Overview:
The article presents seven inspiring case studies demonstrating the transformative role of 3D renderings in architectural projects, highlighting their impact on design communication, client engagement, and marketing strategies. By showcasing diverse applications—from luxury homes to sustainable buildings—the article illustrates how these visualizations enhance decision-making, foster collaboration, and ultimately drive investment and project success in modern architecture.
Introduction
The integration of 3D renderings into architectural practice marks a pivotal shift in how designs are conceptualized, communicated, and realized. By transforming abstract ideas into vivid visual narratives, architects can engage clients and stakeholders with unparalleled clarity and precision. This article delves into the multifaceted impact of 3D renderings, exploring their role in:
- Enhancing design communication
- Facilitating informed decision-making
- Serving as powerful marketing tools
Through a series of inspiring case studies, the article illustrates how innovative rendering techniques have been successfully employed in diverse projects, from luxury residences to sustainable office buildings. Furthermore, it examines the technological advancements propelling the future of 3D rendering, including:
- Real-time rendering
- The integration of virtual and augmented reality
Best practices for creating effective renderings are also discussed, highlighting the importance of:
- Quality software
- Lighting
- Iterative refinement
As the architectural landscape continues to evolve, understanding these dynamics will be essential for architects aiming to leverage 3D renderings to their fullest potential.
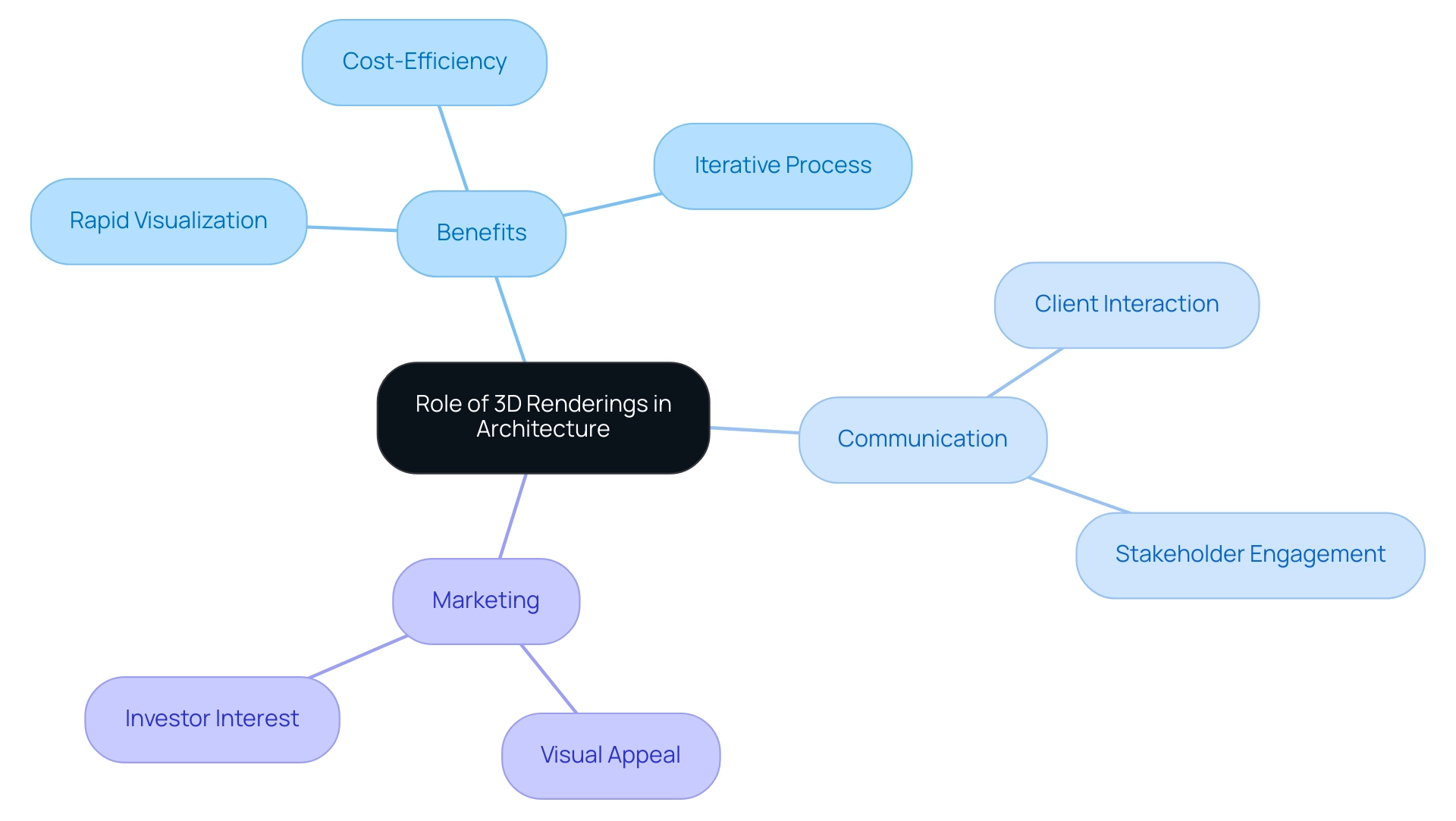
The Role of 3D Renderings in Modern Architecture
3D images have fundamentally transformed architectural practices by offering examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, presenting visual representations of concepts that once existed solely in traditional blueprints. These advanced visualizations, which include examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, empower architects to articulate their vision with precision, significantly enhancing communication with clients and stakeholders. By effectively showcasing materials, lighting, and spatial relationships, examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects aid in informed decision-making early in the project lifecycle.
