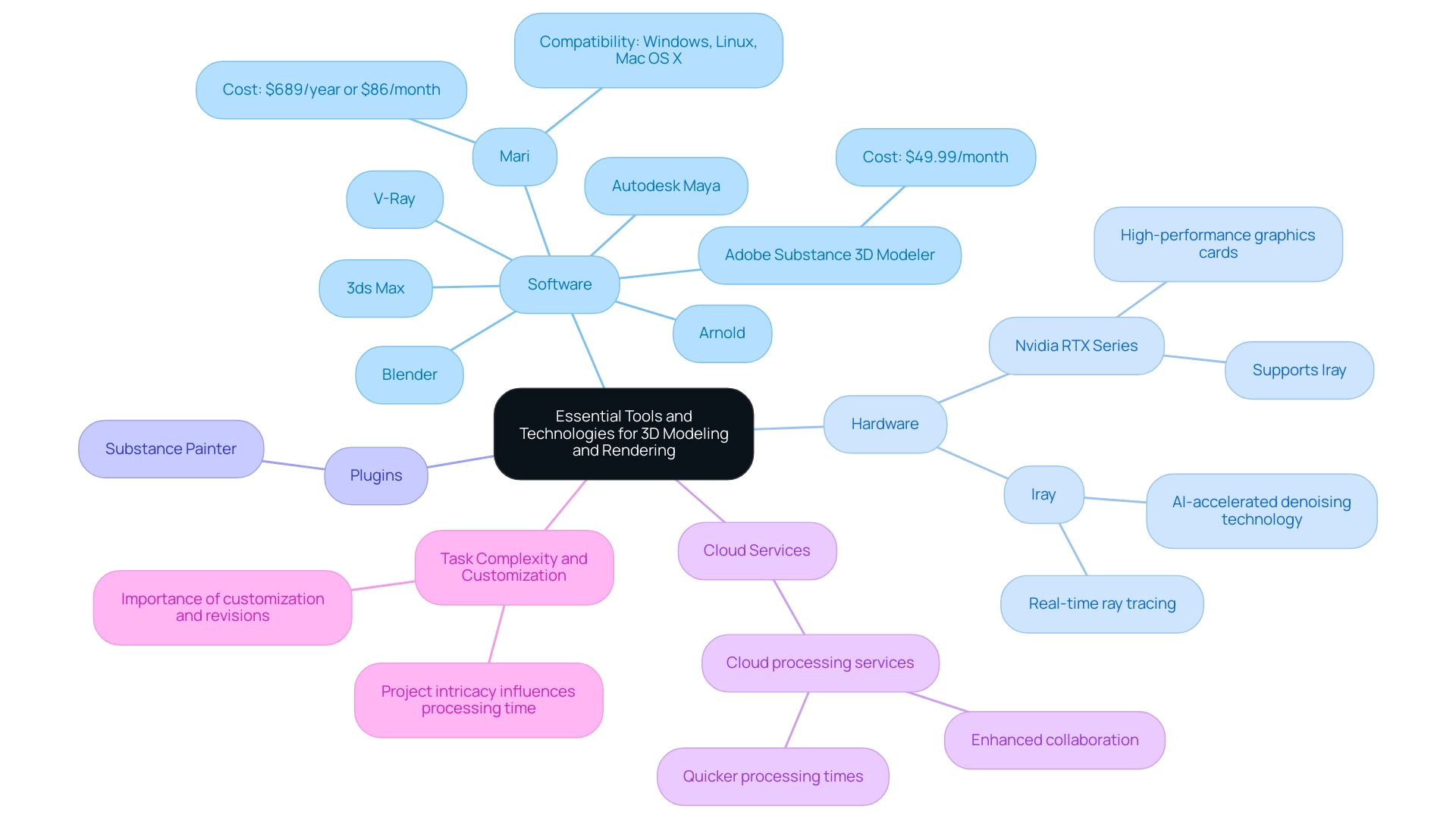
Essential Tools and Technologies for 3D Modeling and Rendering
In the world of 3D modeling and visualization, it’s important to recognize the challenges you may encounter. The right tools and technologies can make a significant difference in overcoming these hurdles.
