Overview
The article outlines seven essential steps for effectively exploring augmented reality (AR) in architectural projects, emphasizing its transformative role in design visualization and client engagement. It supports this by detailing practical applications such as interactive client presentations and real-time construction guidance, which enhance collaboration and decision-making while addressing the growing demand for AR integration in the architecture industry.
Introduction
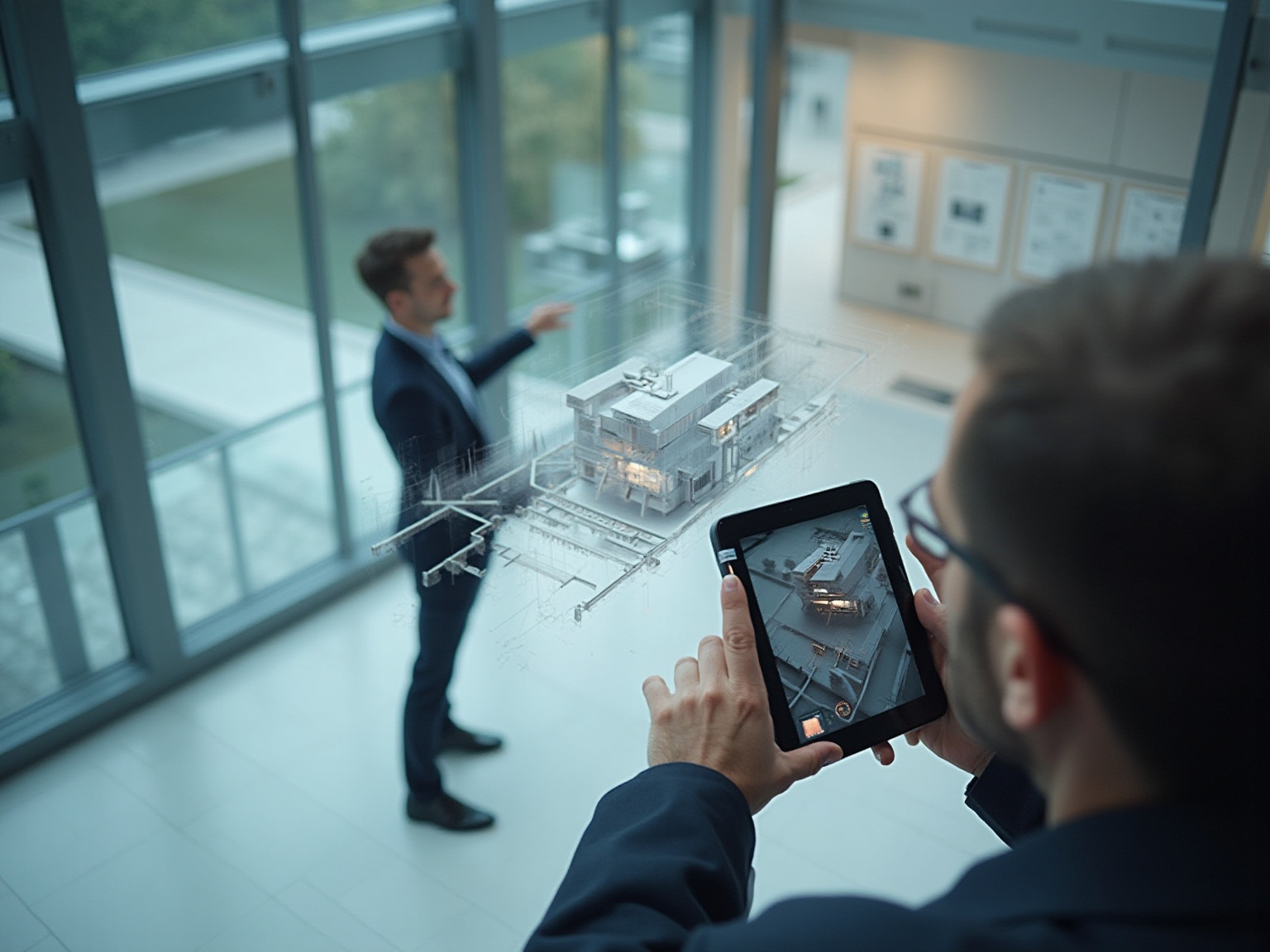
In the realm of architecture, the advent of Augmented Reality (AR) marks a pivotal shift in how designs are conceptualized, presented, and executed. By merging digital information with the physical environment, architects can create immersive experiences that not only enhance visualization but also foster deeper engagement with clients and stakeholders. This integration of AR technology empowers professionals to validate design choices in real-time, streamline construction processes, and improve collaborative efforts among project teams.