Furthermore, initial conceptual representations present several benefits, including examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, as they enable rapid visualization of concepts, are economical for early-stage exploration, and facilitate an iterative creative process, allowing for multiple revisions based on input. These representations also function as powerful marketing instruments, serving as examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, which allow companies to showcase their creations in a visually appealing way that can influence prospective purchasers and investors. Furthermore, the role of pre-sales visualization, as seen in examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, cannot be overstated; it enhances project confidence and generates investment by providing developers with tangible assets that ignite interest long before construction begins.
The integration of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) into the 3D visualization process is revolutionizing the client experience, showcasing examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects that enable interactive exploration of designs prior to construction and ensure a more informed and collaborative decision-making process. Considering recent research, including market feedback and validation from industry experts, the positive influence of 3D visualization on architecture continues to outweigh any potential drawbacks, with examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects solidifying its value as an essential tool in modern architectural practice.
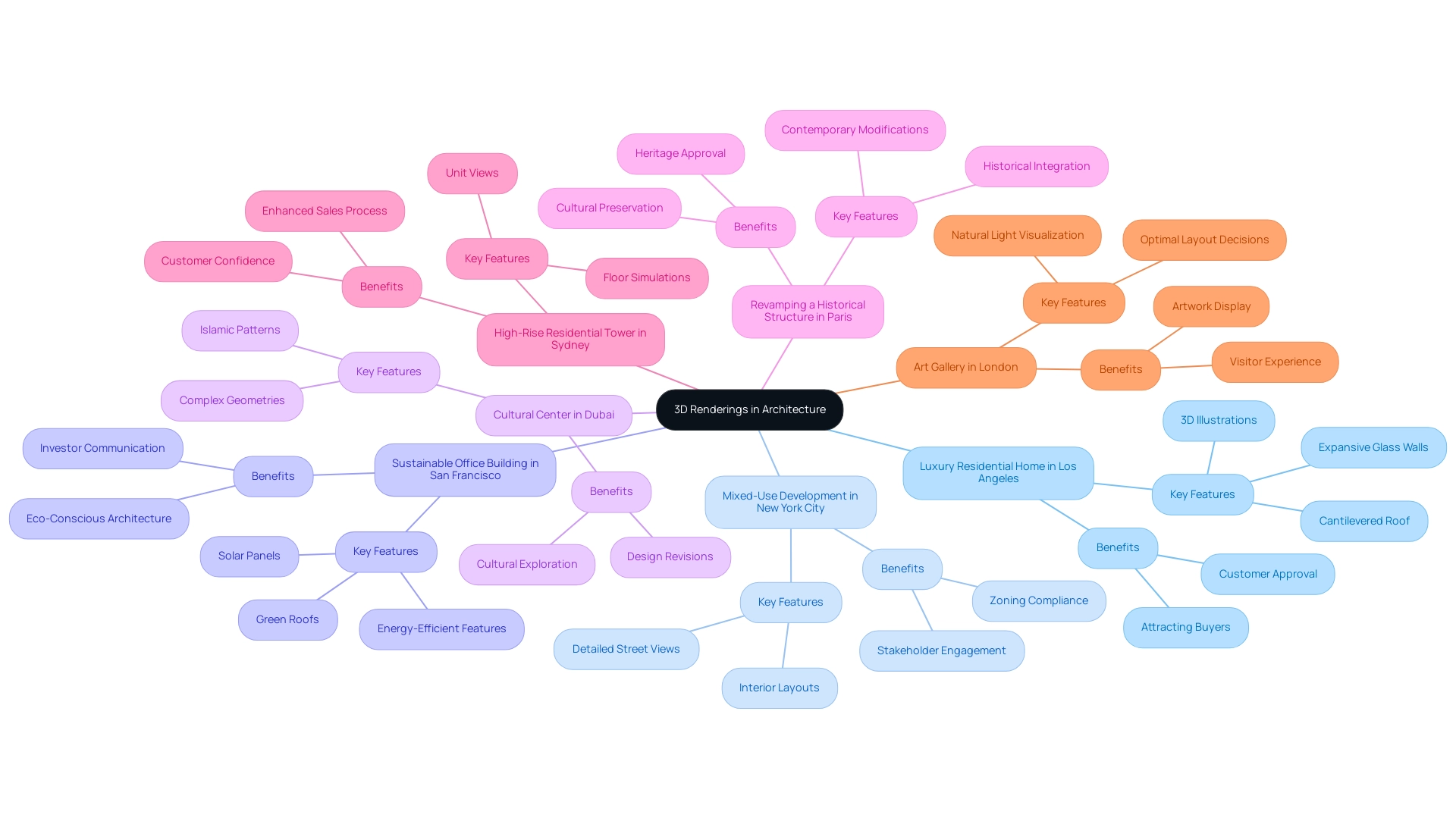
Inspiring Case Studies: 3D Renderings in Action
Luxury Residential Home in Los Angeles: This exceptional endeavor utilized 3D illustrations to create breathtaking visuals that highlighted the home’s distinctive architectural elements, such as its cantilevered roof and expansive glass walls. These illustrations are prime examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, playing a crucial role in obtaining customer approval and attracting potential buyers during the marketing phase, thereby showcasing the effectiveness of pre-sales visualization in luxury real estate. Additionally, the integration of mixed-reality applications allowed for real-time modifications based on performance evaluations, enhancing the development process and reinforcing project confidence. One satisfied client observed, ‘The visuals brought our vision to life and helped us secure buyers even before construction began.’