Software: Leading software options like Blender, Autodesk Maya, and 3ds Max are well-regarded for their robust modeling capabilities. Tools such as V-Ray and Arnold are widely utilized in the industry for image generation, known for their exceptional quality and flexibility. Mari, starting at an annual cost of $689 or $86 per month, is compatible with Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X, making it a versatile choice for various platforms. Adobe Substance 3D Modeler, available at $49.99/month, is another valuable option for professionals in 3D modeling and rendering. It’s essential to choose software that can be tailored to your specific project needs, ensuring that the visuals truly reflect your intended vision.
Hardware: The performance of your setup significantly hinges on your hardware choices. Investing in high-performance graphics cards, particularly Nvidia’s latest RTX series, can greatly enhance processing efficiency and output quality. This is especially crucial for advanced visualization software like Iray, which relies on substantial GPU power and memory, utilizing AI-accelerated denoising technology to improve real-time ray tracing results. As Paul Hanaphy noted on January 9, 2025, modern GPUs are vital for achieving high-quality results that support effective decision-making and client satisfaction.
Plugins: To further extend functionality and streamline your workflow, consider utilizing plugins such as Substance Painter. These can enhance your texturing capabilities and integrate seamlessly with your primary software, alleviating some of the burdens you may face.
Cloud Services: For larger or more resource-intensive tasks, exploring cloud processing services can be transformative. These services enable quicker processing times and foster better collaboration, allowing your team to work more efficiently on challenging design tasks, ultimately leading to enhanced visualization and marketing tools.
Task Complexity and Customization: It’s vital to understand that the intricacy and scale of a project significantly influence processing time and resource requirements. Careful planning and investing in the right tools and technologies is necessary to accommodate these factors. Moreover, customization and revisions are critical in ensuring that the final output aligns with your vision and project goals.
By acknowledging these elements, you can navigate the complexities of 3D modeling with greater confidence and clarity, ensuring that your projects not only meet but exceed expectations.
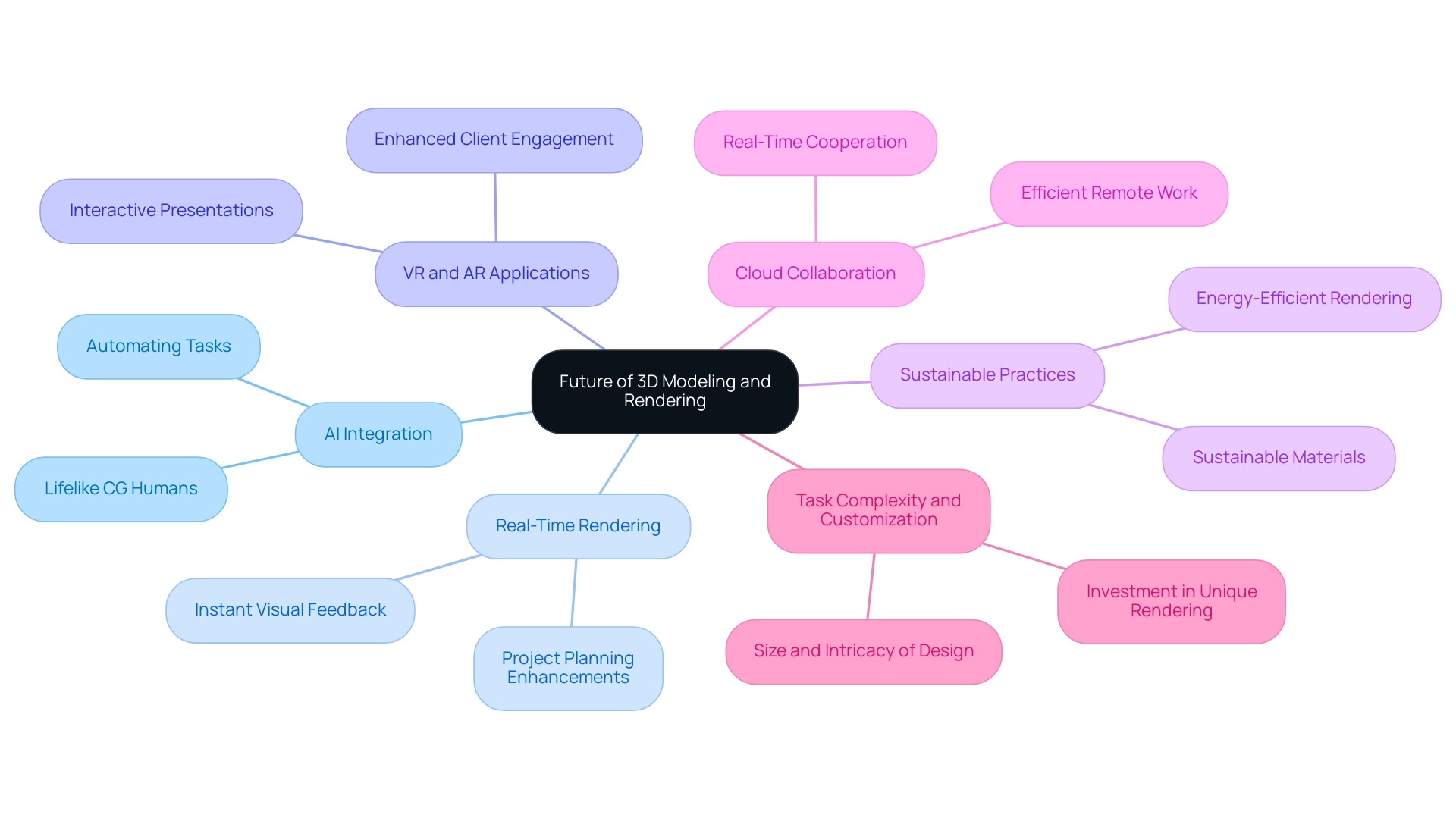
