Overview:
The article discusses ten inspiring examples of how AI is revolutionizing 3D architectural rendering by enhancing efficiency, creativity, and sustainability in architectural practices. These advancements are exemplified by firms like Zaha Hadid Architects and BIG, which utilize AI tools to optimize design processes, improve stakeholder communication, and foster innovative solutions, ultimately transforming the architectural landscape.
Introduction
In an age where innovation drives the architectural landscape, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the very foundations of design and construction. As architects increasingly embrace AI tools, they unlock new realms of efficiency and creativity, allowing for a more strategic approach to their work. This article delves into the transformative impact of AI on architectural practices, highlighting its role in:
- Automating complex processes
- Enhancing design accuracy
- Fostering sustainable solutions
Through compelling real-world applications and a focus on the challenges and future trends, it provides a comprehensive overview of how AI is not just a tool but a catalyst for a new era in architecture, where the boundaries of possibility are continually expanding.
Transforming Architectural Design: The Role of AI
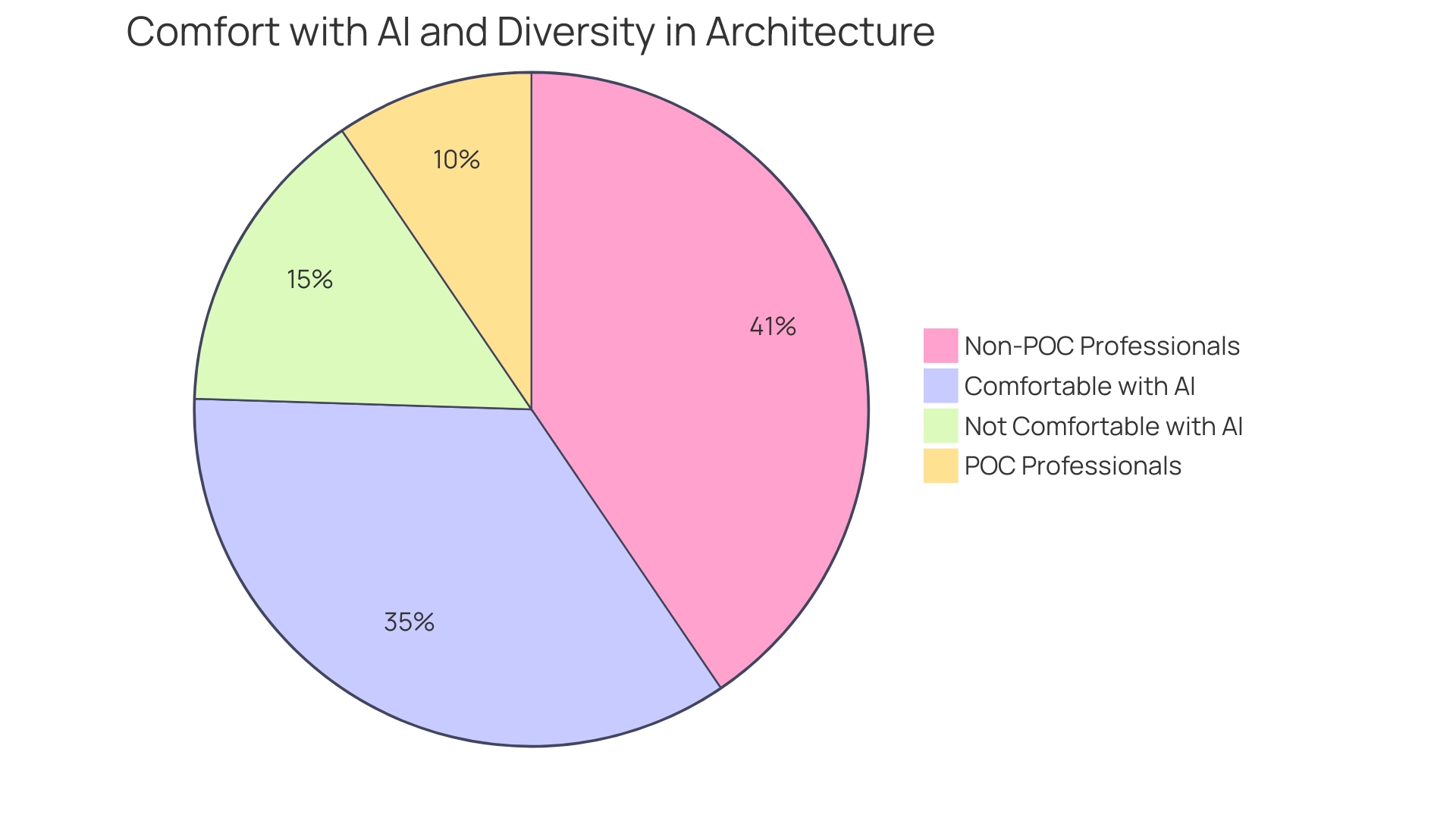
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming architectural planning by providing examples of AI in 3D architectural rendering, automating complex procedures, and enhancing the creative abilities of builders. In 2023, about 70% of professionals reported comfort with utilizing AI-generated proposal suggestions, reflecting a growing trend across the field. Notably, in 2023, individuals of color (POC) made up 19% of the total population of professionals, highlighting the importance of diversity within the field.