Mixed-Use Development in New York City: The design team utilized the capabilities of 3D visuals to illustrate the seamless integration of commercial and residential areas. By showcasing detailed street views and interior layouts, the visuals served as examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, facilitating productive discussions with city planners and stakeholders, ensuring compliance with zoning regulations and enhancing stakeholder engagement, ultimately fostering investment and trust in the initiative. A city planner noted, “The clarity of the illustrations made it easier for us to comprehend the initiative’s effect on the community.”
Sustainable Office Building in San Francisco: Focused on environmental sustainability, this initiative utilized 3D renderings to effectively showcase energy-efficient features like solar panels and green roofs. The visuals provided examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects that communicated the project’s sustainability objectives to investors and the community, reinforcing the growing trend of eco-conscious architecture in contemporary design. This approach not only enhances client satisfaction but also aligns with recent studies highlighting the environmental sustainability of 3D printing, which can reduce waste and optimize resource utilization in construction. Investors valued the detailed visualizations, stating, “The illustrations clearly showed our commitment to sustainability, making our investment decision easier.”
Cultural Center in Dubai: The architects utilized 3D visualizations to investigate the complex geometries and intricate patterns characteristic of Islamic architecture. These representations served as examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, aiding design revisions while generating enthusiasm and curiosity surrounding the initiative and allowing for a deeper exploration of the cultural context, thus honoring creativity and maintaining architectural heritage. A local artist conveyed, “Observing the creations made me feel linked to our heritage and enthusiastic about the initiative.”