As the architectural landscape evolves, understanding the multifaceted applications of AR—from client presentations to marketing strategies—becomes crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. Furthermore, as the market for AR continues to expand, the implications for sustainable design practices and future workforce training are profound, signaling a transformative era for architectural innovation.
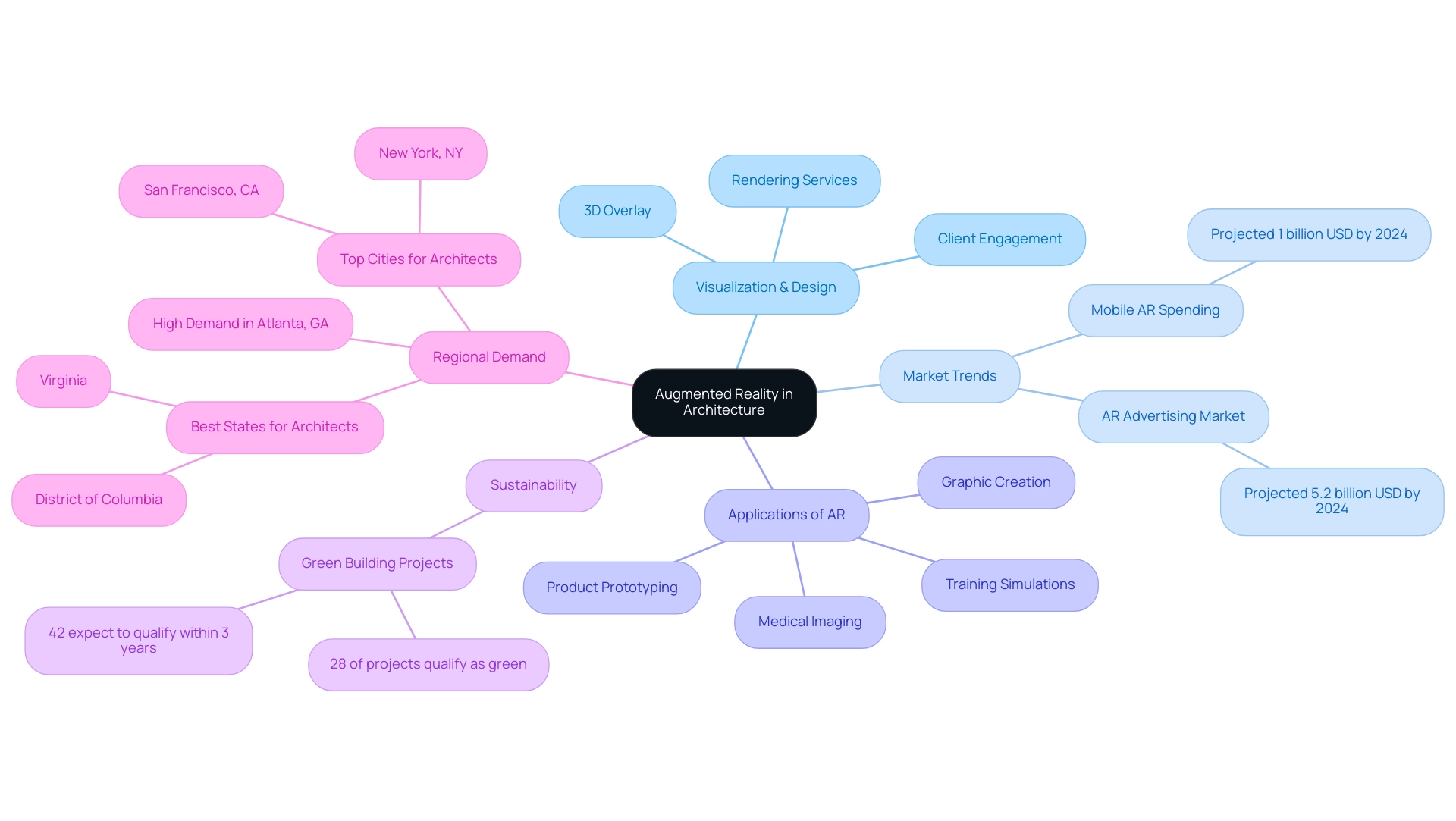
Understanding Augmented Reality in Architecture
The integration of Augmented Reality (AR) in architecture signifies a significant evolution in how architects visualize and present their designs, illustrating the steps to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects by seamlessly merging digital information with the physical environment. This innovative technology is part of the steps to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects, allowing the overlay of 3D models onto real-world environments, resulting in immersive experiences that enhance understanding and interaction with architectural designs. Utilizing devices such as smartphones, tablets, and AR glasses, architects can superimpose digital elements, enabling customers and stakeholders to visualize spaces prior to construction.