AI tools are now capable of analyzing extensive datasets, predicting project outcomes, and proposing optimal solutions, allowing architects to devote more time to creative and strategic considerations rather than routine tasks. This change not only speeds up the creation process but also encourages innovative problem-solving methods, resulting in more effective and sustainable structural solutions. Furthermore, discussions around AI’s role in architecture have expanded to include its potential to streamline workflows within firms, particularly benefiting smaller practices that may face resource constraints.
The anticipated innovations, including examples of AI in 3D architectural rendering such as Text-to-BIM and 3D-form generators, are set to enhance efficiency and creativity in architectural workflows. As part of this evolution, visual renderings play a crucial role in enhancing contractor communication, eliminating misunderstandings, and facilitating early issue resolution. By offering detailed representations that include examples of AI in 3D architectural rendering, planners can remove the uncertainty from creation, ensuring that what builders observe is exactly what is meant.
This process begins with an initial brief, where architects gather essential specifications and understand the client’s vision. Following this, material and lighting selection is meticulously conducted to reflect design intent, further clarifying the endeavor for contractors. As the integration of AI becomes increasingly vital for modern practices, 40% of firms that meet or exceed their goals are planning to invest more in technology, with 70% of architecture firms intending to allocate resources towards advanced project management software in the upcoming year.
According to The Architect’s Newspaper, in 2022, there were nearly 120,000 licensed architects across 55 U.S. jurisdictions. The future of building creation is indeed intertwined with the advancements in AI, setting the stage for a new era of creativity and efficiency.
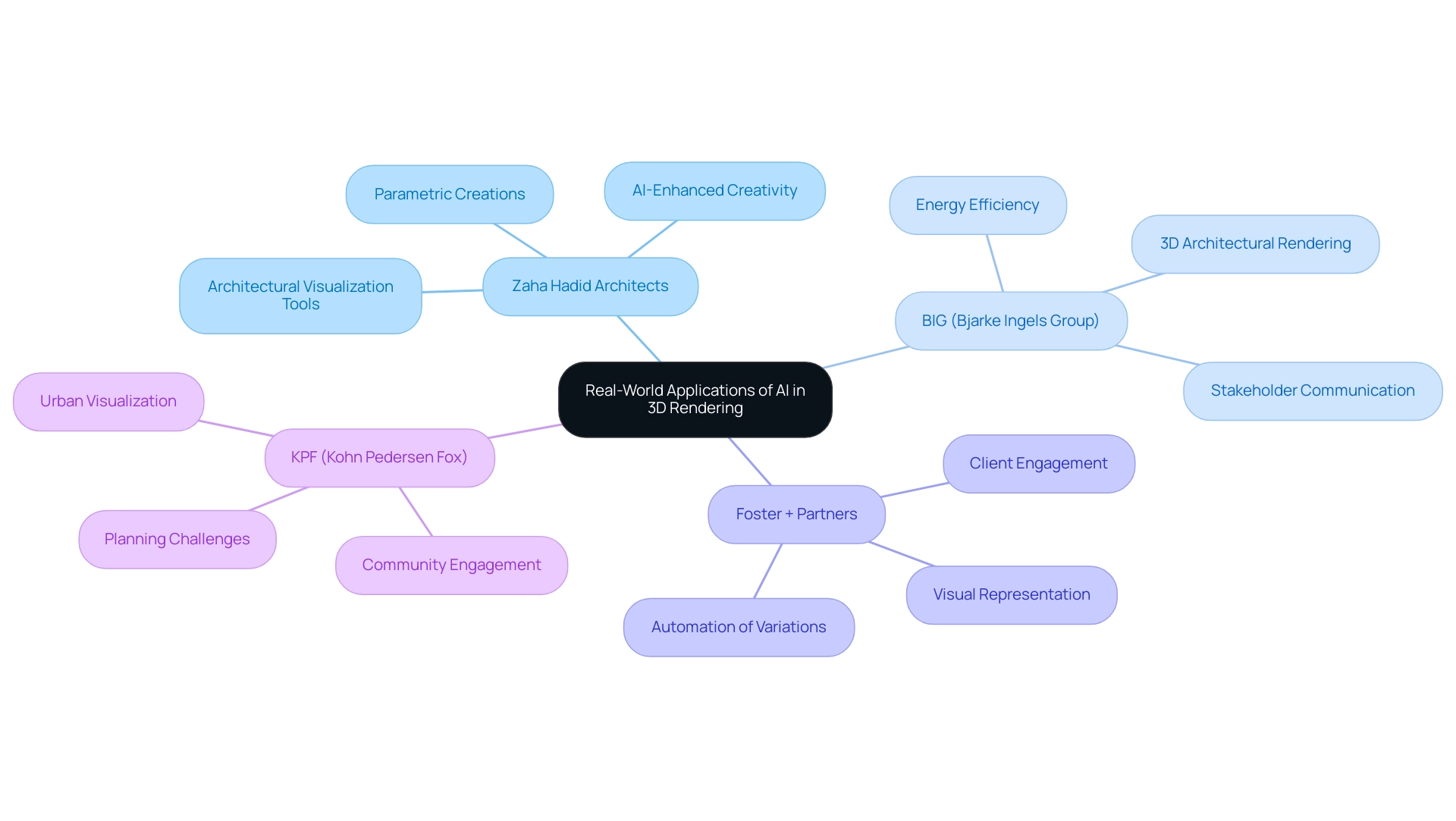