Revamping a Historical Structure in Paris: In this delicate restoration endeavor, 3D visualizations offered a framework for how contemporary modifications could integrate with historical features. The clear visualizations, which serve as examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, were crucial in obtaining approval from heritage conservation authorities, illustrating the importance of thoughtful design in preserving cultural heritage and enhancing the project’s credibility. A heritage conservation officer remarked, ‘The illustrations assisted us in envisioning the combination of new elements while honoring the building’s history.’
High-Rise Residential Tower in Sydney: The architectural team employed 3D visualizations to simulate views from various floors, enabling potential buyers to understand the advantages of different units. This innovative approach significantly enhanced the sales process by providing a realistic preview of living conditions, which includes examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, ultimately boosting customer confidence and satisfaction. One buyer shared, “The ability to see the views from my future apartment made my decision much easier.”
Art Gallery in London: In this project, 3D images were instrumental in visualizing the interplay of natural light throughout the gallery space. These visuals served as examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, assisting the client in making informed decisions about layout and lighting, ensuring that the artwork would be displayed under optimal conditions, thus enhancing the overall visitor experience. As Michael Hansmeyer noted, “It used to be that ornament was something super costly for kings… Now it is free of this social connotation in a way,” reflecting the evolving role of ornamentation and visualization in contemporary architecture.
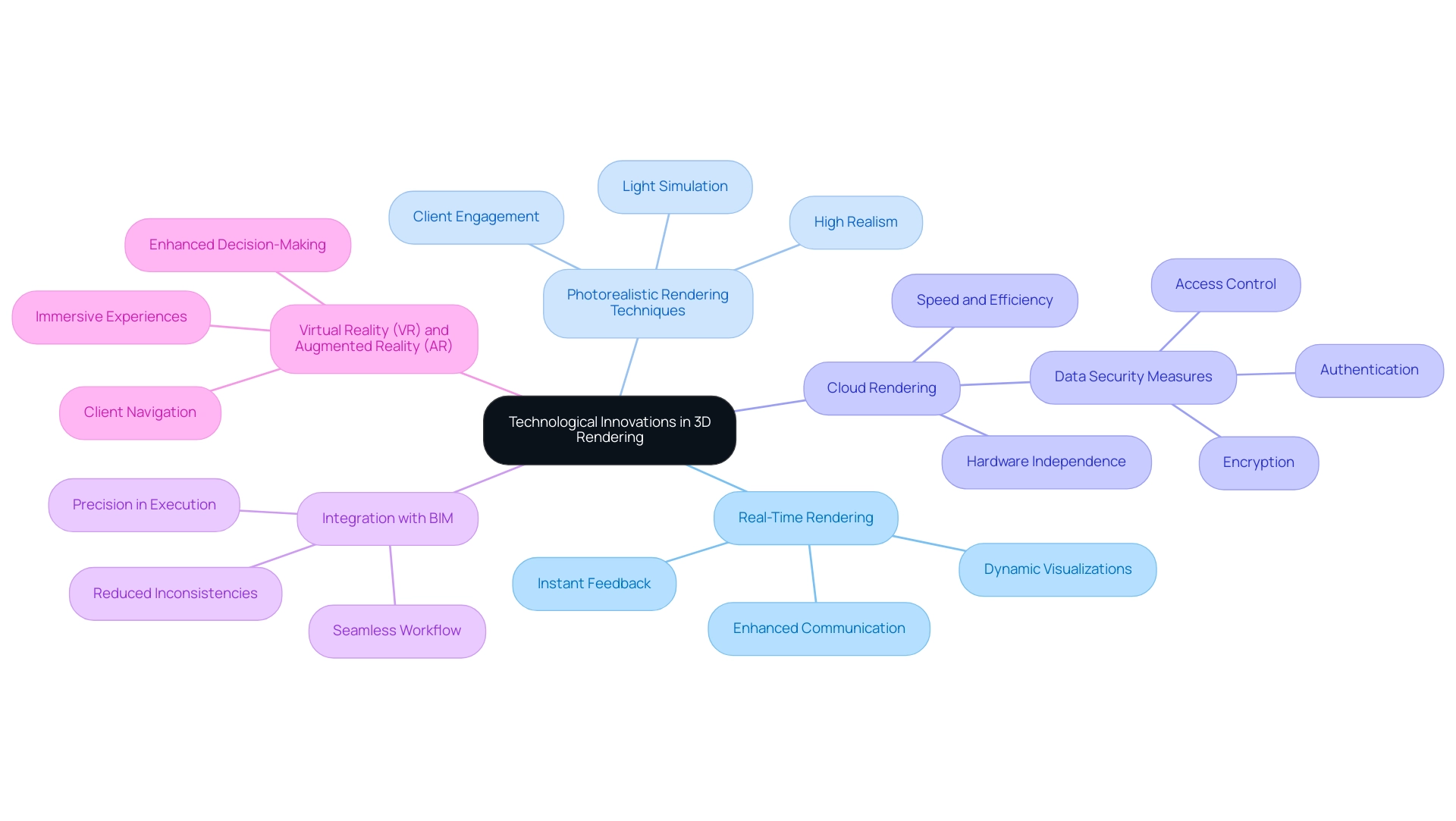
Technological Innovations Enhancing 3D Rendering
Recent advancements in technology have profoundly enhanced the examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects. Notable innovations include:
Real-Time Rendering: Cutting-edge software such as Unreal Engine and Twinmotion enables architects to create dynamic visualizations, facilitating instant feedback and adjustments during design reviews. This immediacy not only enhances communication among stakeholders but also accelerates the decision-making process, reducing the chances of misunderstandings in the project.