This capability is essential; as noted by OpenAsset, 28% of professionals—including architects, engineers, contractors, owners, and investors—indicate that most of their building projects qualify as green, with 42% expecting similar outcomes within three years, suggesting a growing trend towards sustainable practices. Moreover, the role of AI in producing realistic CG humans for visual representations is crucial in bridging the uncanny valley, enhancing client engagement and confidence in the creative process. Specialized 3D rendering services not only assist in the development of construction visions but also play a crucial role in:
- Medical imaging
- Training simulations
- Product prototyping
- Graphic creation
showcasing the diverse applications of this technology.
The principles of AR are essential for architects striving to stay competitive and innovative in a rapidly evolving field, highlighting the steps to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects, especially as consumer spending on mobile AR digital goods is projected to reach 1 billion USD by 2024. Additionally, with 30,068 students enrolled in NAAB-accredited programs in AY 2022-2023, there is a growing interest in architecture, suggesting a future workforce that will increasingly utilize AR technologies. The anticipated growth of the consumer AR advertising market, projected to reach 5.2 billion U.S. dollars in 2024, further emphasizes the broader market trends supporting the adoption of AR in architecture.
Moreover, understanding the regional demand for architects, particularly in cities like Atlanta, GA, where they are most sought after, underscores the relevance of AR in design practices across different regions. Therefore, utilizing AR together with skilled 3D rendering services improves processes by discarding poor concepts and ensuring precision, ultimately enabling architects to more effectively satisfy the needs of contemporary customers. Testimonials from customers highlight the effectiveness of these services, affirming that specialized 3D rendering not only leads to successful project outcomes but also fosters satisfaction, ensuring project success and accuracy.
Practical Applications of Augmented Reality in Architectural Design
Augmented Reality (AR) offers numerous practical uses in architectural planning, significantly improving both the creation and customer engagement processes:
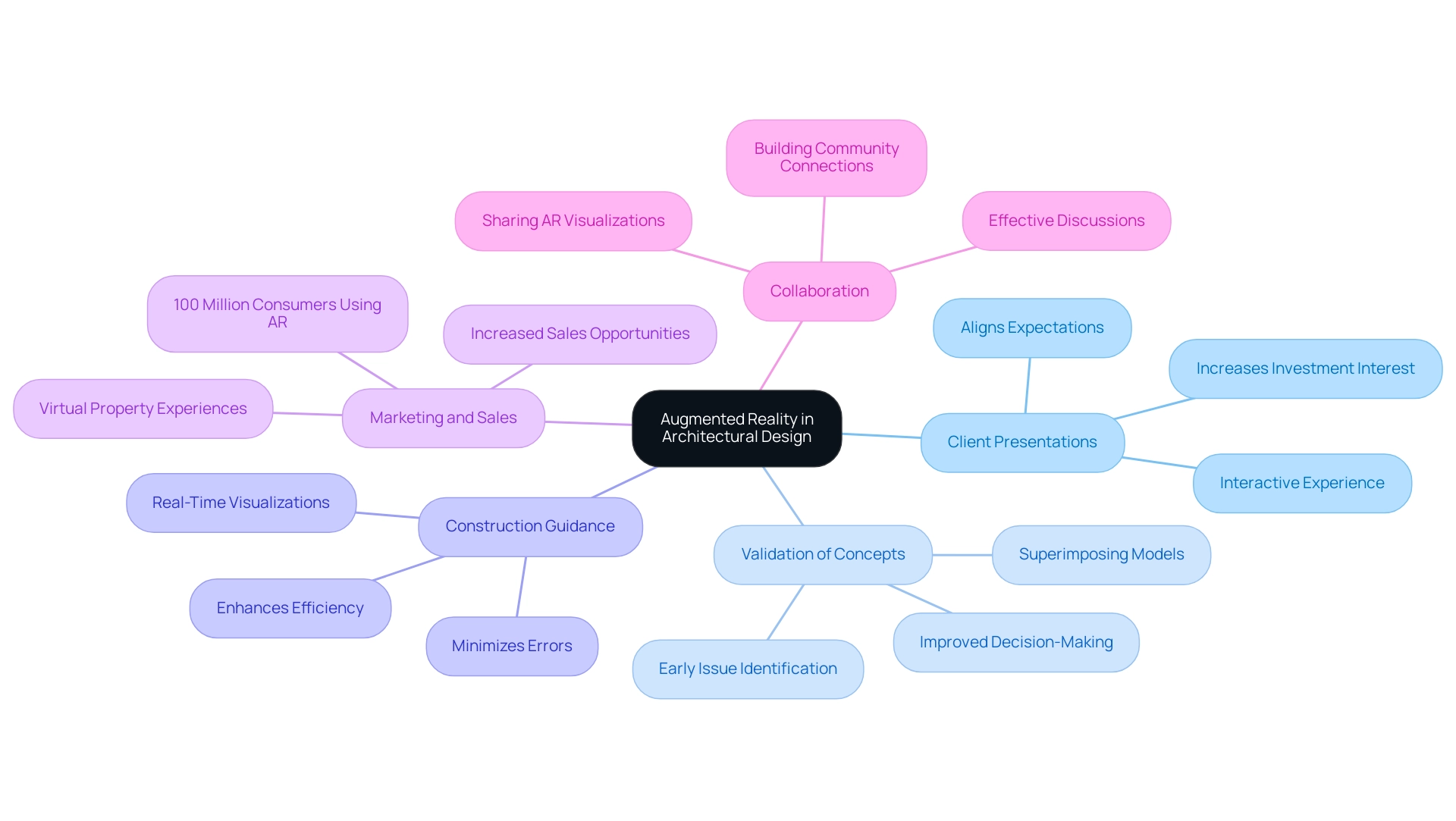
Client Presentations: AR creates an interactive presentation setting where architects can display concepts, allowing stakeholders to envision spaces in real-time. This immersive experience not only aligns client expectations with creative intent but also fosters a deeper connection between the project and its potential residents, enhancing project confidence and increasing investment interest.
Validation of Concepts: By superimposing detailed interior renderings and 3D models onto real-world environments, architects can effectively validate choices and evaluate spatial relationships prior to construction. This proactive approach ensures that potential issues are identified early, leading to more informed decision-making and improved stakeholder communication.
Construction Guidance: AR serves as a critical tool for contractors by providing real-time visualizations of architectural plans directly on-site. This capability ensures that construction activities are executed in alignment with the initial blueprint, minimizing errors and enhancing efficiency.
Marketing and Sales: The integration of AR into marketing strategies allows prospective buyers to virtually experience properties, significantly improving sales opportunities. This innovative approach is supported by the fact that over 100 million consumers utilize augmented reality for shopping, both online and offline, showcasing its potential in generating crucial revenue for construction projects.
Collaboration: AR enhances cooperative efforts among creative teams by enabling the sharing of AR visualizations. This feature promotes effective discussions and constructive feedback throughout the creation process, fostering a deeper connection between the project and its potential residents, ultimately setting the foundation for a strong community from the outset.
The transformative impact of AR in architecture is underscored by Thomas Alsop, a research expert in the global hardware industry, who predicts that AR will become increasingly integral to various fields, including architecture. Furthermore, key statistics reveal that companies are leveraging AR for product development (38%), safety training (27.6%), and remote collaboration (19.4%), highlighting its broad relevance in the industry.