Real-World Applications: Inspiring Examples of AI in 3D Rendering
Zaha Hadid Architects: Pioneering the integration of AI algorithms, Zaha Hadid Architects have redefined possibilities in construction through their intricate and parametric creations. This innovative method enables the exploration of complex geometries that challenge conventional design constraints. As highlighted by Chao Yuan, > Through the examination of the connection between computational creation and AI-assisted creation, this paper proposes a new method of building under the influence of generative AI <. This reflects how Zaha Hadid Architects leverage technology to enhance creativity, fostering a deeper connection between their projects and future residents. Furthermore, recent research indicates that a total of 264 images were produced by DALL-E 2 and Copilot for various motifs, showcasing the abilities of AI in creating diverse architectural concepts that resonate with client aspirations. Architectural visualization tools, featuring interactive components and virtual reality experiences, further immerse prospects in the creation process, allowing for an early identification of potential issues.
BIG (Bjarke Ingels Group): BIG exemplifies the application of examples of AI in 3D architectural rendering to optimize building performance and energy efficiency. Their celebrated project, ‘The Spiral’ in New York, serves as a prime example of how AI can inform sustainable choices, ensuring alignment with contemporary ecological objectives. By utilizing advanced visualization methods, BIG improves stakeholder communication and allows clients to engage more deeply with the creative process. Additionally, a case study titled ‘Evaluating AI Tools for Building Design’ reviews various AI tools that serve as examples of AI in 3D architectural rendering, including DALL-E 2 and Midjourney, assessing their effectiveness in generating images from text for construction purposes, facilitating early identification of issues.