Photorealistic Rendering Techniques: Advanced rendering engines like V-Ray and Corona leverage sophisticated algorithms for light simulation, producing images that closely replicate real-world conditions. These techniques ensure that customers and stakeholders perceive designs with a high degree of realism, enhancing their understanding and engagement with the project. Such clarity in visual communication is essential for aligning with the client’s vision.
Cloud Rendering: By harnessing cloud computing resources, this technology significantly speeds up the processing of complex scenes. Architects can produce high-quality visuals without being limited by their local hardware capabilities, thus optimizing workflow efficiency. However, it is crucial to secure sensitive architectural data in cloud processing through measures such as authentication, access control, encryption, and data masking to mitigate potential risks.
Integration with Building Information Modeling (BIM): The convergence of BIM with 3D rendering tools fosters a seamless workflow, ensuring that visualizations remain aligned with the latest layout updates. This integration reduces inconsistencies between intent and final output, promoting precision in execution and enhancing contractor communication.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): These immersive technologies are increasingly utilized in the architectural design process, enabling users to virtually navigate unbuilt spaces. This case study provides examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, highlighting how the use of VR in architectural visualization allows users and stakeholders to walk through unbuilt structures, thereby gaining a better understanding of the project and enhancing their decision-making process. Encouraging client feedback and collaboration at every stage is vital to align with their vision.
Along with these advancements, supplying the correct information early in the architectural visualization process is crucial. Clear and timely communication helps to optimize time and cost, ensuring that all stakeholders are informed and aligned from the outset. As Apple stated regarding technological advancements, “In June 2023, Apple revealed MacOS Sonoma, the next generation of advanced desktop operating system, bringing high-quality features that elevate the Mac experience.”
Such innovations are pivotal in facilitating enhanced architectural visualization capabilities.
As the 3D visualization market keeps progressing—capturing a 34% share in North America as of 2023—architects must stay informed about these advancements to utilize the full potential of their designs. The significance of delivering clear and timely information in construction projects cannot be overstated; it is crucial to optimize time and cost while ensuring precision in presentations through meticulous detail and client collaboration.