Real-world applications of AR are exemplified by case studies such as Northeastern University’s XR Learning Solutions, where mixed reality training solutions decreased upskilling time by 83%, effectively reducing a 3-hour lesson plan into less than 30 minutes. This showcases the potential of AR in enhancing retention and efficiency in training environments. Additionally, Tim Cook’s vision on AR emphasizes its transformative potential across various sectors, including design, suggesting that AR will play a pivotal role in the future.
As practices evolve, the steps to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects for client presentations and design validation become essential for staying competitive in a rapidly advancing industry. The ongoing projects by global game developers for VR/AR platforms in 2024 further illustrate the advancements in AR technology and its implications for the field of architecture.
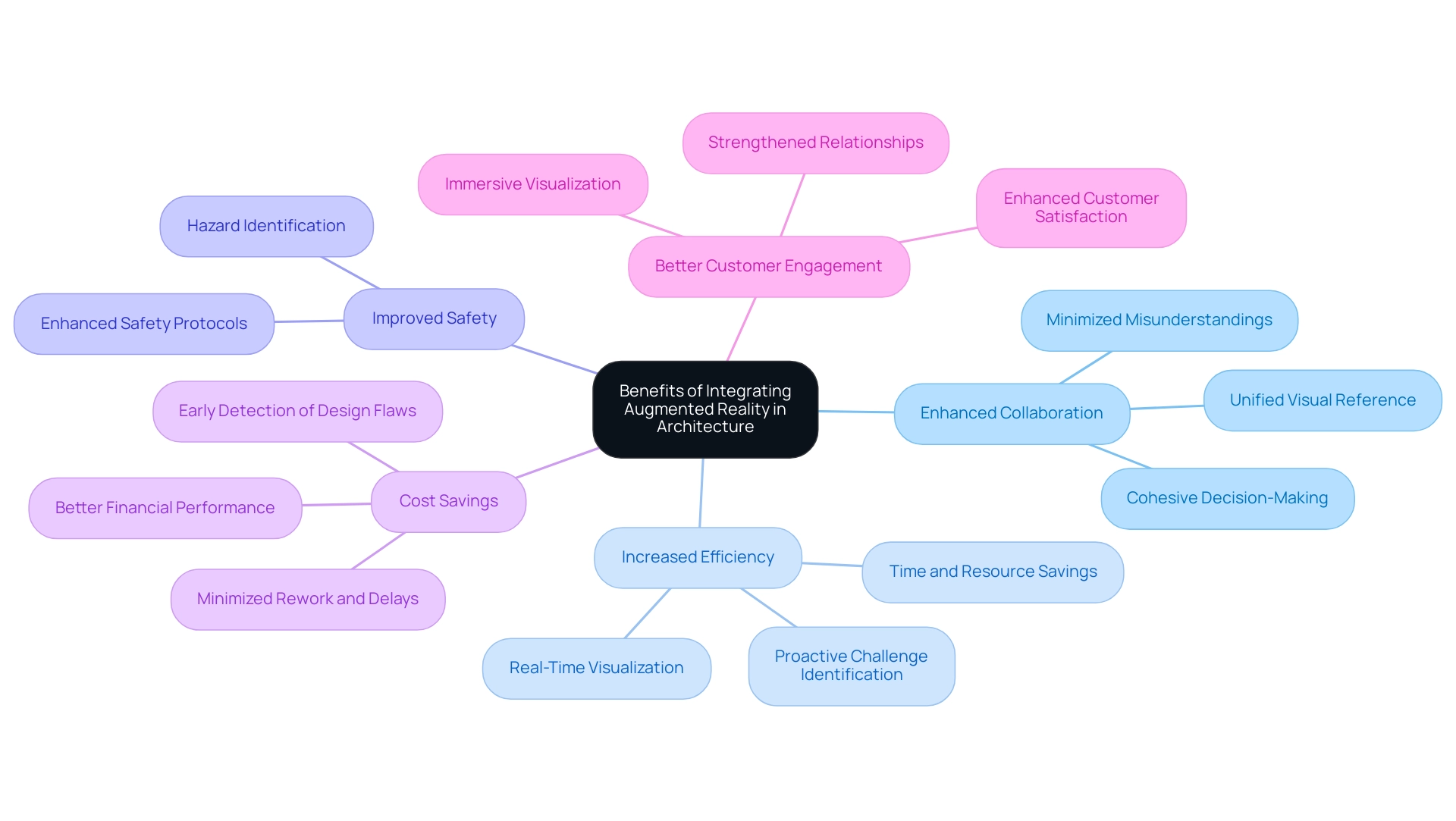
Benefits of Integrating Augmented Reality into Architectural Workflows
Integrating Augmented Reality (AR) into architectural workflows presents a range of significant benefits, which include the steps to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects and building upon the collaborative rendering process at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs. These benefits include:
Enhanced Collaboration: AR facilitates seamless collaboration among architects, clients, and contractors by providing a unified visual reference, akin to the meticulous detailing achieved in our 3D models.