The Future of 3D Modeling and Rendering: Trends and Innovations
As we look toward the future of 3D modeling and rendering, we recognize the challenges many face in this evolving landscape. AI Integration is one of the most promising advancements, set to revolutionize workflows by automating repetitive tasks. This shift allows designers to focus more on creativity and innovation, enhancing productivity and fostering a more dynamic design process. Particularly, it helps bridge the uncanny valley with lifelike CG humans in architectural visualizations, addressing the discomfort often associated with this phenomenon.
AI advancements are increasingly capable of creating realistic human representations, enhancing the emotional connection in visualizations. As the market for 3D modeling and rendering is projected to grow to USD 7.32 billion in 2024, the significance of these technologies continues to rise. Real-Time Rendering is another key trend. Technologies like Unreal Engine are at the forefront, enabling instant visual feedback crucial for project planning. This capability allows architects to make immediate adjustments, presenting their ideas more effectively.
VR and AR Applications are also transforming how designs are experienced. These immersive technologies provide clients with interactive presentations, enhancing understanding and engagement with the design. As industries strive for greener operations, Sustainable Practices are becoming more pronounced. The focus on energy-efficient rendering methods and sustainable materials is essential for aligning with environmental responsibility and meeting consumer demand for sustainability.
The rise of Cloud Collaboration tools is facilitating real-time cooperation among creative teams, making remote work more efficient. This shift is particularly significant in light of the growing trend towards flexible work environments, allowing teams to seamlessly share resources and ideas regardless of location.
When considering Task Complexity and Customization, it’s important to remember that the more intricate your task, the more time and resources are required to bring it to life in visualization. Factors such as the size of the property and the intricacy of the design play a vital role in determining the investment for unique rendering endeavors. For instance, a large-scale development may require more detailed human representations to create an inviting atmosphere, while a smaller endeavor might focus on specific architectural features. Choosing an enthusiastic collaborator for 3D visualization is vital for addressing these challenges.