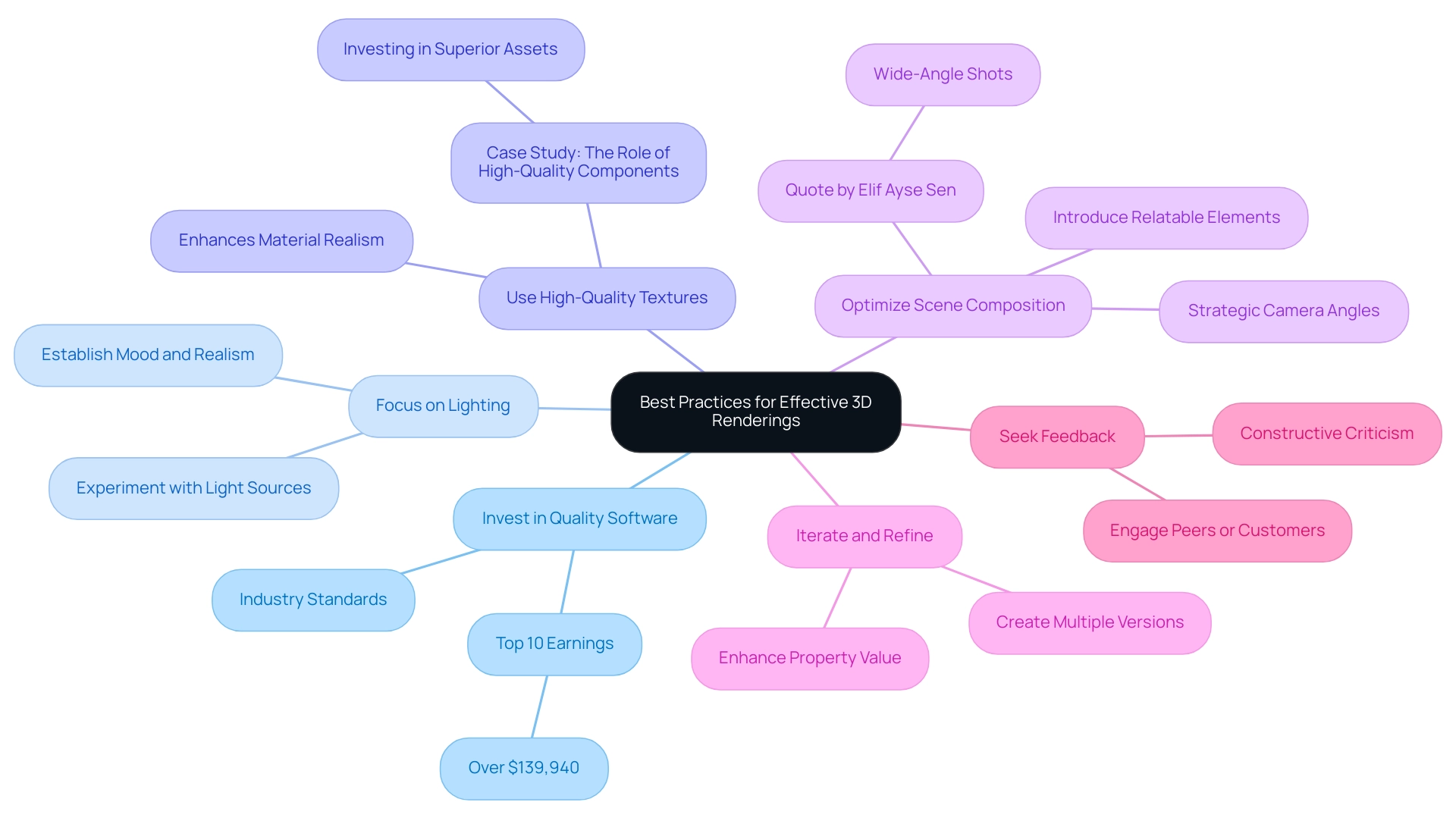
Best Practices for Effective 3D Renderings
To achieve exceptional 3D architectural renderings, architects should adhere to the following best practices:
Invest in Quality Software: Utilize industry-standard design software equipped with the necessary tools to create intricate and realistic visuals. This aligns with the standards seen in the top 10% of multimedia artists and animators, who earn over $139,940.
Focus on Lighting: The significance of lighting cannot be overstated; it is paramount for establishing mood and realism in visualizations. Experimenting with various light sources and intensities can lead to striking outcomes that emotionally resonate with clients.
Use High-Quality Textures: Integrating high-resolution textures enhances material realism, significantly elevating the overall quality of the visual output. As emphasized in the case study titled ‘The Role of High-Quality Components,’ investing in superior assets ensures longevity and quality in examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects.
Optimize Scene Composition: Thoughtful scene composition, including strategic camera angles and focal points, guides the viewer’s gaze and accentuates the design’s key features. As mentioned by architect and author Elif Ayse Sen, ‘The use of wide-angle shots certainly proves beneficial in architectural visualization, providing a broad perspective of the design and adding a dramatic effect.’
Additionally, introducing relatable elements, such as scattered items or surface defects, can enhance viewer connection.
- Iterate and Refine: Create multiple versions of a visual to discover new insights and enhancements, leading to a more polished final product.
This iterative process is vital in achieving high-quality outputs that can significantly enhance property value and market differentiation.