This shared viewpoint minimizes misunderstandings and aligns all stakeholders with the vision, leading to more cohesive decision-making.Increased Efficiency: The ability to visualize creations in real-time allows architects to swiftly identify and address potential challenges.
This proactive method not only speeds up the creation process but saves valuable time and resources, ultimately leading to success.
Just as our detailed modeling process enhances flexibility throughout the rendering stages, AR enhances responsiveness in modifications.Improved Safety: Through AR simulations of construction processes, teams can pinpoint potential hazards before any physical work commences.
This foresight enhances safety protocols, significantly reducing risks associated with on-site construction activities, paralleling our commitment to thorough specifications from the outset.Cost Savings: The early detection of design flaws facilitated by AR can result in substantial cost reductions.
By minimizing rework and delays, projects can remain within budget and on schedule, translating to better overall financial performance, much like the tailored rendering proposals we develop to showcase projects effectively.Better Customer Engagement: Interactive AR experiences enhance customer engagement by enabling them to visualize concepts in an immersive manner.
Such involvement not only enhances customer satisfaction but also fosters trust and strengthens relationships, which are crucial for future collaborations.
This reflects our method of sending progress renderings to clients for early feedback, ensuring their creative vision is perfectly captured.
Statistics indicate that AR layers digital enhancements onto real-world scenes viewed through smartphones, tablets, and smart glasses, highlighting the steps to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects.
Recent advancements in AR technology, such as the TINMITH2 Mobile AR Platform, demonstrate the steps to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects by providing spatial context for construction plans and enhancing stakeholder comprehension of proposed modifications, similar to our detailed 3D renderings.
Additionally, a new contextual approach has been tested on University of Jordan students as part of the steps to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects, merging procedural modeling to tackle challenges of residential building identity in Amman.
This approach has proven effective in achieving spatial congruence, demonstrating the steps to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects to tackle real-world design challenges.
Expert Avinash Patil highlights the innovative potential of AR in architecture, stating,
The multiplier architecture proposed in this paper is based on the urdhva triyakbham sutra of ancient Indian Vedic mathematics (vertical and crosswise).
This highlights how AR can incorporate complex concepts into practical applications, showcasing its transformative role in the architectural sector.
At J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, our collaborative rendering process starts with initial communication and design briefs, followed by detailed modeling and material selection, ensuring that every aspect of the design is meticulously crafted to meet specifications.
By incorporating AR into our workflow, we are taking significant steps to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects, which enhances these phases and fosters a more interactive and satisfying experience for our clients.