Foster + Partners: By integrating AI into their workflow, Foster + Partners have automated the generation of variations, significantly increasing efficiency in large-scale developments. Their work on Apple Park illustrates the effective application of AI technologies, resulting in streamlined processes and innovative design solutions that enhance client understanding. This method not only enhances creative results but also cultivates a sense of community as clients engage actively in imagining their future environments, with visual representation aiding in recognizing issues early in the process.
KPF (Kohn Pedersen Fox): KPF utilizes AI for visualizing urban environments, enabling them to assess the effects of new developments on existing cityscapes. This strategic use of AI demonstrates its vital role in urban planning and community engagement, facilitating informed decisions that resonate with the public interest and foster strong community connections from the outset. The immersive nature of architectural visualization enables stakeholders to experience potential developments interactively, further assisting in the early identification of planning challenges.
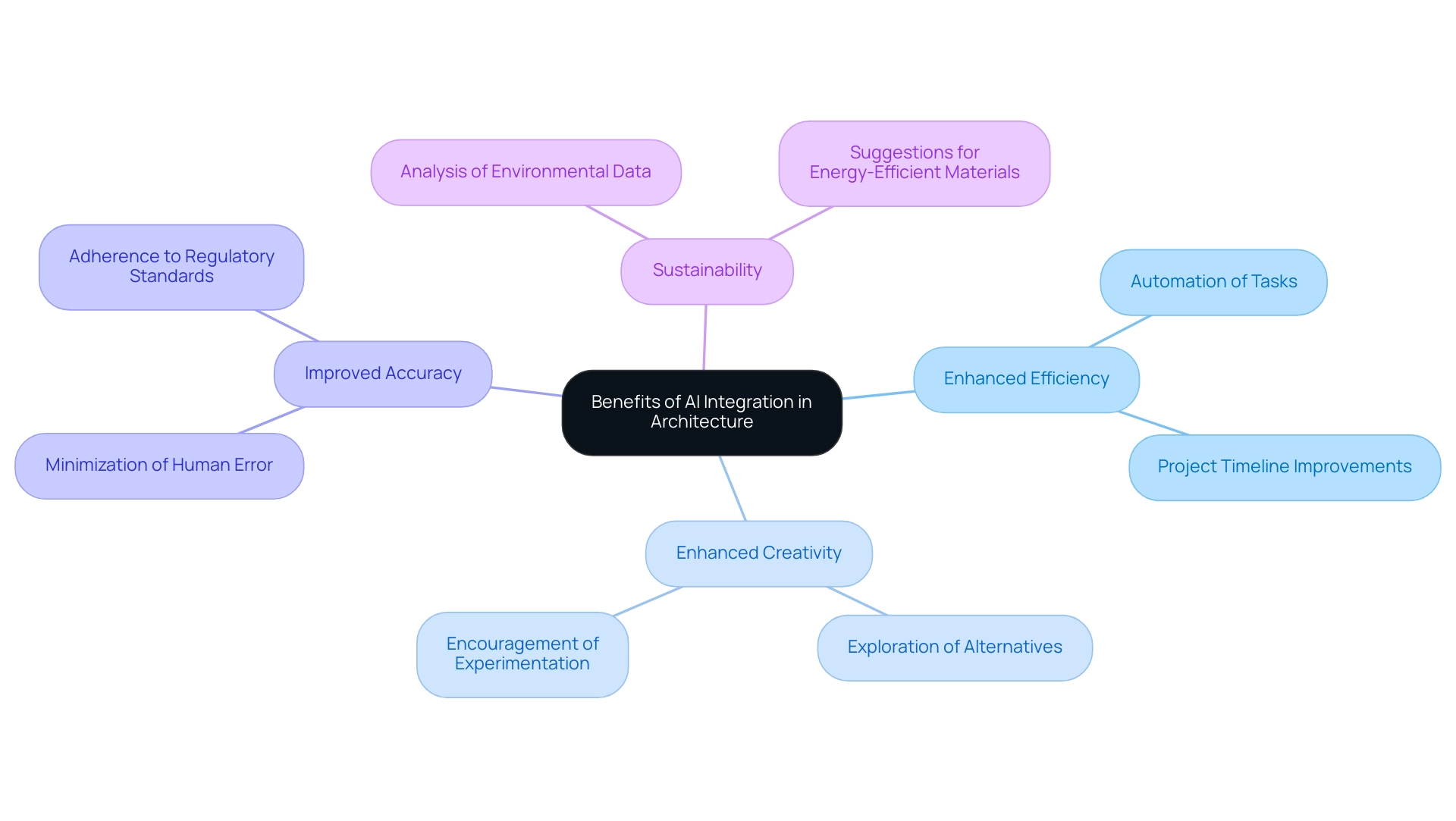
The Benefits of AI Integration in Architecture
The incorporation of AI in architecture offers various significant advantages that are transforming the sector in 2024:
Enhanced Efficiency: By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, AI enables professionals to devote more time to complex creative challenges. This shift not only speeds up project timelines but also improves overall workflow, enabling a deeper focus on innovative solutions. In fact, a significant 65% of CEOs plan to use AI tools like ChatGPT for business purposes, believing it will positively impact operations across various sectors, including architecture.