In 2024, the market for 3D modeling and rendering is projected to expand considerably, with an estimated value of USD 7.32 billion. This indicates the rising significance of these innovations across various sectors, including entertainment, automotive, healthcare, and defense. The Consumer Electronics Association projects that retail revenues will reach USD 485 billion in the United States this year, further underscoring the market’s potential.
Case studies on innovations in 3D mapping reveal that advancements in 3D scanning, photogrammetry, and LiDAR mapping are set to enhance applications in 3D modeling and rendering for architectural modeling. Recent advancements in LiDAR systems allow architects to generate accurate digital replicas of current structures, significantly enhancing the precision and efficiency of planning workflows. These trends not only influence design outcomes but also highlight the transformative power of technology in the architectural field.
Conclusion
Navigating the world of 3D modeling and rendering can often feel overwhelming, especially given their crucial roles in industries like architecture, gaming, and medical imaging. It’s important to recognize the distinction between 3D modeling, which is about crafting the structure of objects, and 3D rendering, which breathes life into those models with stunning visuals. For professionals, mastering these processes is not just beneficial; it’s essential for enhancing visualization, improving decision-making, and fostering effective communication with stakeholders.
Best practices in 3D modeling and rendering underscore the significance of thorough planning, high-quality textures, and the right lighting. Yet, challenges such as managing complexity and achieving realism can weigh heavily on designers. Addressing these hurdles is vital to maintaining efficiency and quality in every project. With advancements in technology—like AI integration and real-time rendering—we’re witnessing a transformative shift toward more innovative workflows, empowering designers to explore their creativity like never before.
As the demand for 3D modeling and rendering grows, embracing new tools and practices becomes essential for professionals who wish to stay competitive. The future holds promising developments, including enhanced cloud collaboration and sustainable practices, which will reshape the digital design landscape. By remaining informed and adaptable, designers can leverage these innovations to craft compelling visual narratives that resonate deeply with clients and audiences alike. Together, we can navigate these exciting changes, ensuring that every project not only meets expectations but also inspires and connects with those who experience it.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 3D modeling and rendering?
3D modeling involves creating a mathematical representation of three-dimensional objects, defining their shape, structure, and surface characteristics. Rendering transforms these 3D models into two-dimensional images, simulating how light interacts with surfaces to produce realistic visuals.
How does 3D visualization benefit different industries?
3D visualization benefits various industries by enhancing concept representation. In architecture, it ensures client satisfaction; in medical imaging, it improves diagnostic accuracy; in training simulations, it offers realistic scenarios; in product prototyping, it allows for rapid iterations; and in graphic creation, it enriches visual storytelling.
What is the expected growth of the 3D modeling and rendering market?
The market for 3D modeling and rendering is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16% from 2024 to 2032, indicating a rising demand for skilled professionals in this field.
Why is detail important in architectural illustrations?
The right level of detail in architectural illustrations is crucial for accurately conveying intent and ensuring that the design meets client expectations.
What tools can enhance efficiency in 3D design?
Utilizing keyboard shortcuts and custom brushes on drawing tablets can significantly enhance efficiency in 3D design, allowing designers to complete tasks more swiftly and foster creativity.
Which software is most popular in the architecture sector for 3D modeling?
ArchiCAD is the most popular software in the architecture sector for 3D modeling, followed closely by Revit, which holds a 33.2% market share.
How do testimonials reflect the importance of 3D visuals in design?
Testimonials, such as those from clients at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, highlight the importance of trust and shared vision in achieving successful outcomes, illustrating how detailed visuals can attract investment and ensure project success.
What other fields benefit from 3D modeling and rendering?
Besides architecture, 3D modeling and rendering are utilized in gaming for creating immersive environments, in film for crafting realistic visual effects, and in the medical field for producing precise anatomical models for education and surgical planning.
What recent advancements have been made in 3D modeling and rendering?
Recent advancements include the completion of the Southern Hemisphere’s first 3D-printed multi-storey home in Melbourne, showcasing how these technologies foster innovation and enhance complexity in practical applications.

0 Comments