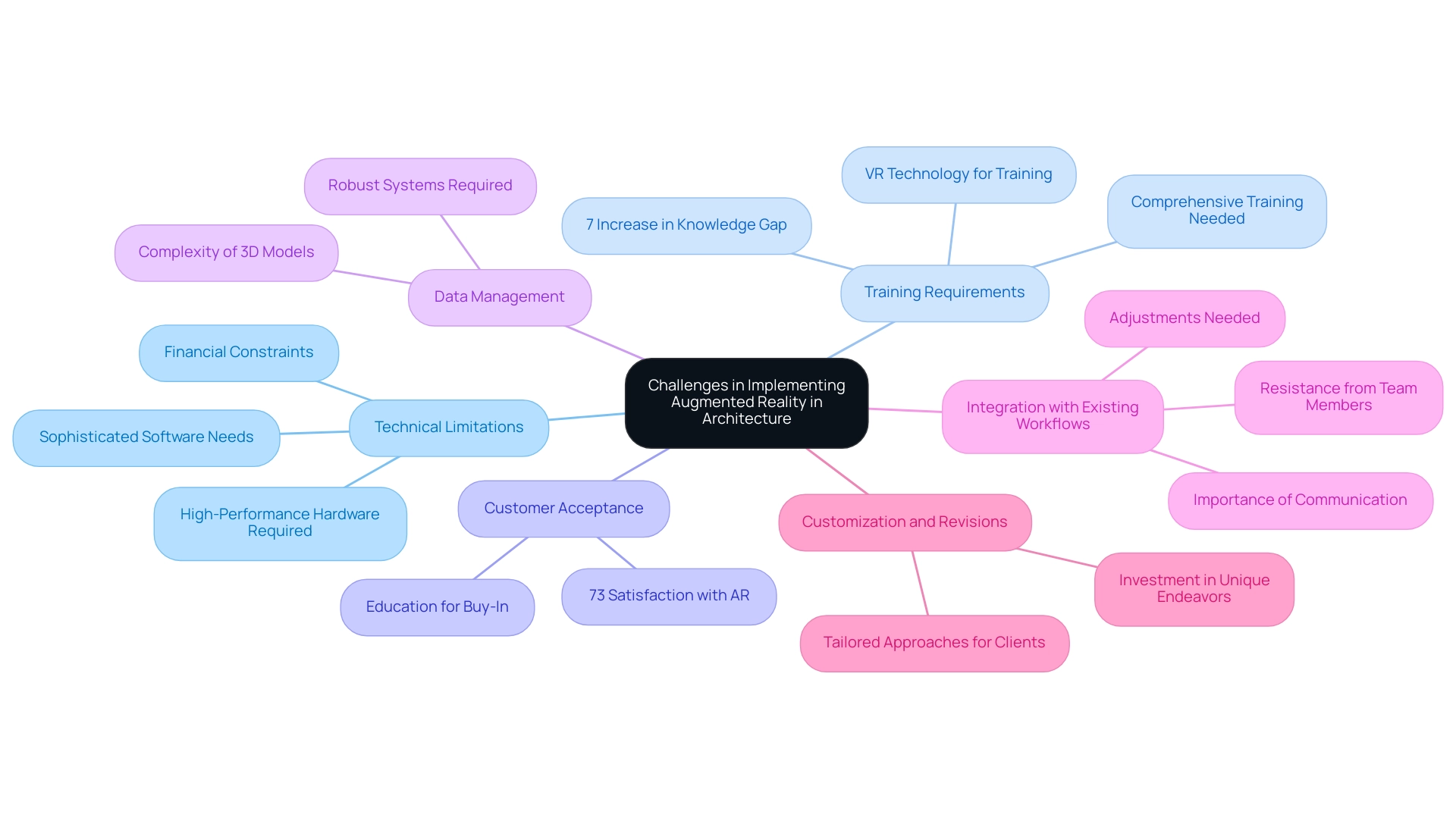
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Augmented Reality
The integration of Augmented Reality (AR) into architectural projects, while offering significant enhancements, presents several technical challenges that architects must critically assess:
Technical Limitations: The deployment of AR technology typically necessitates high-performance hardware and sophisticated software, which can pose substantial barriers for firms with limited budgets. Recent reports indicate that financial constraints remain a primary limitation in adopting AR technologies.
Training Requirements: Effective utilization of AR tools often requires comprehensive training for team members, which can lead to increased time and financial costs during the transition phase. Notably, the knowledge gap within design teams has increased by 7% over the past year, making it increasingly critical to address this factor to ensure successful implementation. Moreover, VR technology can improve training outcomes by providing high-fidelity simulations for workers, showcasing its potential benefits alongside the challenges.
Customer Acceptance: Educating individuals unfamiliar with AR is essential for gaining their buy-in. Research indicates that 73% of shoppers report heightened satisfaction when using AR, suggesting that effective demonstrations can significantly enhance consumer experiences and acceptance. This statistic underscores the potential advantages of AR in enhancing client interactions and satisfaction.
Data Management: The complexity of managing the data required for AR applications cannot be overlooked. Architects must implement robust systems capable of handling intricate 3D models and extensive information, which can complicate workflows. This is where J. Scott Smith Visual Designs excels, as we meticulously craft detailed 3D models that serve as the foundation for rendering, ensuring accuracy and flexibility throughout the process.