- Seek Feedback: Engaging peers or customers for input can provide invaluable constructive criticism for refining visuals and ensuring they meet project expectations.
As 70% of architecture firms plan to enhance their technology investments in the coming year, embracing these best practices is essential to leverage sophisticated visualization techniques in design workflows, ultimately improving client satisfaction and fostering deeper connections. Additionally, when considering outsourcing 3D architectural visualization services, architects should evaluate potential providers based on their adherence to these best practices. This ensures that the quality and precision of the visualizations align with the project’s vision.
Practical tips for hiring include reviewing portfolios, checking testimonials, and ensuring that the service provider is equipped with the latest technology and skilled personnel. By outsourcing, companies can enhance efficiency and concentrate on essential design tasks while gaining from high-quality output.
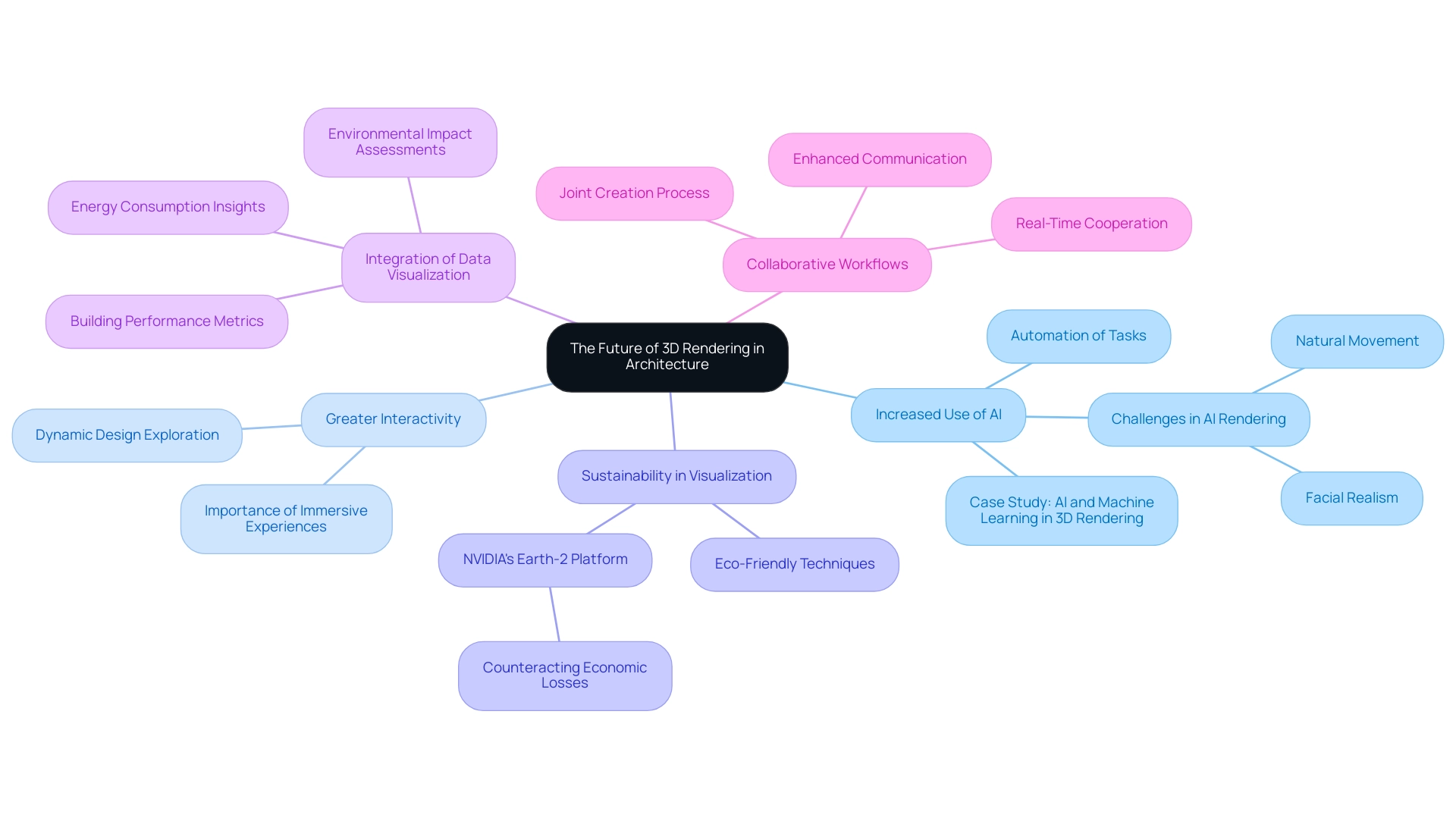
The Future of 3D Rendering in Architecture
The future of 3D visualization in architecture is on the cusp of transformative change, fueled by rapid technological advancements and evolving client expectations. Notable trends that are shaping this landscape include:
Increased Use of AI: The integration of artificial intelligence is set to revolutionize rendering processes, notably in creating lifelike CG humans that help bridge the uncanny valley in architectural visualizations. Challenges such as achieving facial realism and natural movement are being addressed through advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques. AI will automate various tasks, allowing for the generation of hyper-realistic visuals tailored to specific design parameters, thereby significantly enhancing efficiency and output quality. This evolution aligns with predictions that AI integration will streamline workflows and reduce project timelines. A relevant case study titled “AI and Machine Learning in 3D Rendering” is among the examples of case studies of 3D renderings in architectural projects, highlighting how these technologies are improving performance and automating various aspects of the rendering process, ultimately enhancing production efficiency and image quality.
Greater Interactivity: As customer engagement becomes paramount, the architectural visualization sector will witness a surge in demand for interactive experiences. This shift will pave the way for advanced immersive visualization tools that allow clients to explore designs more dynamically, fostering a deeper connection with proposed initiatives.
Sustainability in Visualization: With the architectural industry increasingly prioritizing sustainable practices, visualization processes will evolve to focus on energy-efficient modeling and eco-friendly techniques. This trend is critical as firms respond to the growing pressure to minimize environmental impact, particularly in light of initiatives like NVIDIA’s Earth-2 climate digital twin platform, which aims to counteract US$140 billion in economic losses caused by climate change. Sushmita Roy, a 3D expert, stresses the significance of sustainability in visual creation, stating, ‘When she’s not busy working on a new project, she shares valuable insights from her own experience.’