Enhanced Creativity: AI-driven tools can generate multiple alternatives, serving as a catalyst for architects to explore creative avenues that may have previously been overlooked. This capability broadens the creative palette and encourages experimentation, fostering an environment where creativity flourishes. As noted by the World Economic Forum, the economic significance of AI is substantial, contributing to improved practices in architecture.
Improved Accuracy: Leveraging advanced algorithms, AI significantly minimizes human error in calculations and visualizations. This precision is crucial in ensuring that architectural plans are not only reliable but also adhere to stringent regulatory standards, ultimately leading to more successful project outcomes. The meticulous detail visible in the rendering processes at firms like J. Scott Smith Visual Designs exemplifies this commitment to accuracy.
Sustainability: AI systems can analyze vast amounts of environmental data, providing designers with insights that promote sustainable design practices. By suggesting energy-efficient materials and strategies, AI helps architects create buildings that are aesthetically pleasing and environmentally responsible.
In a recent study titled ‘The Future of AI for Architects,’ a significant majority of architects expressed confidence in AI’s role as a powerful ally in their practice. This case study highlights that many firms anticipate increased usage of AI, reinforcing the notion that the technology is poised to enhance both creative and operational aspects of architectural work. Furthermore, the collaborative rendering process at J. Scott Smith Visual Designs emphasizes the importance of providing clear and timely information in construction endeavors. Initial communication and project briefs are critical for optimizing time and cost, ensuring accuracy, and ultimately achieving client satisfaction. Clients are encouraged to provide accurate specifications early in the process to facilitate high-quality outcomes, reflecting the meticulous detail and advanced software employed in the rendering process.