Integration with Existing Workflows: Integrating AR into established architectural workflows often necessitates significant adjustments. Drawing from our collaborative rendering process, which begins with initial communication and FAQs to clarify objectives, resistance can arise from team members who are accustomed to traditional methods. At J. Scott Smith Visual Designs, we emphasize smooth communication and prompt engagement, which are critical to ensuring that the integration of new technologies like AR complements rather than disrupts existing practices.
Customization and Revisions: The role of customization and revisions in the rendering process is vital in determining investment for unique endeavors. By customizing our approach to satisfy specific client requirements, we guarantee that each project is not only visually engaging but also in line with client expectations.
These challenges highlight the significance of strategic planning and preparation in successfully utilizing AR in architectural creation, specifically addressing the steps to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects, as well as the benefit of investing in high-quality 3D renderings to boost project attractiveness and client satisfaction.
Future Trends in Augmented Reality for Architecture
The future of Augmented Reality (AR) in architecture is poised for substantial growth, driven by several emerging trends that will outline the steps to exploring augmented reality in architectural projects.
Increased Use of AI: The integration of artificial intelligence with AR is poised to revolutionize creative capabilities, enabling architects to develop smarter, more adaptive solutions. This synergy allows for personalized feedback mechanisms, enhancing the design process significantly.
As Mojtaba Noghabaei notes, ‘The presented method can take current safety training programs to another level by providing personalized feedback to the workers,’ underscoring the potential of such technologies in various aspects of architectural practice.Greater Accessibility: As AR technology evolves to become more affordable and user-friendly, smaller firms and individual architects will likely adopt these tools more extensively. This democratization of technology will empower a broader range of practitioners to leverage AR in their projects.
Cloud-Based AR Solutions: The advent of cloud technology will facilitate seamless sharing of AR models among teams and clients. This advancement promotes real-time collaboration, breaking down geographical barriers and streamlining the review process.
Integration with Virtual Reality (VR): The convergence of AR and VR technologies will yield hybrid experiences that enhance immersive presentations. This fusion allows architects to visualize projects in a more holistic manner, improving client engagement and decision-making.
Sustainability Focus: Future AR applications will likely emphasize sustainability, equipping architects with tools to visualize and analyze the environmental effects of their creations. This focus aligns with the growing demand for eco-friendly practices in architecture.
Additionally, there was a significant increase in AR/VR utilization in the AEC industry from 2017 to 2018, highlighting the rapid adoption of these technologies.
The AR market is on an upward trajectory, with the consumer AR advertising sector projected to reach 5.2 billion USD in 2024, while the overall revenue for consumer and enterprise AR glasses is expected to hit 6.4 billion USD the same year. Furthermore, as illustrated in the case study titled ‘AR Applications Beyond Gaming,’ AR technology is expanding beyond gaming and entertainment into sectors like healthcare and manufacturing, showcasing its transformative potential. This growth illustrates the increasing importance of AR in shaping the future of architectural design and presentation.
Conclusion
The integration of Augmented Reality (AR) into architectural practices signifies a transformative leap in how designs are conceptualized, presented, and executed. By offering immersive visualization capabilities, AR empowers architects to engage clients and stakeholders more effectively, enhancing their understanding of projects before ground is even broken. The ability to overlay digital models onto real-world environments not only improves design validation but also fosters collaboration, ensuring that all parties are aligned on project goals and expectations.
As highlighted throughout the article, the benefits of AR extend beyond mere visualization. It streamlines workflows, enhances safety protocols, and drives cost efficiencies by identifying potential design flaws early in the process. Moreover, the growing acceptance of AR tools among clients indicates a shift towards more interactive and satisfying engagement, ultimately leading to stronger relationships and successful project outcomes.
Looking ahead, the future of AR in architecture is bright, with trends such as the integration of AI, cloud-based solutions, and a heightened focus on sustainability poised to reshape the industry. As architects embrace these advancements, they will not only maintain a competitive edge but also contribute to a more innovative and eco-conscious architectural landscape. The ongoing evolution of AR technology is set to redefine the parameters of architectural design, making it an indispensable tool for the modern architect.


0 Comments