Integration of Data Visualization: Future displays will include data visualization, providing users with insights into building performance metrics, energy consumption, and environmental impact assessments. This dual focus on aesthetics and functionality will make visualizations not only appealing but also valuable decision-making tools.
Collaborative Workflows: The future will usher in more robust collaborative platforms that facilitate real-time cooperation among architects, clients, and stakeholders. The joint creation process at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs starts with initial communication and briefings, ensuring all specifications are collected upfront. This environment enhances communication, streamlines project workflows, and ultimately leads to improved project outcomes, reflecting the industry’s shift towards more integrated approaches.
As 3D rendering technology continues to evolve, these trends will define the practices of leading architects, ensuring that they remain at the forefront of innovation and client satisfaction.
Conclusion
The integration of 3D renderings in architecture has revolutionized the field, enabling architects to articulate their visions with unprecedented clarity and precision. By enhancing design communication, facilitating informed decision-making, and serving as powerful marketing tools, 3D renderings have become indispensable in modern architectural practice. The exploration of inspiring case studies demonstrates their effectiveness across various project types, showcasing how these visual narratives help secure client approval, foster stakeholder engagement, and attract investment.
Technological advancements, such as:
- real-time rendering
- photorealistic techniques
- the integration of virtual and augmented reality
continue to enhance the capabilities of 3D renderings. These innovations not only streamline workflows but also improve the overall quality of visualizations, ensuring accurate representations of architectural intent. Best practices, including:
- investment in quality software
- attention to lighting
- iterative refinement
are essential for achieving exceptional outcomes. As firms increasingly prioritize technology, embracing these best practices can lead to improved client satisfaction and deeper connections.
Looking ahead, the future of 3D rendering in architecture is poised for transformative change. The rise of artificial intelligence, greater interactivity, and a focus on sustainability will shape the next generation of architectural visualizations. By remaining attuned to these trends, architects can leverage the full potential of 3D renderings, ensuring they continue to meet evolving client expectations and maintain their competitive edge in the industry. As the architectural landscape evolves, the ability to effectively utilize 3D renderings will be paramount for success in delivering innovative and impactful designs.

0 Comments