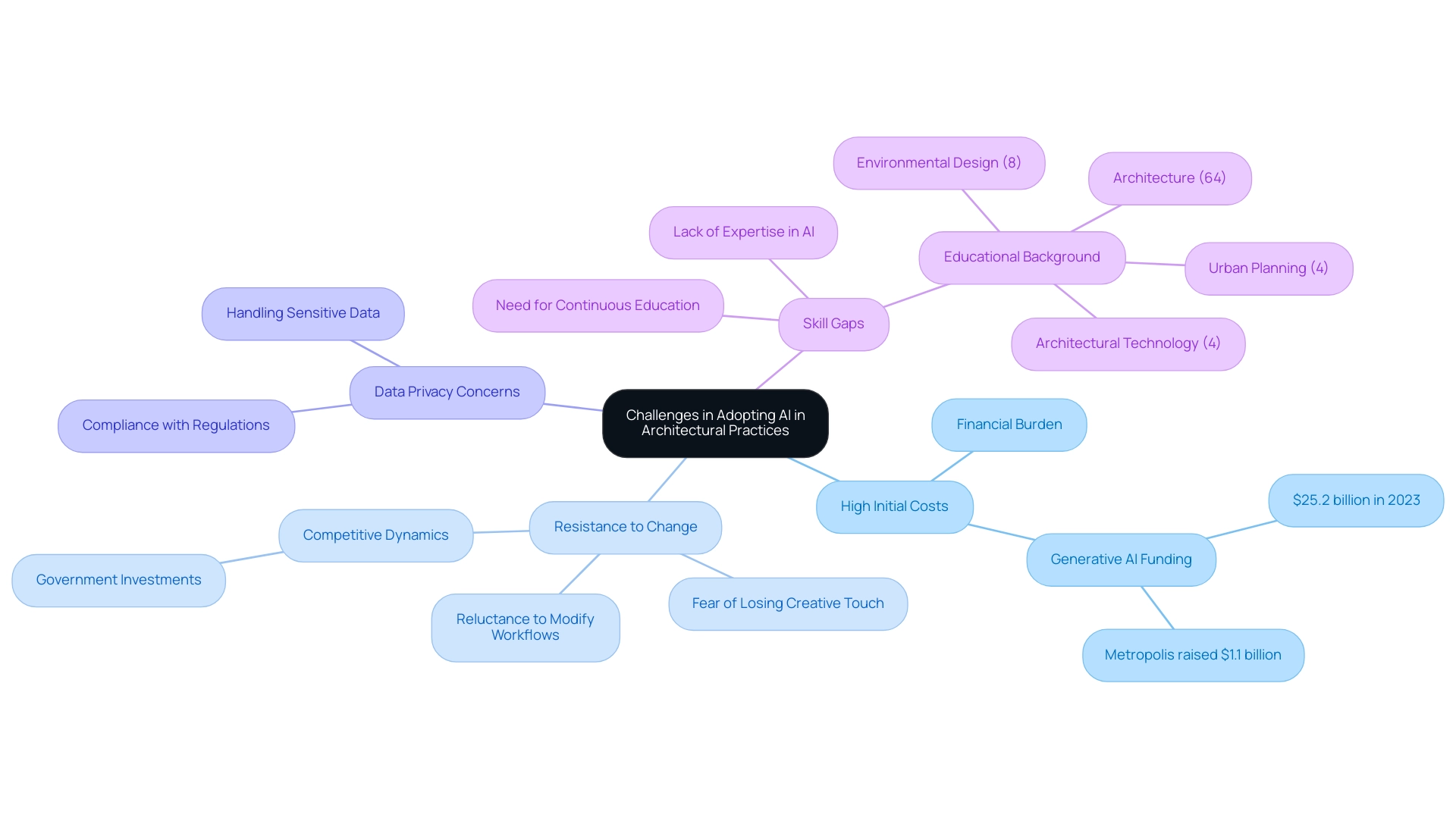
Challenges in Adopting AI in Architectural Practices
The integration of AI in architecture presents substantial benefits; however, several challenges impede its widespread adoption:
- High Initial Costs: The financial burden of implementing AI technologies can be considerable. Architectural firms often face steep costs associated with software acquisition and staff training, creating barriers, particularly for smaller entities. For instance, the investment in generative AI solutions has surged, with funding reaching $25.2 billion in 2023, indicating a significant financial commitment required for effective implementation.
Additionally, the recent funding of $1.1 billion raised by Metropolis highlights the financial landscape surrounding AI implementation in architecture.
Resistance to Change: Many professionals in the field demonstrate reluctance to modify their established workflows, driven by a concern that AI might compromise their creative processes. As mentioned by industry specialists, this resistance arises from a fear of losing the personal touch that characterizes structure creation. This is further complicated by the competitive dynamics among AI developers, where significant government investments are enhancing technological capabilities, thus intensifying the pressure on firms to adapt.
Data Privacy Concerns: The deployment of AI necessitates the handling of vast amounts of sensitive data, which raises critical issues related to privacy and security. Firms must navigate the complexities of data protection regulations to safeguard client information, making compliance a priority in AI integration strategies.
Skill Gaps: A pronounced lack of expertise in AI technologies can hinder firms’ capacity to fully exploit these tools. According to Zippia, the most popular fields of study for personnel in this profession include architecture (64%), environmental design (8%), building technology (4%), and urban planning (4%). This educational background highlights the need for continuous education and training, as architects must develop a robust understanding of AI to effectively incorporate it into their practice. This ongoing need for skill enhancement underscores the importance of investing in professional development to remain competitive in an evolving landscape.
In summary, while the potential of AI to transform architectural practices is significant, these challenges must be proactively addressed to facilitate its successful adoption.
The Future of AI in Architecture: Trends and Innovations
The future of AI in architecture is set to revolutionize the industry through several key advancements:
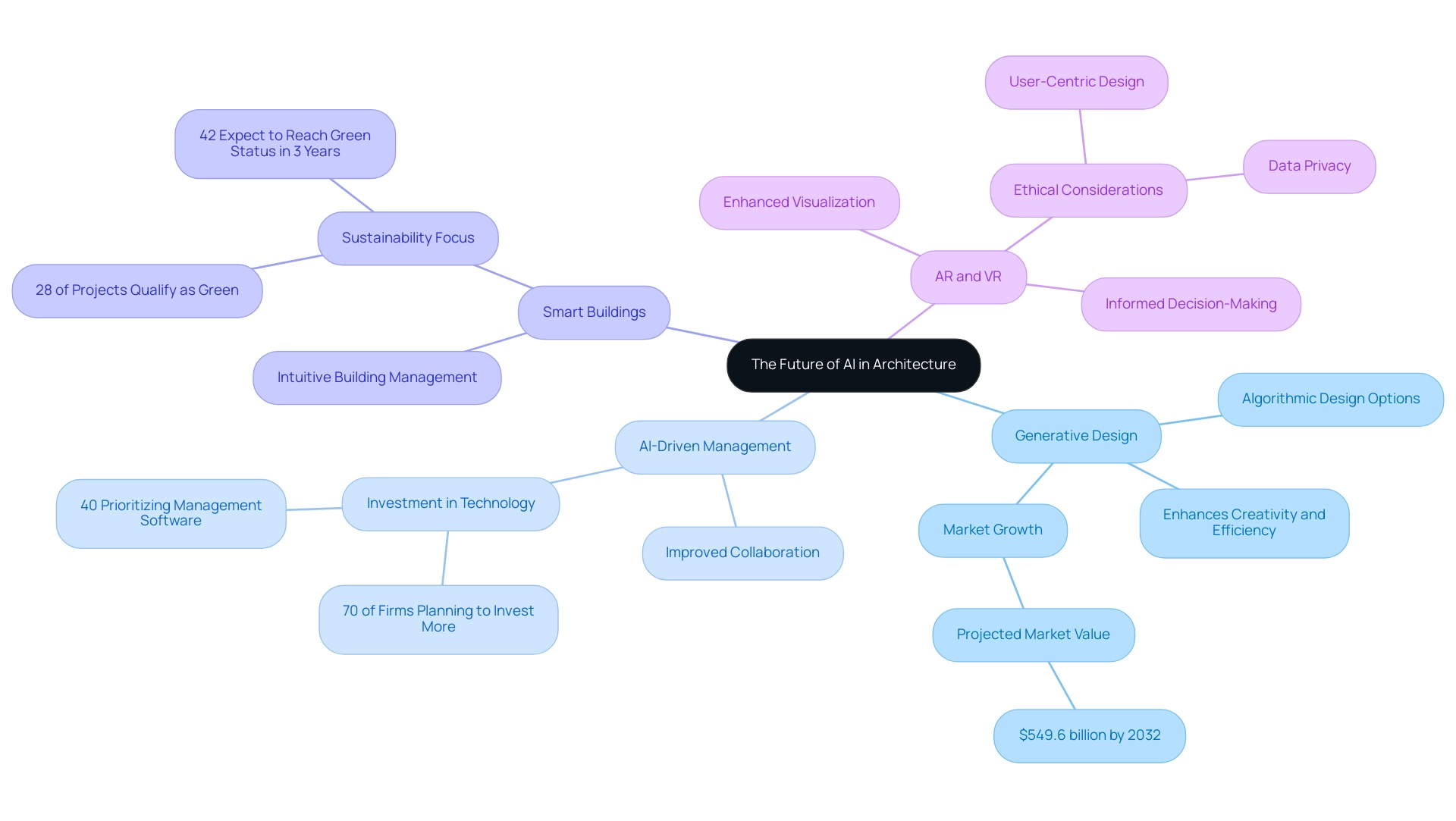
Generative Design: This cutting-edge methodology employs algorithms to generate a multitude of design options based on predetermined parameters. This not only fosters creativity but also significantly enhances efficiency in the design process. With the global architectural services market projected to reach approximately $549.6 billion by 2032, the demand for such innovative solutions is expected to grow exponentially.
AI-Driven Management: The integration of AI is set to transform management practices, facilitating improved collaboration and communication among team members. Insights from the case study titled ‘Architecture Firm Investment and Planning Strategies’ reveal that 70% of architecture firms plan to invest more in technology, with 40% identifying management software as a priority. This strategic shift underscores the importance of AI in optimizing workflow and resource allocation.
Smart Buildings: The incorporation of AI into building management systems will yield environments that can intuitively respond to the needs of occupants in real time. This trend is supported by data from OpenAsset, which indicates that 28% of global architects, engineers, contractors, owners, and investors report that most of their projects qualify as green. Furthermore, 42% anticipate reaching this level within the next three years, expanding that group by 50%. Such statistics highlight the growing emphasis on sustainability in architectural planning.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): As these immersive technologies continue to evolve, AI will play a pivotal role in enhancing the creative experience. Clients will be able to visualize projects before construction begins, leading to more informed decision-making and client satisfaction. However, the ethical considerations surrounding data privacy and user-centric approaches must be carefully navigated, aligning with the strategic planning and technological readiness necessary for responsible implementation.
In this transformative landscape, partner with J. Scott Smith Visual Designs to visualize and validate your architectural concepts through our preliminary renderings, which include examples of AI in 3D architectural rendering. Our collaborative creation phase involves iterative renderings based on your feedback, ensuring your vision is accurately represented. For instance, our recent project with XYZ Architects showcased how our preliminary renderings helped refine their concepts, leading to a successful client presentation and project approval.
Contact us today to schedule a consultation and explore how our professional 3D modeling services can help bring your design concepts to life. In conclusion, the future trends of AI in architecture are not only about innovation but also about the strategic planning and ethical considerations necessary for successful implementation.
Conclusion
The integration of Artificial Intelligence in architecture is fundamentally transforming the industry, enhancing both efficiency and creativity. By automating complex processes, architects can focus on high-level design challenges, ultimately accelerating project timelines and fostering innovative solutions. The widespread adoption of AI tools is evident, with a significant percentage of architects reporting comfort with AI-generated design suggestions, showcasing a shift towards embracing technology in the design process.
Real-world applications from leading firms illustrate the tangible benefits of AI. Companies like Zaha Hadid Architects and BIG are leveraging AI-driven simulations and generative design to push the boundaries of architectural possibilities, while improving energy efficiency and stakeholder communication. The ability of AI to enhance design accuracy and foster sustainable practices is further emphasizing its role as a critical ally in modern architectural workflows.
However, challenges such as high initial costs, resistance to change, and data privacy concerns must be addressed to fully harness the potential of AI. As the architectural landscape evolves, continuous education and investment in technology will be essential for firms to remain competitive. The future of architecture is intertwined with AI advancements, presenting opportunities for innovative design and improved project outcomes.
In light of these developments, it is clear that AI is not merely a tool but a catalyst for a new era in architecture. As firms navigate the complexities of integrating AI, they are poised to redefine their practices, ultimately leading to a more efficient, creative, and sustainable architectural environment. Embracing these changes is crucial for architects aiming to thrive in an increasingly technology-driven industry.

0 Comments